ff5a299c3dcee06f4b4ef0c7e719af1d.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 36
 –PROM used at patient level Niels Henrik Hjollund Consultant, Associate Professor, Ph. D. Hospital Unit West Jutland DK – 7400 Herning Denmark http: //westchronic. dk
–PROM used at patient level Niels Henrik Hjollund Consultant, Associate Professor, Ph. D. Hospital Unit West Jutland DK – 7400 Herning Denmark http: //westchronic. dk
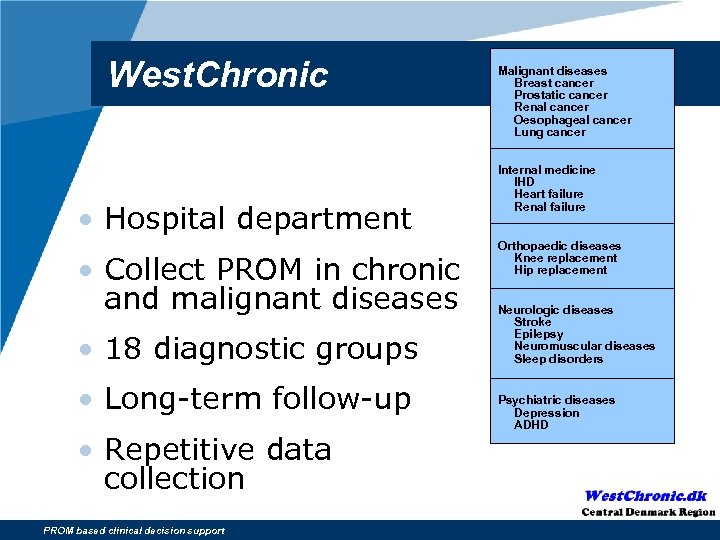 West. Chronic • Hospital department • Collect PROM in chronic and malignant diseases • 18 diagnostic groups • Long-term follow-up • Repetitive data collection PROM based clinical decision support Malignant diseases Breast cancer Prostatic cancer Renal cancer Oesophageal cancer Lung cancer Internal medicine IHD Heart failure Renal failure Orthopaedic diseases Knee replacement Hip replacement Neurologic diseases Stroke Epilepsy Neuromuscular diseases Sleep disorders Psychiatric diseases Depression ADHD
West. Chronic • Hospital department • Collect PROM in chronic and malignant diseases • 18 diagnostic groups • Long-term follow-up • Repetitive data collection PROM based clinical decision support Malignant diseases Breast cancer Prostatic cancer Renal cancer Oesophageal cancer Lung cancer Internal medicine IHD Heart failure Renal failure Orthopaedic diseases Knee replacement Hip replacement Neurologic diseases Stroke Epilepsy Neuromuscular diseases Sleep disorders Psychiatric diseases Depression ADHD
 Demands now - and in the future • More patients! • Better quality of care! • Same resources (if lucky) > Can PROM provide solution? PROM based clinical decision support
Demands now - and in the future • More patients! • Better quality of care! • Same resources (if lucky) > Can PROM provide solution? PROM based clinical decision support
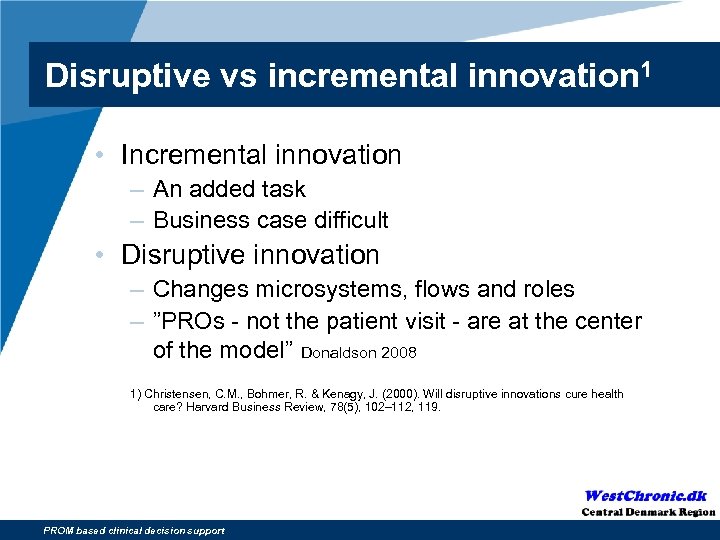 Disruptive vs incremental innovation 1 • Incremental innovation – An added task – Business case difficult • Disruptive innovation – Changes microsystems, flows and roles – ”PROs - not the patient visit - are at the center of the model” Donaldson 2008 1) Christensen, C. M. , Bohmer, R. & Kenagy, J. (2000). Will disruptive innovations cure health care? Harvard Business Review, 78(5), 102– 112, 119. PROM based clinical decision support
Disruptive vs incremental innovation 1 • Incremental innovation – An added task – Business case difficult • Disruptive innovation – Changes microsystems, flows and roles – ”PROs - not the patient visit - are at the center of the model” Donaldson 2008 1) Christensen, C. M. , Bohmer, R. & Kenagy, J. (2000). Will disruptive innovations cure health care? Harvard Business Review, 78(5), 102– 112, 119. PROM based clinical decision support
 PROM potentials at patient level Quality of care • Flagging important symptoms • Better documentation Patient involvement • Patient education • Visits focused on patient’s need Resurce optimation • More efficient visits • Eliminate needless visits? PROM based clinical decision support
PROM potentials at patient level Quality of care • Flagging important symptoms • Better documentation Patient involvement • Patient education • Visits focused on patient’s need Resurce optimation • More efficient visits • Eliminate needless visits? PROM based clinical decision support
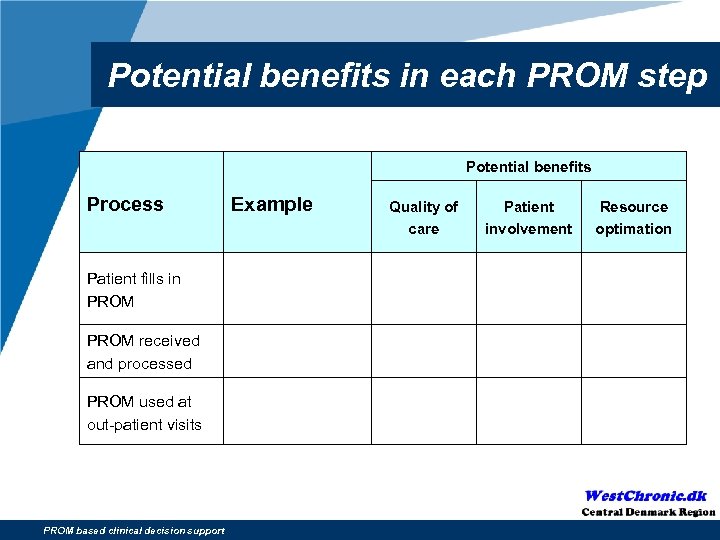 Potential benefits in each PROM step Potential benefits Process Patient fills in PROM received and processed PROM used at out-patient visits PROM based clinical decision support Example Quality of care Patient involvement Resource optimation
Potential benefits in each PROM step Potential benefits Process Patient fills in PROM received and processed PROM used at out-patient visits PROM based clinical decision support Example Quality of care Patient involvement Resource optimation
 Two PROM approaches • Hospital-PROM • Tele-PROM based clinical decision support
Two PROM approaches • Hospital-PROM • Tele-PROM based clinical decision support
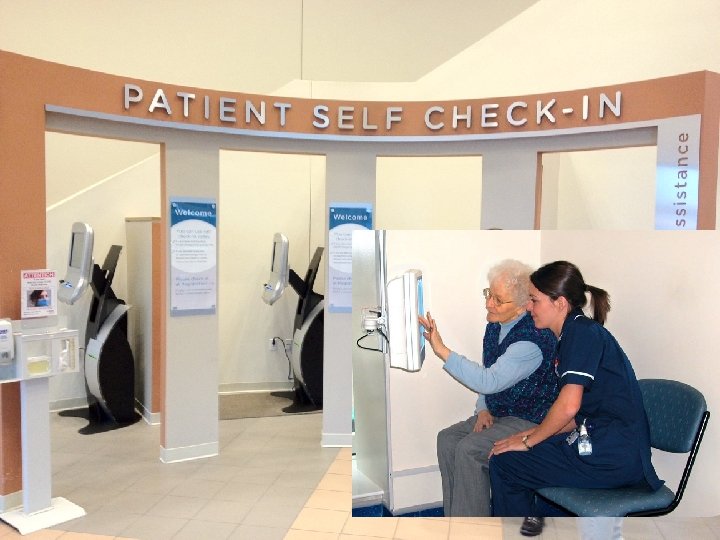


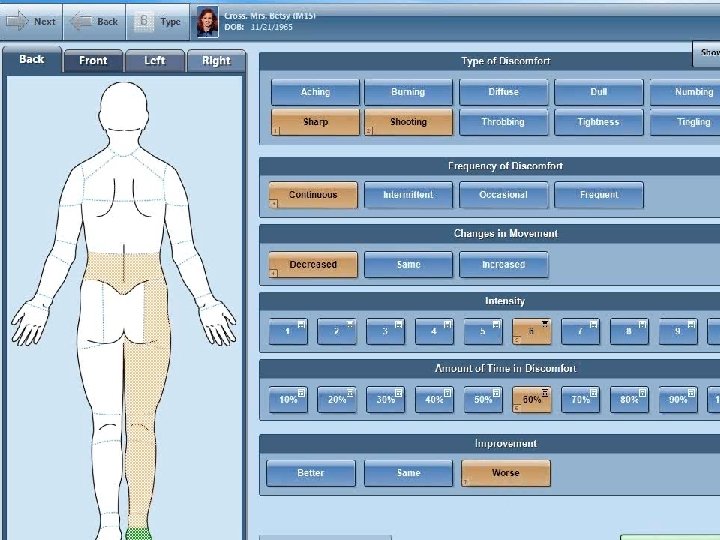

 PROM potentials at patient level • • Simple technology High response-rate Useful However: – Resources for support – Patient has to show up PROM based clinical decision support
PROM potentials at patient level • • Simple technology High response-rate Useful However: – Resources for support – Patient has to show up PROM based clinical decision support
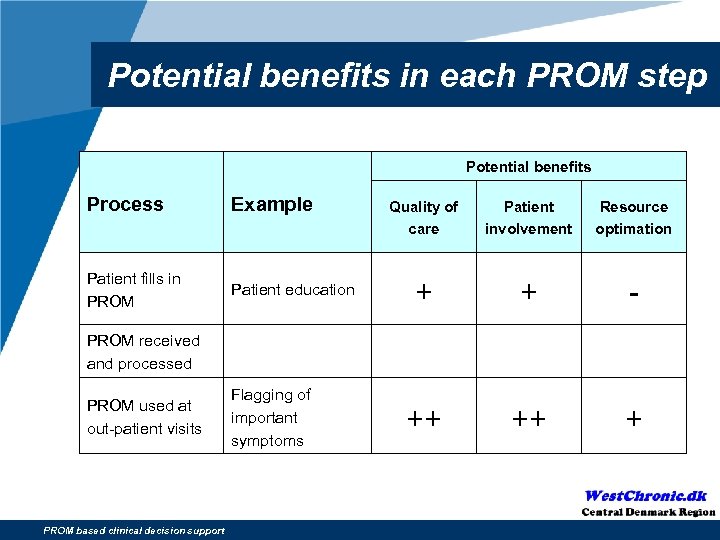 Potential benefits in each PROM step Potential benefits Process Example Patient fills in PROM Patient education Quality of care Patient involvement Resource optimation + + - ++ ++ + PROM received and processed PROM used at out-patient visits PROM based clinical decision support Flagging of important symptoms
Potential benefits in each PROM step Potential benefits Process Example Patient fills in PROM Patient education Quality of care Patient involvement Resource optimation + + - ++ ++ + PROM received and processed PROM used at out-patient visits PROM based clinical decision support Flagging of important symptoms
 Two PROM approaches • Hospital-PROM • Tele-PROM based clinical decision support
Two PROM approaches • Hospital-PROM • Tele-PROM based clinical decision support

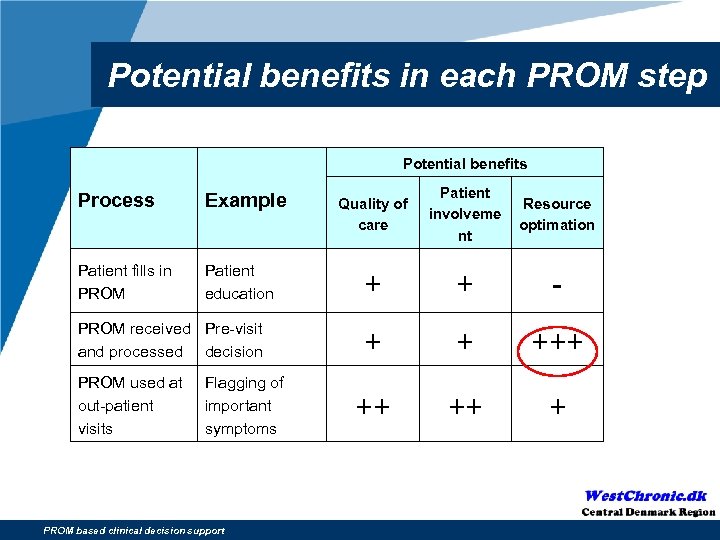 Potential benefits in each PROM step Potential benefits Process Example Patient fills in PROM Patient education PROM received Pre-visit and processed decision PROM used at out-patient visits Flagging of important symptoms PROM based clinical decision support Quality of care Patient involveme nt Resource optimation + + - + + ++ ++ +
Potential benefits in each PROM step Potential benefits Process Example Patient fills in PROM Patient education PROM received Pre-visit and processed decision PROM used at out-patient visits Flagging of important symptoms PROM based clinical decision support Quality of care Patient involveme nt Resource optimation + + - + + ++ ++ +
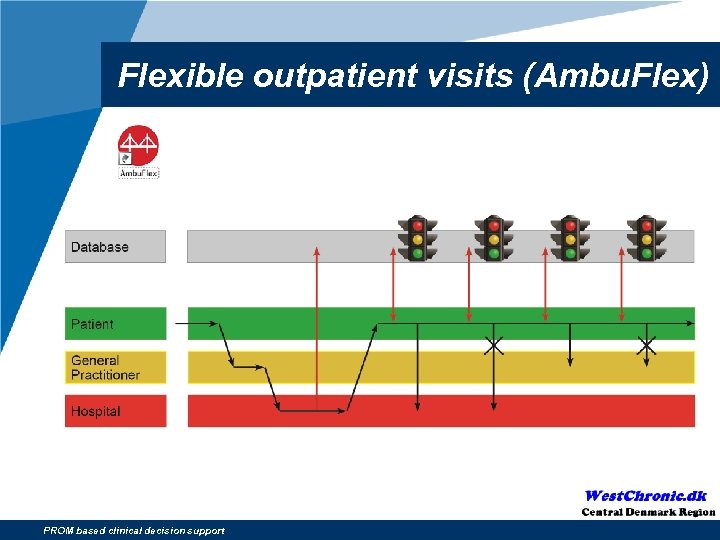 Flexible outpatient visits (Ambu. Flex) PROM based clinical decision support
Flexible outpatient visits (Ambu. Flex) PROM based clinical decision support
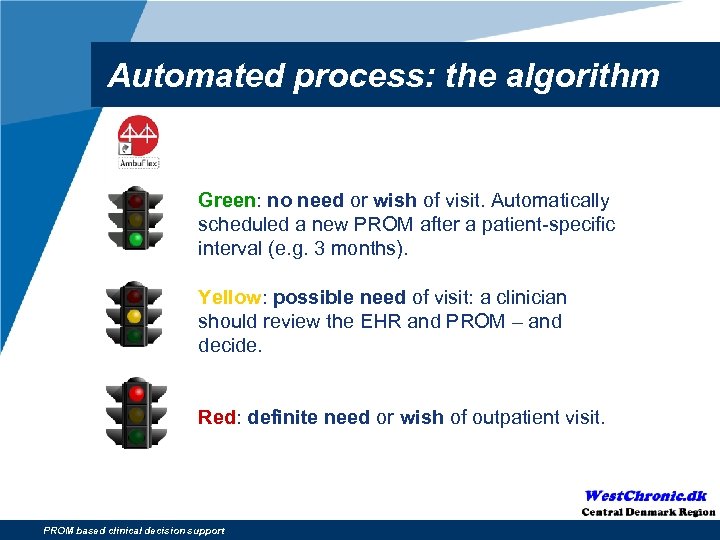 Automated process: the algorithm Green: no need or wish of visit. Automatically scheduled a new PROM after a patient-specific interval (e. g. 3 months). Yellow: possible need of visit: a clinician should review the EHR and PROM – and decide. Red: definite need or wish of outpatient visit. PROM based clinical decision support
Automated process: the algorithm Green: no need or wish of visit. Automatically scheduled a new PROM after a patient-specific interval (e. g. 3 months). Yellow: possible need of visit: a clinician should review the EHR and PROM – and decide. Red: definite need or wish of outpatient visit. PROM based clinical decision support
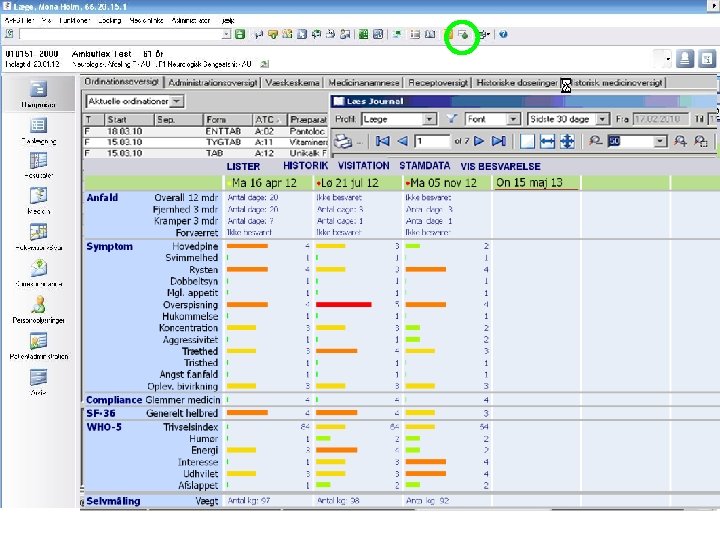
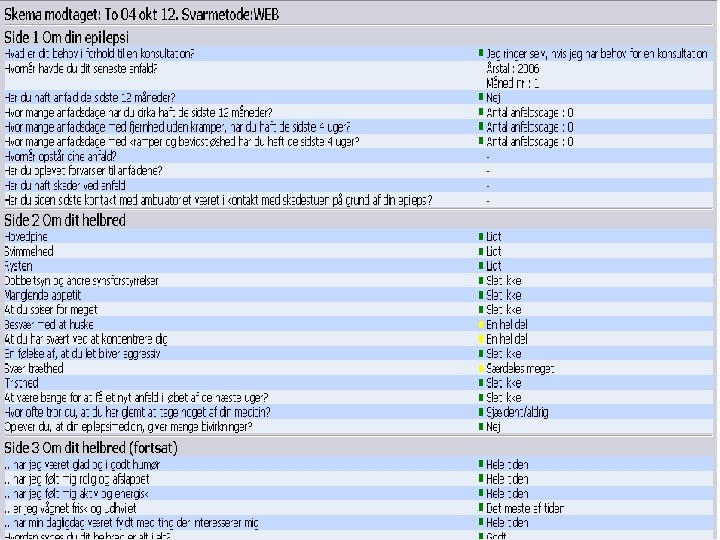
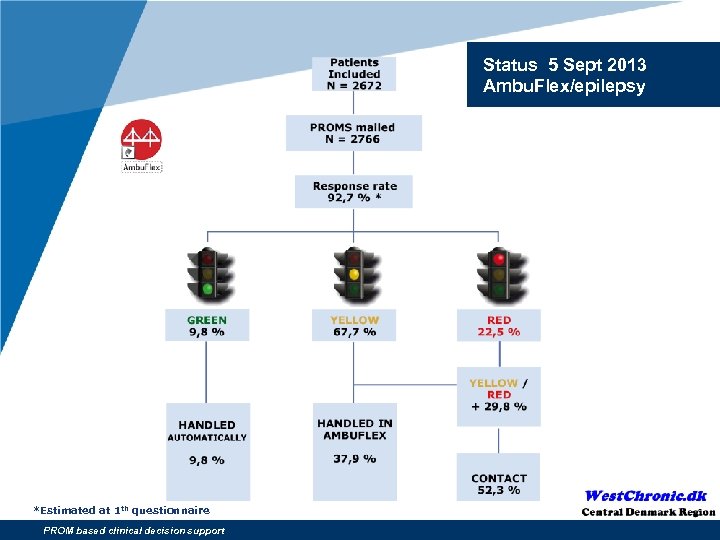 Status 5 Sept 2013 Ambu. Flex/epilepsy *Estimated at 1 th questionnaire PROM based clinical decision support
Status 5 Sept 2013 Ambu. Flex/epilepsy *Estimated at 1 th questionnaire PROM based clinical decision support
 What do the patients say? • • Saves time and resources Less interference with job More comprehensive than visits Paper PROM option acknowledged PROM based clinical decision support
What do the patients say? • • Saves time and resources Less interference with job More comprehensive than visits Paper PROM option acknowledged PROM based clinical decision support
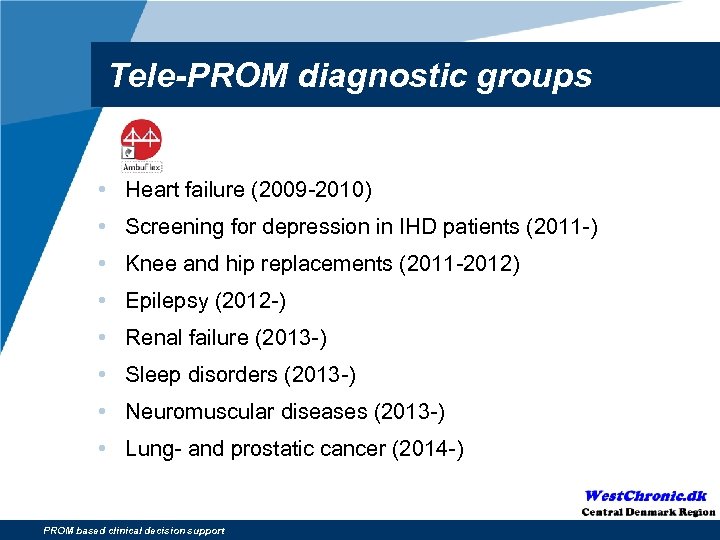 Tele-PROM diagnostic groups • Heart failure (2009 -2010) • Screening for depression in IHD patients (2011 -) • Knee and hip replacements (2011 -2012) • Epilepsy (2012 -) • Renal failure (2013 -) • Sleep disorders (2013 -) • Neuromuscular diseases (2013 -) • Lung- and prostatic cancer (2014 -) PROM based clinical decision support
Tele-PROM diagnostic groups • Heart failure (2009 -2010) • Screening for depression in IHD patients (2011 -) • Knee and hip replacements (2011 -2012) • Epilepsy (2012 -) • Renal failure (2013 -) • Sleep disorders (2013 -) • Neuromuscular diseases (2013 -) • Lung- and prostatic cancer (2014 -) PROM based clinical decision support
 Receipt of a good Ambu. Flex Diagnostic group • Out-patients • Many visits • Patient information essential, not hands-on • No need for visit, given OK PROM Organisation • Clinician ownership • Department management support PROM based clinical decision support
Receipt of a good Ambu. Flex Diagnostic group • Out-patients • Many visits • Patient information essential, not hands-on • No need for visit, given OK PROM Organisation • Clinician ownership • Department management support PROM based clinical decision support
 Logistic demands for clinical use of tele-PROM • High response rate >80% PROM based clinical decision support
Logistic demands for clinical use of tele-PROM • High response rate >80% PROM based clinical decision support
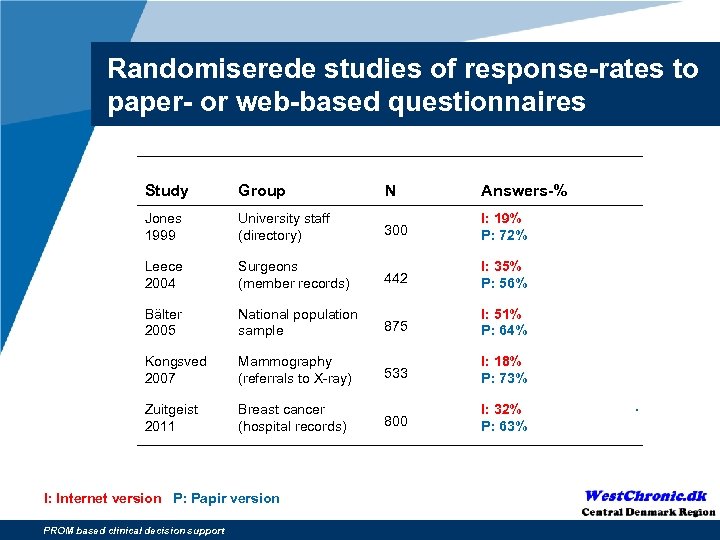 Randomiserede studies of response-rates to paper- or web-based questionnaires Study Group N Answers-% Jones 1999 University staff (directory) 300 I: 19% P: 72% Leece 2004 Surgeons (member records) 442 I: 35% P: 56% Bälter 2005 National population sample 875 I: 51% P: 64% Kongsved 2007 Mammography (referrals to X-ray) 533 I: 18% P: 73% Zuitgeist 2011 Breast cancer (hospital records) 800 I: 32% P: 63% I: Internet version P: Papir version PROM based clinical decision support .
Randomiserede studies of response-rates to paper- or web-based questionnaires Study Group N Answers-% Jones 1999 University staff (directory) 300 I: 19% P: 72% Leece 2004 Surgeons (member records) 442 I: 35% P: 56% Bälter 2005 National population sample 875 I: 51% P: 64% Kongsved 2007 Mammography (referrals to X-ray) 533 I: 18% P: 73% Zuitgeist 2011 Breast cancer (hospital records) 800 I: 32% P: 63% I: Internet version P: Papir version PROM based clinical decision support .
 Why? • Many patients prefer paper-PROMs • Advantages for data-collector, not the data-provider • Internet fatigue… • We cannot send nurse Ratched home to all the patients PROM based clinical decision support
Why? • Many patients prefer paper-PROMs • Advantages for data-collector, not the data-provider • Internet fatigue… • We cannot send nurse Ratched home to all the patients PROM based clinical decision support
 Response rates • e. PRO will work: – If the patient have to show up anyway • e. PRO will not work: – Tele. PROM Let the patient choose: use mixed mode! PROM based clinical decision support
Response rates • e. PRO will work: – If the patient have to show up anyway • e. PRO will not work: – Tele. PROM Let the patient choose: use mixed mode! PROM based clinical decision support
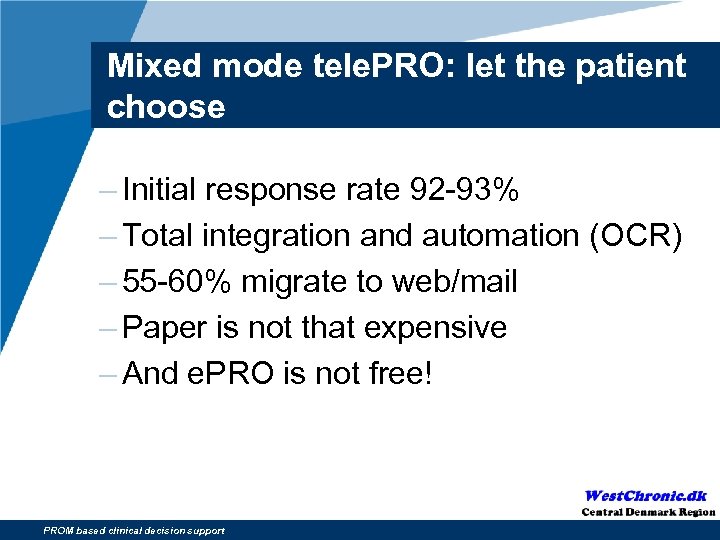 Mixed mode tele. PRO: let the patient choose – Initial response rate 92 -93% – Total integration and automation (OCR) – 55 -60% migrate to web/mail – Paper is not that expensive – And e. PRO is not free! PROM based clinical decision support
Mixed mode tele. PRO: let the patient choose – Initial response rate 92 -93% – Total integration and automation (OCR) – 55 -60% migrate to web/mail – Paper is not that expensive – And e. PRO is not free! PROM based clinical decision support
 One-step creation of multi-mode PROMS
One-step creation of multi-mode PROMS
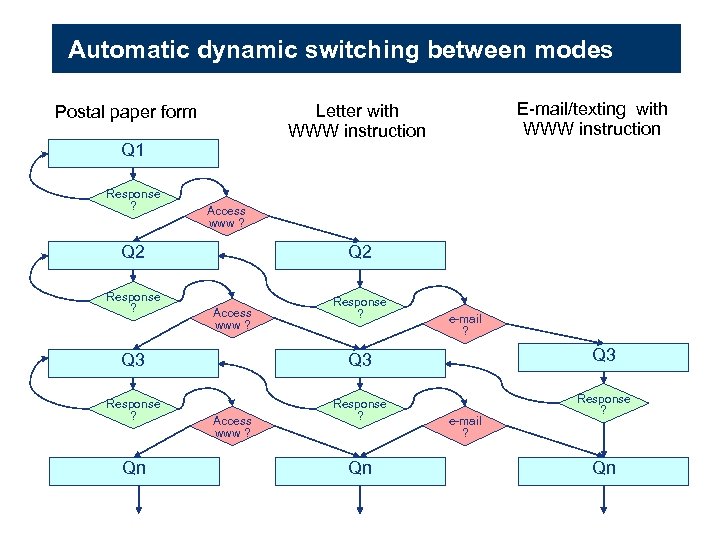 Automatic dynamic switching between modes Q 1 Response ? Access www ? Q 2 Response ? E-mail/texting with WWW instruction Letter with WWW instruction Postal paper form Q 2 Access www ? Response ? e-mail ? Q 3 Q 3 Response ? Qn Access www ? Qn e-mail ? Qn
Automatic dynamic switching between modes Q 1 Response ? Access www ? Q 2 Response ? E-mail/texting with WWW instruction Letter with WWW instruction Postal paper form Q 2 Access www ? Response ? e-mail ? Q 3 Q 3 Response ? Qn Access www ? Qn e-mail ? Qn
 What do we need to achieve succes with clinical tele-PROM? • Relevant diagnostic groups – Many visits, PROM is essential • High coverage – Multimode, shared technology • Close cooperation with front-desk clinicians – Dedicated personnel at index-department • Models for development – Interactive: Clinicians do not know what they need • Flexibility – Generic configurable systems • Connectivity – EHR-system + population registers etc PROM based clinical decision support
What do we need to achieve succes with clinical tele-PROM? • Relevant diagnostic groups – Many visits, PROM is essential • High coverage – Multimode, shared technology • Close cooperation with front-desk clinicians – Dedicated personnel at index-department • Models for development – Interactive: Clinicians do not know what they need • Flexibility – Generic configurable systems • Connectivity – EHR-system + population registers etc PROM based clinical decision support
 Disruptive vs incremental innovation 1 • Incremental innovation – An added task – Business case difficult • Disruptive innovation – Changes microsystems, flows and roles – ”PROs - not the patient visit - are at the center of the model” Donaldson 2008 – Realistic business 1) Christensen, C. M. , Bohmer, R. & Kenagy, J. (2000). Will disruptive innovations cure health care? Harvard Business Review, 78(5), 102– 112, 119. PROM based clinical decision support
Disruptive vs incremental innovation 1 • Incremental innovation – An added task – Business case difficult • Disruptive innovation – Changes microsystems, flows and roles – ”PROs - not the patient visit - are at the center of the model” Donaldson 2008 – Realistic business 1) Christensen, C. M. , Bohmer, R. & Kenagy, J. (2000). Will disruptive innovations cure health care? Harvard Business Review, 78(5), 102– 112, 119. PROM based clinical decision support
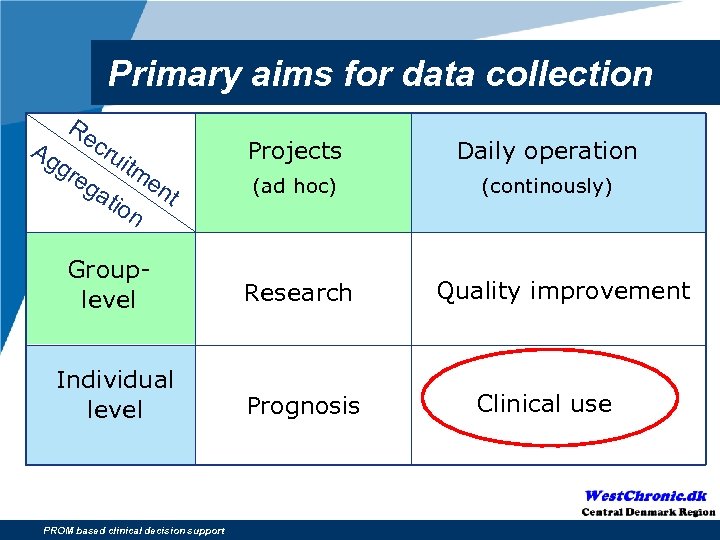 Primary aims for data collection Re cru Ag gre itm en ga t tio n Projects Daily operation (ad hoc) (continously) Grouplevel Research Individual level Prognosis PROM based clinical decision support Quality improvement Clinical use
Primary aims for data collection Re cru Ag gre itm en ga t tio n Projects Daily operation (ad hoc) (continously) Grouplevel Research Individual level Prognosis PROM based clinical decision support Quality improvement Clinical use


