f90616f9cbb817f4fccecf219070e189.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 34
 Projects Summarized John H. Vande Vate Spring, 2008 1 1
Projects Summarized John H. Vande Vate Spring, 2008 1 1
 Projects Review • GE: Look over the models to be sure you understand how they handled the fact that deliveries can be either early or late and these involve different costs • Sikorsky: Look over the model to be sure you understand the difficulties of modeling the flow of transport assets (helicopters) required to support the flow of cargo (passengers). Equipment balance is a major area of concern in every mode of transportation. 2 2
Projects Review • GE: Look over the models to be sure you understand how they handled the fact that deliveries can be either early or late and these involve different costs • Sikorsky: Look over the model to be sure you understand the difficulties of modeling the flow of transport assets (helicopters) required to support the flow of cargo (passengers). Equipment balance is a major area of concern in every mode of transportation. 2 2
 Projects Summarized • CARE: Forecasting offers the opportunity for planning. What we didn’t quite get to – and it’s not surprising, because things take time in this kind of organization – is the segmentation of response: what demand must be met immediately, what can wait. 3 3
Projects Summarized • CARE: Forecasting offers the opportunity for planning. What we didn’t quite get to – and it’s not surprising, because things take time in this kind of organization – is the segmentation of response: what demand must be met immediately, what can wait. 3 3
 Projects Summarized • Alternative Apparel and BMW: Be sure you understand the computation of safety stock in these contexts especially the computation of safety stock in terms of time, i. e. , days of supply. • DIN/ABC and Disney: These are real cases of the material from part 1 of the course. Be sure you understand why inventory is less relevant for DIN/ABC and how variability complicates the idealized setting we considered in class. 4 4
Projects Summarized • Alternative Apparel and BMW: Be sure you understand the computation of safety stock in these contexts especially the computation of safety stock in terms of time, i. e. , days of supply. • DIN/ABC and Disney: These are real cases of the material from part 1 of the course. Be sure you understand why inventory is less relevant for DIN/ABC and how variability complicates the idealized setting we considered in class. 4 4
 Projects Summarized • Coca Cola and J&J projects: Be sure you understand the “news vendor” nature of the economics involved in committing to “contract” supply vs “spot” supply. J&J takes this one step further to illustrate the meaning of collaboration in the supply chain – sharing risk to mutual benefit. Be sure you understand the value of strengthening your supply base and how collaboration can help do that. • More on the “news vendor” nature of Coca Cola to follow 5 5
Projects Summarized • Coca Cola and J&J projects: Be sure you understand the “news vendor” nature of the economics involved in committing to “contract” supply vs “spot” supply. J&J takes this one step further to illustrate the meaning of collaboration in the supply chain – sharing risk to mutual benefit. Be sure you understand the value of strengthening your supply base and how collaboration can help do that. • More on the “news vendor” nature of Coca Cola to follow 5 5
 Projects Summarized • Intel: Recall we started with a Financial perspective. The three drivers are: Growth, Profitability and Return on Assets. This case illustrates the tensions among these drivers. Growth via the low cost pc product puts pressure on margins and return on assets. • New models of VMI • Improving Return on Assets (ATM Capacity) via a combination of MTS and MTO 6 6
Projects Summarized • Intel: Recall we started with a Financial perspective. The three drivers are: Growth, Profitability and Return on Assets. This case illustrates the tensions among these drivers. Growth via the low cost pc product puts pressure on margins and return on assets. • New models of VMI • Improving Return on Assets (ATM Capacity) via a combination of MTS and MTO 6 6
 Coca Cola Brazil Reprised John H. Vande Vate Spring, 2008 7 7
Coca Cola Brazil Reprised John H. Vande Vate Spring, 2008 7 7
 The Setting • The bottlers deliver KO products to – Large format stores (modern) and – Small format stores (traditional) from distribution centers across Brazil using a combination of owned or leased trucks and trucks provided by 3 rd parties as needed. • Different distribution centers are operated by different bottlers. Some are owned by CCE, some are franchises • Each distribution center has its own fleet of trucks (the dcs are hundreds of miles apart and moving vehicles from one state in Brazil to another has significant tax implications) 8 8
The Setting • The bottlers deliver KO products to – Large format stores (modern) and – Small format stores (traditional) from distribution centers across Brazil using a combination of owned or leased trucks and trucks provided by 3 rd parties as needed. • Different distribution centers are operated by different bottlers. Some are owned by CCE, some are franchises • Each distribution center has its own fleet of trucks (the dcs are hundreds of miles apart and moving vehicles from one state in Brazil to another has significant tax implications) 8 8
 The Problem • Recommend an appropriate fleet composition at each DC, i. e. , • What numbers and types of vehicles should each DC purchase or lease? 9 9
The Problem • Recommend an appropriate fleet composition at each DC, i. e. , • What numbers and types of vehicles should each DC purchase or lease? 9 9
 Considerations • Delivery requirements vary from day to day in terms of both – The number of stops required – The number of cases to be delivered • Different types of vehicles have different capabilities, e. g. , an investment in small trucks yields more capacity to make stops than the same investment in large trucks. The large trucks yield more capacity to deliver cases. • Delivering to small format stores requires experience. KO will not allow a third party to handle this portion of its business. 10 10
Considerations • Delivery requirements vary from day to day in terms of both – The number of stops required – The number of cases to be delivered • Different types of vehicles have different capabilities, e. g. , an investment in small trucks yields more capacity to make stops than the same investment in large trucks. The large trucks yield more capacity to deliver cases. • Delivering to small format stores requires experience. KO will not allow a third party to handle this portion of its business. 10 10
 Trade-offs • This is the typical trade-off of capital costs and operating costs • Owned or leased vehicles are generally less expensive to operate than 3 rd party vehicles, but the more vehicles we own the lower the utilization on these vehicles 11 11
Trade-offs • This is the typical trade-off of capital costs and operating costs • Owned or leased vehicles are generally less expensive to operate than 3 rd party vehicles, but the more vehicles we own the lower the utilization on these vehicles 11 11
 Current Situation (Roughly) • KO’s current approach is clever, but faces three challenges: – Data requirements: The current approach employs a daily history of stops and cases delivered from the DC over the course of a year or more to capture the variability. That’s cumbersome – Computational requirements: The quantity of data and the level of detail in these models precludes relying on readily available tools like Solver. KO resorts to heuristics – The current tool does not recommend a fleet composition. It just indicates the total capacity of the fleet. 12 12
Current Situation (Roughly) • KO’s current approach is clever, but faces three challenges: – Data requirements: The current approach employs a daily history of stops and cases delivered from the DC over the course of a year or more to capture the variability. That’s cumbersome – Computational requirements: The quantity of data and the level of detail in these models precludes relying on readily available tools like Solver. KO resorts to heuristics – The current tool does not recommend a fleet composition. It just indicates the total capacity of the fleet. 12 12
 General Approach • Step 1: Develop a distribution of daily demand in terms of stops and cases. – The first observation here is that given a list of daily demands, the order in which those days occur has no effect on the answer. For a given fleet composition, the utilization will be the same regardless of the order. – There is an exception to this observation: If the highest demand days occur together, it probably makes sense to develop isolate that peak season and develop a separate business strategy for dealing with it. This is exactly what KO does during the peak season in December. 13 13
General Approach • Step 1: Develop a distribution of daily demand in terms of stops and cases. – The first observation here is that given a list of daily demands, the order in which those days occur has no effect on the answer. For a given fleet composition, the utilization will be the same regardless of the order. – There is an exception to this observation: If the highest demand days occur together, it probably makes sense to develop isolate that peak season and develop a separate business strategy for dealing with it. This is exactly what KO does during the peak season in December. 13 13
 General Approach • Use the distribution rather than a detailed “simulation” of demand. This offers several advantages: – If we observe that demands at different DCs follow standard distributions, we can quickly adjust our representations of the variability in demand using appropriate summary statistics rather than extensive and detailed data. For example, if daily demand for cases is normally distributed, we can simply work with the mean and standard deviation in daily demand rather than long lists of 365 days of demand. – Standard distributions also simplify the computations without unduly compromising the fidelity of the analysis, e. g. , we can rely on standard functions like Norm. Dist rather than counting days with demands less than a given quantity, etc. 14 14
General Approach • Use the distribution rather than a detailed “simulation” of demand. This offers several advantages: – If we observe that demands at different DCs follow standard distributions, we can quickly adjust our representations of the variability in demand using appropriate summary statistics rather than extensive and detailed data. For example, if daily demand for cases is normally distributed, we can simply work with the mean and standard deviation in daily demand rather than long lists of 365 days of demand. – Standard distributions also simplify the computations without unduly compromising the fidelity of the analysis, e. g. , we can rely on standard functions like Norm. Dist rather than counting days with demands less than a given quantity, etc. 14 14
 General Approach • Employ a “News Vendor” type analysis to make the appropriate trade-offs. – The news vendor gives a simple critical ratio and is easy to work with – We will need to extend the basic approach to address • The two dimensions of demand: stops and cases • Traditional vs Modern customers • The differences among the vehicle types 15 15
General Approach • Employ a “News Vendor” type analysis to make the appropriate trade-offs. – The news vendor gives a simple critical ratio and is easy to work with – We will need to extend the basic approach to address • The two dimensions of demand: stops and cases • Traditional vs Modern customers • The differences among the vehicle types 15 15
 Two dimensions of demand • Let’s assume for the time being that we have a pdf for the number of stops and number of cases on a given day. This looks something like • Prob{demand for cases < C and demand for stops < S on a given day} = • We can build f from historical data and then fit that data to a standard distribution. 16 16
Two dimensions of demand • Let’s assume for the time being that we have a pdf for the number of stops and number of cases on a given day. This looks something like • Prob{demand for cases < C and demand for stops < S on a given day} = • We can build f from historical data and then fit that data to a standard distribution. 16 16
 Two Dimensions of Demand • To keep things simple, let’s ignore for now the Traditional vs Modern issue and simply work with the pdf f. • We’ll also assume for the time being that we only have one type of vehicle in our fleet – it can make s* stops per day and deliver c* cases per day. • How many of these vehicles should we own? 17 17
Two Dimensions of Demand • To keep things simple, let’s ignore for now the Traditional vs Modern issue and simply work with the pdf f. • We’ll also assume for the time being that we only have one type of vehicle in our fleet – it can make s* stops per day and deliver c* cases per day. • How many of these vehicles should we own? 17 17
 A News Vendor Approach • We’ll need to understand the economics of the decision • For owned or leased vehicles we have – F_owned: the amortized fixed costs of owning a vehicle on a per day basis. This includes the cost of money, insurance, etc. that we incur even if we don’t use the vehicle – V_owned: the variable cost of operating one of our vehicles to its capacity on a given day. This includes the mileage (fuel, …) and time (driver pay, …) related costs of operating the vehicle. 18 18
A News Vendor Approach • We’ll need to understand the economics of the decision • For owned or leased vehicles we have – F_owned: the amortized fixed costs of owning a vehicle on a per day basis. This includes the cost of money, insurance, etc. that we incur even if we don’t use the vehicle – V_owned: the variable cost of operating one of our vehicles to its capacity on a given day. This includes the mileage (fuel, …) and time (driver pay, …) related costs of operating the vehicle. 18 18
 A News Vendor Approach • For 3 rd party vehicles we have – F_3 pl: the amortized fixed costs of owning vehicle on a per day basis. This includes Noa fixed costs. The 3 pl builds these the cost of money, insurance, etc. that we into even variable price we pay the if we don’t use the vehicle incur – V_3 pl: the variable cost of hiring a 3 pl vehicle for a day. – We assume F_owned+V_owned < V_3 pl Otherwise, there would be no point in owning any vehicles 19 19
A News Vendor Approach • For 3 rd party vehicles we have – F_3 pl: the amortized fixed costs of owning vehicle on a per day basis. This includes Noa fixed costs. The 3 pl builds these the cost of money, insurance, etc. that we into even variable price we pay the if we don’t use the vehicle incur – V_3 pl: the variable cost of hiring a 3 pl vehicle for a day. – We assume F_owned+V_owned < V_3 pl Otherwise, there would be no point in owning any vehicles 19 19
 News Vendor • The risk we incur from the last vehicle is the fixed cost of owning it whenever demand is less than the capacity of our fleet so • F_owned * P • We have to do some work to determine the prob. P that demand is less than the capacity of n vehicles. 20 20
News Vendor • The risk we incur from the last vehicle is the fixed cost of owning it whenever demand is less than the capacity of our fleet so • F_owned * P • We have to do some work to determine the prob. P that demand is less than the capacity of n vehicles. 20 20
 The Probability • P= This is the probability n vehicles is enough to meet demand both for cases and for stops. 21 21
The Probability • P= This is the probability n vehicles is enough to meet demand both for cases and for stops. 21 21
 News Vendor • If we have n vehicles in our fleet, the incremental value of an additional vehicle is: – It saves us from hiring a 3 pl vehicle whenever demand exceeds the capacity of our fleet. So (V_3 pl – F_owned – V_owned)*(1 -P) – We have to do some work to determine the prob. 1 -P that demand exceeds the capacity of n vehicles. 22 22
News Vendor • If we have n vehicles in our fleet, the incremental value of an additional vehicle is: – It saves us from hiring a 3 pl vehicle whenever demand exceeds the capacity of our fleet. So (V_3 pl – F_owned – V_owned)*(1 -P) – We have to do some work to determine the prob. 1 -P that demand exceeds the capacity of n vehicles. 22 22
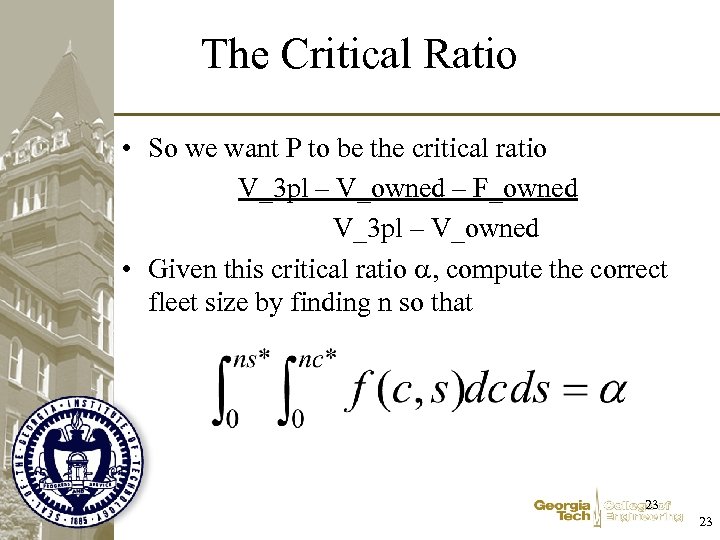 The Critical Ratio • So we want P to be the critical ratio V_3 pl – V_owned – F_owned V_3 pl – V_owned • Given this critical ratio , compute the correct fleet size by finding n so that 23 23
The Critical Ratio • So we want P to be the critical ratio V_3 pl – V_owned – F_owned V_3 pl – V_owned • Given this critical ratio , compute the correct fleet size by finding n so that 23 23
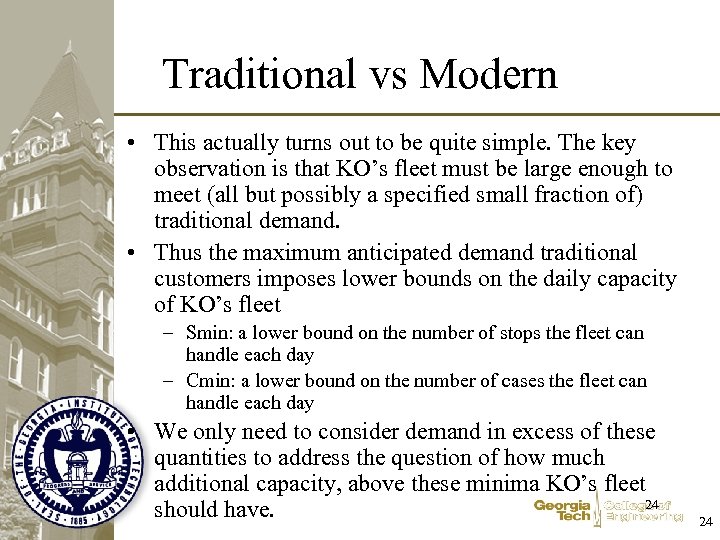 Traditional vs Modern • This actually turns out to be quite simple. The key observation is that KO’s fleet must be large enough to meet (all but possibly a specified small fraction of) traditional demand. • Thus the maximum anticipated demand traditional customers imposes lower bounds on the daily capacity of KO’s fleet – Smin: a lower bound on the number of stops the fleet can handle each day – Cmin: a lower bound on the number of cases the fleet can handle each day • We only need to consider demand in excess of these quantities to address the question of how much additional capacity, above these minima KO’s fleet 24 should have. 24
Traditional vs Modern • This actually turns out to be quite simple. The key observation is that KO’s fleet must be large enough to meet (all but possibly a specified small fraction of) traditional demand. • Thus the maximum anticipated demand traditional customers imposes lower bounds on the daily capacity of KO’s fleet – Smin: a lower bound on the number of stops the fleet can handle each day – Cmin: a lower bound on the number of cases the fleet can handle each day • We only need to consider demand in excess of these quantities to address the question of how much additional capacity, above these minima KO’s fleet 24 should have. 24
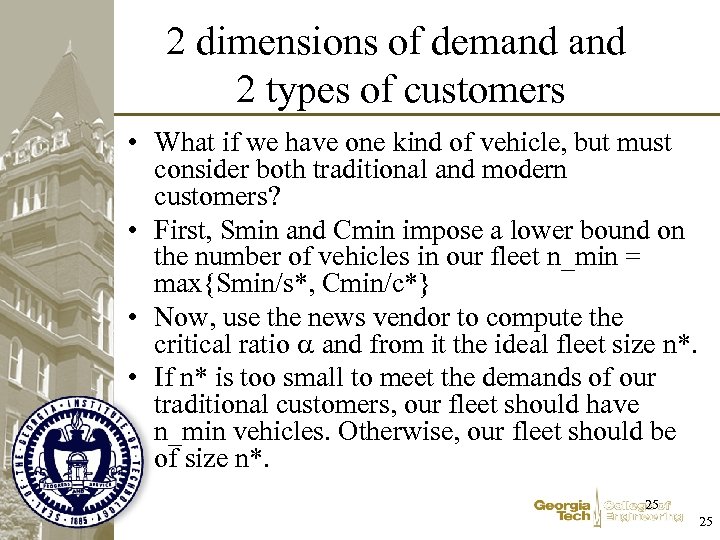 2 dimensions of demand 2 types of customers • What if we have one kind of vehicle, but must consider both traditional and modern customers? • First, Smin and Cmin impose a lower bound on the number of vehicles in our fleet n_min = max{Smin/s*, Cmin/c*} • Now, use the news vendor to compute the critical ratio and from it the ideal fleet size n*. • If n* is too small to meet the demands of our traditional customers, our fleet should have n_min vehicles. Otherwise, our fleet should be of size n*. 25 25
2 dimensions of demand 2 types of customers • What if we have one kind of vehicle, but must consider both traditional and modern customers? • First, Smin and Cmin impose a lower bound on the number of vehicles in our fleet n_min = max{Smin/s*, Cmin/c*} • Now, use the news vendor to compute the critical ratio and from it the ideal fleet size n*. • If n* is too small to meet the demands of our traditional customers, our fleet should have n_min vehicles. Otherwise, our fleet should be of size n*. 25 25
 Many Vehicle Types • Assume the 3 pl has a single type of vehicle with capacities c* and s*, which makes sense since modern customers are pretty homogeneous (this just simplifies things a little) • We have several types of vehicles characterized by: • s(i): stop capacity • c(i): case capacity • F(i): Fixed cost • V(i): Variable cost 26 26
Many Vehicle Types • Assume the 3 pl has a single type of vehicle with capacities c* and s*, which makes sense since modern customers are pretty homogeneous (this just simplifies things a little) • We have several types of vehicles characterized by: • s(i): stop capacity • c(i): case capacity • F(i): Fixed cost • V(i): Variable cost 26 26
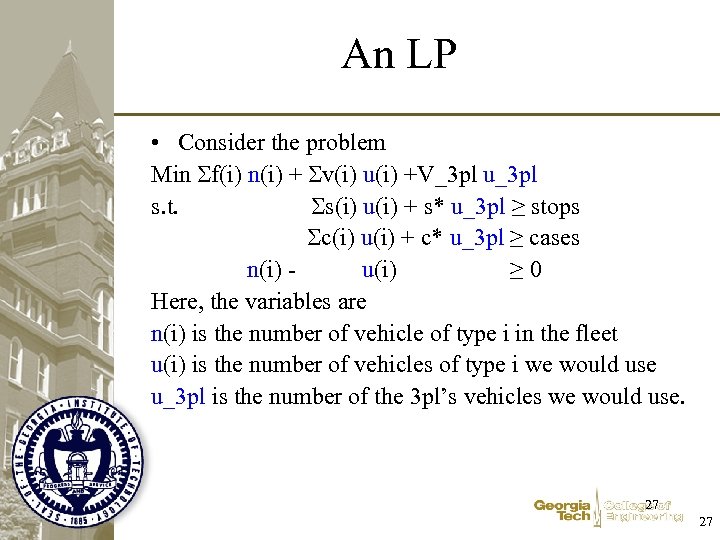 An LP • Consider the problem Min f(i) n(i) + v(i) u(i) +V_3 pl u_3 pl s. t. s(i) u(i) + s* u_3 pl ≥ stops c(i) u(i) + c* u_3 pl ≥ cases n(i) u(i) ≥ 0 Here, the variables are n(i) is the number of vehicle of type i in the fleet u(i) is the number of vehicles of type i we would use u_3 pl is the number of the 3 pl’s vehicles we would use. 27 27
An LP • Consider the problem Min f(i) n(i) + v(i) u(i) +V_3 pl u_3 pl s. t. s(i) u(i) + s* u_3 pl ≥ stops c(i) u(i) + c* u_3 pl ≥ cases n(i) u(i) ≥ 0 Here, the variables are n(i) is the number of vehicle of type i in the fleet u(i) is the number of vehicles of type i we would use u_3 pl is the number of the 3 pl’s vehicles we would use. 27 27
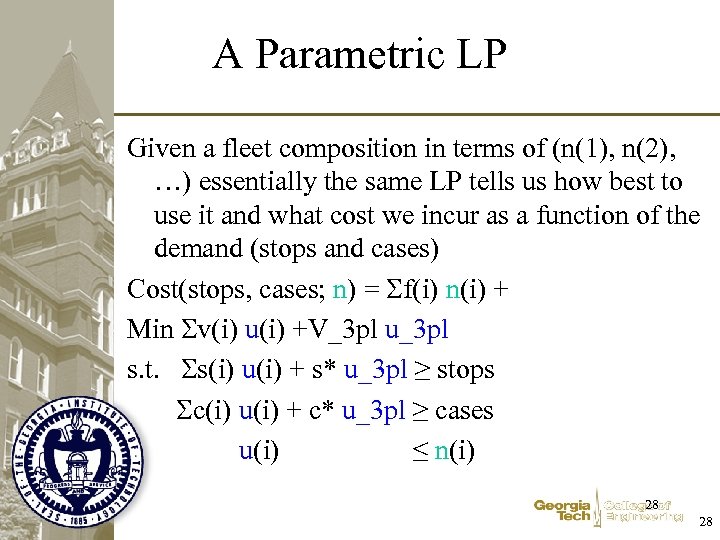 A Parametric LP Given a fleet composition in terms of (n(1), n(2), …) essentially the same LP tells us how best to use it and what cost we incur as a function of the demand (stops and cases) Cost(stops, cases; n) = f(i) n(i) + Min v(i) u(i) +V_3 pl u_3 pl s. t. s(i) u(i) + s* u_3 pl ≥ stops c(i) u(i) + c* u_3 pl ≥ cases u(i) ≤ n(i) 28 28
A Parametric LP Given a fleet composition in terms of (n(1), n(2), …) essentially the same LP tells us how best to use it and what cost we incur as a function of the demand (stops and cases) Cost(stops, cases; n) = f(i) n(i) + Min v(i) u(i) +V_3 pl u_3 pl s. t. s(i) u(i) + s* u_3 pl ≥ stops c(i) u(i) + c* u_3 pl ≥ cases u(i) ≤ n(i) 28 28
 The Bases • For each choice of demands (stops, cases) an optimal solution to this problem will occur at a basic feasible solution. • Basic feasible solutions to this problem have at most two basic variables (there are two “structural constraints”), but we must also specify for each non-basic u(i) whether it is nonbasic at 0 or non-basic at its upper bound n(i). • In other words, we use none or all of the vehicles of each type in our fleet except for at most two types. If we use 3 pl capacity then only at most one type can be partially utilized. 29 29
The Bases • For each choice of demands (stops, cases) an optimal solution to this problem will occur at a basic feasible solution. • Basic feasible solutions to this problem have at most two basic variables (there are two “structural constraints”), but we must also specify for each non-basic u(i) whether it is nonbasic at 0 or non-basic at its upper bound n(i). • In other words, we use none or all of the vehicles of each type in our fleet except for at most two types. If we use 3 pl capacity then only at most one type can be partially utilized. 29 29
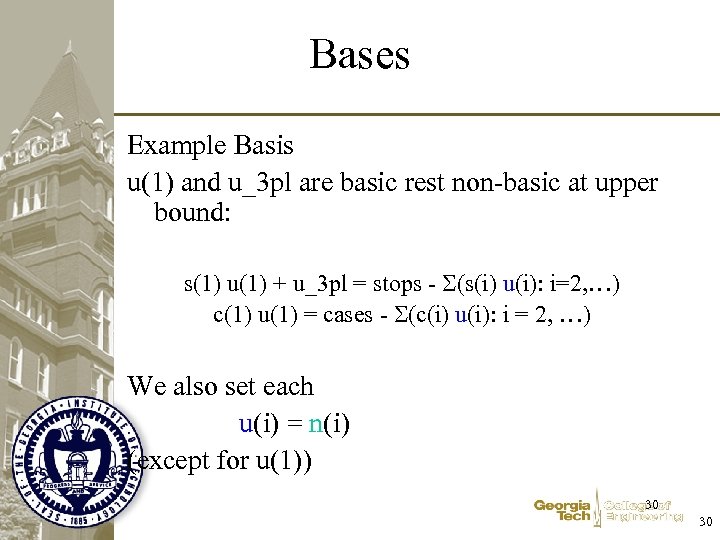 Bases Example Basis u(1) and u_3 pl are basic rest non-basic at upper bound: s(1) u(1) + u_3 pl = stops - (s(i) u(i): i=2, …) c(1) u(1) = cases - (c(i) u(i): i = 2, …) We also set each u(i) = n(i) (except for u(1)) 30 30
Bases Example Basis u(1) and u_3 pl are basic rest non-basic at upper bound: s(1) u(1) + u_3 pl = stops - (s(i) u(i): i=2, …) c(1) u(1) = cases - (c(i) u(i): i = 2, …) We also set each u(i) = n(i) (except for u(1)) 30 30
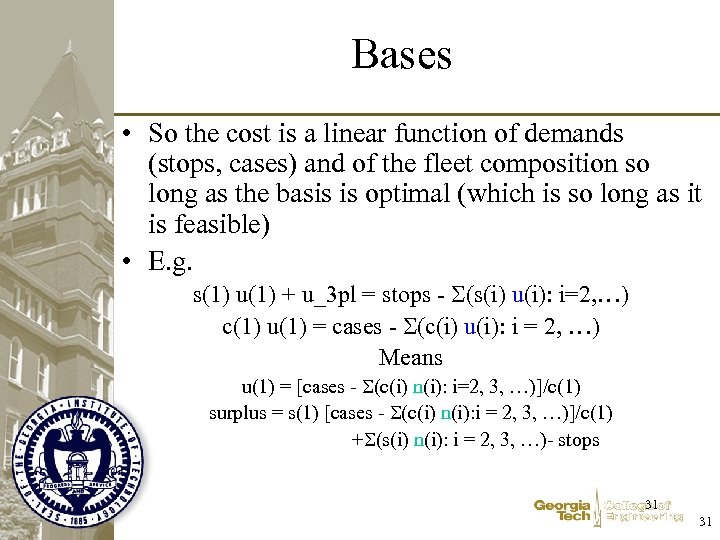 Bases • So the cost is a linear function of demands (stops, cases) and of the fleet composition so long as the basis is optimal (which is so long as it is feasible) • E. g. s(1) u(1) + u_3 pl = stops - (s(i) u(i): i=2, …) c(1) u(1) = cases - (c(i) u(i): i = 2, …) Means u(1) = [cases - (c(i) n(i): i=2, 3, …)]/c(1) surplus = s(1) [cases - (c(i) n(i): i = 2, 3, …)]/c(1) + (s(i) n(i): i = 2, 3, …)- stops 31 31
Bases • So the cost is a linear function of demands (stops, cases) and of the fleet composition so long as the basis is optimal (which is so long as it is feasible) • E. g. s(1) u(1) + u_3 pl = stops - (s(i) u(i): i=2, …) c(1) u(1) = cases - (c(i) u(i): i = 2, …) Means u(1) = [cases - (c(i) n(i): i=2, 3, …)]/c(1) surplus = s(1) [cases - (c(i) n(i): i = 2, 3, …)]/c(1) + (s(i) n(i): i = 2, 3, …)- stops 31 31
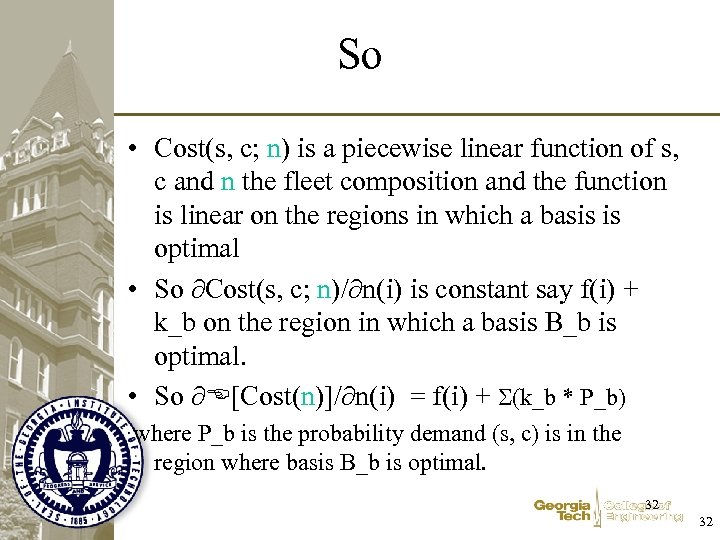 So • Cost(s, c; n) is a piecewise linear function of s, c and n the fleet composition and the function is linear on the regions in which a basis is optimal • So Cost(s, c; n)/ n(i) is constant say f(i) + k_b on the region in which a basis B_b is optimal. • So [Cost(n)]/ n(i) = f(i) + (k_b * P_b) where P_b is the probability demand (s, c) is in the region where basis B_b is optimal. 32 32
So • Cost(s, c; n) is a piecewise linear function of s, c and n the fleet composition and the function is linear on the regions in which a basis is optimal • So Cost(s, c; n)/ n(i) is constant say f(i) + k_b on the region in which a basis B_b is optimal. • So [Cost(n)]/ n(i) = f(i) + (k_b * P_b) where P_b is the probability demand (s, c) is in the region where basis B_b is optimal. 32 32
 Finding P • So, we compute the terms c_b and solve the system • f(i) + (k_b * P_b) = 0 for each vehicle type • To obtain the probabilities P_b • Then find the fleet composition to match these probabilities (it might not be integral, but we can round) • That’s just 5 constraints! 33 33
Finding P • So, we compute the terms c_b and solve the system • f(i) + (k_b * P_b) = 0 for each vehicle type • To obtain the probabilities P_b • Then find the fleet composition to match these probabilities (it might not be integral, but we can round) • That’s just 5 constraints! 33 33
 Wrapping it up • If the recommended fleet composition is not sufficient to meet the demands of our traditional customers, then we use the partial derivatives to move to a minimum cost fleet that does. • This requires a bit more elaboration, but could be accomplished with a Lagrangean approach. 34 34
Wrapping it up • If the recommended fleet composition is not sufficient to meet the demands of our traditional customers, then we use the partial derivatives to move to a minimum cost fleet that does. • This requires a bit more elaboration, but could be accomplished with a Lagrangean approach. 34 34


