7e9378bde4b7680dd1ad7c4335f7abc3.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 22
 Projects and Scope in Germany and D-A-Ch Where is the CIM? Dr. -Ing. Mathias Uslar, OFFIS Folie 1
Projects and Scope in Germany and D-A-Ch Where is the CIM? Dr. -Ing. Mathias Uslar, OFFIS Folie 1
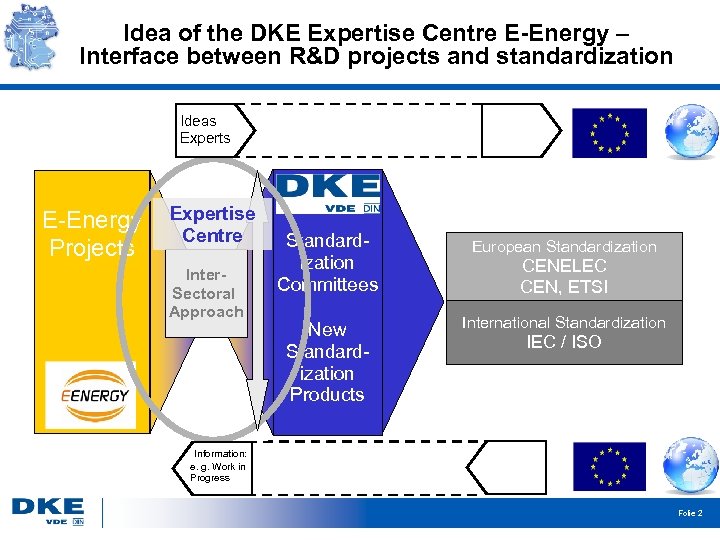 Idea of the DKE Expertise Centre E-Energy – Interface between R&D projects and standardization Ideas Experts E-Energy Projects Expertise Centre Inter. Sectoral Approach Standardization Committees European Standardization New Standardization Products International Standardization CENELEC CEN, ETSI IEC / ISO Information: e. g. Work in Progress Folie 2
Idea of the DKE Expertise Centre E-Energy – Interface between R&D projects and standardization Ideas Experts E-Energy Projects Expertise Centre Inter. Sectoral Approach Standardization Committees European Standardization New Standardization Products International Standardization CENELEC CEN, ETSI IEC / ISO Information: e. g. Work in Progress Folie 2
 Motivation for the German Standardization Roadmap Support of the vision „Smart Grid“ during realization The importance of standardization is emphasized in all discussion about Smart Grid Chapter 3. 4 – Benefits of Smart Grids and their standardization A lot of standardization activities are starting Intersectoral topic with a lot of stakeholders and interfaces Standardization roadmap as basis for a German position in national and international standardization Providing the knowledge from R&D projects like the German EEnergy-Projects in standardization Collecting and summarizing various national activities Information about existing standards and current activities – „Not reinventing the wheel again and again“ Folie 3
Motivation for the German Standardization Roadmap Support of the vision „Smart Grid“ during realization The importance of standardization is emphasized in all discussion about Smart Grid Chapter 3. 4 – Benefits of Smart Grids and their standardization A lot of standardization activities are starting Intersectoral topic with a lot of stakeholders and interfaces Standardization roadmap as basis for a German position in national and international standardization Providing the knowledge from R&D projects like the German EEnergy-Projects in standardization Collecting and summarizing various national activities Information about existing standards and current activities – „Not reinventing the wheel again and again“ Folie 3
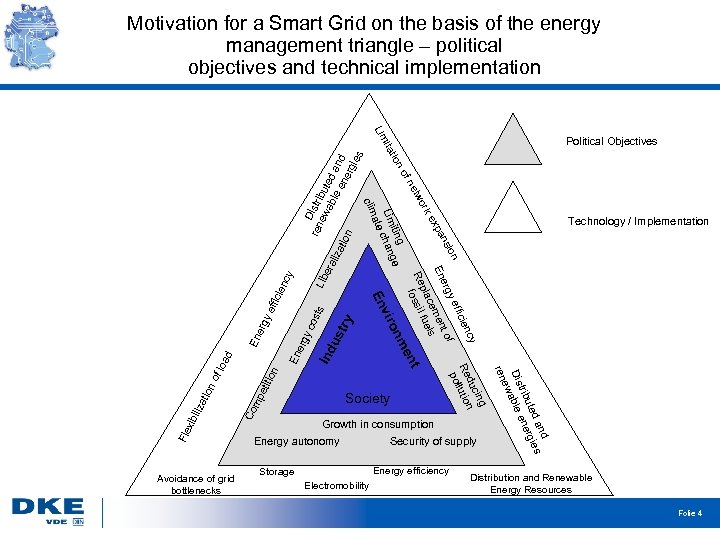 Motivation for a Smart Grid on the basis of the energy management triangle – political objectives and technical implementation fn no tio D ren istri ew but era ab ed liza le en and tio erg n ies ita Lim Political Objectives Lib ncy icie try us Ind En erg y cos t s eff erg y En ad etit ion f lo mp Co Energy autonomy Security of supply Energy efficiency Storage Electromobility nd d a gies r ute trib ene Dis able ew Growth in consumption ren Society g cin du Re llution po t no en nm atio o vir iliz En Fle xib cy ien ffic ye ion of ns erg ent En pa ex cem uels pla f ork Re ossil etw f g itin ge Lim chan ate clim Avoidance of grid bottlenecks Technology / Implementation Distribution and Renewable Energy Resources Folie 4
Motivation for a Smart Grid on the basis of the energy management triangle – political objectives and technical implementation fn no tio D ren istri ew but era ab ed liza le en and tio erg n ies ita Lim Political Objectives Lib ncy icie try us Ind En erg y cos t s eff erg y En ad etit ion f lo mp Co Energy autonomy Security of supply Energy efficiency Storage Electromobility nd d a gies r ute trib ene Dis able ew Growth in consumption ren Society g cin du Re llution po t no en nm atio o vir iliz En Fle xib cy ien ffic ye ion of ns erg ent En pa ex cem uels pla f ork Re ossil etw f g itin ge Lim chan ate clim Avoidance of grid bottlenecks Technology / Implementation Distribution and Renewable Energy Resources Folie 4
 Definition of „Smart Grid“ – One example of the DKE-Committee SMART. GRID The term „Smart Grid“ (an intelligent energy supply system) comprises networking and control of intelligent generators, storage facilities, loads and network operating equipment in power transmission and distribution networks with the aid of Information and Communication Technologies (ICT). The objective is to ensure sustainable and environmentally sound power supply by means of transparent, energy- and cost-efficient, safe and reliable system operation. Folie 5
Definition of „Smart Grid“ – One example of the DKE-Committee SMART. GRID The term „Smart Grid“ (an intelligent energy supply system) comprises networking and control of intelligent generators, storage facilities, loads and network operating equipment in power transmission and distribution networks with the aid of Information and Communication Technologies (ICT). The objective is to ensure sustainable and environmentally sound power supply by means of transparent, energy- and cost-efficient, safe and reliable system operation. Folie 5
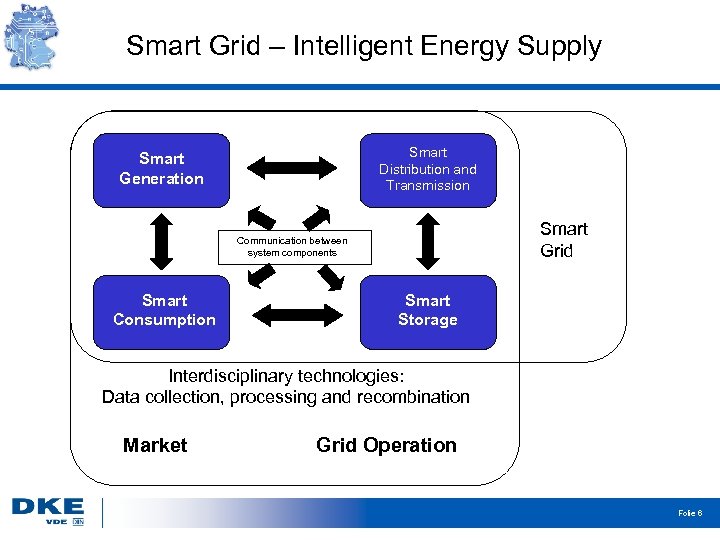 Smart Grid – Intelligent Energy Supply Smart Distribution and Transmission Smart Generation Smart Grid Communication between system components Smart Consumption Smart Storage Interdisciplinary technologies: Data collection, processing and recombination Market Grid Operation Folie 6
Smart Grid – Intelligent Energy Supply Smart Distribution and Transmission Smart Generation Smart Grid Communication between system components Smart Consumption Smart Storage Interdisciplinary technologies: Data collection, processing and recombination Market Grid Operation Folie 6
 A lot of further definitions about the term „Smart Grid“ IEC European Technology Platform ETP Smart Grids ERGEG – European Regulators BDEW - German Association of Energy and Water Industries NIST National Institute for Standards and Technology … Folie 7
A lot of further definitions about the term „Smart Grid“ IEC European Technology Platform ETP Smart Grids ERGEG – European Regulators BDEW - German Association of Energy and Water Industries NIST National Institute for Standards and Technology … Folie 7
 What is a Smart Grid? Like blinded men with an elephant. Various perspectives on a Smart Grid Quelle: E-Energy Jahreskongress 2009, Prof. Gunter Dueck Folie 8
What is a Smart Grid? Like blinded men with an elephant. Various perspectives on a Smart Grid Quelle: E-Energy Jahreskongress 2009, Prof. Gunter Dueck Folie 8
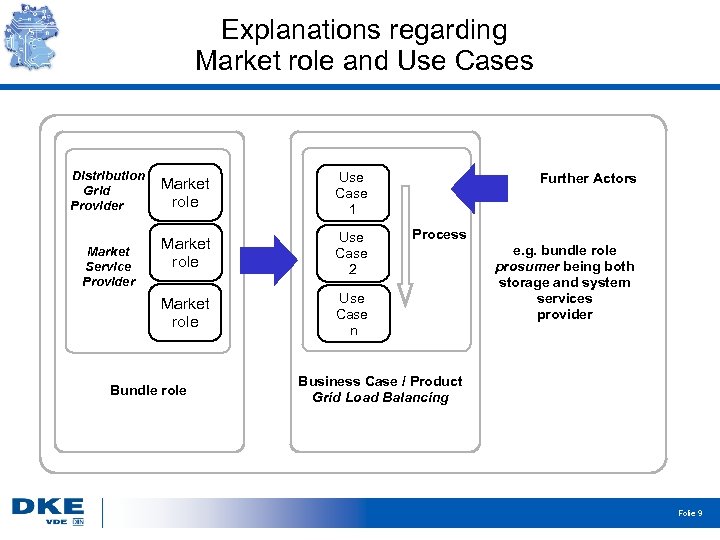 Explanations regarding Market role and Use Cases Distribution Grid Provider Use Case 1 Market role Use Case 2 Market role Market Service Provider Market role Use Case n Bundle role Further Actors Process e. g. bundle role prosumer being both storage and system services provider Business Case / Product Grid Load Balancing Folie 9
Explanations regarding Market role and Use Cases Distribution Grid Provider Use Case 1 Market role Use Case 2 Market role Market Service Provider Market role Use Case n Bundle role Further Actors Process e. g. bundle role prosumer being both storage and system services provider Business Case / Product Grid Load Balancing Folie 9
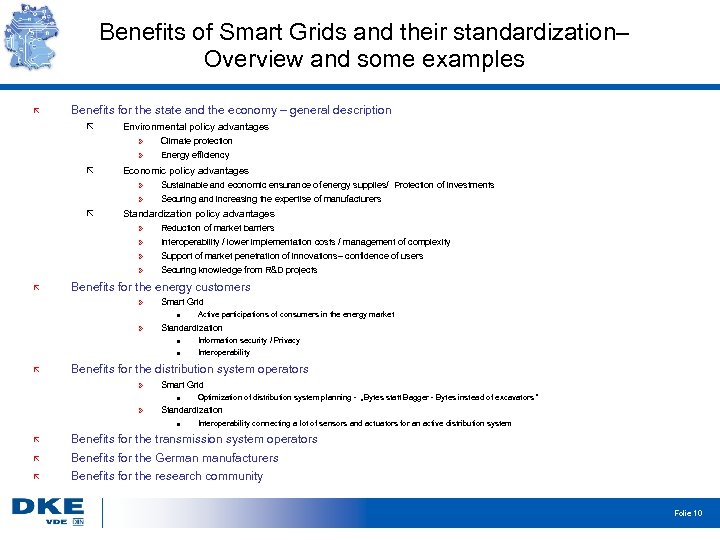 Benefits of Smart Grids and their standardization– Overview and some examples Benefits for the state and the economy – general description Environmental policy advantages » » Sustainable and economic ensurance of energy supplies/ Protection of investments Securing and increasing the expertise of manufacturers Standardization policy advantages » » Energy efficiency Economic policy advantages » » Climate protection Reduction of market barriers Interoperability / lower implementation costs / management of complexity Support of market penetration of innovations– confidence of users Securing knowledge from R&D projects Benefits for the energy customers » Smart Grid » Standardization Active participations of consumers in the energy market Information security / Privacy Interoperability Benefits for the distribution system operators » Smart Grid » Optimization of distribution system planning - „Bytes statt Bagger - Bytes instead of excavators “ Standardization Interoperability connecting a lot of sensors and actuators for an active distribution system Benefits for the transmission system operators Benefits for the German manufacturers Benefits for the research community Folie 10
Benefits of Smart Grids and their standardization– Overview and some examples Benefits for the state and the economy – general description Environmental policy advantages » » Sustainable and economic ensurance of energy supplies/ Protection of investments Securing and increasing the expertise of manufacturers Standardization policy advantages » » Energy efficiency Economic policy advantages » » Climate protection Reduction of market barriers Interoperability / lower implementation costs / management of complexity Support of market penetration of innovations– confidence of users Securing knowledge from R&D projects Benefits for the energy customers » Smart Grid » Standardization Active participations of consumers in the energy market Information security / Privacy Interoperability Benefits for the distribution system operators » Smart Grid » Optimization of distribution system planning - „Bytes statt Bagger - Bytes instead of excavators “ Standardization Interoperability connecting a lot of sensors and actuators for an active distribution system Benefits for the transmission system operators Benefits for the German manufacturers Benefits for the research community Folie 10
 National and international studies considered for the roadmap Basis for the Roadmap and the comparison of various studies on Smart Grid standardization Uslar, et al. : „Investigations on the standardization environment of the R&D Project „ E-Energy - ICT-based energy system of the future” - Untersuchung des Normungsumfeldes zum BMWi-Förderschwerpunkt E-Energy – IKT-basiertes Energiesystem der Zukunft”, Study for the German Federal Ministry of Economics and Technology 2009, www. e-energy. de Further studies and publications International / European studies » » » Studies in Germany » » » IEC/Technical Committee (TC) 57 IEC/SMB Strategy Group 3 (SG 3) „Smart Grid“ - Roadmap CEN / CENELEC / ETSI Smart Meters Co-ordination Group zum EU-Mandat M/441 CIGRE D 2. 24 UCAiug - Open Smart Grid Subcommittee „BDI initiativ“ - Internet for Energy Identification of future fields of standardization 2009 – Basic study by DIN Deutsches Institut für Normung e. V. ZVEI - Automation 2020+ Energy integrated technology roadmap National Studies / Activities » » » NIST Framework and Roadmap for Smart Grid Interoperability Standards IEEE P 2030 Futu. Red – Spanish Electrical Grid Platform Smart Grids-Roadmap Österreich Electricity Networks Strategy Group (UK) - A Smart Grid Routemap Japan’s roadmap to international standardisation for Smart Grid and collaborations with other countries Folie 11
National and international studies considered for the roadmap Basis for the Roadmap and the comparison of various studies on Smart Grid standardization Uslar, et al. : „Investigations on the standardization environment of the R&D Project „ E-Energy - ICT-based energy system of the future” - Untersuchung des Normungsumfeldes zum BMWi-Förderschwerpunkt E-Energy – IKT-basiertes Energiesystem der Zukunft”, Study for the German Federal Ministry of Economics and Technology 2009, www. e-energy. de Further studies and publications International / European studies » » » Studies in Germany » » » IEC/Technical Committee (TC) 57 IEC/SMB Strategy Group 3 (SG 3) „Smart Grid“ - Roadmap CEN / CENELEC / ETSI Smart Meters Co-ordination Group zum EU-Mandat M/441 CIGRE D 2. 24 UCAiug - Open Smart Grid Subcommittee „BDI initiativ“ - Internet for Energy Identification of future fields of standardization 2009 – Basic study by DIN Deutsches Institut für Normung e. V. ZVEI - Automation 2020+ Energy integrated technology roadmap National Studies / Activities » » » NIST Framework and Roadmap for Smart Grid Interoperability Standards IEEE P 2030 Futu. Red – Spanish Electrical Grid Platform Smart Grids-Roadmap Österreich Electricity Networks Strategy Group (UK) - A Smart Grid Routemap Japan’s roadmap to international standardisation for Smart Grid and collaborations with other countries Folie 11
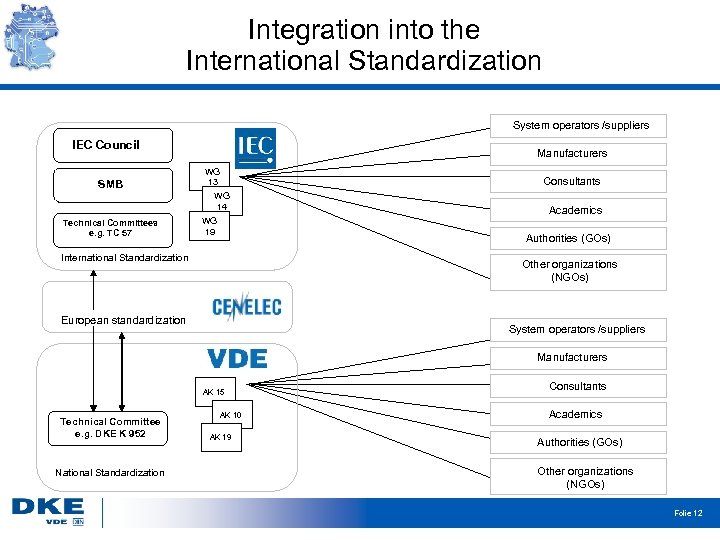 Integration into the International Standardization System operators /suppliers IEC Council SMB Technical Committees e. g. TC 57 Manufacturers WG 13 WG 14 WG 19 Consultants Academics Authorities (GOs) International Standardization Other organizations (NGOs) European standardization System operators /suppliers Manufacturers AK 15 Technical Committee e. g. DKE K 952 National Standardization AK 10 AK 19 Consultants Academics Authorities (GOs) Other organizations (NGOs) Folie 12
Integration into the International Standardization System operators /suppliers IEC Council SMB Technical Committees e. g. TC 57 Manufacturers WG 13 WG 14 WG 19 Consultants Academics Authorities (GOs) International Standardization Other organizations (NGOs) European standardization System operators /suppliers Manufacturers AK 15 Technical Committee e. g. DKE K 952 National Standardization AK 10 AK 19 Consultants Academics Authorities (GOs) Other organizations (NGOs) Folie 12
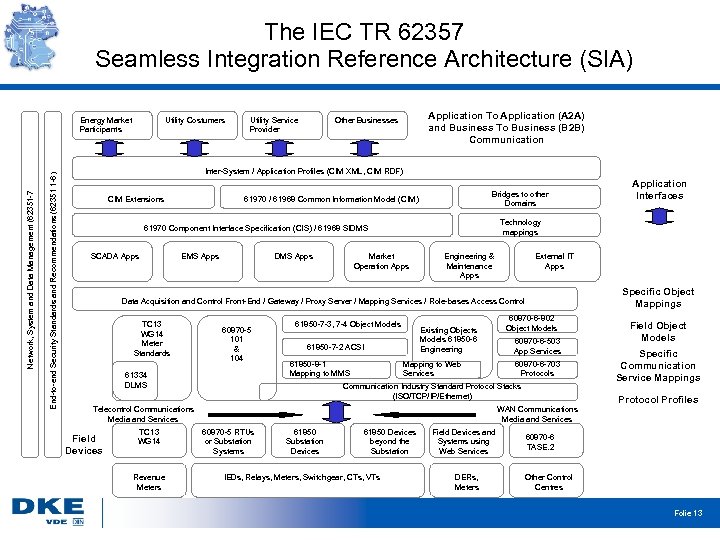 The IEC TR 62357 Seamless Integration Reference Architecture (SIA) End-to-end Security Standards and Recommendations (62351 1 -6) Network, System and Data Management (62351 -7 Energy Market Participants Utility Costumers Utility Service Provider Application To Application (A 2 A) and Business To Business (B 2 B) Communication Other Businesses Inter-System / Application Profiles (CIM XML, CIM RDF) CIM Extensions Bridges to other Domains 61970 / 61968 Common Information Model (CIM) Technology mappings 61970 Component Interface Specification (CIS) / 61968 SIDMS SCADA Apps EMS Apps DMS Apps Market Operation Apps Engineering & Maintenance Apps External IT Apps Specific Object Mappings Data Acquisition and Control Front-End / Gateway / Proxy Server / Mapping Services / Role-bases Access Control TC 13 WG 14 Meter Standards 60870 -5 101 & 104 61334 DLMS 61850 -7 -3, 7 -4 Object Models Existing Objects Models 61850 -6 Engineering 61850 -7 -2 ACSI 61850 -8 -1 Mapping to MMS Mapping to Web Services TC 13 WG 14 Revenue Meters 60870 -6 -802 Object Models 60870 -6 -503 App Services 60870 -6 -703 Protocols Communication Industry Standard Protocol Stacks (ISO/TCP/IP/Ethernet) Telecontrol Communications Media and Services Field Devices WAN Communications Media and Services 60870 -5 RTUs or Substation Systems 61850 Substation Devices 61850 Devices beyond the Substation IEDs, Relays, Meters, Switchgear, CTs, VTs Application Interfaces Field Devices and Systems using Web Services DERs, Meters Field Object Models Specific Communication Service Mappings Protocol Profiles 60870 -6 TASE. 2 Other Control Centres Folie 13
The IEC TR 62357 Seamless Integration Reference Architecture (SIA) End-to-end Security Standards and Recommendations (62351 1 -6) Network, System and Data Management (62351 -7 Energy Market Participants Utility Costumers Utility Service Provider Application To Application (A 2 A) and Business To Business (B 2 B) Communication Other Businesses Inter-System / Application Profiles (CIM XML, CIM RDF) CIM Extensions Bridges to other Domains 61970 / 61968 Common Information Model (CIM) Technology mappings 61970 Component Interface Specification (CIS) / 61968 SIDMS SCADA Apps EMS Apps DMS Apps Market Operation Apps Engineering & Maintenance Apps External IT Apps Specific Object Mappings Data Acquisition and Control Front-End / Gateway / Proxy Server / Mapping Services / Role-bases Access Control TC 13 WG 14 Meter Standards 60870 -5 101 & 104 61334 DLMS 61850 -7 -3, 7 -4 Object Models Existing Objects Models 61850 -6 Engineering 61850 -7 -2 ACSI 61850 -8 -1 Mapping to MMS Mapping to Web Services TC 13 WG 14 Revenue Meters 60870 -6 -802 Object Models 60870 -6 -503 App Services 60870 -6 -703 Protocols Communication Industry Standard Protocol Stacks (ISO/TCP/IP/Ethernet) Telecontrol Communications Media and Services Field Devices WAN Communications Media and Services 60870 -5 RTUs or Substation Systems 61850 Substation Devices 61850 Devices beyond the Substation IEDs, Relays, Meters, Switchgear, CTs, VTs Application Interfaces Field Devices and Systems using Web Services DERs, Meters Field Object Models Specific Communication Service Mappings Protocol Profiles 60870 -6 TASE. 2 Other Control Centres Folie 13
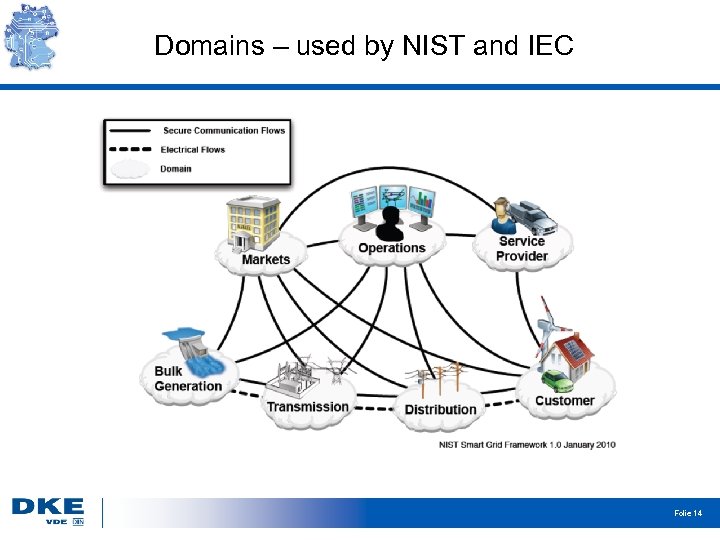 Domains – used by NIST and IEC Folie 14
Domains – used by NIST and IEC Folie 14
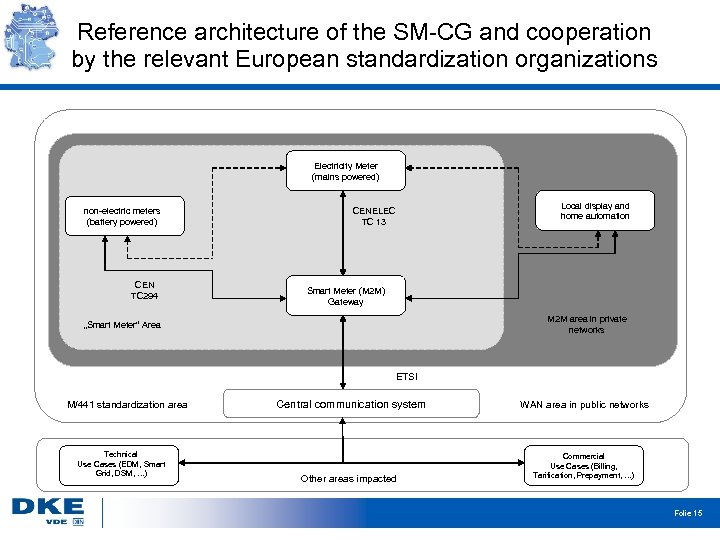 Reference architecture of the SM-CG and cooperation by the relevant European standardization organizations Electricity Meter (mains powered) non-electric meters (battery powered) CEN TC 294 Local display and home automation CENELEC TC 13 Smart Meter (M 2 M) Gateway M 2 M area in private networks „Smart Meter“ Area ETSI M/441 standardization area Technical Use Cases (EDM, Smart Grid, DSM, . . . ) Central communication system Other areas impacted WAN area in public networks Commercial Use Cases (Billing, Tarification, Prepayment, . . . ) Folie 15
Reference architecture of the SM-CG and cooperation by the relevant European standardization organizations Electricity Meter (mains powered) non-electric meters (battery powered) CEN TC 294 Local display and home automation CENELEC TC 13 Smart Meter (M 2 M) Gateway M 2 M area in private networks „Smart Meter“ Area ETSI M/441 standardization area Technical Use Cases (EDM, Smart Grid, DSM, . . . ) Central communication system Other areas impacted WAN area in public networks Commercial Use Cases (Billing, Tarification, Prepayment, . . . ) Folie 15
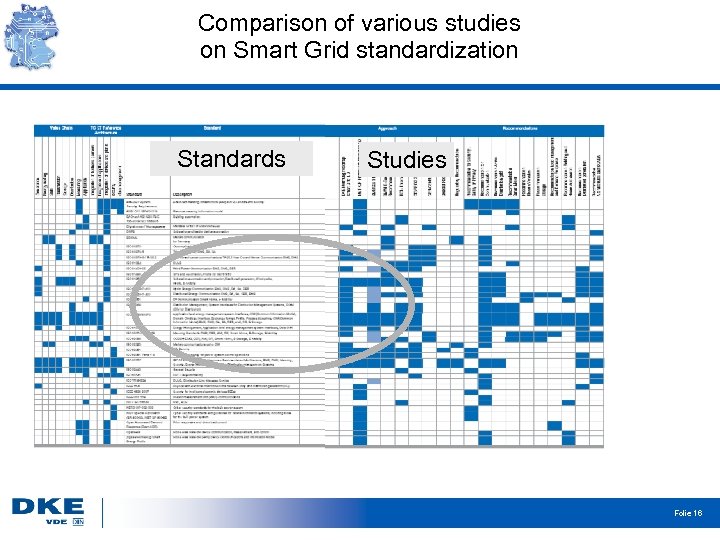 Comparison of various studies on Smart Grid standardization Standards Studies Folie 16
Comparison of various studies on Smart Grid standardization Standards Studies Folie 16
 A lot is available – Recognized Core Standards for the Smart Grid IEC 62357: Seamless Integration Reference Architecture IEC 60870: Transport protocols IEC 61970/61968: Common Information Model CIM IEC 62325: Market Communications using CIM IEC 61850, 61850 -7 -4 XX: SAS, Communications, DER IEC 61400: Communications for monitoring and control of wind power plants IEC 62351: Security for Smart Grid IEC 61334: DLMS IEC 62056: COSEM EN 50090 (KNX) (ISO/IEC JTC 1 SC 25 - ISO/IEC 14543 -3, CEN/TC 247 (BACS/HLK) - EN 13321 -1 und -2) Zig. Bee EN 50523 (Home Appliances) Market communication Integration of DER IT Security Smart Metering Inhouse Automation Folie 17
A lot is available – Recognized Core Standards for the Smart Grid IEC 62357: Seamless Integration Reference Architecture IEC 60870: Transport protocols IEC 61970/61968: Common Information Model CIM IEC 62325: Market Communications using CIM IEC 61850, 61850 -7 -4 XX: SAS, Communications, DER IEC 61400: Communications for monitoring and control of wind power plants IEC 62351: Security for Smart Grid IEC 61334: DLMS IEC 62056: COSEM EN 50090 (KNX) (ISO/IEC JTC 1 SC 25 - ISO/IEC 14543 -3, CEN/TC 247 (BACS/HLK) - EN 13321 -1 und -2) Zig. Bee EN 50523 (Home Appliances) Market communication Integration of DER IT Security Smart Metering Inhouse Automation Folie 17
 Recommendations - Overview Cross-cutting topics Regulatory and legislative recommendations Recommendations on Information Security, Privacy and Data Protection (4) Recommendations of the area of Communications General recommendations Recommendations of the areas of Architectures, Communications and Power System Management Processes (4) (13) (4) Domain-specific areas Recommendations for the area of Active Distribution Systems Recommendations for the area of Smart Meters (5) Recommendations for the area of Distributed Generation Recommendations of the area of Electro mobility (3) Recommendations for the area of Storage (3) Recommendations for the area of Load Management / Demand Response (2) Recommendations for the area of Building and In-house Automation (6) (2) (3) Folie 18
Recommendations - Overview Cross-cutting topics Regulatory and legislative recommendations Recommendations on Information Security, Privacy and Data Protection (4) Recommendations of the area of Communications General recommendations Recommendations of the areas of Architectures, Communications and Power System Management Processes (4) (13) (4) Domain-specific areas Recommendations for the area of Active Distribution Systems Recommendations for the area of Smart Meters (5) Recommendations for the area of Distributed Generation Recommendations of the area of Electro mobility (3) Recommendations for the area of Storage (3) Recommendations for the area of Load Management / Demand Response (2) Recommendations for the area of Building and In-house Automation (6) (2) (3) Folie 18
 Recommendations – Samples (I) Great importance of standards for the realization of Smart Grids Coordinating task for the DKE Expertise Centre for E-Energy on national level International Standards as Basis Modular approach for standards – first generic and later specific on national or regional level in case Experts should participate also in the international standardization Link to the work of IEC/TC 57 Framework Information security, data protection (privacy), critical infrastructure and product / system safety – Precondition for user confidence Interoperability, data models and semantics Interoperability tests Support for the market launch (of standards and Smart Grid) Training of specialist Information of the public Recommendations on regulatory and legislative changes – Market communication, bandwidth, framework conditions for variable tariffs Folie 19
Recommendations – Samples (I) Great importance of standards for the realization of Smart Grids Coordinating task for the DKE Expertise Centre for E-Energy on national level International Standards as Basis Modular approach for standards – first generic and later specific on national or regional level in case Experts should participate also in the international standardization Link to the work of IEC/TC 57 Framework Information security, data protection (privacy), critical infrastructure and product / system safety – Precondition for user confidence Interoperability, data models and semantics Interoperability tests Support for the market launch (of standards and Smart Grid) Training of specialist Information of the public Recommendations on regulatory and legislative changes – Market communication, bandwidth, framework conditions for variable tariffs Folie 19
 Recommendations – Samples (II) Securing knowledge from R&D projects on Smart Grids Use Cases – Basis for architecture, interfaces and standards CIM IEC 61970 and IEC 61850 Consolidation Use of the framework also for non-electrical media Further developments of the models, especially regarding DER (IEC 61850 -7420) Distribution system automation – distributed automation on lower voltage levels Smart Meter Standardization profiles of VDE|FNN to be used and und further enhanced with new developments (Mandate M/441, information security) Intersectoral cooperation Cooperation of TC 57 and TC 13 on international level Folie 20
Recommendations – Samples (II) Securing knowledge from R&D projects on Smart Grids Use Cases – Basis for architecture, interfaces and standards CIM IEC 61970 and IEC 61850 Consolidation Use of the framework also for non-electrical media Further developments of the models, especially regarding DER (IEC 61850 -7420) Distribution system automation – distributed automation on lower voltage levels Smart Meter Standardization profiles of VDE|FNN to be used and und further enhanced with new developments (Mandate M/441, information security) Intersectoral cooperation Cooperation of TC 57 and TC 13 on international level Folie 20
 Recommendations – Samples (III) Electro mobility Convergence of sectors – further cooperation needed Building and home automation (Inhouse automation) New functions for the energy management Motivation to use demand or generation management: e. g. new tariffs Use also in existing buildings and of existing devices as far as possible Cooperation with other domains and media (AAL, security / heat, gas) Phase 2 Transmission system Convergence of transport, IKT, Multi-Utility Folie 21
Recommendations – Samples (III) Electro mobility Convergence of sectors – further cooperation needed Building and home automation (Inhouse automation) New functions for the energy management Motivation to use demand or generation management: e. g. new tariffs Use also in existing buildings and of existing devices as far as possible Cooperation with other domains and media (AAL, security / heat, gas) Phase 2 Transmission system Convergence of transport, IKT, Multi-Utility Folie 21
 Executive Summary Use and marketing of existing standards Coordination and focus Further development of standards Support for innovation Speed / International orientation Involvement in standardization Political support Many of the necessary standards already exist. There are internationally recognized standards in the fields of power, industrial and building automation. These will have to be used and promotef accordingly. The Smart Grid is characterised by a large number of players and disciplines. Inter-domain cooperation and coordination by the establishment of a steering group and groups dealing with focal and interdisciplinary topics are necessary if duplication of effort is to be avoided. The fundamental need for action consists in linking the established domains. In order to promote innovation, standardization should focus on interoperability and avoid specification of technical solutions. There is at present competition between different national and regional standardization concepts. Rapid implementation of the results achieved in Germany (Europe) in standards is therefore essential. Increased participation in standardization activities on national, regional and international levels is necessary for achievement of the objectives. German companies should therefore make greater contributions to German, European and international standardization. Close dovetailing cooperation of research and development, regulation and the legal framework with standardization is necessary. Folie 22
Executive Summary Use and marketing of existing standards Coordination and focus Further development of standards Support for innovation Speed / International orientation Involvement in standardization Political support Many of the necessary standards already exist. There are internationally recognized standards in the fields of power, industrial and building automation. These will have to be used and promotef accordingly. The Smart Grid is characterised by a large number of players and disciplines. Inter-domain cooperation and coordination by the establishment of a steering group and groups dealing with focal and interdisciplinary topics are necessary if duplication of effort is to be avoided. The fundamental need for action consists in linking the established domains. In order to promote innovation, standardization should focus on interoperability and avoid specification of technical solutions. There is at present competition between different national and regional standardization concepts. Rapid implementation of the results achieved in Germany (Europe) in standards is therefore essential. Increased participation in standardization activities on national, regional and international levels is necessary for achievement of the objectives. German companies should therefore make greater contributions to German, European and international standardization. Close dovetailing cooperation of research and development, regulation and the legal framework with standardization is necessary. Folie 22


