3263d680df9c71751a373b4c3bd1c259.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 55
 Project Planning: Resources Assignment José Onofre Montesa Andrés Universidad Politécnica de Valencia Escuela Superior de Informática Aplicada 2003 -2004 GPI-2 E Project Planning: Resources Assignment
Project Planning: Resources Assignment José Onofre Montesa Andrés Universidad Politécnica de Valencia Escuela Superior de Informática Aplicada 2003 -2004 GPI-2 E Project Planning: Resources Assignment
 Resources Assignment • It’s the process in which we associate to each one of the project tasks the necessary people and materials so that tasks can be accomplished • Human resources are the most important economic issues in software projects. More important than the material resources (Hardware and installations). GPI-2 E Project Planning: Resources Assignment 1
Resources Assignment • It’s the process in which we associate to each one of the project tasks the necessary people and materials so that tasks can be accomplished • Human resources are the most important economic issues in software projects. More important than the material resources (Hardware and installations). GPI-2 E Project Planning: Resources Assignment 1
 Human Resources? • People are not human resources. They are human beings, with they right to be different. • In future enterprises – They will have the knowledge as their main resource, – The organizations will be mainly made of specialists that work accordingly to the information they receive. GPI-2 E Project Planning: Resources Assignment 2
Human Resources? • People are not human resources. They are human beings, with they right to be different. • In future enterprises – They will have the knowledge as their main resource, – The organizations will be mainly made of specialists that work accordingly to the information they receive. GPI-2 E Project Planning: Resources Assignment 2
 Other important resources: HARDWARE • Hw costs are decrease continuously. • The hardware resources use depends on the quantity of people assign to the project. GPI-2 E Project Planning: Resources Assignment 3
Other important resources: HARDWARE • Hw costs are decrease continuously. • The hardware resources use depends on the quantity of people assign to the project. GPI-2 E Project Planning: Resources Assignment 3
 Other important resources: CONSULTANTS • They are outside professionals. • They support tasks were the enterprise has no experience. • In complex projects they can reach a cost similar to the developers cost. GPI-2 E Project Planning: Resources Assignment 4
Other important resources: CONSULTANTS • They are outside professionals. • They support tasks were the enterprise has no experience. • In complex projects they can reach a cost similar to the developers cost. GPI-2 E Project Planning: Resources Assignment 4
 Other important resources: Clients and users • The user are present in every stage of the project, mainly in analysis and test. • Usually they aren’t taken into account when planning, this fault is noticed when: – Users complain: “We have wasted so much time and. . . ” – When a user excuses himself for not attending a meeting due to work problems. GPI-2 E Project Planning: Resources Assignment 5
Other important resources: Clients and users • The user are present in every stage of the project, mainly in analysis and test. • Usually they aren’t taken into account when planning, this fault is noticed when: – Users complain: “We have wasted so much time and. . . ” – When a user excuses himself for not attending a meeting due to work problems. GPI-2 E Project Planning: Resources Assignment 5
 In addition to the project assignment tasks. • In other to a team accomplish their work it’s necessary: – tasks themselves. – the team maintenance tasks: – cohesion maintenance, motivation and general willing to achieve the task. – To satisfy individuals needs: – which helps the member to feel part of the team and empowers him to do his best. GPI-2 E Project Planning: Resources Assignment 6
In addition to the project assignment tasks. • In other to a team accomplish their work it’s necessary: – tasks themselves. – the team maintenance tasks: – cohesion maintenance, motivation and general willing to achieve the task. – To satisfy individuals needs: – which helps the member to feel part of the team and empowers him to do his best. GPI-2 E Project Planning: Resources Assignment 6
 Don´t force the plans below what is foreseeable. • The plans condemn the project to failure, whatever the personnel quality or the used tools and processes. • If the elapsed time or budget are shortened. . . – the staff won´t be efficient, – they won’t try harder if the goal is impossible to reach. • Even worse, when the delays start, – The moral will suffer and the project will probably take more time than if it had been made in a reasonable way. GPI-2 E Project Planning: Resources Assignment 7
Don´t force the plans below what is foreseeable. • The plans condemn the project to failure, whatever the personnel quality or the used tools and processes. • If the elapsed time or budget are shortened. . . – the staff won´t be efficient, – they won’t try harder if the goal is impossible to reach. • Even worse, when the delays start, – The moral will suffer and the project will probably take more time than if it had been made in a reasonable way. GPI-2 E Project Planning: Resources Assignment 7
 Determining project elapsed time. • Points of view: – from software developer: • Software is the creation goal. • Project is the way. – from user and client • Software: “Is what I need to reach my business goals” • Project: “It’s the hard time” GPI-2 E Project Planning: Resources Assignment 8
Determining project elapsed time. • Points of view: – from software developer: • Software is the creation goal. • Project is the way. – from user and client • Software: “Is what I need to reach my business goals” • Project: “It’s the hard time” GPI-2 E Project Planning: Resources Assignment 8
 Determining project elapsed time. • Balance: – How much this project will cost, – When it will be available for the user. GPI-2 E Project Planning: Resources Assignment 9
Determining project elapsed time. • Balance: – How much this project will cost, – When it will be available for the user. GPI-2 E Project Planning: Resources Assignment 9
 Project temporal limits vs. resources assignment • A project effort of 165 person/month • One person in 15 Years – It won’t be necessary – Opportunity costs – Out of date when delivered – It can require specialists • 3. 300 Persons in one day – Tasks sequence GPI-2 E Project Planning: Resources Assignment 10
Project temporal limits vs. resources assignment • A project effort of 165 person/month • One person in 15 Years – It won’t be necessary – Opportunity costs – Out of date when delivered – It can require specialists • 3. 300 Persons in one day – Tasks sequence GPI-2 E Project Planning: Resources Assignment 10
 The elapsed time must be adjusted to: • Business aspects, • Development technical aspects – maximum quantity of resources in each tasks, • Management aspects – development team as smallest as possible, – avoid communication and coordination problems GPI-2 E Project Planning: Resources Assignment 11
The elapsed time must be adjusted to: • Business aspects, • Development technical aspects – maximum quantity of resources in each tasks, • Management aspects – development team as smallest as possible, – avoid communication and coordination problems GPI-2 E Project Planning: Resources Assignment 11
 Determining the delivery time. • Negotiation. • Selecting an alternative • Empirical method (Putnam and Norden). GPI-2 E Project Planning: Resources Assignment 12
Determining the delivery time. • Negotiation. • Selecting an alternative • Empirical method (Putnam and Norden). GPI-2 E Project Planning: Resources Assignment 12
 Negotiation. • It’s right, commercial spirit, but dangerous if. . . – We start to negotiate without a clear – – specification from the client. The user knows but little about present development techniques. The user needs the software as soon as possible. The DPC director or the project chief negotiates with a higher hierarchical level user. The users work is to contract services to outside enterprises and they know that the offer can always be decreased. GPI-2 E Project Planning: Resources Assignment 13
Negotiation. • It’s right, commercial spirit, but dangerous if. . . – We start to negotiate without a clear – – specification from the client. The user knows but little about present development techniques. The user needs the software as soon as possible. The DPC director or the project chief negotiates with a higher hierarchical level user. The users work is to contract services to outside enterprises and they know that the offer can always be decreased. GPI-2 E Project Planning: Resources Assignment 13
 negotiation (only) can lead to: • Strong personal commitment from the project manager. • The developer take little participation when fixing the timetable. • This is an ideal situation for failure: • Unknowing the user’s needs leads to underestimating them. • The manager own commitment will hardly be supported by his subordinates. GPI-2 E Project Planning: Resources Assignment 14
negotiation (only) can lead to: • Strong personal commitment from the project manager. • The developer take little participation when fixing the timetable. • This is an ideal situation for failure: • Unknowing the user’s needs leads to underestimating them. • The manager own commitment will hardly be supported by his subordinates. GPI-2 E Project Planning: Resources Assignment 14
 Selecting an alternative. • I want to have a funny evening. . . • … Each one has his own taste. . . GPI-2 E Project Planning: Resources Assignment 15
Selecting an alternative. • I want to have a funny evening. . . • … Each one has his own taste. . . GPI-2 E Project Planning: Resources Assignment 15
 We can offer: • Different designs… • Different plans for a given design. • Different points of view to development: – In house development, – Outsourcing, – Software of the shelf. GPI-2 E Project Planning: Resources Assignment 16
We can offer: • Different designs… • Different plans for a given design. • Different points of view to development: – In house development, – Outsourcing, – Software of the shelf. GPI-2 E Project Planning: Resources Assignment 16
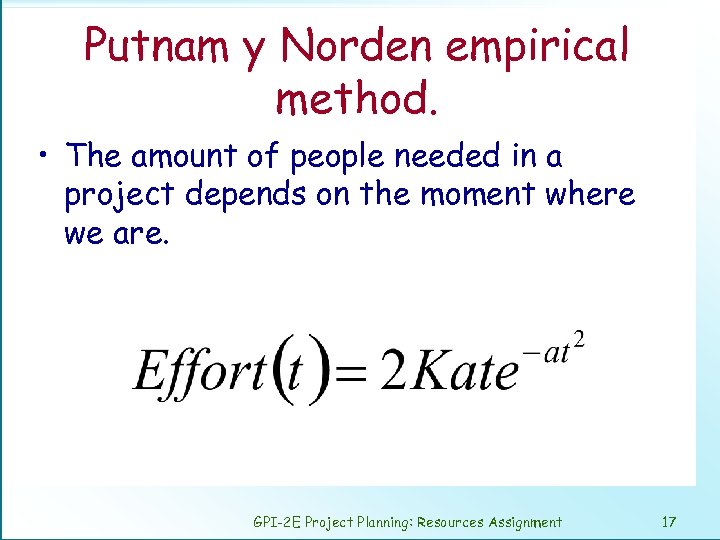 Putnam y Norden empirical method. • The amount of people needed in a project depends on the moment where we are. GPI-2 E Project Planning: Resources Assignment 17
Putnam y Norden empirical method. • The amount of people needed in a project depends on the moment where we are. GPI-2 E Project Planning: Resources Assignment 17
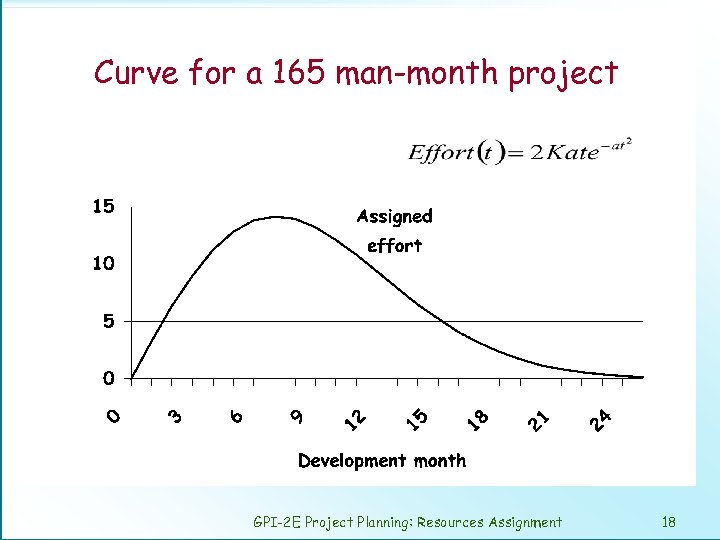 Curve for a 165 man-month project GPI-2 E Project Planning: Resources Assignment 18
Curve for a 165 man-month project GPI-2 E Project Planning: Resources Assignment 18
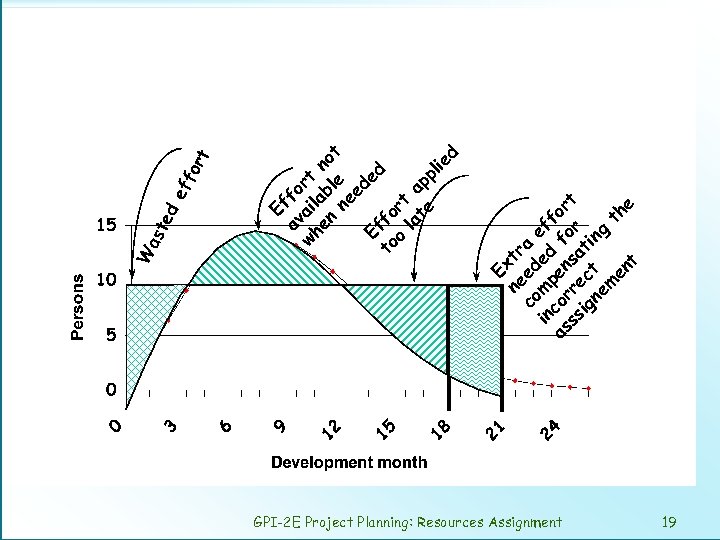 GPI-2 E Project Planning: Resources Assignment 19 ne tr co ed a in mp ed eff as cor en f or ss re sa or t ig ct ti ng ne m th en e t Ex rt fo ef av fo wh ail rt en ab no ne le t ed ed Ef to fo o rt la a te pp lie d Ef ted as W
GPI-2 E Project Planning: Resources Assignment 19 ne tr co ed a in mp ed eff as cor en f or ss re sa or t ig ct ti ng ne m th en e t Ex rt fo ef av fo wh ail rt en ab no ne le t ed ed Ef to fo o rt la a te pp lie d Ef ted as W
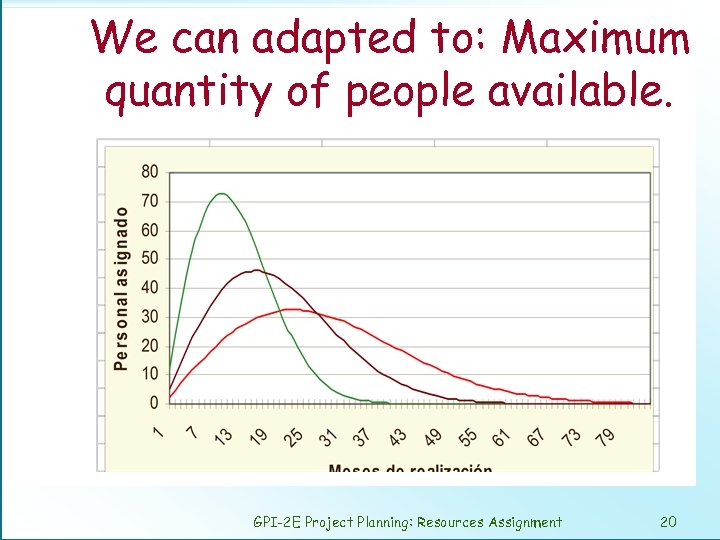 We can adapted to: Maximum quantity of people available. GPI-2 E Project Planning: Resources Assignment 20
We can adapted to: Maximum quantity of people available. GPI-2 E Project Planning: Resources Assignment 20
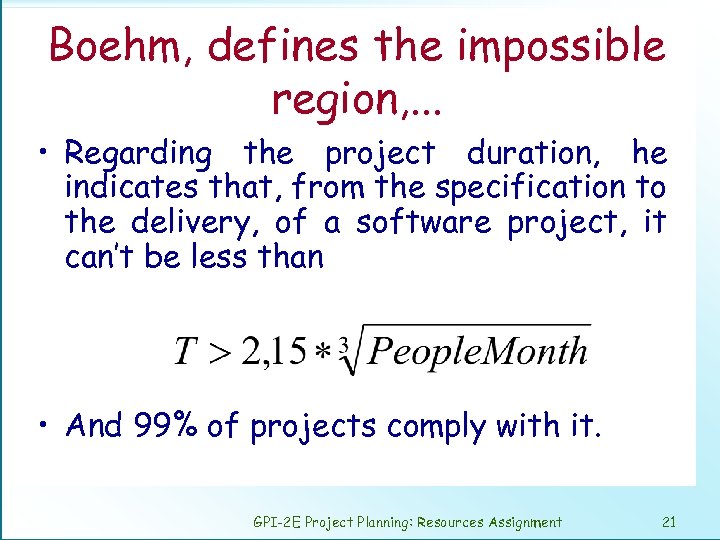 Boehm, defines the impossible region, . . . • Regarding the project duration, he indicates that, from the specification to the delivery, of a software project, it can’t be less than • And 99% of projects comply with it. GPI-2 E Project Planning: Resources Assignment 21
Boehm, defines the impossible region, . . . • Regarding the project duration, he indicates that, from the specification to the delivery, of a software project, it can’t be less than • And 99% of projects comply with it. GPI-2 E Project Planning: Resources Assignment 21
 Usual types of resources. • • • Work Place of work Equipment Basic material for the development office material GPI-2 E Project Planning: Resources Assignment 22
Usual types of resources. • • • Work Place of work Equipment Basic material for the development office material GPI-2 E Project Planning: Resources Assignment 22
 Usual types of resources: work • Development team • Development support • Clients y users GPI-2 E Project Planning: Resources Assignment 23
Usual types of resources: work • Development team • Development support • Clients y users GPI-2 E Project Planning: Resources Assignment 23
 Usual types of resources: Place of work • Meeting rooms • Development environment: Silent quiet • Data withdrawal areas GPI-2 E Project Planning: Resources Assignment 24
Usual types of resources: Place of work • Meeting rooms • Development environment: Silent quiet • Data withdrawal areas GPI-2 E Project Planning: Resources Assignment 24
 Usual types of resources: Equipment • Office furniture • Computers • Presentations material GPI-2 E Project Planning: Resources Assignment 25
Usual types of resources: Equipment • Office furniture • Computers • Presentations material GPI-2 E Project Planning: Resources Assignment 25
 Usual types of resources: Basic development material • O. S. , development languages, development tools (case). • Software manuals: initiation, user’s manual, libraries, etc. . • Books regarding development techniques GPI-2 E Project Planning: Resources Assignment 26
Usual types of resources: Basic development material • O. S. , development languages, development tools (case). • Software manuals: initiation, user’s manual, libraries, etc. . • Books regarding development techniques GPI-2 E Project Planning: Resources Assignment 26
 Usual types of resources: office material • Desk materials: pens, clips, staples. . . • Needed material for the equipment: printer’s ink, toner. . . GPI-2 E Project Planning: Resources Assignment 27
Usual types of resources: office material • Desk materials: pens, clips, staples. . . • Needed material for the equipment: printer’s ink, toner. . . GPI-2 E Project Planning: Resources Assignment 27
 Lasting of tasks Resources effort Lasting • Effort and lasting of tasks • Assigning people to tasks • Task type and lasting according to de number of people assigned. GPI-2 E Project Planning: Resources Assignment 28
Lasting of tasks Resources effort Lasting • Effort and lasting of tasks • Assigning people to tasks • Task type and lasting according to de number of people assigned. GPI-2 E Project Planning: Resources Assignment 28
 Effort and lasting of tasks GPI-2 E Project Planning: Resources Assignment 29
Effort and lasting of tasks GPI-2 E Project Planning: Resources Assignment 29
 Difference between work effort and elapsed duration. . . • Re-work or defect repair on previously completed dependent tasks. • Holidays, weekends and public holidays. • Consulting or coaching other teams members. • Rostered days off. • Non project administration. • Non project education and team coaching. GPI-2 E Project Planning: Resources Assignment 30
Difference between work effort and elapsed duration. . . • Re-work or defect repair on previously completed dependent tasks. • Holidays, weekends and public holidays. • Consulting or coaching other teams members. • Rostered days off. • Non project administration. • Non project education and team coaching. GPI-2 E Project Planning: Resources Assignment 30
 Difference between work effort and elapsed duration. . . • • • Non project meetings. Interruptions including phone calls. Non project paperwork. Wait time for meetings, results. Switch time, e. g. , the time required to “switch” between tasks. • It is not unusual for this factors to account for 30% to 50% of the elapsed day. GPI-2 E Project Planning: Resources Assignment 31
Difference between work effort and elapsed duration. . . • • • Non project meetings. Interruptions including phone calls. Non project paperwork. Wait time for meetings, results. Switch time, e. g. , the time required to “switch” between tasks. • It is not unusual for this factors to account for 30% to 50% of the elapsed day. GPI-2 E Project Planning: Resources Assignment 31
 the more experienced people the more affected • They must train and teach the project personnel in unforeseen subjects; • They are consulted by others projects, and • they are usually asked to attend meetings, presentations. . . which had no relation with the present project. GPI-2 E Project Planning: Resources Assignment 32
the more experienced people the more affected • They must train and teach the project personnel in unforeseen subjects; • They are consulted by others projects, and • they are usually asked to attend meetings, presentations. . . which had no relation with the present project. GPI-2 E Project Planning: Resources Assignment 32
 Assigning people to tasks GPI-2 E Project Planning: Resources Assignment 33
Assigning people to tasks GPI-2 E Project Planning: Resources Assignment 33
 Assigning people to tasks • It’s better to have a small team with good professionals. • With the right people, even if tools, languages and processes are not enough, it can be successful. • Otherwise it seems impossible. • But: – If we entrust everything to few people. – What happen if they leave the company? • We need to balance the personnel. GPI-2 E Project Planning: Resources Assignment 34
Assigning people to tasks • It’s better to have a small team with good professionals. • With the right people, even if tools, languages and processes are not enough, it can be successful. • Otherwise it seems impossible. • But: – If we entrust everything to few people. – What happen if they leave the company? • We need to balance the personnel. GPI-2 E Project Planning: Resources Assignment 34
 We evaluate employee-task according to this aspects: • The KAS, technical capability: – Knowledge to carry out the task, – Ability to have the task done, and – Skills necessaries in the subject. • The MAC, cognitive, willpower: – Motivation, – Assurance, and – Commitment. GPI-2 E Project Planning: Resources Assignment 35
We evaluate employee-task according to this aspects: • The KAS, technical capability: – Knowledge to carry out the task, – Ability to have the task done, and – Skills necessaries in the subject. • The MAC, cognitive, willpower: – Motivation, – Assurance, and – Commitment. GPI-2 E Project Planning: Resources Assignment 35
 Assigning people to tasks. Either the person: • • Can do the job and wants to do it. Can do the job and is prepared to do it. Can do the job and isn’t prepared to do it. Can be trained/instructed into doing the job. • Cannot do the job. GPI-2 E Project Planning: Resources Assignment 36
Assigning people to tasks. Either the person: • • Can do the job and wants to do it. Can do the job and is prepared to do it. Can do the job and isn’t prepared to do it. Can be trained/instructed into doing the job. • Cannot do the job. GPI-2 E Project Planning: Resources Assignment 36
 Can do the job and wants to do it. • it is the ideal one – If as part of your project, you can get a person doing what he or she wants to do, you have harnessed the greatest power on the earth. GPI-2 E Project Planning: Resources Assignment 37
Can do the job and wants to do it. • it is the ideal one – If as part of your project, you can get a person doing what he or she wants to do, you have harnessed the greatest power on the earth. GPI-2 E Project Planning: Resources Assignment 37
 Can do the job and is prepared to do it. • It’s still OK. – If what people are asked to do doesn’t fit in with their own personal plans then in the long term, I believe that you are swimming against the tide. GPI-2 E Project Planning: Resources Assignment 38
Can do the job and is prepared to do it. • It’s still OK. – If what people are asked to do doesn’t fit in with their own personal plans then in the long term, I believe that you are swimming against the tide. GPI-2 E Project Planning: Resources Assignment 38
 Can do the job and isn’t prepared to do it. • You’ve got a problem. The person can do the job but won't. . revert to either situation 1 or 5. GPI-2 E Project Planning: Resources Assignment 39
Can do the job and isn’t prepared to do it. • You’ve got a problem. The person can do the job but won't. . revert to either situation 1 or 5. GPI-2 E Project Planning: Resources Assignment 39
 Can be trained/instructed into doing the job. • Then provided: – You are prepared to put in the training time and money. – and you allow for training time in the project schedule. – and you allow for the extra management overhead. – and you’re prepared to run with the risk that if it might not work out. GPI-2 E Project Planning: Resources Assignment 40
Can be trained/instructed into doing the job. • Then provided: – You are prepared to put in the training time and money. – and you allow for training time in the project schedule. – and you allow for the extra management overhead. – and you’re prepared to run with the risk that if it might not work out. GPI-2 E Project Planning: Resources Assignment 40
 Cannot do the job. • You have a major problem. • you need to find jobs within your project that the person can do. GPI-2 E Project Planning: Resources Assignment 41
Cannot do the job. • You have a major problem. • you need to find jobs within your project that the person can do. GPI-2 E Project Planning: Resources Assignment 41
 Task type and lasting according to de number of people assigned • We can assign a certain number of people to one task. • The proportion between number of people assigned to a task and effort has no lineal relation. • Assigning more people to a project when it is in it’s half way doesn’t necessary reduce its duration. GPI-2 E Project Planning: Resources Assignment 42
Task type and lasting according to de number of people assigned • We can assign a certain number of people to one task. • The proportion between number of people assigned to a task and effort has no lineal relation. • Assigning more people to a project when it is in it’s half way doesn’t necessary reduce its duration. GPI-2 E Project Planning: Resources Assignment 42
 Task type and lasting according to de number of people assigned 1) Task can be partitioned perfectly. 2) Task cannot be partitioned. 3) Task can be partitioned but require communication among the subtasks. 4) the task is complex adding more workers lengthen the schedule. GPI-2 E Project Planning: Resources Assignment 43
Task type and lasting according to de number of people assigned 1) Task can be partitioned perfectly. 2) Task cannot be partitioned. 3) Task can be partitioned but require communication among the subtasks. 4) the task is complex adding more workers lengthen the schedule. GPI-2 E Project Planning: Resources Assignment 43
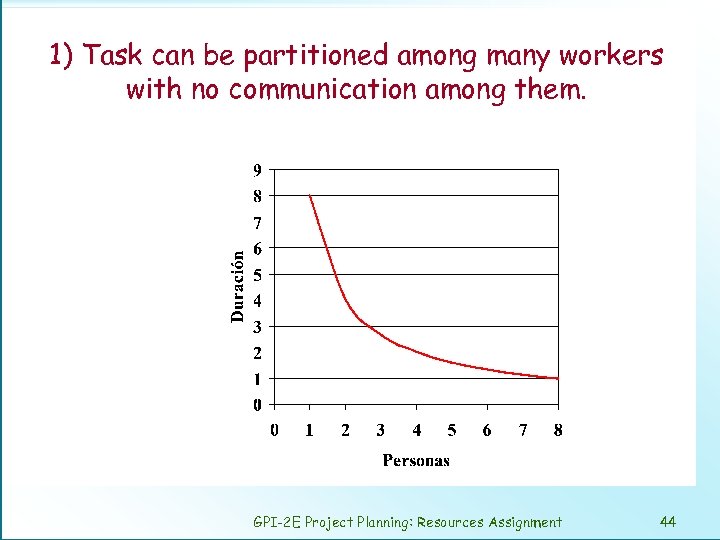 1) Task can be partitioned among many workers with no communication among them. GPI-2 E Project Planning: Resources Assignment 44
1) Task can be partitioned among many workers with no communication among them. GPI-2 E Project Planning: Resources Assignment 44
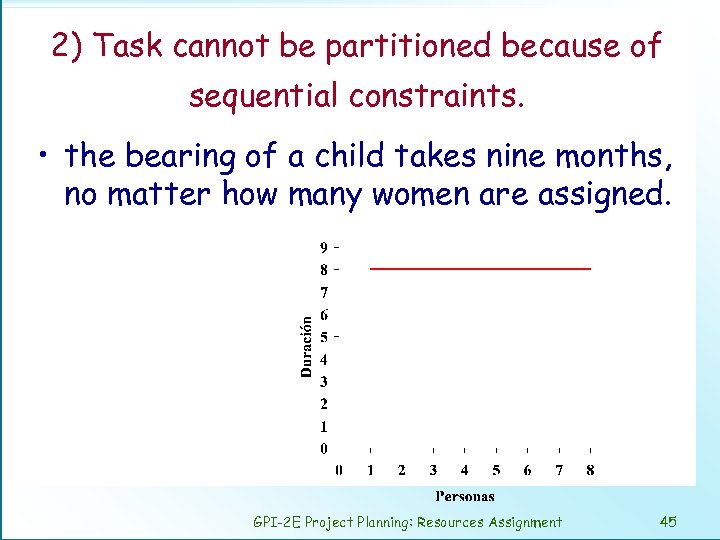 2) Task cannot be partitioned because of sequential constraints. • the bearing of a child takes nine months, no matter how many women are assigned. GPI-2 E Project Planning: Resources Assignment 45
2) Task cannot be partitioned because of sequential constraints. • the bearing of a child takes nine months, no matter how many women are assigned. GPI-2 E Project Planning: Resources Assignment 45
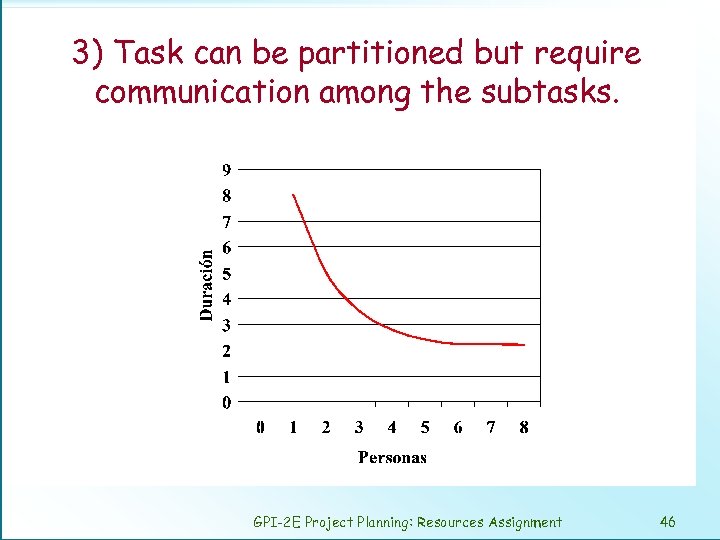 3) Task can be partitioned but require communication among the subtasks. GPI-2 E Project Planning: Resources Assignment 46
3) Task can be partitioned but require communication among the subtasks. GPI-2 E Project Planning: Resources Assignment 46
 4) If the task is complex • the communication increases in a way that adding more workers lengthen the schedule. GPI-2 E Project Planning: Resources Assignment 47
4) If the task is complex • the communication increases in a way that adding more workers lengthen the schedule. GPI-2 E Project Planning: Resources Assignment 47
 Once the task assigned, we’ll have Human resources Assigning PROJECT TASKS GPI-2 E Project Planning: Resources Assignment 48
Once the task assigned, we’ll have Human resources Assigning PROJECT TASKS GPI-2 E Project Planning: Resources Assignment 48
 Tasks consistent assigning. • Manager’s vision of the job differs from employee vision. • Assign the people the tasks they want. • Work assignments with employees. • Have a list of goals per employee. • Meet till the assigning is clear. GPI-2 E Project Planning: Resources Assignment 49
Tasks consistent assigning. • Manager’s vision of the job differs from employee vision. • Assign the people the tasks they want. • Work assignments with employees. • Have a list of goals per employee. • Meet till the assigning is clear. GPI-2 E Project Planning: Resources Assignment 49
 Some Conclusions • Minimum development cost – Time: • Use specialists in each work area. (As much as you can). – Money • Use the necessary workers to carry the tasks and with some knowledge about the work areas. GPI-2 E Project Planning: Resources Assignment 50
Some Conclusions • Minimum development cost – Time: • Use specialists in each work area. (As much as you can). – Money • Use the necessary workers to carry the tasks and with some knowledge about the work areas. GPI-2 E Project Planning: Resources Assignment 50
 Some Conclusions. • Long term minimum cost (future maintenance and other projects) – Less experienced workers work in the development, with same guidance by expert people. – Promote each person. Identify people objectives and made each project a step toward their own objectives. GPI-2 E Project Planning: Resources Assignment 51
Some Conclusions. • Long term minimum cost (future maintenance and other projects) – Less experienced workers work in the development, with same guidance by expert people. – Promote each person. Identify people objectives and made each project a step toward their own objectives. GPI-2 E Project Planning: Resources Assignment 51
 It’s interesting to remember that: • The programmers productivity have a high variation, it’s usual the relation 1: 5. • In one study, they find variability between 1 a 26 in the productivity level. • This want to said. . . – In the critical tasks put people with experience, reputation and motivation. – It´s expected that they are the more productive ones. GPI-2 E Project Planning: Resources Assignment 52
It’s interesting to remember that: • The programmers productivity have a high variation, it’s usual the relation 1: 5. • In one study, they find variability between 1 a 26 in the productivity level. • This want to said. . . – In the critical tasks put people with experience, reputation and motivation. – It´s expected that they are the more productive ones. GPI-2 E Project Planning: Resources Assignment 52
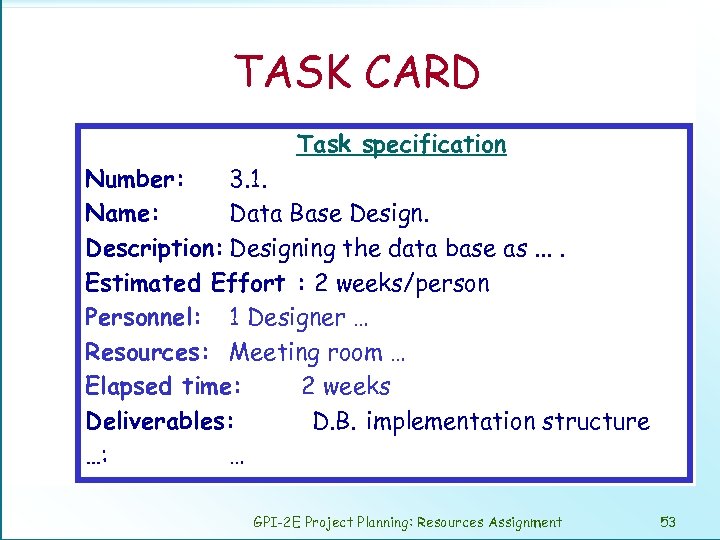 TASK CARD Task specification Number: 3. 1. Name: Data Base Design. Description: Designing the data base as. . Estimated Effort : 2 weeks/person Personnel: 1 Designer … Resources: Meeting room … Elapsed time: 2 weeks Deliverables: D. B. implementation structure …: … GPI-2 E Project Planning: Resources Assignment 53
TASK CARD Task specification Number: 3. 1. Name: Data Base Design. Description: Designing the data base as. . Estimated Effort : 2 weeks/person Personnel: 1 Designer … Resources: Meeting room … Elapsed time: 2 weeks Deliverables: D. B. implementation structure …: … GPI-2 E Project Planning: Resources Assignment 53
 Bibliography • Blanchard, K. , Johnson, S. “El ejecutivo al minuto”. Grijalbo Mandadori, S. A. 1983. • Brooks, Frederick P. The mythical man-month: essays on software engineering. Addison-Wesley, 1995. • De. Marco, Tom. Controlling Software Projects. Prentice Hall, 1982. • Fergus O'Connell. "How to run successful projects". Prentice Hall, 1994. • Metzger, P. Boddie, J. “Managing a programming project: people and processes” 3 ed. Prentice Hall, 1996. • Thomsett, R. “Third Wave Project Management”. Prentice Hall, 1993. • Yourdon, Edward. Análisis Estructurado Moderno. Prentice Hall, 1993. GPI-2 E Project Planning: Resources Assignment 54
Bibliography • Blanchard, K. , Johnson, S. “El ejecutivo al minuto”. Grijalbo Mandadori, S. A. 1983. • Brooks, Frederick P. The mythical man-month: essays on software engineering. Addison-Wesley, 1995. • De. Marco, Tom. Controlling Software Projects. Prentice Hall, 1982. • Fergus O'Connell. "How to run successful projects". Prentice Hall, 1994. • Metzger, P. Boddie, J. “Managing a programming project: people and processes” 3 ed. Prentice Hall, 1996. • Thomsett, R. “Third Wave Project Management”. Prentice Hall, 1993. • Yourdon, Edward. Análisis Estructurado Moderno. Prentice Hall, 1993. GPI-2 E Project Planning: Resources Assignment 54


