82d19b39c35b59f8eb510a4229134740.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 34
 Project Planning and Estimation 1
Project Planning and Estimation 1
 Project Planning Software project management begins with a set of activities called project planning which involves proper estimation of time, schedule, work and resources.
Project Planning Software project management begins with a set of activities called project planning which involves proper estimation of time, schedule, work and resources.
 Project Planning When: need for software has already been established; stakeholders are on-board; coding is ready to begin What: project planning spans five major activities —estimation, scheduling, risk analysis, quality management planning, and change management planning Who: software project managers, with information from stakeholders and engineers 3
Project Planning When: need for software has already been established; stakeholders are on-board; coding is ready to begin What: project planning spans five major activities —estimation, scheduling, risk analysis, quality management planning, and change management planning Who: software project managers, with information from stakeholders and engineers 3
 Objectives of planning Framework that will help in the estimation of cost , time and schedule Define the best case and worst case scenarios so that project outcomes can be bounded. 4
Objectives of planning Framework that will help in the estimation of cost , time and schedule Define the best case and worst case scenarios so that project outcomes can be bounded. 4
 Task set for project planning 1. Establish project scope 2. Determine feasibility 3. Analyze risks 4, Define required resources human resource needed , software resources, environmental resources 5. Estimate cost and effort decompose the problem, use estimation techniques 6. Develop project schedule
Task set for project planning 1. Establish project scope 2. Determine feasibility 3. Analyze risks 4, Define required resources human resource needed , software resources, environmental resources 5. Estimate cost and effort decompose the problem, use estimation techniques 6. Develop project schedule
 Software project scope and feasibility The first step in planning is establishing project scope Software scope describes the functions and features that are to be delivered. It is a narrative description of scope is developed after communicating with stakeholders Function ( cost, schedule) and performance(response time, processing time) is to be measured Once scope is defined we go to step 2
Software project scope and feasibility The first step in planning is establishing project scope Software scope describes the functions and features that are to be delivered. It is a narrative description of scope is developed after communicating with stakeholders Function ( cost, schedule) and performance(response time, processing time) is to be measured Once scope is defined we go to step 2
 Feasibility Can we build a software to meet this scope Is project technically feasible Financial feasibility Time Resources
Feasibility Can we build a software to meet this scope Is project technically feasible Financial feasibility Time Resources
 RESOURCES Three categories of software engineering resources are 1. people (location , skills and number) 2. reusable software components(off shelf components, full experience component , partial experience component and new component) c. Environmental resources ( hardware and software tools needed ) Offshelf: existing s/w that can be acquired from a 3 rd party Full Experience : s/w that is already developed for past projects Partial experience: s/w that is already developed for past projects but needs some modification to be used for the current project New component: build from scratch
RESOURCES Three categories of software engineering resources are 1. people (location , skills and number) 2. reusable software components(off shelf components, full experience component , partial experience component and new component) c. Environmental resources ( hardware and software tools needed ) Offshelf: existing s/w that can be acquired from a 3 rd party Full Experience : s/w that is already developed for past projects Partial experience: s/w that is already developed for past projects but needs some modification to be used for the current project New component: build from scratch
 Estimation requires… experience access to good historical information 9
Estimation requires… experience access to good historical information 9
 Reliability of estimates is affected by… Project complexity Project size Degree of structural uncertainty Availability of historical information 10
Reliability of estimates is affected by… Project complexity Project size Degree of structural uncertainty Availability of historical information 10
 Options for estimation Delay estimation until late in the project (not feasible) Base estimation based on previous similar projects Use simple decomposition techniques to generate cost and effort estimation Decomposition technique adopt a divide and conquer technique. For each decomposition the cost and effort estimation is done. Use one or more empirical models for estimation
Options for estimation Delay estimation until late in the project (not feasible) Base estimation based on previous similar projects Use simple decomposition techniques to generate cost and effort estimation Decomposition technique adopt a divide and conquer technique. For each decomposition the cost and effort estimation is done. Use one or more empirical models for estimation
 Estimation techniques Problem-based Estimation LOC Function – Point Process-based Estimation COCOMO
Estimation techniques Problem-based Estimation LOC Function – Point Process-based Estimation COCOMO
 Loc based estimation Cost per LOC = burdened rate /LOC produced per PM Project Cost = Cost per LOC * LOCE Project Effort = Project Cost/ burdened labor rate 13
Loc based estimation Cost per LOC = burdened rate /LOC produced per PM Project Cost = Cost per LOC * LOCE Project Effort = Project Cost/ burdened labor rate 13
 Assuming that your organization produces 620 LOC/PM with a burdened labor rate of 8000 BD/PM, estimate the cost and the effort required to build the software using LOC-based estimation technique. LOC(e)=30000 14
Assuming that your organization produces 620 LOC/PM with a burdened labor rate of 8000 BD/PM, estimate the cost and the effort required to build the software using LOC-based estimation technique. LOC(e)=30000 14
 Function Point Use measure of functionality Derived directly from 5 information domain characteristics - User Input = distinct data input by user - User Output = reports, screens, error messages - User Inquiries = on-line input results in generation of immediate software response - Files = Logical grouping of data that may be one part of large database or separate file - External interfaces = all machine readable interfaces used to transmit information to another system 15
Function Point Use measure of functionality Derived directly from 5 information domain characteristics - User Input = distinct data input by user - User Output = reports, screens, error messages - User Inquiries = on-line input results in generation of immediate software response - Files = Logical grouping of data that may be one part of large database or separate file - External interfaces = all machine readable interfaces used to transmit information to another system 15
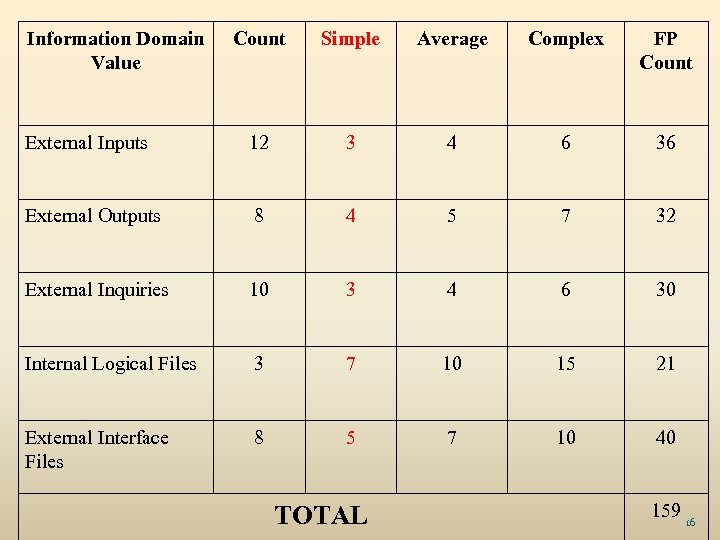 Information Domain Value Count Simple Average Complex FP Count External Inputs 12 3 4 6 36 External Outputs 8 4 5 7 32 External Inquiries 10 3 4 6 30 Internal Logical Files 3 7 10 15 21 External Interface Files 8 5 7 10 40 TOTAL 159 16
Information Domain Value Count Simple Average Complex FP Count External Inputs 12 3 4 6 36 External Outputs 8 4 5 7 32 External Inquiries 10 3 4 6 30 Internal Logical Files 3 7 10 15 21 External Interface Files 8 5 7 10 40 TOTAL 159 16
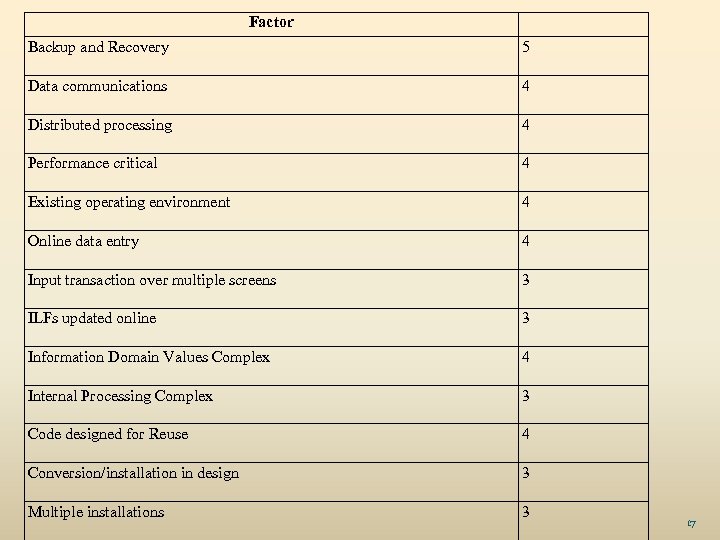 Factor Backup and Recovery 5 Data communications 4 Distributed processing 4 Performance critical 4 Existing operating environment 4 Online data entry 4 Input transaction over multiple screens 3 ILFs updated online 3 Information Domain Values Complex 4 Internal Processing Complex 3 Code designed for Reuse 4 Conversion/installation in design 3 Multiple installations 3 17
Factor Backup and Recovery 5 Data communications 4 Distributed processing 4 Performance critical 4 Existing operating environment 4 Online data entry 4 Input transaction over multiple screens 3 ILFs updated online 3 Information Domain Values Complex 4 Internal Processing Complex 3 Code designed for Reuse 4 Conversion/installation in design 3 Multiple installations 3 17
 FPE = count total*[0. 65 + 0. 01 * ∑Fi) Project Effort = FPE / average productivity on FP Project Cost = Project Effort * burdened rate 18
FPE = count total*[0. 65 + 0. 01 * ∑Fi) Project Effort = FPE / average productivity on FP Project Cost = Project Effort * burdened rate 18
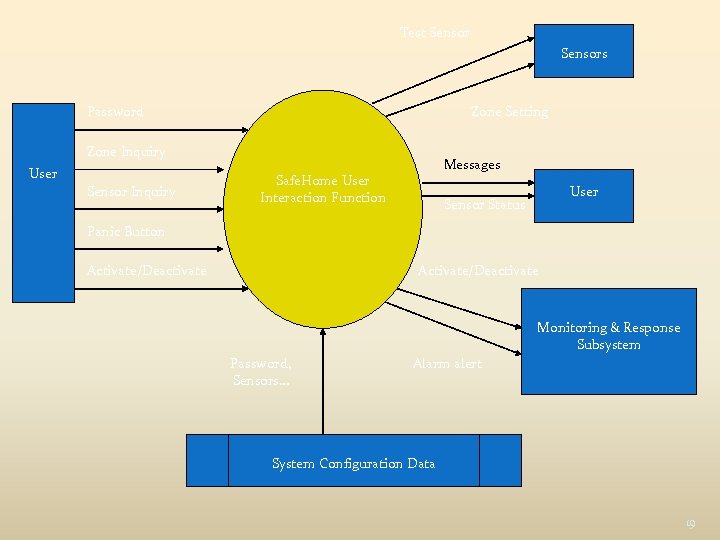 Test Sensors Password Zone Setting Zone Inquiry User Sensor Inquiry Messages Safe. Home User Interaction Function User Sensor Status Panic Button Activate/Deactivate Monitoring & Response Subsystem Password, Sensors… Alarm alert System Configuration Data 19
Test Sensors Password Zone Setting Zone Inquiry User Sensor Inquiry Messages Safe. Home User Interaction Function User Sensor Status Panic Button Activate/Deactivate Monitoring & Response Subsystem Password, Sensors… Alarm alert System Configuration Data 19
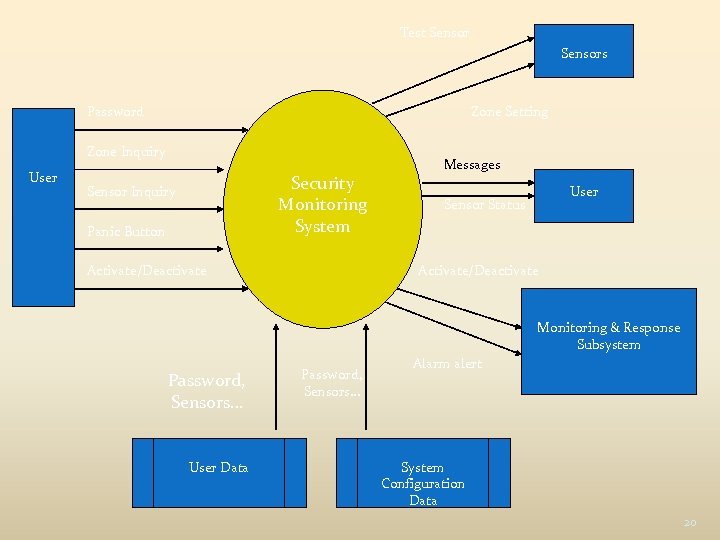 Test Sensors Password Zone Setting Zone Inquiry User Security Monitoring System Sensor Inquiry Panic Button Activate/Deactivate Messages User Sensor Status Activate/Deactivate Monitoring & Response Subsystem Password, Sensors… User Data Password, Sensors… Alarm alert System Configuration Data 20
Test Sensors Password Zone Setting Zone Inquiry User Security Monitoring System Sensor Inquiry Panic Button Activate/Deactivate Messages User Sensor Status Activate/Deactivate Monitoring & Response Subsystem Password, Sensors… User Data Password, Sensors… Alarm alert System Configuration Data 20
 External Input : orginates from user and represents control information External Output : its derived from application and provides information to user. it can be reports, screens, error messages External Inquiries: Its is a online input that result in the generation of some software response. Internal logical file : File that resides within system boundary External interface file : it resides external to application
External Input : orginates from user and represents control information External Output : its derived from application and provides information to user. it can be reports, screens, error messages External Inquiries: Its is a online input that result in the generation of some software response. Internal logical file : File that resides within system boundary External interface file : it resides external to application
 3 External inputs 1. 2. 3. Password panic button and activate/deactivate 2 external inquiries 1. 2. zone inquiry and sensor inquiry One ILF (system configuration file) 2 external outputs 1. 2. messages and sensor status Four EIF’s 1. 2. 3. 4. test sensor zone setting activate/deactivate alarm alert 22
3 External inputs 1. 2. 3. Password panic button and activate/deactivate 2 external inquiries 1. 2. zone inquiry and sensor inquiry One ILF (system configuration file) 2 external outputs 1. 2. messages and sensor status Four EIF’s 1. 2. 3. 4. test sensor zone setting activate/deactivate alarm alert 22
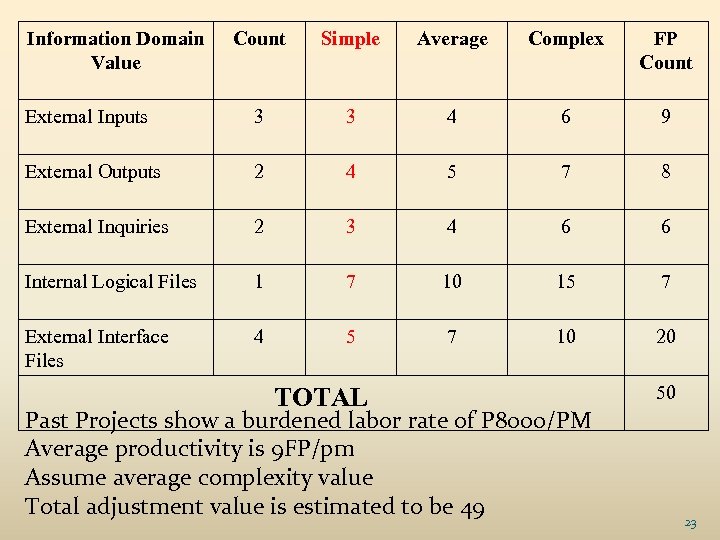 Information Domain Value Count Simple Average Complex FP Count External Inputs 3 3 4 6 9 External Outputs 2 4 5 7 8 External Inquiries 2 3 4 6 6 Internal Logical Files 1 7 10 15 7 External Interface Files 4 5 7 10 20 TOTAL Past Projects show a burdened labor rate of P 8000/PM Average productivity is 9 FP/pm Assume average complexity value Total adjustment value is estimated to be 49 50 23
Information Domain Value Count Simple Average Complex FP Count External Inputs 3 3 4 6 9 External Outputs 2 4 5 7 8 External Inquiries 2 3 4 6 6 Internal Logical Files 1 7 10 15 7 External Interface Files 4 5 7 10 20 TOTAL Past Projects show a burdened labor rate of P 8000/PM Average productivity is 9 FP/pm Assume average complexity value Total adjustment value is estimated to be 49 50 23
 FPE = count total*[0. 65 + 0. 01 * ∑Fi) Project Effort = FPE / average productivity on FP Project Cost = Project Effort * burdened rate
FPE = count total*[0. 65 + 0. 01 * ∑Fi) Project Effort = FPE / average productivity on FP Project Cost = Project Effort * burdened rate
 COCOMO II (Constructive cost model) uses object points, using counts of the number of - screens - reports - components that is needed to build the application Each object instance is classified into one of the three complexity levels (simple, medium or difficult) 25
COCOMO II (Constructive cost model) uses object points, using counts of the number of - screens - reports - components that is needed to build the application Each object instance is classified into one of the three complexity levels (simple, medium or difficult) 25
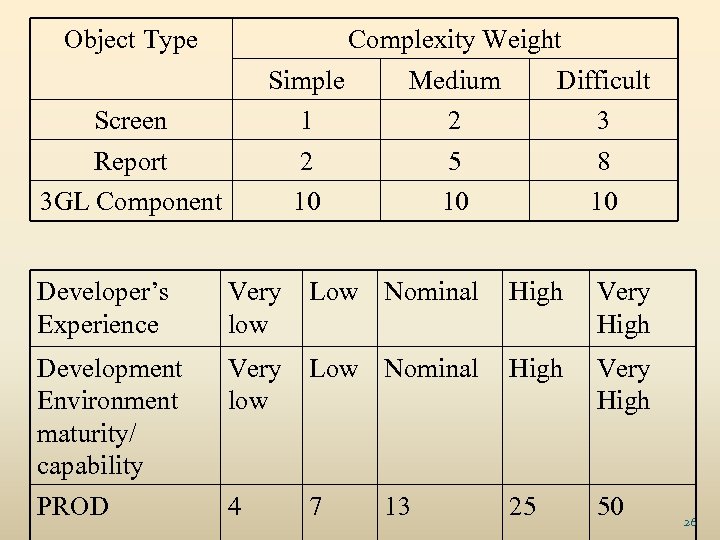 Object Type Complexity Weight Simple Medium Difficult 1 2 10 2 5 10 3 8 10 Screen Report 3 GL Component Developer’s Experience Very low Low Nominal High Very High Development Environment maturity/ capability Very low Low Nominal High Very High PROD 4 7 25 50 13 26
Object Type Complexity Weight Simple Medium Difficult 1 2 10 2 5 10 3 8 10 Screen Report 3 GL Component Developer’s Experience Very low Low Nominal High Very High Development Environment maturity/ capability Very low Low Nominal High Very High PROD 4 7 25 50 13 26
 NOP = (object points) * ((100 - %reuse)/100) PROD =NOP / person-month Estimated Effort = NOP/PROD Estimated Cost = Estimated Effort * Burdened rate 27
NOP = (object points) * ((100 - %reuse)/100) PROD =NOP / person-month Estimated Effort = NOP/PROD Estimated Cost = Estimated Effort * Burdened rate 27
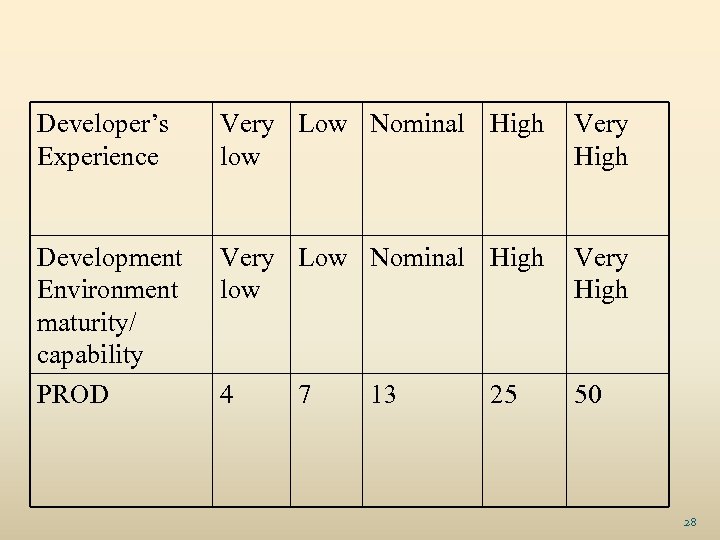 Developer’s Experience Very Low Nominal High low Very High Development Environment maturity/ capability Very Low Nominal High low Very High PROD 4 50 7 13 25 28
Developer’s Experience Very Low Nominal High low Very High Development Environment maturity/ capability Very Low Nominal High low Very High PROD 4 50 7 13 25 28
 Use the COCOMO II model to estimate the effort required to build software for a simple ATM that produces 12 screens, 10 reports, and will require approximately 80 software components Past projects show a burdened rate of 9000 BD/pm Assume nominal complexity and nominal developer/environment maturity 29
Use the COCOMO II model to estimate the effort required to build software for a simple ATM that produces 12 screens, 10 reports, and will require approximately 80 software components Past projects show a burdened rate of 9000 BD/pm Assume nominal complexity and nominal developer/environment maturity 29
 Tasks You are working for a software company ABC software and SBI Bank has granted a project to computerise its operations. The Manager for SBI Mr Ahmed has been involved in deciding the various aspects of the project. You are appointed by ABC software to manage the project and there a team of 20 people working with you. The bank employs 20 people and has 100 account holders Who are the stake holders for the project. Which are the different team organisations? Which one would you choose and why?
Tasks You are working for a software company ABC software and SBI Bank has granted a project to computerise its operations. The Manager for SBI Mr Ahmed has been involved in deciding the various aspects of the project. You are appointed by ABC software to manage the project and there a team of 20 people working with you. The bank employs 20 people and has 100 account holders Who are the stake holders for the project. Which are the different team organisations? Which one would you choose and why?
 You are the project manager for a company that buids software for house hold robots. You are contacted to build a software for a robot that mows the lawn for a homeowner. Write a statement of scope that describes the software. If you are unfamiliar about robots do a little research on robots before starting. State your assumptions about what hardware is needed.
You are the project manager for a company that buids software for house hold robots. You are contacted to build a software for a robot that mows the lawn for a homeowner. Write a statement of scope that describes the software. If you are unfamiliar about robots do a little research on robots before starting. State your assumptions about what hardware is needed.
 Use. COCOMO model to estimate the effort needed to build a software for a simple ATM machine that produce 12 screens , 10 reports and 80 software components. Assume average complexity and average developer /envt maturity.
Use. COCOMO model to estimate the effort needed to build a software for a simple ATM machine that produce 12 screens , 10 reports and 80 software components. Assume average complexity and average developer /envt maturity.
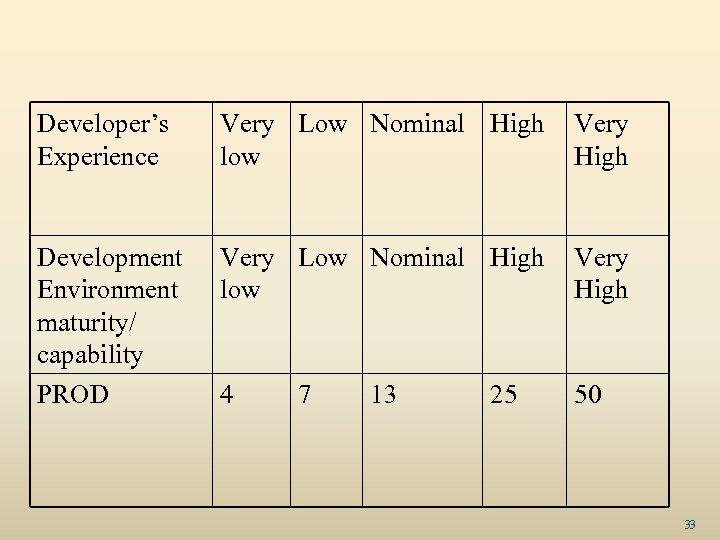 Developer’s Experience Very Low Nominal High low Very High Development Environment maturity/ capability Very Low Nominal High low Very High PROD 4 50 7 13 25 33
Developer’s Experience Very Low Nominal High low Very High Development Environment maturity/ capability Very Low Nominal High low Very High PROD 4 50 7 13 25 33
 Comment on the statement “It seems odd the cost and schedule estimates to be developed during software project planning-before detailed analysis and design is conducted? why
Comment on the statement “It seems odd the cost and schedule estimates to be developed during software project planning-before detailed analysis and design is conducted? why


