ec62897851ed976cb2121ae7d7308b3d.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 68

Project Management x 470 Project Baseline (Scope, Time) UC Berkeley Extension, Business and Management Week 2 – 30 April Jennifer Russell 415. 385. 1749 jr@mastodonconsulting. com Ray Ju 415. 845. 8880 rayju@sbcglobal. net

Agenda n n n n PMBOK Knowledge Framework Project Initiation Team Exercises Project Lifecycles Work Breakdown Schedule Project Estimate Cost Quiz #1 Think TEAM 2
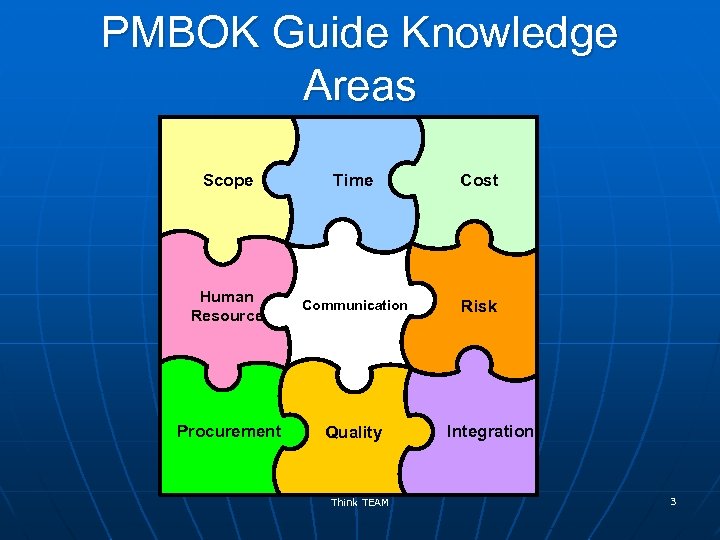
PMBOK Guide Knowledge Areas Scope Time Cost Human Resource Communication Risk Procurement Quality Think TEAM Integration 3

PMBOK Guide Layout n Section I, Chap 1 -2 PM Framework • Introduction • Project Lifecycle and Organization n Section II, Chap 3 Standard for PM of a Project • PM Processes for a Project n Section III, Chap 4 -12 PM Knowledge Areas (nine) n n Section IV Appendices Section V Glossary and Index Think TEAM 4
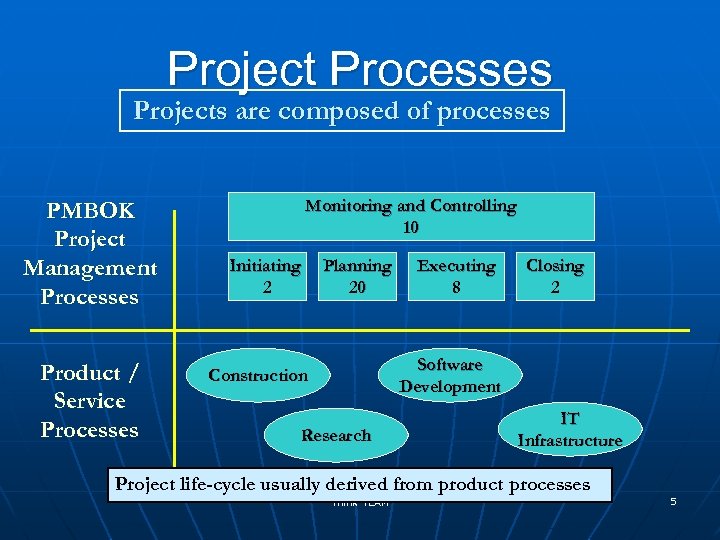
Project Processes Projects are composed of processes PMBOK Project Management Processes Product / Service Processes Monitoring and Controlling 10 Initiating 2 Planning 20 Executing 8 Closing 2 Software Development Construction Research IT Infrastructure Project life-cycle usually derived from product processes Think TEAM 5
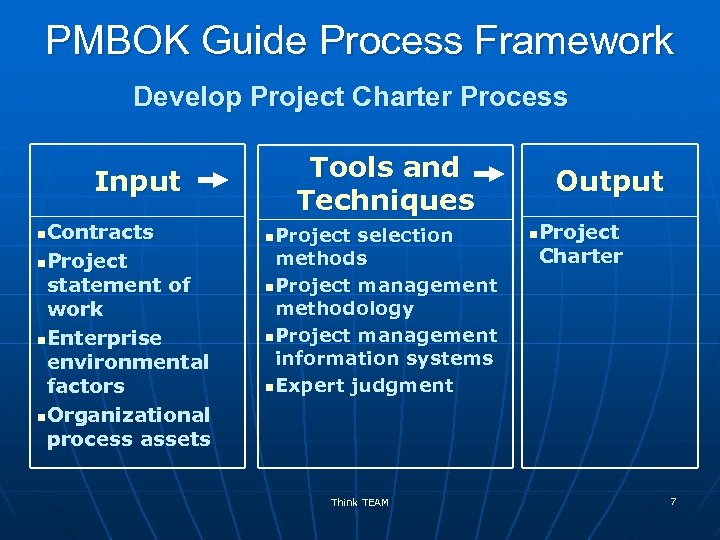
PMBOK Guide Process Framework Develop Project Charter Process Input Contracts n. Project statement of work n. Enterprise environmental factors n. Organizational process assets n Tools and Techniques n Project selection methods n Project management methodology n Project management information systems n Expert judgment Think TEAM Output Project Charter n 7
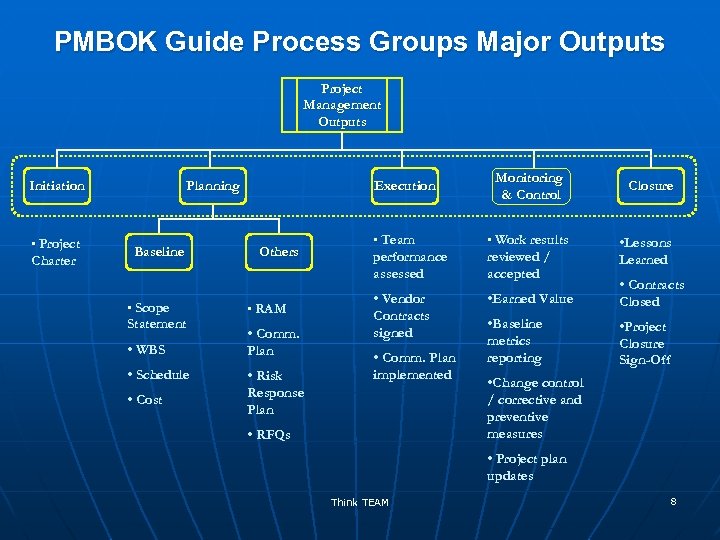
PMBOK Guide Process Groups Major Outputs Project Management Outputs Initiation • Project Charter Planning Baseline • Scope Statement • WBS • Schedule • Cost Execution Others • RAM • Comm. Plan • Risk Response Plan Monitoring & Control Closure • Team • Work results performance assessed reviewed / accepted • Vendor Contracts signed • Earned Value • Contracts Closed • Baseline metrics reporting • Project Closure Sign-Off • Comm. Plan implemented • RFQs • Lessons Learned • Change control / corrective and preventive measures • Project plan updates Think TEAM 8
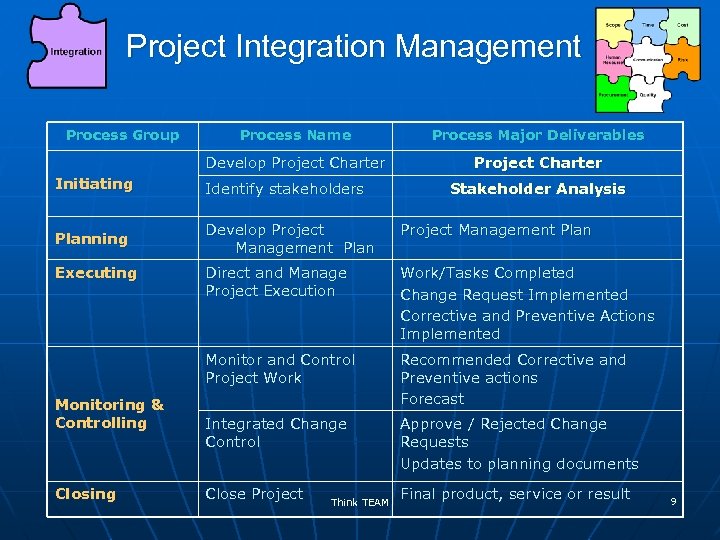
Project Integration Management Process Group Process Name Process Major Deliverables Develop Project Charter Initiating Identify stakeholders Planning Develop Project Management Plan Direct and Manage Project Execution Work/Tasks Completed Change Request Implemented Corrective and Preventive Actions Implemented Monitor and Control Project Work Recommended Corrective and Preventive actions Forecast Integrated Change Control Approve / Rejected Change Requests Updates to planning documents Close Project Final product, service or result Executing Monitoring & Controlling Closing Think TEAM Stakeholder Analysis 9

Starting the Project n Project stimuli n • Problems • Opportunities • Business requirements n • “Must Do” n SOX, HIPAA, compliance • “Keep the Lights On” Considerations • Contract / Project Statement of Work • Enterprise environmental factors • Organizational process assets Project Type - I n Infrastructure projects • Enhancements • New Products/ Opportunities n Think TEAM Project Type - II alignment with the business strategy 10

Mission, Vision, Values n Mission: Describes the overall purpose of the organization n Vision: Vivid description of the organization as it effectively carries out its operations n Values: Represent the core priorities in the organization’s culture, including what drives members’ priorities and how they truly act in the organization Carter Mc. Namara, 2008 Think TEAM 12

Major Project Documents Project Charter • Formally authorizes the project defines the why Scope Statement • States what work is to be accomplished and what deliverables need to be produced Project Plan • States how the work is to be performed and by who, when, and where • Scope, Cost, Schedule, Risk, Communication, Staffing, Quality, and Procurement Expansion explanation of these documents later in slide show Think TEAM 13
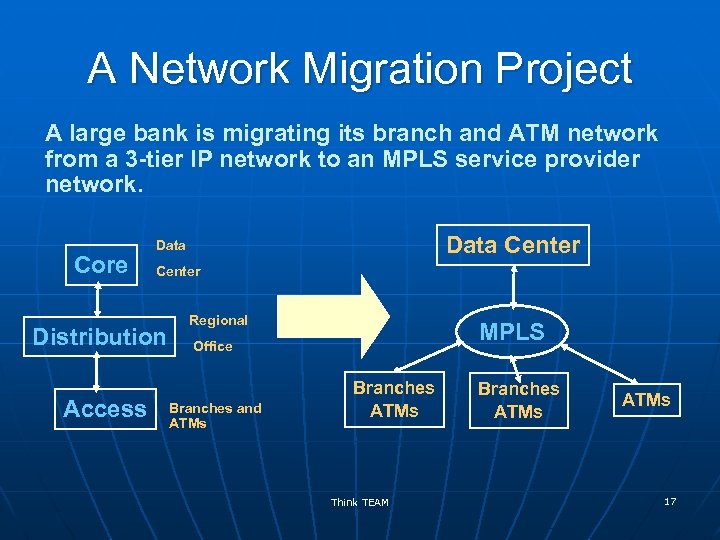
A Network Migration Project A large bank is migrating its branch and ATM network from a 3 -tier IP network to an MPLS service provider network. Core Center Distribution Access Data Center Data Regional MPLS Office Branches and ATMs Branches ATMs Think TEAM Branches ATMs 17
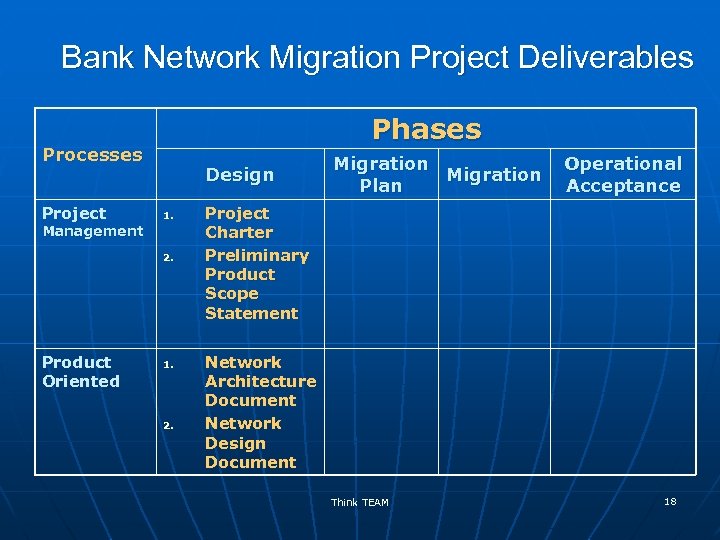
Bank Network Migration Project Deliverables Phases Processes Project Design 1. Management 2. Product Oriented 1. 2. Migration Plan Operational Acceptance Project Charter Preliminary Product Scope Statement Network Architecture Document Network Design Document Think TEAM 18

Project Initiation Challenges n n Timing of Project Manager engagement Degree of accuracy for project and product documents Speed vs. Accuracy vs. Change Control culture Functional Areas Concern: Spending precious resources’ time on projects that will be disapproved Think TEAM 19

Planning Fundamentals n n n If the deliverable is well understood prior to being performed, much of the work can be preplanned If the deliverable is not understood, then during the actual task execution more knowledge is gained that, in turn, leads to changes The more uncertain the deliverable, the greater the need is for frequent “validation cycles” Project life cycle approach depends on deliverable (goal and solutions & requirements) certainty Detail plan only up to the next point of knowledge “Failing to plan is planning to fail. ” - Harold Kerzner Think TEAM 21
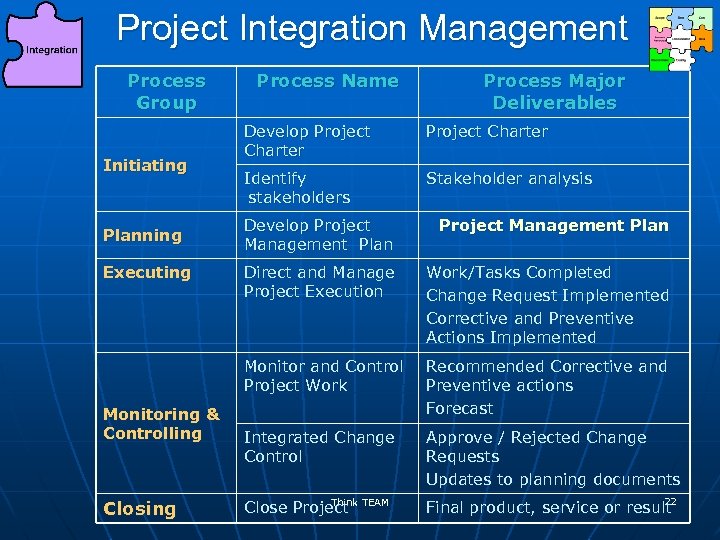
Project Integration Management Process Group Initiating Process Name Process Major Deliverables Develop Project Charter Identify stakeholders Stakeholder analysis Executing Monitoring & Controlling Closing Develop Project Management Plan Direct and Manage Project Execution Work/Tasks Completed Change Request Implemented Corrective and Preventive Actions Implemented Monitor and Control Project Work Planning Recommended Corrective and Preventive actions Forecast Integrated Change Control Approve / Rejected Change Requests Updates to planning documents Think Close Project TEAM 22 Final product, service or result 22
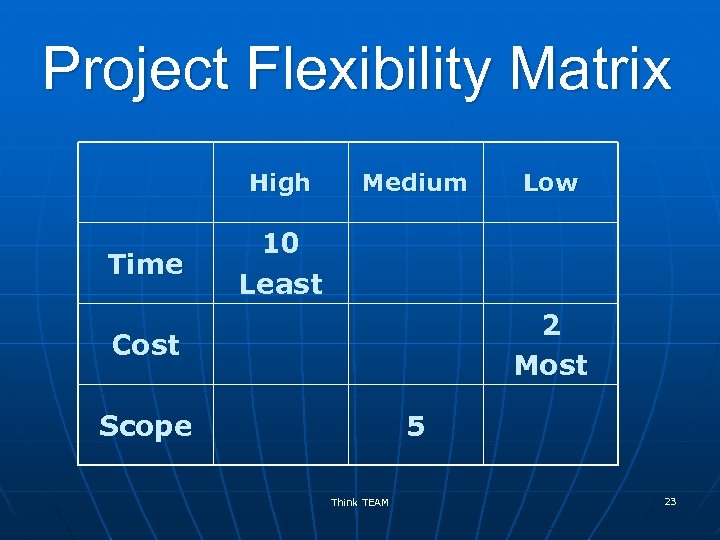
Project Flexibility Matrix High Time Medium Low 10 Least 2 Most Cost Scope 5 Think TEAM 23

Scope Statement
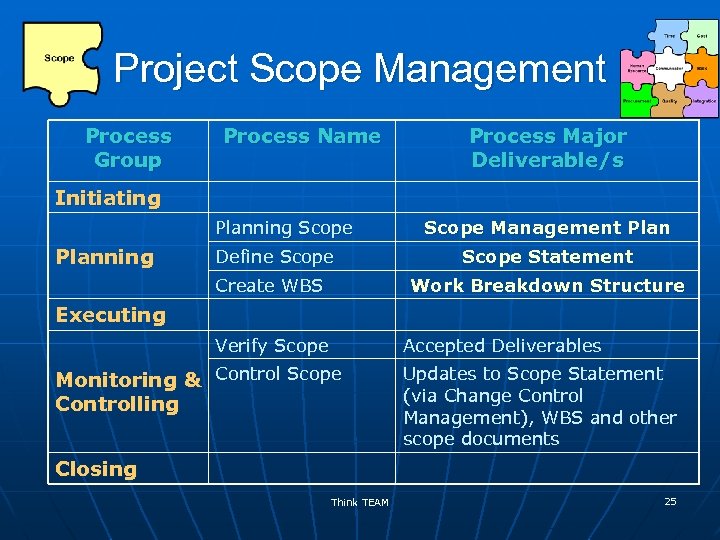
Project Scope Management Process Group Process Name Process Major Deliverable/s Initiating Planning Scope Management Plan Define Scope Statement Create WBS Work Breakdown Structure Executing Verify Scope Accepted Deliverables Monitoring & Control Scope Controlling Updates to Scope Statement (via Change Control Management), WBS and other scope documents Closing Think TEAM 25

Project Scope Statement n n n n Project/product objectives Product scope description Project requirements Project boundaries Deliverables Product acceptance criteria Project assumptions and constraints Initial project organization n n n n Think TEAM Initial defined risks Schedule milestones Fund limitation Initial WBS Cost estimate Project configuration management requirements Approval requirements Project specifications 26

Customer Needs vs. Wants Needs, are more associated with the underlying problem Wants, are more associated with a solution Think TEAM 27

Project Lifecycle Approaches n Linear n • Standard waterfall • Rapid development waterfall n • Dynamic systems development method • Evolutionary development waterfall • Regional Unified Process • SCRUM Incremental • Staged delivery waterfall • Feature driven development* n Adaptive* • Adaptive software development • Adaptive project framework Iterative* n Extreme* • INSPIRE *a. k. a. Agile Project Management Which lifecycle approach makes sense for the project? Think TEAM From: Robert K. Wysocki 28
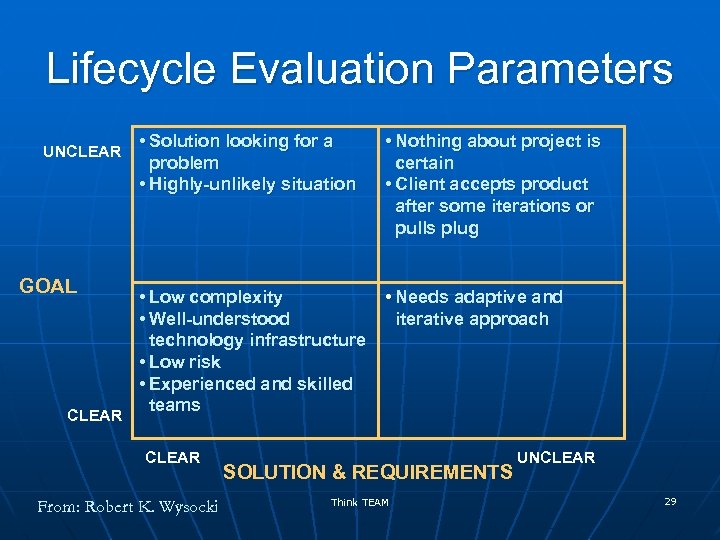
Lifecycle Evaluation Parameters UNCLEAR GOAL CLEAR • Solution looking for a problem • Highly-unlikely situation • Nothing about project is certain • Client accepts product after some iterations or pulls plug • Low complexity • Well-understood technology infrastructure • Low risk • Experienced and skilled teams • Needs adaptive and iterative approach CLEAR From: Robert K. Wysocki SOLUTION & REQUIREMENTS Think TEAM UNCLEAR 29
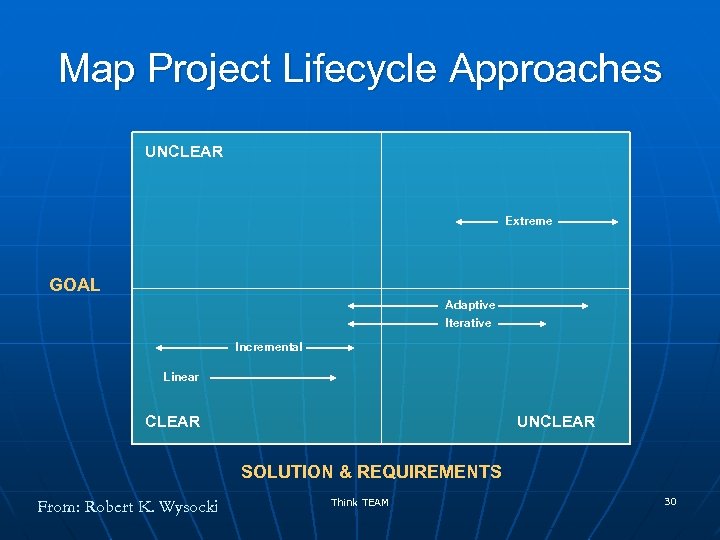
Map Project Lifecycle Approaches UNCLEAR Extreme GOAL Adaptive Iterative Incremental Linear CLEAR UNCLEAR SOLUTION & REQUIREMENTS From: Robert K. Wysocki Think TEAM 30
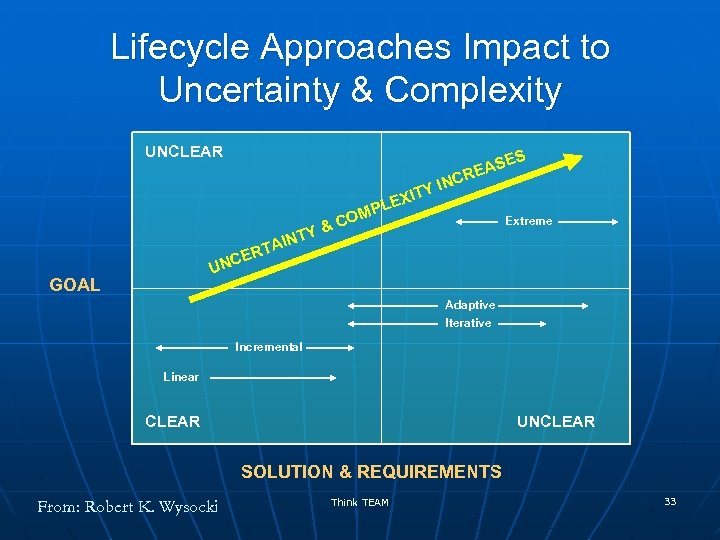
Lifecycle Approaches Impact to Uncertainty & Complexity UNCLEAR S Y XIT & NTY PLE OM C E EAS R INC Extreme I A ERT NC U GOAL Adaptive Iterative Incremental Linear CLEAR UNCLEAR SOLUTION & REQUIREMENTS From: Robert K. Wysocki Think TEAM 33

Project Complexity/Uncertainty n n As projects become more complex, they become more uncertain As complexity increases: • • • Nailing down requirements decreases Process flexibility must increase Processes must be more adaptable Change requests become more frequent Risk increases The need for greater team cohesiveness increases • More communication is needed From: Robert K. Wysocki Think TEAM 34

Project Complexity/Uncertainty n Customer involvement must increase as complexity increases • The customer will resist because: n n The Customer’s Comfort Zone Customer may be reluctant to take ownership of product Customer may refuse to sign off because needs change Business Value • As projects move from clarity of goal and solutions (& requirements) to less clarity of goal and /or solutions (& requirements) the higher the Business Value • The risk of project failure is also higher !!!!! From: Robert K. Wysocki Think TEAM 35
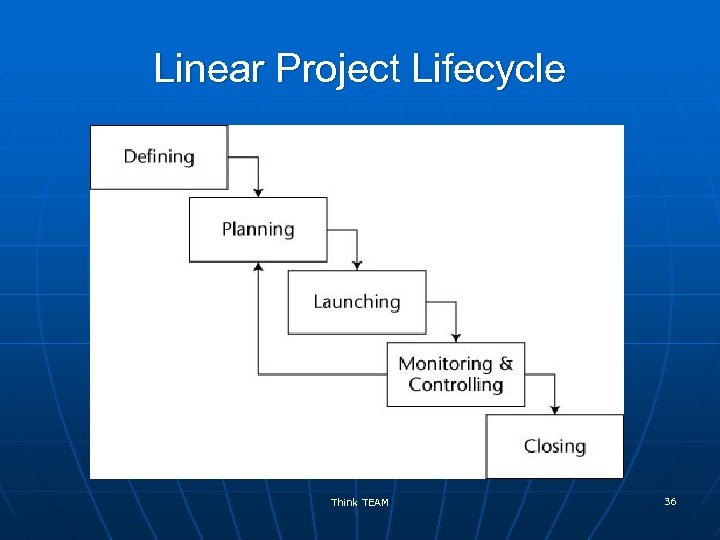
Linear Project Lifecycle Think TEAM 36
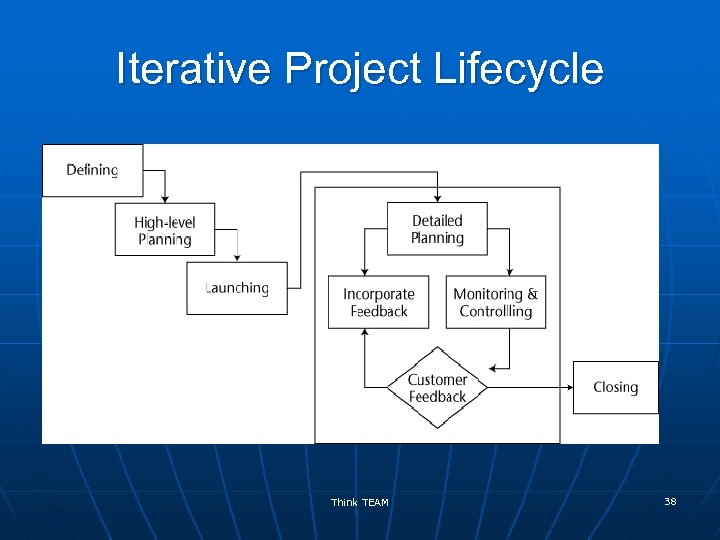
Iterative Project Lifecycle Think TEAM 38

Scope Statement Exercise n n Create a Scope Statement for your project Use the Project Workbook template as a guide Presentations Class discussion Think TEAM 39

Team Project Time and Scope Guardrails n n Involve the entire project team talents Build and develop weekly not week 9 Time: Can do within 6 -12 months Scope: Have fun and be realistic • Business, Community, Philanthropy, Social Responsibility, Event, Actual n Cost: Blank Checkbook $$$$$ • Justifiable and budgeted • What if? Think TEAM 40

W ork B reakdown S tructure

Decomposition Steps: Definition: Subdivision of major project deliverables or sub-deliverables into smaller, more manageable components until the deliverables are defined in sufficient detail to support development of project activities (planning, executing, etc. . ) 1. 2. 3. 4. Think TEAM Identify major project deliverables Decide if adequate cost and duration estimate can be made at this level of detail for each deliverable Identify constituent components of the deliverable if necessary Verify correctness of decomposition (necessity, definition, cost, duration, 42 responsibility)

Work Breakdown Structure n n A deliverable oriented grouping of project components that organizes and defines the total scope of the project Defines products, not tasks Can be developed using a topdown or bottom-up approach Can be hardware-related, function -related, life cycle-related or a combination Foundation of all planning! Think TEAM 43

Work Breakdown Structure n n WBS items assigned an identifier for hierarchical summation of cost and resources WBS dictionary – work package description, schedule dates, cost budget, staff assignment and other data points as needed Think TEAM 44

Work Package n n n Lowest level deliverable in a WBS Work effort guideline 40 to 80 hrs Ownership assigned at this level Tasks are identified under this level Task size guideline - not to exceed 80 hrs; less for high risk project Think TEAM 45
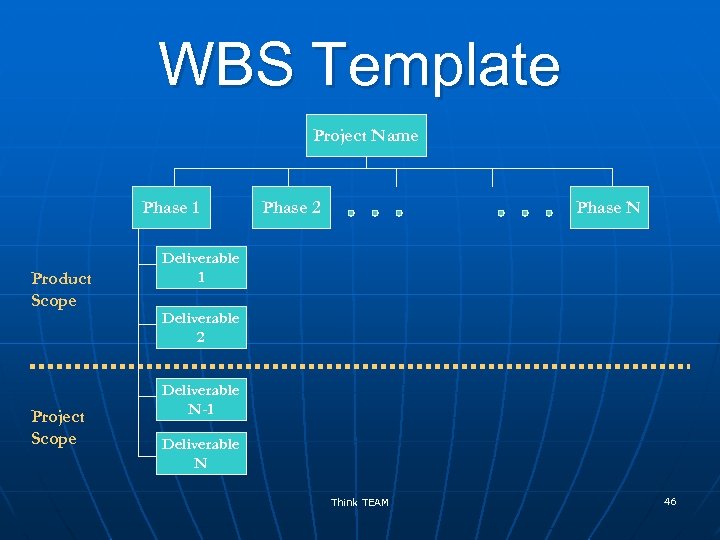
WBS Template Project Name Phase 1 Product Scope Project Scope Phase 2 Phase N Deliverable 1 Deliverable 2 Deliverable N-1 Deliverable N Think TEAM 46

Scope Baseline n n n Scope Statement WBS Dictionary Think TEAM 47
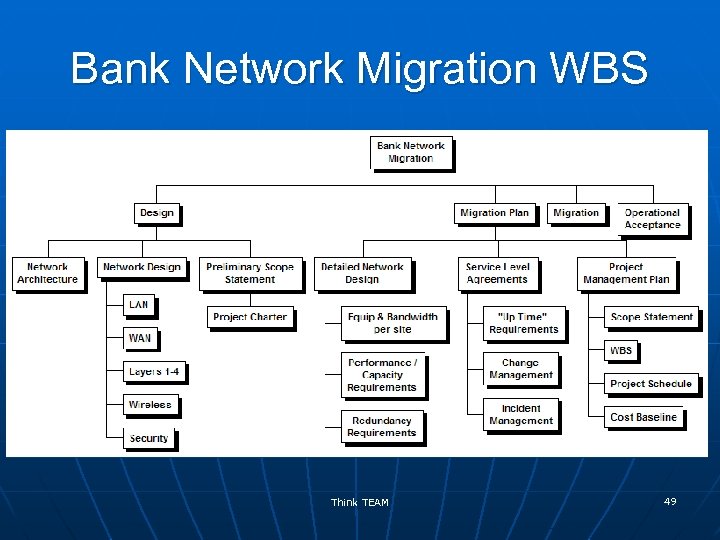
Bank Network Migration WBS Think TEAM 49

WBS Discussions n Questions on WBS construction • Who prepares the WBS? • Who needs to be involved? • Who approves the WBS? Think TEAM 50

WBS Team Exercise n n Construct a life-cycle based WBS for your project Use a Post-It-Note sheet for each deliverable Concentrate on product deliverables Add project management process deliverable that have already been discussed in class Think TEAM 52

The Project Schedule (Time Baseline)

Scheduling Techniques n n n Gantt or bar charts Milestone charts (zero duration) Networks (show interdependencies) • Project Evaluation and Review Technique (PERT) • Conditional Diagram Method • Precedence Diagram Method (PDM) for use with Critical Path Management (CPM) Think TEAM 55
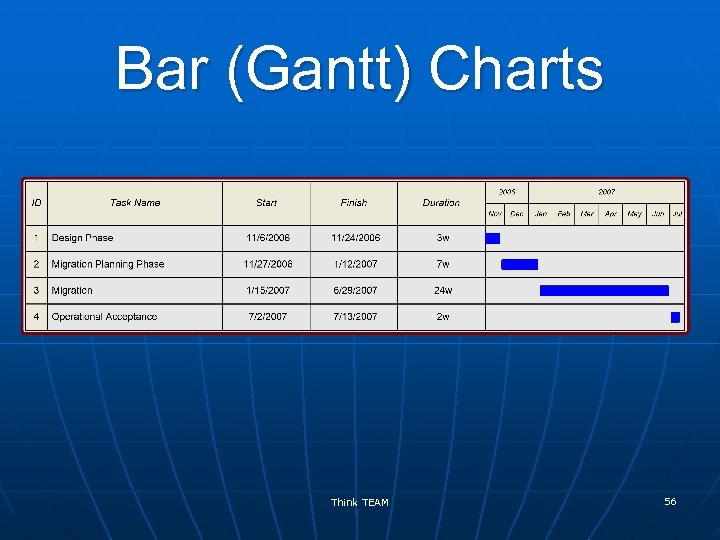
Bar (Gantt) Charts Think TEAM 56
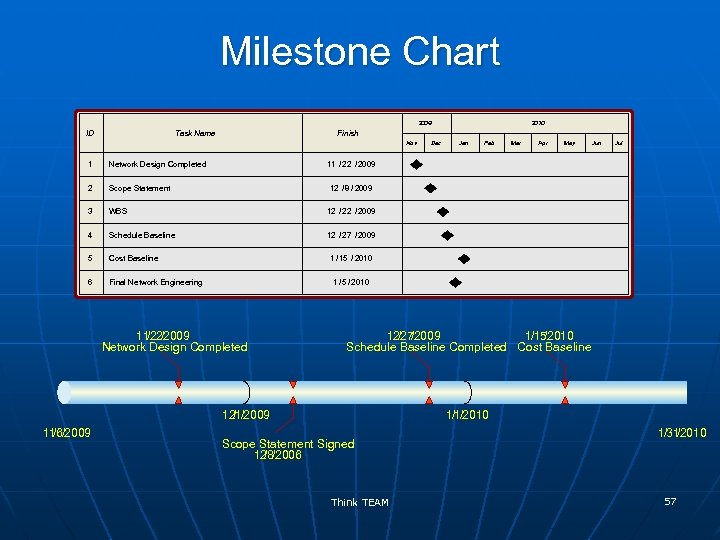
Milestone Chart 2009 ID Task Name 2010 Finish Nov 1 Network Design Completed 2 Scope Statement 3 WBS Schedule Baseline Cost Baseline 6 Final Network Engineering Feb Mar Apr May Jun Jul 12 / 27 / 2009 5 Jan 12 / 2009 4 Dec 11 / 22 / 2009 12 / 8 / 2009 1 / 15 / 2010 1 / 5 / 2010 11 /2009 /22 Network Design Completed 12 /2009 /27 1/15 /2010 Schedule Baseline Completed Cost Baseline 12 /1/2009 11 /6/2009 1/1/2010 Scope Statement Signed 12 /8/2006 Think TEAM 1/31 /2010 57

Activity Dependency n n n Mandatory – inherent in the nature of the work being done, a. k. a. hard logic Discretionary – defined by the project team, a. k. a. preferred logic, preferential logic, soft logic External – involve relationships between project activities and non -project activities Think TEAM 58

Precedence Diagramming Method n n Method of constructing network diagram that uses boxes (nodes) to represent activities and connects them with arrows to show dependencies Activity On Node Think TEAM 59
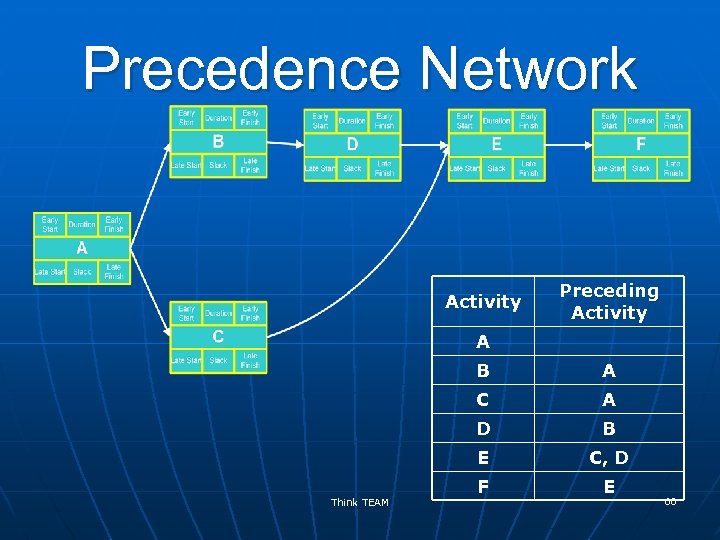
Precedence Network Activity Preceding Activity A B C A D B E Think TEAM A C, D F E 60
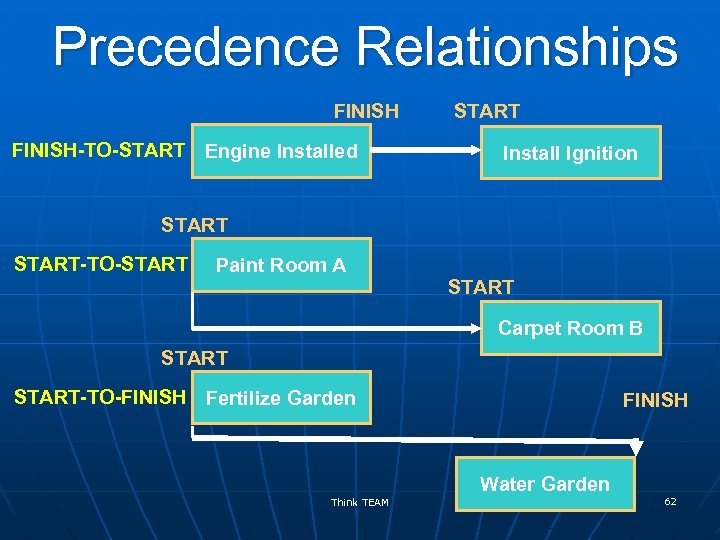
Precedence Relationships FINISH-TO-START Engine Installed START Install Ignition START-TO-START Paint Room A START Carpet Room B START-TO-FINISH Fertilize Garden FINISH Water Garden Think TEAM 62
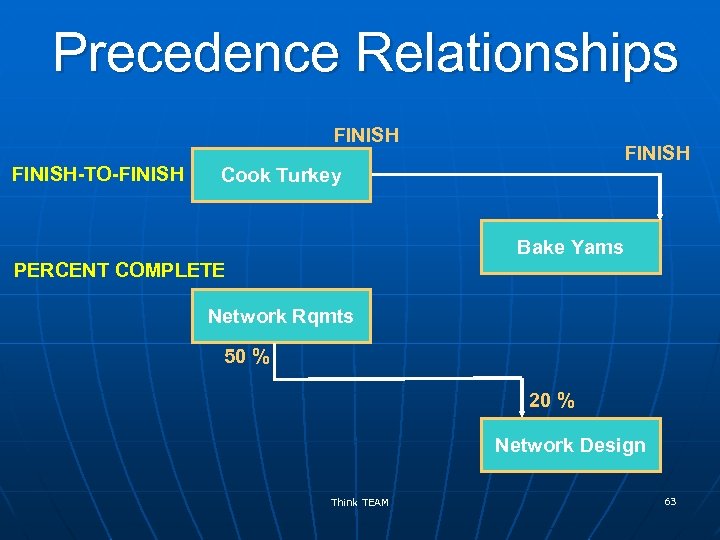
Precedence Relationships FINISH-TO-FINISH Cook Turkey Bake Yams PERCENT COMPLETE Network Rqmts 50 % 20 % Network Design Think TEAM 63

Critical Path and Float n Critical Path • Longest time span through the total system of activities / events • Delay in any activity / task in the critical path delays the whole project • Improvement in total project time means reducing time for activities / events in the critical path n Slack Time (Float) - Time differential between the scheduled completion date and the required date to meet critical path. Think TEAM 64

Critical Path Calculation n n Critical path is determined by doing a forward and backward pass calculations Forward pass • • • n Calculates early start and early finish dates Project end date Longest path • • • Calculates late start and late finish dates Task / project float Identifies tasks in critical path Backward pass Think TEAM 65

Forward Pass n n Early Start (ES) and Early Finish (EF) dates are calculated by adding the Task Duration (TD) to the earliest date a task can start The first predecessor task(s) have an ES of zero The EF date of the predecessor becomes the ES date for the successor When there are multiple predecessors, ES is the larger of the EFs for the task Think TEAM 66

Backward Pass n n Late Start (LS) and Late Finish (LF) dates are calculated starting from the end of the project LS is calculated by subtracting the TD from the LF of the task LS for the successor task becomes the LF for the predecessor task When there are multiple successors, LF is the smaller of the LS Think TEAM 67

Critical Path and Float n n Task Float = Late Finish – Early Finish Those tasks with zero float are on the critical path Think TEAM 68

Critical Path Exercises n Refer to your PM Workbook • Page 10 • Homework n How to calculate Critical Path • http: //syque. com/quality_tools/T OOLS 16. htm Think TEAM 69

Project Evaluation Review Technique (PERT) • Polaris Ballistic Missile Submarine program • Booz Allen Hamilton and US Navy – 1958 • Simplify large scale complex projects • Analyze the interdependencies and time to complete activities • A modeling tool that facilitates decision making Think TEAM 70
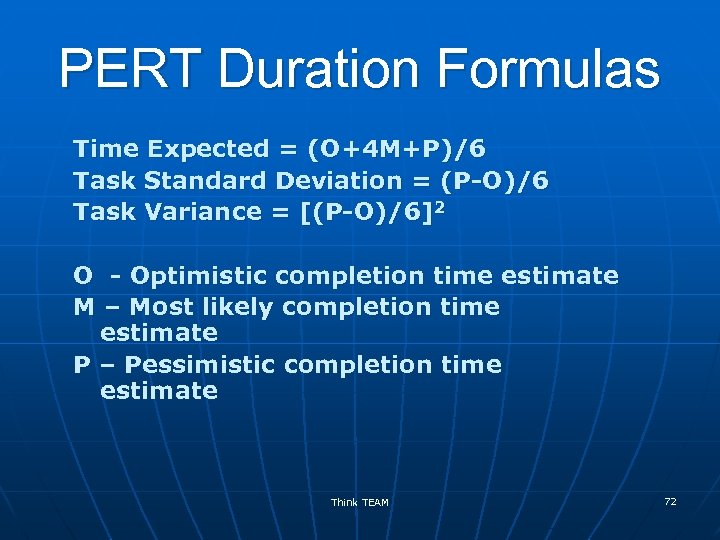
PERT Duration Formulas Time Expected = (O+4 M+P)/6 Task Standard Deviation = (P-O)/6 Task Variance = [(P-O)/6]2 O - Optimistic completion time estimate M – Most likely completion time estimate P – Pessimistic completion time estimate Think TEAM 72

Conditional Diagramming Method n n Similar to PERT Allows for branching, looping, and multiple project end results Example: If test activity resulted in failure, test can be repeated several times or based on results of a test, one of several branches can be selected to proceed with the project GERT (Graphical Evaluation and Review Technique) Think TEAM 73
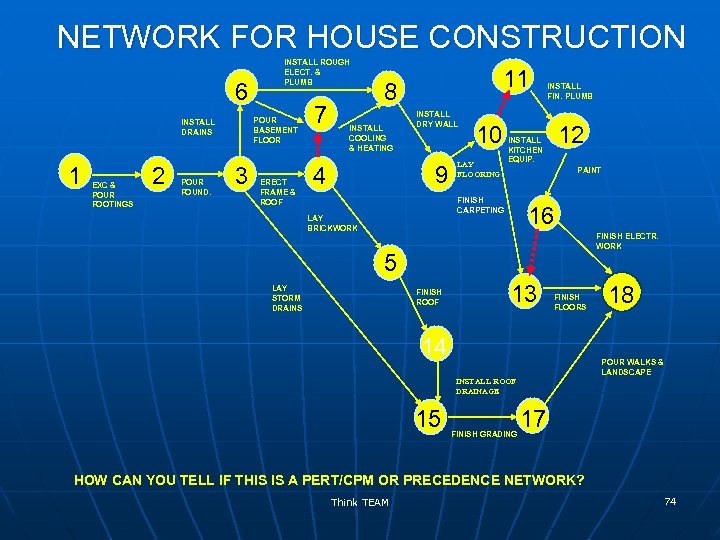
NETWORK FOR HOUSE CONSTRUCTION 6 POUR BASEMENT FLOOR INSTALL DRAINS 1 EXC & POUR FOOTINGS 2 POUR FOUND. INSTALL ROUGH ELECT. & PLUMB 3 ERECT FRAME & ROOF 7 11 8 INSTALL COOLING & HEATING INSTALL DRY WALL 9 4 10 LAY FLOORING 12 INSTALL KITCHEN EQUIP. PAINT FINISH CARPETING LAY BRICKWORK INSTALL FIN. PLUMB 16 FINISH ELECTR. WORK 5 LAY STORM DRAINS FINISH ROOF 13 FINISH FLOORS 14 18 POUR WALKS & LANDSCAPE INSTALL ROOF DRAINAGE 15 FINISH GRADING 17 HOW CAN YOU TELL IF THIS IS A PERT/CPM OR PRECEDENCE NETWORK? Think TEAM 74

Estimating Activity Duration n n Expert judgment Analogous estimating Quantitatively based durations Reserve time (contingency) Think TEAM 75

Analogous Estimating n n Use actual duration of a previous similar activity as basis to estimate duration of the future activity Approximate (rule of thumb) estimate Made without any detailed engineering data AKA “Top-down estimating” Think TEAM 76

Quantitatively Based Durations n n Quantities to be performed for each work category defined by the engineering/design effort multiplied by the productivity unit rate Example: Number of drawings x number of hours per drawing Think TEAM 77

Schedule Development Considerations n Constraints • Imposed dates on activities (start/finish) • Key events / major milestones n n Leads and lags: dependency relationship among activities Schedule compression • Crashing • Fast Tracking Think TEAM 78
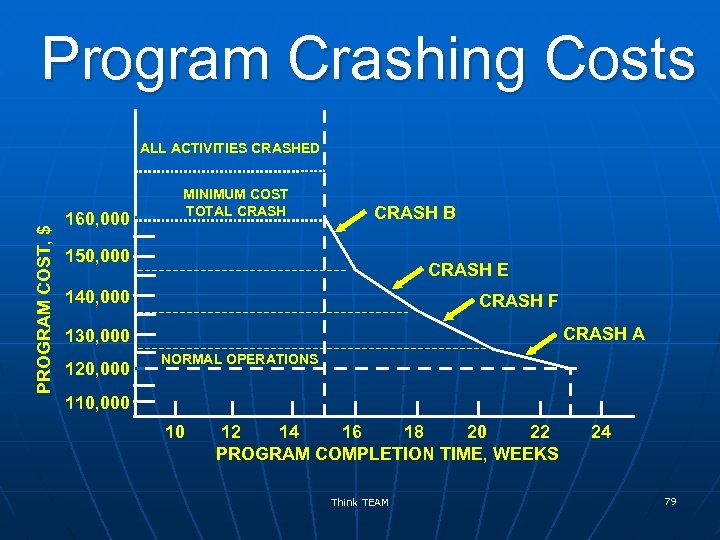
Program Crashing Costs PROGRAM COST, $ ALL ACTIVITIES CRASHED 160, 000 MINIMUM COST TOTAL CRASH B 150, 000 CRASH E 140, 000 CRASH F CRASH A 130, 000 120, 000 NORMAL OPERATIONS 110, 000 10 12 14 16 18 20 22 PROGRAM COMPLETION TIME, WEEKS Think TEAM 24 79

Project Schedule Should include planned start and finish dates for each activity n Tabular form n Graphical form • • • Network diagrams Bar / Gantt Chart Milestone chart Think TEAM 80
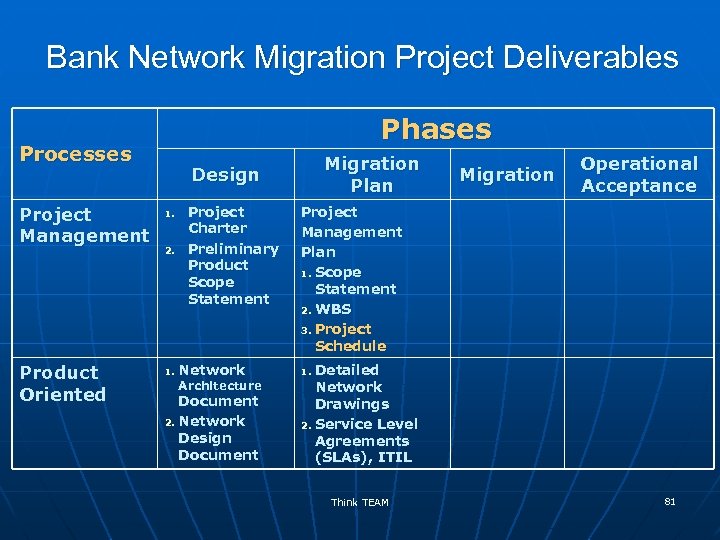
Bank Network Migration Project Deliverables Phases Processes Project Management Product Oriented Migration Plan Design 1. 2. 1. Project Charter Preliminary Product Scope Statement Network Architecture Document 2. Network Design Document Migration Operational Acceptance Project Management Plan 1. Scope Statement 2. WBS 3. Project Schedule Detailed Network Drawings 2. Service Level Agreements (SLAs), ITIL 1. Think TEAM 81

Best Practices Summary n n Use Scope Statement / WBS to baseline project scope Develop a project schedule to baseline project time Think TEAM 82
ec62897851ed976cb2121ae7d7308b3d.ppt