b43921cc99e6abac93e8866b55b53391.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 32
 Project Management Office (PMO) Overview DOM Administration Grand Round June 17, 2014 Lori Siracusa Senior ITS Project Manager Boston Medical Center Project Management Office (PMO)
Project Management Office (PMO) Overview DOM Administration Grand Round June 17, 2014 Lori Siracusa Senior ITS Project Manager Boston Medical Center Project Management Office (PMO)
 Project Management Office: Purpose • The BMC PMO is a dedicated business unit, which defines and maintains standards for project management within the organization • The primary goal of BMC PMO is to achieve benefits from developing and following standardized project management policies, processes and methods • Projects and project management are carried out in an environment broader than that of the project itself • The project management team must understand this broader context so it can select the life cycle phases, processes, documents and tools that appropriately fit the project • Project management is the discipline of planning, organizing, motivating, and controlling resources to achieve specific goals, related to managing and implementing projects within the organization |
Project Management Office: Purpose • The BMC PMO is a dedicated business unit, which defines and maintains standards for project management within the organization • The primary goal of BMC PMO is to achieve benefits from developing and following standardized project management policies, processes and methods • Projects and project management are carried out in an environment broader than that of the project itself • The project management team must understand this broader context so it can select the life cycle phases, processes, documents and tools that appropriately fit the project • Project management is the discipline of planning, organizing, motivating, and controlling resources to achieve specific goals, related to managing and implementing projects within the organization |
 Project Management Office: Mission Statement The BMC Project Management Office provides a standardized approach to identify, prioritize, and successfully execute a project portfolio. Project management leadership is responsible for establishing and implementing best practices to encourage collaboration, standardization, and overall improvement to managing and prioritizing projects. The primary focus is to manage and control projects to ensure they are implemented on schedule, within scope, and budget. Goal: Complete a successful project for our customers! |
Project Management Office: Mission Statement The BMC Project Management Office provides a standardized approach to identify, prioritize, and successfully execute a project portfolio. Project management leadership is responsible for establishing and implementing best practices to encourage collaboration, standardization, and overall improvement to managing and prioritizing projects. The primary focus is to manage and control projects to ensure they are implemented on schedule, within scope, and budget. Goal: Complete a successful project for our customers! |
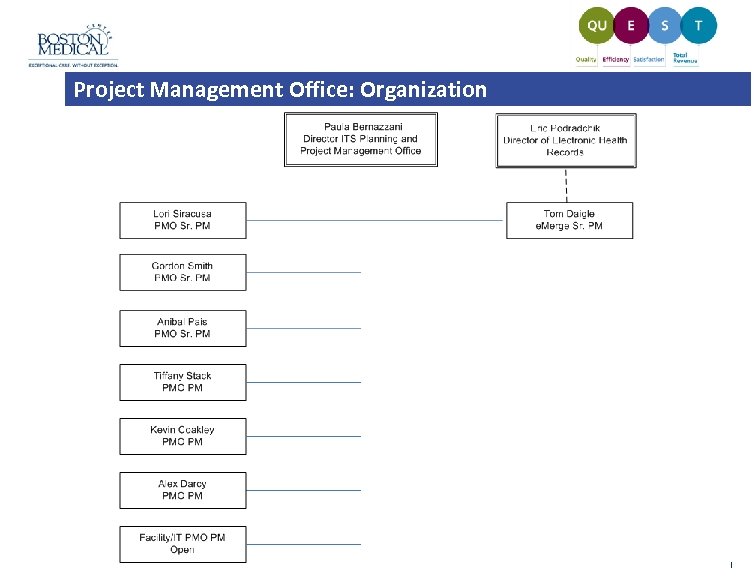 Project Management Office: Organization |
Project Management Office: Organization |
 Project Management Office - Governance ITS Prioritization Committee: Meet Bi-Monthly • • Key strategic and policy decisions – approach, direction, priorities, rules, governance Implementation, oversight and conflict resolution Strategic level coordination among BMC entities Committee Members: BMC Vice Presidents o Clinical – Physician, Clinical – Nursing, Financial, Strategic, Operations, Information Technology Services ITS Internal Governance Committee: Meet Weekly • • Affinity groups formed to research key issues Champions from functional area working groups to drive development of business cases Implementation of decisions made by Operations Group Liaison to end users Approved VP Projects review of required resources/timelines Project Phase Change Requests (e. g. Assessment to Planning) Committee Members: o IT Directors, IT Leadership, PMO Staff, other ITS staff as needed Boston Medical Center - Proprietary & Confidential |5
Project Management Office - Governance ITS Prioritization Committee: Meet Bi-Monthly • • Key strategic and policy decisions – approach, direction, priorities, rules, governance Implementation, oversight and conflict resolution Strategic level coordination among BMC entities Committee Members: BMC Vice Presidents o Clinical – Physician, Clinical – Nursing, Financial, Strategic, Operations, Information Technology Services ITS Internal Governance Committee: Meet Weekly • • Affinity groups formed to research key issues Champions from functional area working groups to drive development of business cases Implementation of decisions made by Operations Group Liaison to end users Approved VP Projects review of required resources/timelines Project Phase Change Requests (e. g. Assessment to Planning) Committee Members: o IT Directors, IT Leadership, PMO Staff, other ITS staff as needed Boston Medical Center - Proprietary & Confidential |5
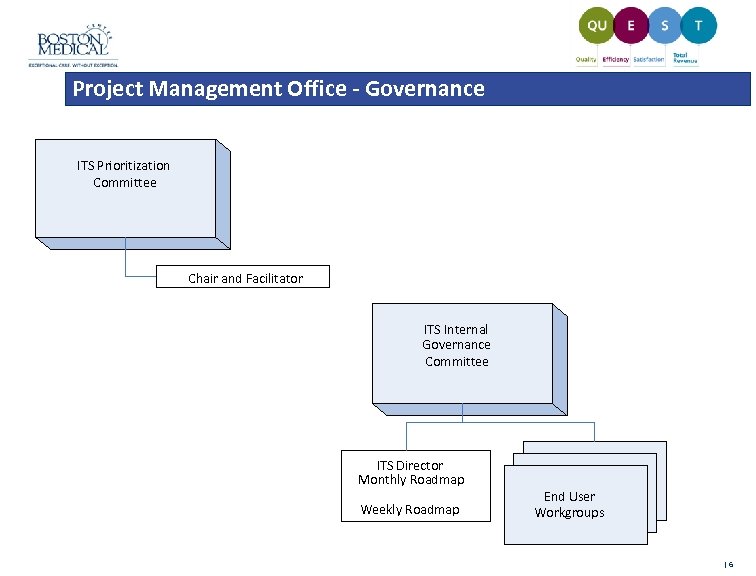 Project Management Office - Governance ITS Prioritization Committee Chair and Facilitator ITS Internal Governance Committee ITS Director Monthly Roadmap Weekly Roadmap Boston Medical Center - Proprietary & Confidential End User Workgroups |6
Project Management Office - Governance ITS Prioritization Committee Chair and Facilitator ITS Internal Governance Committee ITS Director Monthly Roadmap Weekly Roadmap Boston Medical Center - Proprietary & Confidential End User Workgroups |6
 Project Manager Assignment Criteria Project Size: • Small Project: 5 to 25 FTE days • Medium Project: 26 to 75 FTE days • Large Project: 76+ FTE days Timeline: • Project defined start and end date Exception Criteria: • Several of these should be met to drive the assignment of a PM (subjective decision) Characteristic Analyst as PM or Project Lead PMO Project Manager Predictability Vision of what lies ahead Activities / Tasks Activity durations Confidence in deadlines Complexity Issues / Risks Resources Highly Predictable Clear Standard, documented Known, low uncertainty High Managed Known, seen before Allocated/Available/Same group: team Constantly changing or evolving Cloudy Flexible, non-documented Unknown or unclear Moderate to low Evolving Unknown, evolving, not seen before Resource conflicts probable; Spans multiple group: teams or departments |
Project Manager Assignment Criteria Project Size: • Small Project: 5 to 25 FTE days • Medium Project: 26 to 75 FTE days • Large Project: 76+ FTE days Timeline: • Project defined start and end date Exception Criteria: • Several of these should be met to drive the assignment of a PM (subjective decision) Characteristic Analyst as PM or Project Lead PMO Project Manager Predictability Vision of what lies ahead Activities / Tasks Activity durations Confidence in deadlines Complexity Issues / Risks Resources Highly Predictable Clear Standard, documented Known, low uncertainty High Managed Known, seen before Allocated/Available/Same group: team Constantly changing or evolving Cloudy Flexible, non-documented Unknown or unclear Moderate to low Evolving Unknown, evolving, not seen before Resource conflicts probable; Spans multiple group: teams or departments |
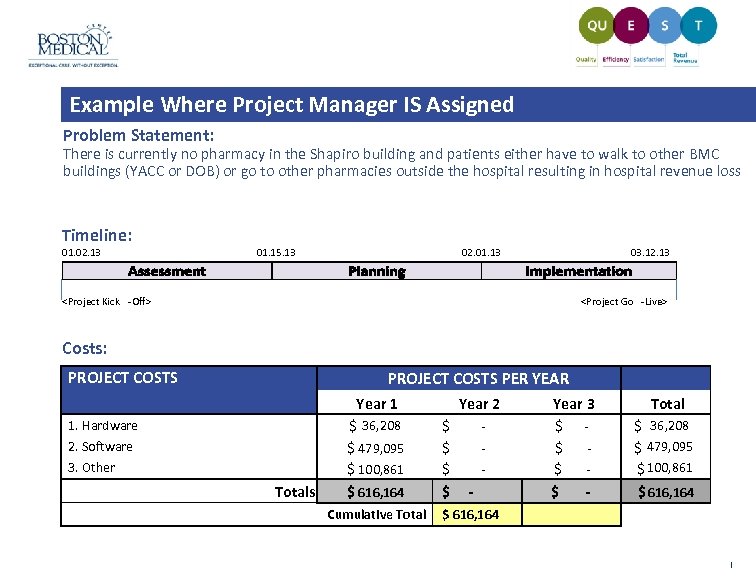 Example Where Project Manager IS Assigned Problem Statement: There is currently no pharmacy in the Shapiro building and patients either have to walk to other BMC buildings (YACC or DOB) or go to other pharmacies outside the hospital resulting in hospital revenue loss Timeline: 01. 02. 13
Example Where Project Manager IS Assigned Problem Statement: There is currently no pharmacy in the Shapiro building and patients either have to walk to other BMC buildings (YACC or DOB) or go to other pharmacies outside the hospital resulting in hospital revenue loss Timeline: 01. 02. 13
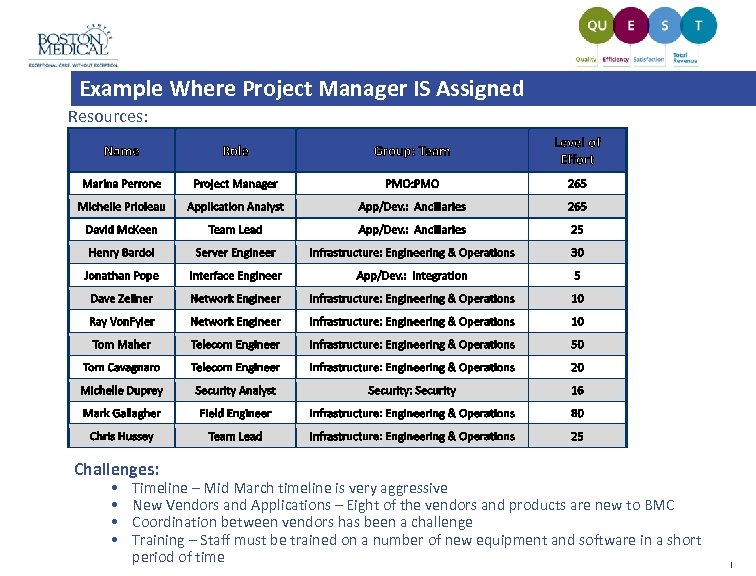 Example Where Project Manager IS Assigned Resources: Challenges: • • Timeline – Mid March timeline is very aggressive New Vendors and Applications – Eight of the vendors and products are new to BMC Coordination between vendors has been a challenge Training – Staff must be trained on a number of new equipment and software in a short period of time |
Example Where Project Manager IS Assigned Resources: Challenges: • • Timeline – Mid March timeline is very aggressive New Vendors and Applications – Eight of the vendors and products are new to BMC Coordination between vendors has been a challenge Training – Staff must be trained on a number of new equipment and software in a short period of time |
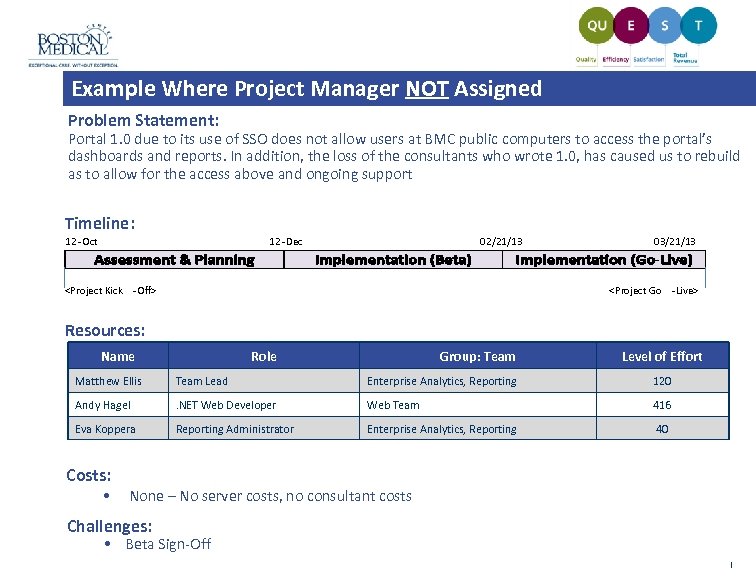 Example Where Project Manager NOT Assigned Problem Statement: Portal 1. 0 due to its use of SSO does not allow users at BMC public computers to access the portal’s dashboards and reports. In addition, the loss of the consultants who wrote 1. 0, has caused us to rebuild as to allow for the access above and ongoing support Timeline: 12 -Oct 12 -Dec 02/21/13 03/21/13
Example Where Project Manager NOT Assigned Problem Statement: Portal 1. 0 due to its use of SSO does not allow users at BMC public computers to access the portal’s dashboards and reports. In addition, the loss of the consultants who wrote 1. 0, has caused us to rebuild as to allow for the access above and ongoing support Timeline: 12 -Oct 12 -Dec 02/21/13 03/21/13
 Why Projects Fail? er ag The following is a list of primary project failure causes: • Poor Planning ct je ro • Unclear Goals and Objectives • Objectives changing during the project an M P a • Unrealistic time or resource estimates ge a g • Lack of executive support and user involvement • Failure to communicate and act as a team n E • Inappropriate skills |
Why Projects Fail? er ag The following is a list of primary project failure causes: • Poor Planning ct je ro • Unclear Goals and Objectives • Objectives changing during the project an M P a • Unrealistic time or resource estimates ge a g • Lack of executive support and user involvement • Failure to communicate and act as a team n E • Inappropriate skills |
 Project Life Cycle: Overview • Traditional project management life cycle consists of a number of phases • Regardless of the methodology or terminology used, the same basic management processes are utilized • Connects the beginning of the project to its end completion • PMO utilizes 6 basic phases to direct and control projects: o Request o Assessment o Planning o Implementation o Go Live o Closure |
Project Life Cycle: Overview • Traditional project management life cycle consists of a number of phases • Regardless of the methodology or terminology used, the same basic management processes are utilized • Connects the beginning of the project to its end completion • PMO utilizes 6 basic phases to direct and control projects: o Request o Assessment o Planning o Implementation o Go Live o Closure |
 Project Life Cycle: Phase Definitions Request • Reviewed via the VP Governance Process; ITS Prioritization Committee (approves, denies, additional information) Assessment • Careful examination of whether or not the project benefits the organization and can realistically be completed given budget, timeline, resource constraints, etc Planning • Detailed planning of time, cost, and resources to estimate the work needed and manage risk during project execution • Failure to adequately plan greatly reduces the project's chances of successfully accomplishing its goals Implementation • Coordinating people and resources, as well as integrating and performing the activities of the project in accordance with the project management plan • Deliverables are produced as outputs from the processes performed as defined in the project management plan and other frameworks Go-Live • Project is moved into production Project Closure • Evaluation conducted to highlight project success and lessons learned • Transitioned to appropriate operations resources 2 weeks post go-live |
Project Life Cycle: Phase Definitions Request • Reviewed via the VP Governance Process; ITS Prioritization Committee (approves, denies, additional information) Assessment • Careful examination of whether or not the project benefits the organization and can realistically be completed given budget, timeline, resource constraints, etc Planning • Detailed planning of time, cost, and resources to estimate the work needed and manage risk during project execution • Failure to adequately plan greatly reduces the project's chances of successfully accomplishing its goals Implementation • Coordinating people and resources, as well as integrating and performing the activities of the project in accordance with the project management plan • Deliverables are produced as outputs from the processes performed as defined in the project management plan and other frameworks Go-Live • Project is moved into production Project Closure • Evaluation conducted to highlight project success and lessons learned • Transitioned to appropriate operations resources 2 weeks post go-live |
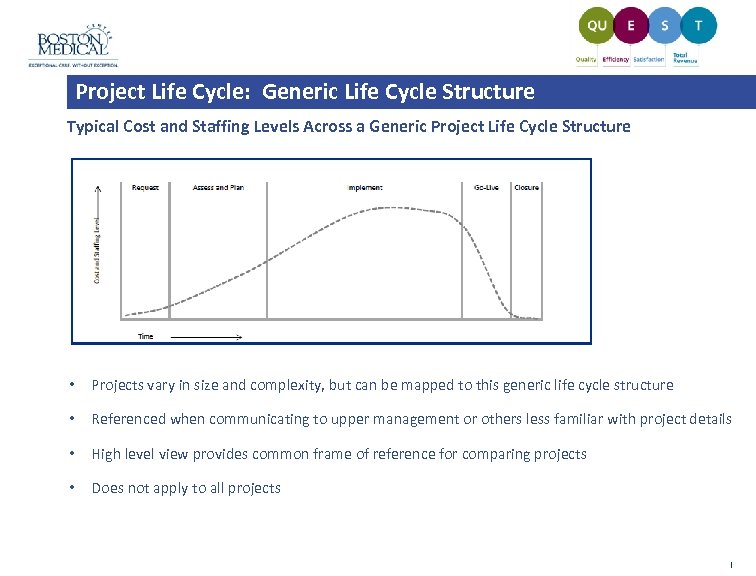 Project Life Cycle: Generic Life Cycle Structure Typical Cost and Staffing Levels Across a Generic Project Life Cycle Structure • Projects vary in size and complexity, but can be mapped to this generic life cycle structure • Referenced when communicating to upper management or others less familiar with project details • High level view provides common frame of reference for comparing projects • Does not apply to all projects |
Project Life Cycle: Generic Life Cycle Structure Typical Cost and Staffing Levels Across a Generic Project Life Cycle Structure • Projects vary in size and complexity, but can be mapped to this generic life cycle structure • Referenced when communicating to upper management or others less familiar with project details • High level view provides common frame of reference for comparing projects • Does not apply to all projects |
 Project Life Cycle: Summary • Defined as the completion and approval of one or more deliverables • Phase can be closed and no additional phases initiated (i. e. assessment is completed and determines the risk or cost is too great for the project to continue • Phases could be further subdivided into sub-phases for reasons of size, complexity, risk, or cash flow constraints • PMO Governance Process is utilized to transition projects from one phase to another • The ITS PMO Toolkit and Project Document Life Cycle were developed to assist the management of ITS projects |
Project Life Cycle: Summary • Defined as the completion and approval of one or more deliverables • Phase can be closed and no additional phases initiated (i. e. assessment is completed and determines the risk or cost is too great for the project to continue • Phases could be further subdivided into sub-phases for reasons of size, complexity, risk, or cash flow constraints • PMO Governance Process is utilized to transition projects from one phase to another • The ITS PMO Toolkit and Project Document Life Cycle were developed to assist the management of ITS projects |
 PMO Toolkit • Project Management Office Team has developed a standardized set of tools to assist in the management of Initiatives/Projects • The toolkit is a guide to assist in the management of projects across all phases of the project lifecycle o The PMO Toolkit helps standardize how a project’s scope, timeline, requirements and strategies are documented • The tools build upon each other as the project moves from Request to Go Live (Project Document Lifecycle) o Some tools will be used throughout a project’s lifecycle – – – Contact List Sign In Sheet Meeting Agenda Meeting Minutes Status Report Resource Tracking o Other tools are used during a specific phase (i. e. Assessment) o Many tools are started in one phase, refined throughout the project and closed at the conclusion (i. e. Project Plan) |
PMO Toolkit • Project Management Office Team has developed a standardized set of tools to assist in the management of Initiatives/Projects • The toolkit is a guide to assist in the management of projects across all phases of the project lifecycle o The PMO Toolkit helps standardize how a project’s scope, timeline, requirements and strategies are documented • The tools build upon each other as the project moves from Request to Go Live (Project Document Lifecycle) o Some tools will be used throughout a project’s lifecycle – – – Contact List Sign In Sheet Meeting Agenda Meeting Minutes Status Report Resource Tracking o Other tools are used during a specific phase (i. e. Assessment) o Many tools are started in one phase, refined throughout the project and closed at the conclusion (i. e. Project Plan) |
 Project Document Lifecycle Request Assessment Planning Implementation Go Live Project Closure |
Project Document Lifecycle Request Assessment Planning Implementation Go Live Project Closure |
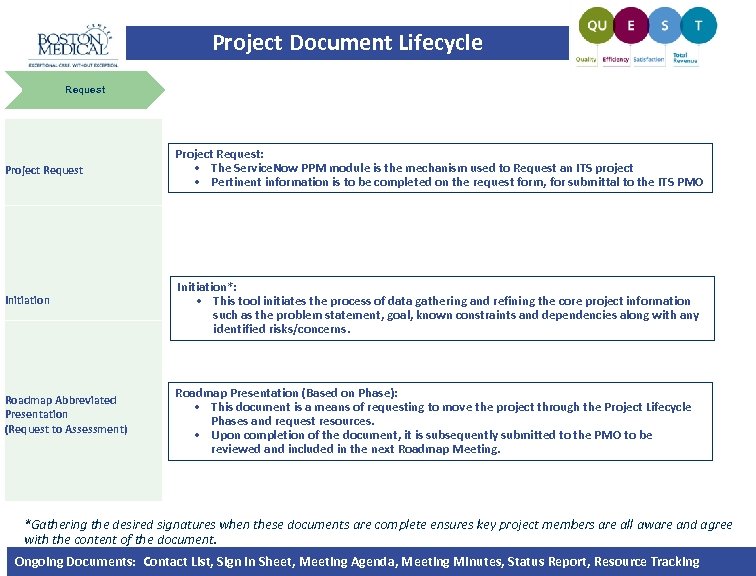 Project Document Lifecycle Request Project Request Initiation Roadmap Abbreviated Presentation (Request to Assessment) Project Request: • The Service. Now PPM module is the mechanism used to Request an ITS project • Pertinent information is to be completed on the request form, for submittal to the ITS PMO Initiation*: • This tool initiates the process of data gathering and refining the core project information such as the problem statement, goal, known constraints and dependencies along with any identified risks/concerns. Roadmap Presentation (Based on Phase): • This document is a means of requesting to move the project through the Project Lifecycle Phases and request resources. • Upon completion of the document, it is subsequently submitted to the PMO to be reviewed and included in the next Roadmap Meeting. *Gathering the desired signatures when these documents are complete ensures key project members are all aware and agree with the content of the document. Ongoing Documents: Contact List, Sign In Sheet, Meeting Agenda, Meeting Minutes, Status Report, Resource Tracking |
Project Document Lifecycle Request Project Request Initiation Roadmap Abbreviated Presentation (Request to Assessment) Project Request: • The Service. Now PPM module is the mechanism used to Request an ITS project • Pertinent information is to be completed on the request form, for submittal to the ITS PMO Initiation*: • This tool initiates the process of data gathering and refining the core project information such as the problem statement, goal, known constraints and dependencies along with any identified risks/concerns. Roadmap Presentation (Based on Phase): • This document is a means of requesting to move the project through the Project Lifecycle Phases and request resources. • Upon completion of the document, it is subsequently submitted to the PMO to be reviewed and included in the next Roadmap Meeting. *Gathering the desired signatures when these documents are complete ensures key project members are all aware and agree with the content of the document. Ongoing Documents: Contact List, Sign In Sheet, Meeting Agenda, Meeting Minutes, Status Report, Resource Tracking |
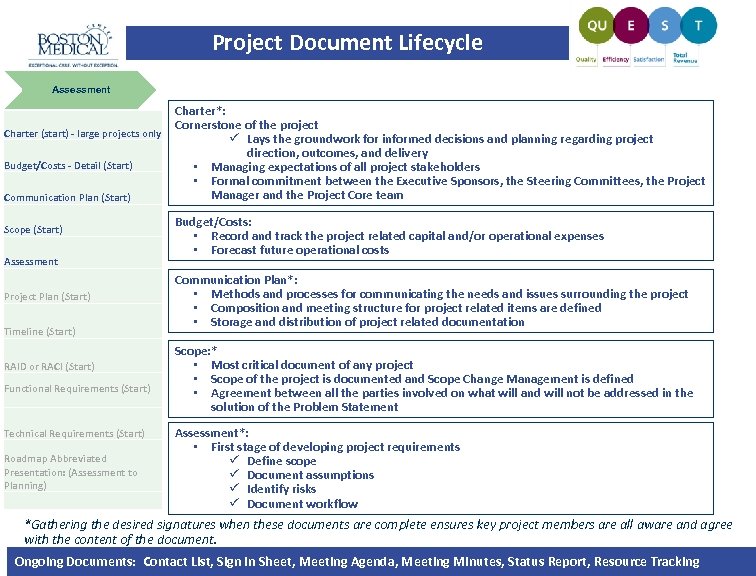 Project Document Lifecycle Assessment Charter (start) - large projects only Budget/Costs - Detail (Start) Communication Plan (Start) Scope (Start) Assessment Project Plan (Start) Timeline (Start) RAID or RACI (Start) Functional Requirements (Start) Technical Requirements (Start) Roadmap Abbreviated Presentation: (Assessment to Planning) Charter*: Cornerstone of the project ü Lays the groundwork for informed decisions and planning regarding project direction, outcomes, and delivery • Managing expectations of all project stakeholders • Formal commitment between the Executive Sponsors, the Steering Committees, the Project Manager and the Project Core team Budget/Costs: • Record and track the project related capital and/or operational expenses • Forecast future operational costs Communication Plan*: • Methods and processes for communicating the needs and issues surrounding the project • Composition and meeting structure for project related items are defined • Storage and distribution of project related documentation Scope: * • Most critical document of any project • Scope of the project is documented and Scope Change Management is defined • Agreement between all the parties involved on what will and will not be addressed in the solution of the Problem Statement Assessment*: • First stage of developing project requirements ü Define scope ü Document assumptions ü Identify risks ü Document workflow *Gathering the desired signatures when these documents are complete ensures key project members are all aware and agree with the content of the document. Ongoing Documents: Contact List, Sign In Sheet, Meeting Agenda, Meeting Minutes, Status Report, Resource Tracking |
Project Document Lifecycle Assessment Charter (start) - large projects only Budget/Costs - Detail (Start) Communication Plan (Start) Scope (Start) Assessment Project Plan (Start) Timeline (Start) RAID or RACI (Start) Functional Requirements (Start) Technical Requirements (Start) Roadmap Abbreviated Presentation: (Assessment to Planning) Charter*: Cornerstone of the project ü Lays the groundwork for informed decisions and planning regarding project direction, outcomes, and delivery • Managing expectations of all project stakeholders • Formal commitment between the Executive Sponsors, the Steering Committees, the Project Manager and the Project Core team Budget/Costs: • Record and track the project related capital and/or operational expenses • Forecast future operational costs Communication Plan*: • Methods and processes for communicating the needs and issues surrounding the project • Composition and meeting structure for project related items are defined • Storage and distribution of project related documentation Scope: * • Most critical document of any project • Scope of the project is documented and Scope Change Management is defined • Agreement between all the parties involved on what will and will not be addressed in the solution of the Problem Statement Assessment*: • First stage of developing project requirements ü Define scope ü Document assumptions ü Identify risks ü Document workflow *Gathering the desired signatures when these documents are complete ensures key project members are all aware and agree with the content of the document. Ongoing Documents: Contact List, Sign In Sheet, Meeting Agenda, Meeting Minutes, Status Report, Resource Tracking |
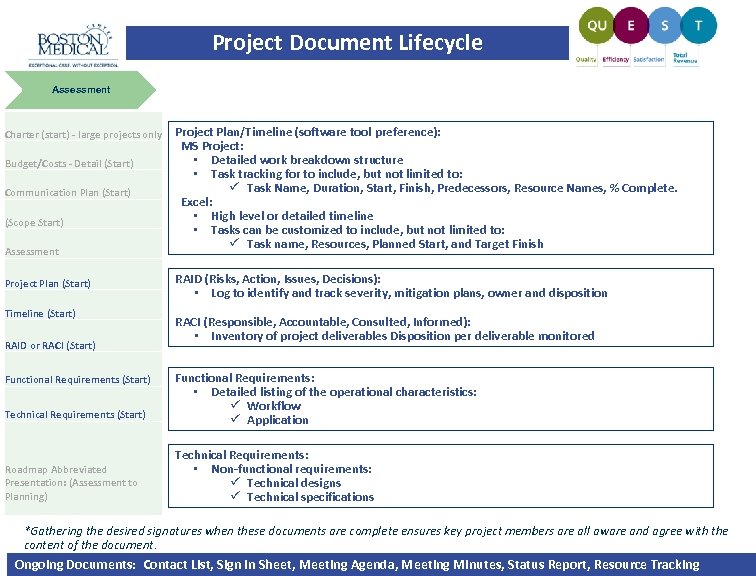 Project Document Lifecycle Assessment Charter (start) - large projects only Budget/Costs - Detail (Start) Communication Plan (Start) (Scope Start) Assessment Project Plan (Start) Timeline (Start) RAID or RACI (Start) Functional Requirements (Start) Technical Requirements (Start) Roadmap Abbreviated Presentation: (Assessment to Planning) Project Plan/Timeline (software tool preference): MS Project: • Detailed work breakdown structure • Task tracking for to include, but not limited to: ü Task Name, Duration, Start, Finish, Predecessors, Resource Names, % Complete. Excel: • High level or detailed timeline • Tasks can be customized to include, but not limited to: ü Task name, Resources, Planned Start, and Target Finish RAID (Risks, Action, Issues, Decisions): • Log to identify and track severity, mitigation plans, owner and disposition RACI (Responsible, Accountable, Consulted, Informed): • Inventory of project deliverables Disposition per deliverable monitored Functional Requirements: • Detailed listing of the operational characteristics: ü Workflow ü Application Technical Requirements: • Non-functional requirements: ü Technical designs ü Technical specifications *Gathering the desired signatures when these documents are complete ensures key project members are all aware and agree with the content of the document. Ongoing Documents: Contact List, Sign In Sheet, Meeting Agenda, Meeting Minutes, Status Report, Resource Tracking |
Project Document Lifecycle Assessment Charter (start) - large projects only Budget/Costs - Detail (Start) Communication Plan (Start) (Scope Start) Assessment Project Plan (Start) Timeline (Start) RAID or RACI (Start) Functional Requirements (Start) Technical Requirements (Start) Roadmap Abbreviated Presentation: (Assessment to Planning) Project Plan/Timeline (software tool preference): MS Project: • Detailed work breakdown structure • Task tracking for to include, but not limited to: ü Task Name, Duration, Start, Finish, Predecessors, Resource Names, % Complete. Excel: • High level or detailed timeline • Tasks can be customized to include, but not limited to: ü Task name, Resources, Planned Start, and Target Finish RAID (Risks, Action, Issues, Decisions): • Log to identify and track severity, mitigation plans, owner and disposition RACI (Responsible, Accountable, Consulted, Informed): • Inventory of project deliverables Disposition per deliverable monitored Functional Requirements: • Detailed listing of the operational characteristics: ü Workflow ü Application Technical Requirements: • Non-functional requirements: ü Technical designs ü Technical specifications *Gathering the desired signatures when these documents are complete ensures key project members are all aware and agree with the content of the document. Ongoing Documents: Contact List, Sign In Sheet, Meeting Agenda, Meeting Minutes, Status Report, Resource Tracking |
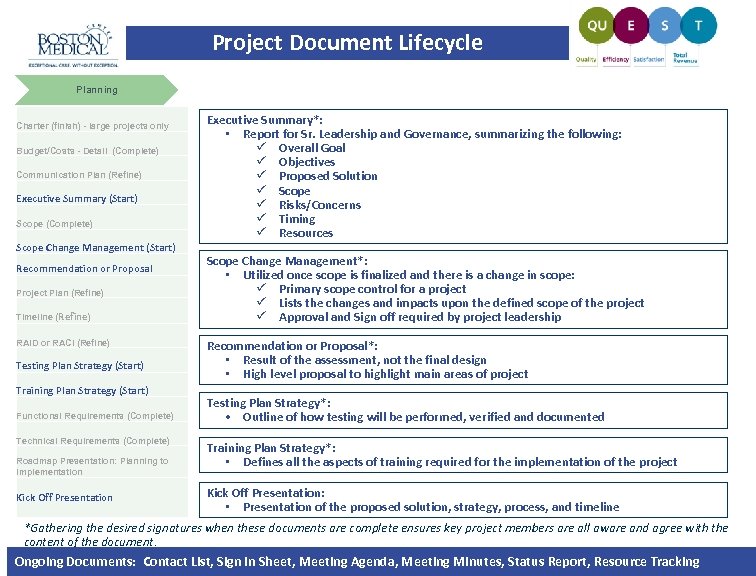 Project Document Lifecycle Planning Charter (finish) - large projects only Budget/Costs - Detail (Complete) Communication Plan (Refine) Executive Summary (Start) Scope (Complete) Scope Change Management (Start) Recommendation or Proposal Project Plan (Refine) Timeline (Refine) RAID or RACI (Refine) Testing Plan Strategy (Start) Training Plan Strategy (Start) Functional Requirements (Complete) Technical Requirements (Complete) Roadmap Presentation: Planning to Implementation Kick Off Presentation Executive Summary*: • Report for Sr. Leadership and Governance, summarizing the following: ü Overall Goal ü Objectives ü Proposed Solution ü Scope ü Risks/Concerns ü Timing ü Resources Scope Change Management*: • Utilized once scope is finalized and there is a change in scope: ü Primary scope control for a project ü Lists the changes and impacts upon the defined scope of the project ü Approval and Sign off required by project leadership Recommendation or Proposal*: • Result of the assessment, not the final design • High level proposal to highlight main areas of project Testing Plan Strategy*: • Outline of how testing will be performed, verified and documented Training Plan Strategy*: • Defines all the aspects of training required for the implementation of the project Kick Off Presentation: • Presentation of the proposed solution, strategy, process, and timeline *Gathering the desired signatures when these documents are complete ensures key project members are all aware and agree with the content of the document. Ongoing Documents: Contact List, Sign In Sheet, Meeting Agenda, Meeting Minutes, Status Report, Resource Tracking |
Project Document Lifecycle Planning Charter (finish) - large projects only Budget/Costs - Detail (Complete) Communication Plan (Refine) Executive Summary (Start) Scope (Complete) Scope Change Management (Start) Recommendation or Proposal Project Plan (Refine) Timeline (Refine) RAID or RACI (Refine) Testing Plan Strategy (Start) Training Plan Strategy (Start) Functional Requirements (Complete) Technical Requirements (Complete) Roadmap Presentation: Planning to Implementation Kick Off Presentation Executive Summary*: • Report for Sr. Leadership and Governance, summarizing the following: ü Overall Goal ü Objectives ü Proposed Solution ü Scope ü Risks/Concerns ü Timing ü Resources Scope Change Management*: • Utilized once scope is finalized and there is a change in scope: ü Primary scope control for a project ü Lists the changes and impacts upon the defined scope of the project ü Approval and Sign off required by project leadership Recommendation or Proposal*: • Result of the assessment, not the final design • High level proposal to highlight main areas of project Testing Plan Strategy*: • Outline of how testing will be performed, verified and documented Training Plan Strategy*: • Defines all the aspects of training required for the implementation of the project Kick Off Presentation: • Presentation of the proposed solution, strategy, process, and timeline *Gathering the desired signatures when these documents are complete ensures key project members are all aware and agree with the content of the document. Ongoing Documents: Contact List, Sign In Sheet, Meeting Agenda, Meeting Minutes, Status Report, Resource Tracking |
 Project Document Lifecycle Implementation Communication Plan (Complete) Executive Summary (Complete) Scope Edits (Change Mgmt Required) Project Plan (Refine) Timeline (Refine) RAID or RACI (Refine) Testing Plan Strategy (Complete) Training Plan Strategy (Complete) Go Live Readiness (Start) Go Live Checklist (Start) Go Live Readiness*: • Highlights all items for Go-Live: ü Staff to support Go Live ü Environment for go-live Note: Check off items and sections can be customized based on project deliverables. Go Live Checklist*: Itemized plan for the Go-Live event consisting of: ü Pre Go-Live ü Post Go-Live • Detailed tasks: ü Responsible party ü Dates, times, and duration ü Task status Note: The checklist can be customized based on project deliverables. *Gathering the desired signatures when these documents are complete ensures key project members are all aware and agree with the content of the document Ongoing Documents: Contact List, Sign In Sheet, Meeting Agenda, Meeting Minutes, Status Report, Resource Tracking |
Project Document Lifecycle Implementation Communication Plan (Complete) Executive Summary (Complete) Scope Edits (Change Mgmt Required) Project Plan (Refine) Timeline (Refine) RAID or RACI (Refine) Testing Plan Strategy (Complete) Training Plan Strategy (Complete) Go Live Readiness (Start) Go Live Checklist (Start) Go Live Readiness*: • Highlights all items for Go-Live: ü Staff to support Go Live ü Environment for go-live Note: Check off items and sections can be customized based on project deliverables. Go Live Checklist*: Itemized plan for the Go-Live event consisting of: ü Pre Go-Live ü Post Go-Live • Detailed tasks: ü Responsible party ü Dates, times, and duration ü Task status Note: The checklist can be customized based on project deliverables. *Gathering the desired signatures when these documents are complete ensures key project members are all aware and agree with the content of the document Ongoing Documents: Contact List, Sign In Sheet, Meeting Agenda, Meeting Minutes, Status Report, Resource Tracking |
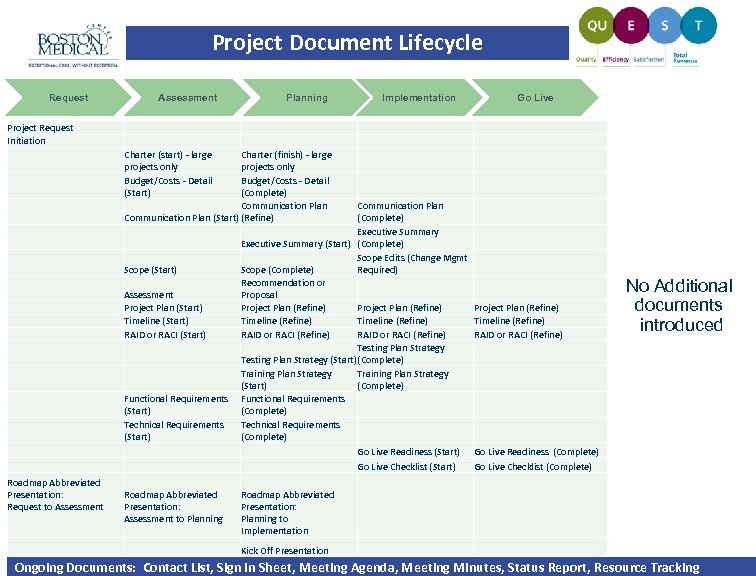 Project Document Lifecycle Request Assessment Planning Implementation Go Live Project Request Initiation Charter (start) - large projects only Budget/Costs - Detail (Start) Charter (finish) - large projects only Budget/Costs - Detail (Complete) Communication Plan (Start) (Refine) Scope (Start) Assessment Project Plan (Start) Timeline (Start) RAID or RACI (Start) Functional Requirements (Start) Technical Requirements (Start) Communication Plan (Complete) Executive Summary (Start) (Complete) Scope Edits (Change Mgmt Scope (Complete) Required) Recommendation or Proposal Project Plan (Refine) Timeline (Refine) RAID or RACI (Refine) Testing Plan Strategy (Start) (Complete) Training Plan Strategy (Start) (Complete) Functional Requirements (Complete) Technical Requirements (Complete) Go Live Readiness (Start) Go Live Checklist (Start) Roadmap Abbreviated Presentation: Request to Assessment Roadmap Abbreviated Presentation: Assessment to Planning Project Plan (Refine) Timeline (Refine) RAID or RACI (Refine) No Additional documents introduced Go Live Readiness (Complete) Go Live Checklist (Complete) Roadmap Abbreviated Presentation: Planning to Implementation Kick Off Presentation Ongoing Documents: Contact List, Sign In Sheet, Meeting Agenda, Meeting Minutes, Status Report, Resource Tracking |
Project Document Lifecycle Request Assessment Planning Implementation Go Live Project Request Initiation Charter (start) - large projects only Budget/Costs - Detail (Start) Charter (finish) - large projects only Budget/Costs - Detail (Complete) Communication Plan (Start) (Refine) Scope (Start) Assessment Project Plan (Start) Timeline (Start) RAID or RACI (Start) Functional Requirements (Start) Technical Requirements (Start) Communication Plan (Complete) Executive Summary (Start) (Complete) Scope Edits (Change Mgmt Scope (Complete) Required) Recommendation or Proposal Project Plan (Refine) Timeline (Refine) RAID or RACI (Refine) Testing Plan Strategy (Start) (Complete) Training Plan Strategy (Start) (Complete) Functional Requirements (Complete) Technical Requirements (Complete) Go Live Readiness (Start) Go Live Checklist (Start) Roadmap Abbreviated Presentation: Request to Assessment Roadmap Abbreviated Presentation: Assessment to Planning Project Plan (Refine) Timeline (Refine) RAID or RACI (Refine) No Additional documents introduced Go Live Readiness (Complete) Go Live Checklist (Complete) Roadmap Abbreviated Presentation: Planning to Implementation Kick Off Presentation Ongoing Documents: Contact List, Sign In Sheet, Meeting Agenda, Meeting Minutes, Status Report, Resource Tracking |
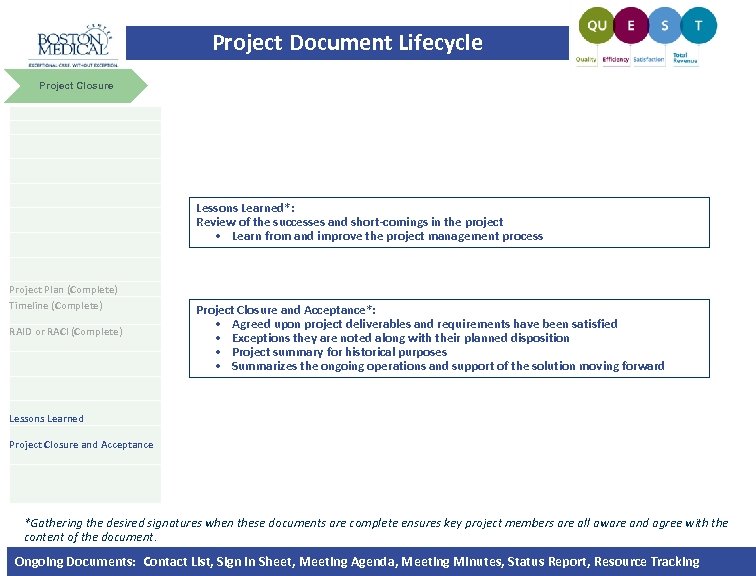 Project Document Lifecycle Project Closure Lessons Learned*: Review of the successes and short-comings in the project • Learn from and improve the project management process Project Plan (Complete) Timeline (Complete) RAID or RACI (Complete) Project Closure and Acceptance*: • Agreed upon project deliverables and requirements have been satisfied • Exceptions they are noted along with their planned disposition • Project summary for historical purposes • Summarizes the ongoing operations and support of the solution moving forward Lessons Learned Project Closure and Acceptance *Gathering the desired signatures when these documents are complete ensures key project members are all aware and agree with the content of the document. Ongoing Documents: Contact List, Sign In Sheet, Meeting Agenda, Meeting Minutes, Status Report, Resource Tracking |
Project Document Lifecycle Project Closure Lessons Learned*: Review of the successes and short-comings in the project • Learn from and improve the project management process Project Plan (Complete) Timeline (Complete) RAID or RACI (Complete) Project Closure and Acceptance*: • Agreed upon project deliverables and requirements have been satisfied • Exceptions they are noted along with their planned disposition • Project summary for historical purposes • Summarizes the ongoing operations and support of the solution moving forward Lessons Learned Project Closure and Acceptance *Gathering the desired signatures when these documents are complete ensures key project members are all aware and agree with the content of the document. Ongoing Documents: Contact List, Sign In Sheet, Meeting Agenda, Meeting Minutes, Status Report, Resource Tracking |
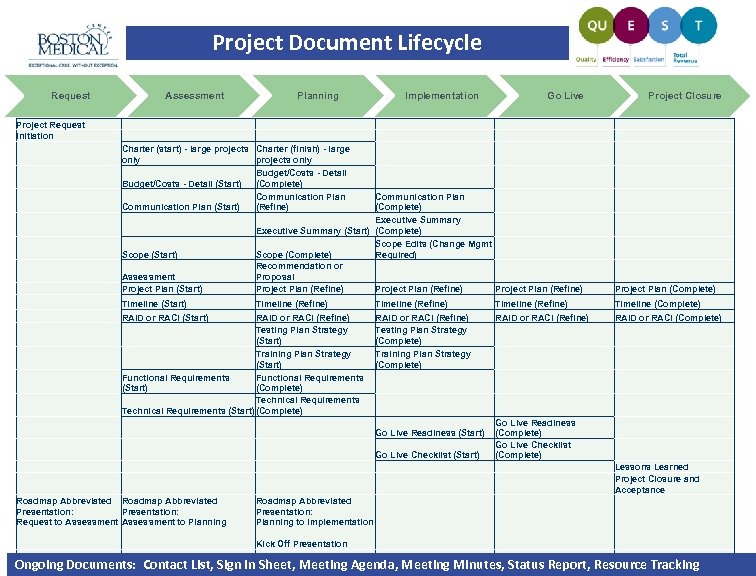 Project Document Lifecycle Request Assessment Planning Implementation Go Live Project Closure Project Request Initiation Charter (start) - large projects Charter (finish) - large only projects only Budget/Costs - Detail (Start) (Complete) Communication Plan (Start) (Refine) Assessment Project Plan (Start) Communication Plan (Complete) Executive Summary (Start) (Complete) Scope Edits (Change Mgmt Scope (Complete) Required) Recommendation or Proposal Project Plan (Refine) Project Plan (Complete) Timeline (Start) Timeline (Refine) Scope (Start) RAID or RACI (Refine) Testing Plan Strategy (Start) Training Plan Strategy (Start) Functional Requirements (Start) (Complete) Technical Requirements (Start) (Complete) Timeline (Refine) Timeline (Complete) RAID or RACI (Refine) Testing Plan Strategy (Complete) Training Plan Strategy (Complete) RAID or RACI (Refine) RAID or RACI (Complete) Go Live Readiness (Start) Go Live Checklist (Start) Go Live Readiness (Complete) Go Live Checklist (Complete) Lessons Learned Project Closure and Acceptance Roadmap Abbreviated Presentation: Request to Assessment to Planning Roadmap Abbreviated Presentation: Planning to Implementation Kick Off Presentation Ongoing Documents: Contact List, Sign In Sheet, Meeting Agenda, Meeting Minutes, Status Report, Resource Tracking |
Project Document Lifecycle Request Assessment Planning Implementation Go Live Project Closure Project Request Initiation Charter (start) - large projects Charter (finish) - large only projects only Budget/Costs - Detail (Start) (Complete) Communication Plan (Start) (Refine) Assessment Project Plan (Start) Communication Plan (Complete) Executive Summary (Start) (Complete) Scope Edits (Change Mgmt Scope (Complete) Required) Recommendation or Proposal Project Plan (Refine) Project Plan (Complete) Timeline (Start) Timeline (Refine) Scope (Start) RAID or RACI (Refine) Testing Plan Strategy (Start) Training Plan Strategy (Start) Functional Requirements (Start) (Complete) Technical Requirements (Start) (Complete) Timeline (Refine) Timeline (Complete) RAID or RACI (Refine) Testing Plan Strategy (Complete) Training Plan Strategy (Complete) RAID or RACI (Refine) RAID or RACI (Complete) Go Live Readiness (Start) Go Live Checklist (Start) Go Live Readiness (Complete) Go Live Checklist (Complete) Lessons Learned Project Closure and Acceptance Roadmap Abbreviated Presentation: Request to Assessment to Planning Roadmap Abbreviated Presentation: Planning to Implementation Kick Off Presentation Ongoing Documents: Contact List, Sign In Sheet, Meeting Agenda, Meeting Minutes, Status Report, Resource Tracking |
 PMO Toolkit and Document Lifecycle Summary • The ITS PMO Toolkit and Project Document Lifecycle were developed to assist the management of ITS projects • The templates are guides to standardize project activities • Project managers and leads should become familiar with the toolkit and incorporate these templates into their project management activities • The templates use the < and > symbols to note whenever a project specific entry should be added • Not all projects require all templates, however, all projects should minimally include: o o Scope Timeline |
PMO Toolkit and Document Lifecycle Summary • The ITS PMO Toolkit and Project Document Lifecycle were developed to assist the management of ITS projects • The templates are guides to standardize project activities • Project managers and leads should become familiar with the toolkit and incorporate these templates into their project management activities • The templates use the < and > symbols to note whenever a project specific entry should be added • Not all projects require all templates, however, all projects should minimally include: o o Scope Timeline |
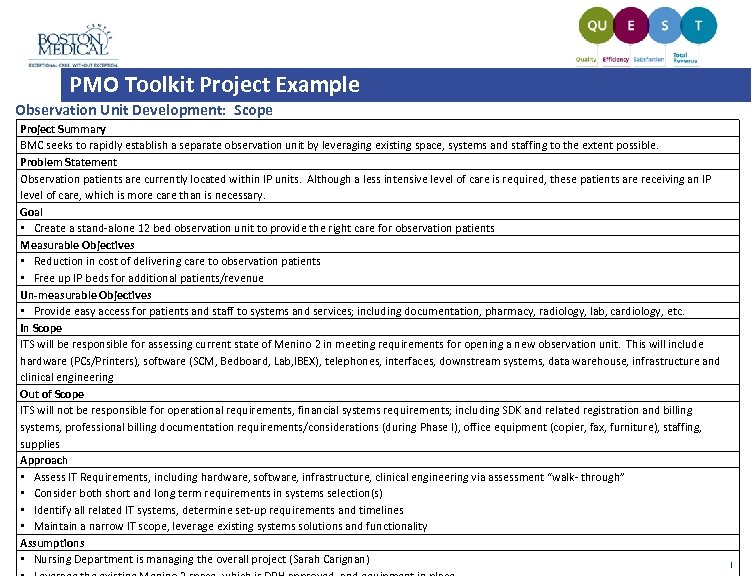 PMO Toolkit Project Example Observation Unit Development: Scope Project Summary BMC seeks to rapidly establish a separate observation unit by leveraging existing space, systems and staffing to the extent possible. Problem Statement Observation patients are currently located within IP units. Although a less intensive level of care is required, these patients are receiving an IP level of care, which is more care than is necessary. Goal • Create a stand-alone 12 bed observation unit to provide the right care for observation patients Measurable Objectives • Reduction in cost of delivering care to observation patients • Free up IP beds for additional patients/revenue Un-measurable Objectives • Provide easy access for patients and staff to systems and services; including documentation, pharmacy, radiology, lab, cardiology, etc. In Scope ITS will be responsible for assessing current state of Menino 2 in meeting requirements for opening a new observation unit. This will include hardware (PCs/Printers), software (SCM, Bedboard, Lab, IBEX), telephones, interfaces, downstream systems, data warehouse, infrastructure and clinical engineering Out of Scope ITS will not be responsible for operational requirements, financial systems requirements; including SDK and related registration and billing systems, professional billing documentation requirements/considerations (during Phase I), office equipment (copier, fax, furniture), staffing, supplies Approach • Assess IT Requirements, including hardware, software, infrastructure, clinical engineering via assessment “walk- through” • Consider both short and long term requirements in systems selection(s) • Identify all related IT systems, determine set-up requirements and timelines • Maintain a narrow IT scope, leverage existing systems solutions and functionality Assumptions • Nursing Department is managing the overall project (Sarah Carignan) |
PMO Toolkit Project Example Observation Unit Development: Scope Project Summary BMC seeks to rapidly establish a separate observation unit by leveraging existing space, systems and staffing to the extent possible. Problem Statement Observation patients are currently located within IP units. Although a less intensive level of care is required, these patients are receiving an IP level of care, which is more care than is necessary. Goal • Create a stand-alone 12 bed observation unit to provide the right care for observation patients Measurable Objectives • Reduction in cost of delivering care to observation patients • Free up IP beds for additional patients/revenue Un-measurable Objectives • Provide easy access for patients and staff to systems and services; including documentation, pharmacy, radiology, lab, cardiology, etc. In Scope ITS will be responsible for assessing current state of Menino 2 in meeting requirements for opening a new observation unit. This will include hardware (PCs/Printers), software (SCM, Bedboard, Lab, IBEX), telephones, interfaces, downstream systems, data warehouse, infrastructure and clinical engineering Out of Scope ITS will not be responsible for operational requirements, financial systems requirements; including SDK and related registration and billing systems, professional billing documentation requirements/considerations (during Phase I), office equipment (copier, fax, furniture), staffing, supplies Approach • Assess IT Requirements, including hardware, software, infrastructure, clinical engineering via assessment “walk- through” • Consider both short and long term requirements in systems selection(s) • Identify all related IT systems, determine set-up requirements and timelines • Maintain a narrow IT scope, leverage existing systems solutions and functionality Assumptions • Nursing Department is managing the overall project (Sarah Carignan) |
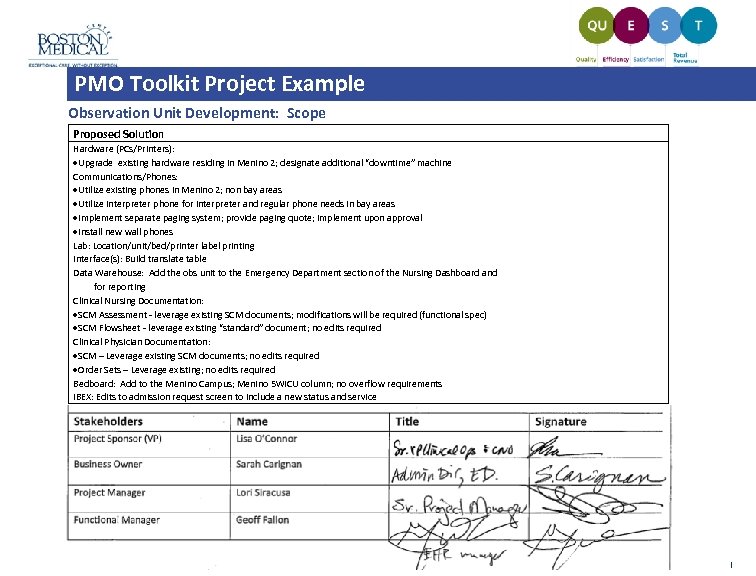 PMO Toolkit Project Example Observation Unit Development: Scope Proposed Solution Hardware (PCs/Printers): Upgrade existing hardware residing in Menino 2; designate additional “downtime” machine Communications/Phones: Utilize existing phones in Menino 2; non bay areas Utilize interpreter phone for interpreter and regular phone needs in bay areas Implement separate paging system; provide paging quote; implement upon approval Install new wall phones Lab: Location/unit/bed/printer label printing Interface(s): Build translate table Data Warehouse: Add the obs unit to the Emergency Department section of the Nursing Dashboard and for reporting Clinical Nursing Documentation: SCM Assessment - leverage existing SCM documents; modifications will be required (functional spec) SCM Flowsheet - leverage existing “standard” document; no edits required Clinical Physician Documentation: SCM – Leverage existing SCM documents; no edits required Order Sets – Leverage existing; no edits required Bedboard: Add to the Menino Campus; Menino 5 WICU column; no overflow requirements IBEX: Edits to admission request screen to include a new status and service |
PMO Toolkit Project Example Observation Unit Development: Scope Proposed Solution Hardware (PCs/Printers): Upgrade existing hardware residing in Menino 2; designate additional “downtime” machine Communications/Phones: Utilize existing phones in Menino 2; non bay areas Utilize interpreter phone for interpreter and regular phone needs in bay areas Implement separate paging system; provide paging quote; implement upon approval Install new wall phones Lab: Location/unit/bed/printer label printing Interface(s): Build translate table Data Warehouse: Add the obs unit to the Emergency Department section of the Nursing Dashboard and for reporting Clinical Nursing Documentation: SCM Assessment - leverage existing SCM documents; modifications will be required (functional spec) SCM Flowsheet - leverage existing “standard” document; no edits required Clinical Physician Documentation: SCM – Leverage existing SCM documents; no edits required Order Sets – Leverage existing; no edits required Bedboard: Add to the Menino Campus; Menino 5 WICU column; no overflow requirements IBEX: Edits to admission request screen to include a new status and service |
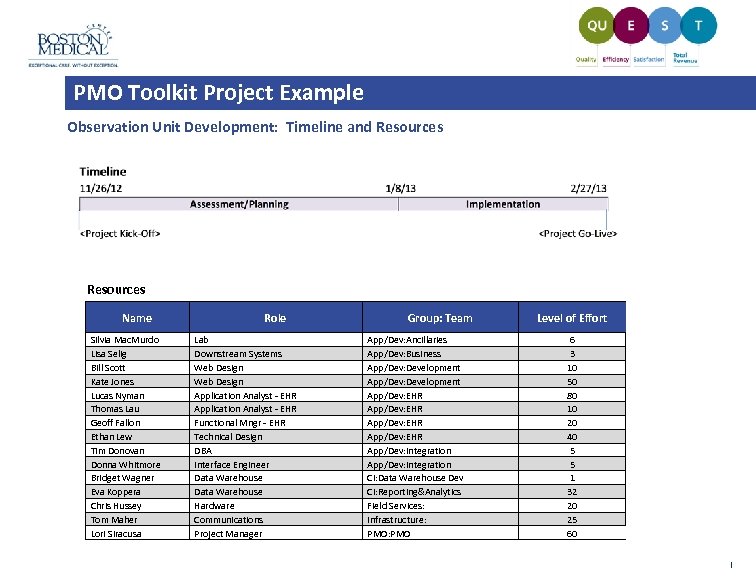 PMO Toolkit Project Example Observation Unit Development: Timeline and Resources Name Silvia Mac. Murdo Lisa Selig Bill Scott Kate Jones Lucas Nyman Thomas Lau Geoff Fallon Ethan Lew Tim Donovan Donna Whitmore Bridget Wagner Eva Koppera Chris Hussey Tom Maher Lori Siracusa Role Lab Downstream Systems Web Design Application Analyst - EHR Functional Mngr - EHR Technical Design DBA Interface Engineer Data Warehouse Hardware Communications Project Manager Group: Team App/Dev: Ancillaries App/Dev: Business App/Dev: Development App/Dev: EHR App/Dev: Integration CI: Data Warehouse Dev CI: Reporting&Analytics Field Services: Infrastructure: PMO Level of Effort 6 3 10 50 80 10 20 40 5 5 1 32 20 25 60 |
PMO Toolkit Project Example Observation Unit Development: Timeline and Resources Name Silvia Mac. Murdo Lisa Selig Bill Scott Kate Jones Lucas Nyman Thomas Lau Geoff Fallon Ethan Lew Tim Donovan Donna Whitmore Bridget Wagner Eva Koppera Chris Hussey Tom Maher Lori Siracusa Role Lab Downstream Systems Web Design Application Analyst - EHR Functional Mngr - EHR Technical Design DBA Interface Engineer Data Warehouse Hardware Communications Project Manager Group: Team App/Dev: Ancillaries App/Dev: Business App/Dev: Development App/Dev: EHR App/Dev: Integration CI: Data Warehouse Dev CI: Reporting&Analytics Field Services: Infrastructure: PMO Level of Effort 6 3 10 50 80 10 20 40 5 5 1 32 20 25 60 |
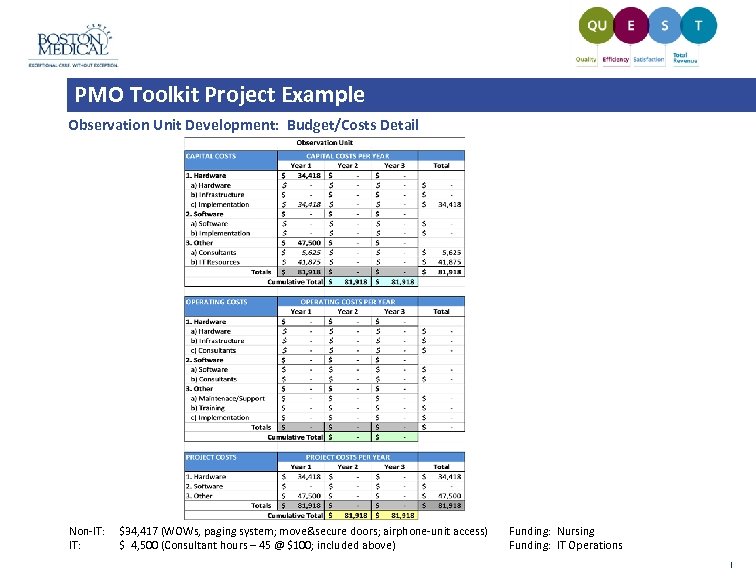 PMO Toolkit Project Example Observation Unit Development: Budget/Costs Detail Non-IT: $34, 417 (WOWs, paging system; move&secure doors; airphone-unit access) IT: $ 4, 500 (Consultant hours – 45 @ $100; included above) Funding: Nursing Funding: IT Operations |
PMO Toolkit Project Example Observation Unit Development: Budget/Costs Detail Non-IT: $34, 417 (WOWs, paging system; move&secure doors; airphone-unit access) IT: $ 4, 500 (Consultant hours – 45 @ $100; included above) Funding: Nursing Funding: IT Operations |
 PMO Overview - Review 1. Where can you find the purpose/role of the Project Management Office Team? In the Mission statement! 2. How many phases in the Project Lifecycle? Six 3. Does the Assessment Phase come after the Implementation phase? No! 4. Name the phases in the Project Lifecycle? Request – Assessment – Planning – Implementation – Go Live – Project Closure 5. Benefits of engaging the Project Management Office Coaching Services; Standardized Toolkit; Proven track record 6. Purpose of PMO Toolkit documentation? Standardization across project lifecycle 7. Are all the documents in the PMO Document Lifecycle required for each phase? No! 8. How many ITS Governance Committees are established at BMC? Two: VP Governance and ITS Internal Governance! 9. What is the first Step to request a project? Complete and submit the Request form in Service. Now! 10. What is the most important project document in the PMO Document Lifecycle? Scope! |
PMO Overview - Review 1. Where can you find the purpose/role of the Project Management Office Team? In the Mission statement! 2. How many phases in the Project Lifecycle? Six 3. Does the Assessment Phase come after the Implementation phase? No! 4. Name the phases in the Project Lifecycle? Request – Assessment – Planning – Implementation – Go Live – Project Closure 5. Benefits of engaging the Project Management Office Coaching Services; Standardized Toolkit; Proven track record 6. Purpose of PMO Toolkit documentation? Standardization across project lifecycle 7. Are all the documents in the PMO Document Lifecycle required for each phase? No! 8. How many ITS Governance Committees are established at BMC? Two: VP Governance and ITS Internal Governance! 9. What is the first Step to request a project? Complete and submit the Request form in Service. Now! 10. What is the most important project document in the PMO Document Lifecycle? Scope! |
 Project Management Office Tutorial Questions? THANK YOU! If you are interested in utilizing the toolkit, please contact: Lori Siracusa 617 -414 -8564 Lori. Siracusa@BMC. Org |
Project Management Office Tutorial Questions? THANK YOU! If you are interested in utilizing the toolkit, please contact: Lori Siracusa 617 -414 -8564 Lori. Siracusa@BMC. Org |


