PROJECT MANAGEMENT IN ELT D.A. Starkova 2016 Plan























































30946-project_management_in_elt.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 60
 PROJECT MANAGEMENT IN ELT D.A. Starkova 2016
PROJECT MANAGEMENT IN ELT D.A. Starkova 2016
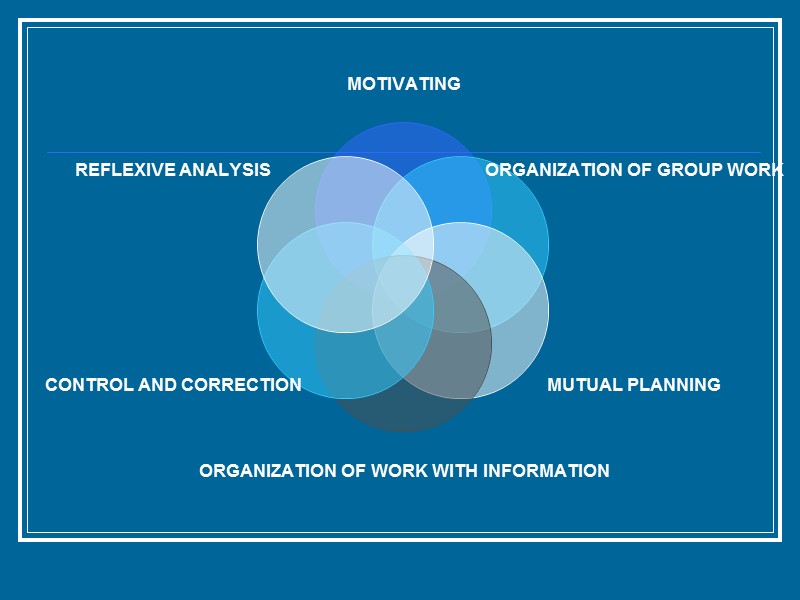
 Plan of the lecture on pedagogical management Methodological management skills for Project Work: Motivating skills Mutual Planning skills Organizing Group Work skills Organizing Work with information skills Control and correction Reflexive Analysis
Plan of the lecture on pedagogical management Methodological management skills for Project Work: Motivating skills Mutual Planning skills Organizing Group Work skills Organizing Work with information skills Control and correction Reflexive Analysis

 Motivating skills Formulation of problem on the basis of students’ needs Apprehensible (for each student) aim formulation Interesting and comprehensible process of problem solving and getting the result
Motivating skills Formulation of problem on the basis of students’ needs Apprehensible (for each student) aim formulation Interesting and comprehensible process of problem solving and getting the result
 Formulation of problem on the basis of students’ needs Questionnairing Quiz Interview Survey Test
Formulation of problem on the basis of students’ needs Questionnairing Quiz Interview Survey Test
 BELIEVE IT OR NOT! Fact № 1 Using slang is officially prohibited at schools in Great Britain True or false?
BELIEVE IT OR NOT! Fact № 1 Using slang is officially prohibited at schools in Great Britain True or false?
 TRUE The authorities are sure that school is the first step of the future career that’s why children should learn to talk in an official way as early as possible
TRUE The authorities are sure that school is the first step of the future career that’s why children should learn to talk in an official way as early as possible
 Fact № 2 The longest lecture in the world took place in the USA, in 2003. It was a lecture in Mathematics and it took 26 hours.
Fact № 2 The longest lecture in the world took place in the USA, in 2003. It was a lecture in Mathematics and it took 26 hours.
 FALSE The longest lecture in the world took place in Australia. It was done by Professor Barrous and it took more than 50 hours. The action itself happened in 1970s.
FALSE The longest lecture in the world took place in Australia. It was done by Professor Barrous and it took more than 50 hours. The action itself happened in 1970s.
 Fact № 3 In Belgium even the children from Primary School are allowed to drink a glass of beer during the lunch-time at schools
Fact № 3 In Belgium even the children from Primary School are allowed to drink a glass of beer during the lunch-time at schools
 TRUE Neither the parents, nor the authorities are against it. Belgians are sure that their beer is much healthier and better than Coca-Cola
TRUE Neither the parents, nor the authorities are against it. Belgians are sure that their beer is much healthier and better than Coca-Cola
 Fact № 4 The academic year in Japan starts in April
Fact № 4 The academic year in Japan starts in April
 TRUE There are 3 academic terms in Japan: the 1st April-July, the 2nd September – December and the 3rd January – March. The only month for summer holiday is August
TRUE There are 3 academic terms in Japan: the 1st April-July, the 2nd September – December and the 3rd January – March. The only month for summer holiday is August
 Fact № 5 Yoga is a compulsory subject at schools in India
Fact № 5 Yoga is a compulsory subject at schools in India
 FALSE Yoga is obligatory for everyone in Vietnam's schools. What about India, some schools and even high education establishments have it as an optional subject
FALSE Yoga is obligatory for everyone in Vietnam's schools. What about India, some schools and even high education establishments have it as an optional subject
 Questionnaire Do you like this subject? Will it be useful for you in the future life? Do you like English classes or they are boring for you? What do you like to do most of all in the English classroom? Do you work well in the English classroom? Would you like to have better marks in English? What do you need to do to have better marks in English? What would you like to add to an English classroom? What would you like to change in an English classroom? What difficulties do you have in the English classroom?
Questionnaire Do you like this subject? Will it be useful for you in the future life? Do you like English classes or they are boring for you? What do you like to do most of all in the English classroom? Do you work well in the English classroom? Would you like to have better marks in English? What do you need to do to have better marks in English? What would you like to add to an English classroom? What would you like to change in an English classroom? What difficulties do you have in the English classroom?
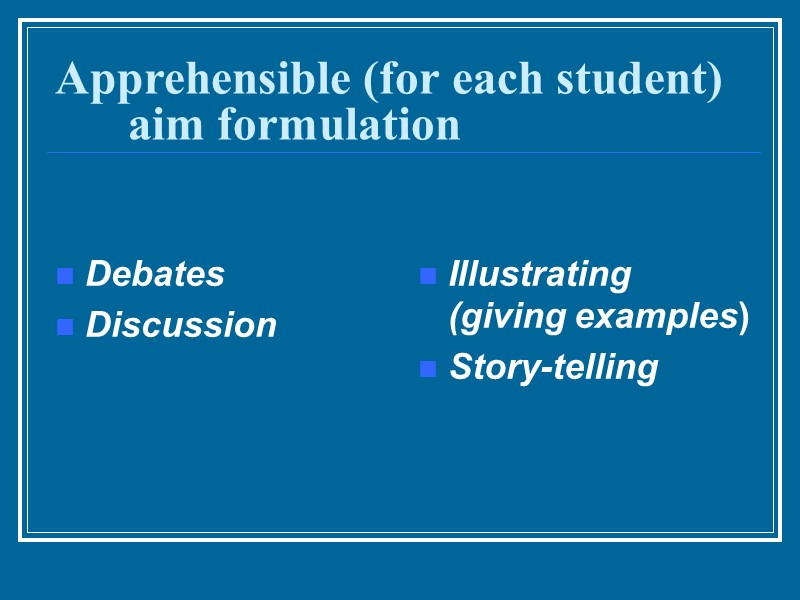
 Apprehensible (for each student) aim formulation Debates Discussion Illustrating (giving examples) Story-telling
Apprehensible (for each student) aim formulation Debates Discussion Illustrating (giving examples) Story-telling

 Interesting and comprehensible process of problem solving and getting the result in the group work Group Discussion Extending ideas Information gap Problem-solving task
Interesting and comprehensible process of problem solving and getting the result in the group work Group Discussion Extending ideas Information gap Problem-solving task
 Extending Story Beginnings In a far away place … Once upon a time… A long time ago in a remote tribe… On the eve of…
Extending Story Beginnings In a far away place … Once upon a time… A long time ago in a remote tribe… On the eve of…
 The indicators of Teacher’s success in motivating students to (project) work in the language classroom Students are interested in the (project) work Students feel the necessity of getting the result and making the product Students understand that it is much easier and more interesting and helpful to cooperate with groupmates on the way of goal-achievement
The indicators of Teacher’s success in motivating students to (project) work in the language classroom Students are interested in the (project) work Students feel the necessity of getting the result and making the product Students understand that it is much easier and more interesting and helpful to cooperate with groupmates on the way of goal-achievement
 Organizing Group Work Skills Why?
Organizing Group Work Skills Why?
 Many heads are much better than one + Distribution of roles Smaller and clearer individual tasks Quicker, in time - Conflicts and misunderstandings Feelings of inequality
Many heads are much better than one + Distribution of roles Smaller and clearer individual tasks Quicker, in time - Conflicts and misunderstandings Feelings of inequality
 Organizing Group Work Skills Dividing students into groups Distribution of roles and responsibilities within the group Group uniting activities
Organizing Group Work Skills Dividing students into groups Distribution of roles and responsibilities within the group Group uniting activities
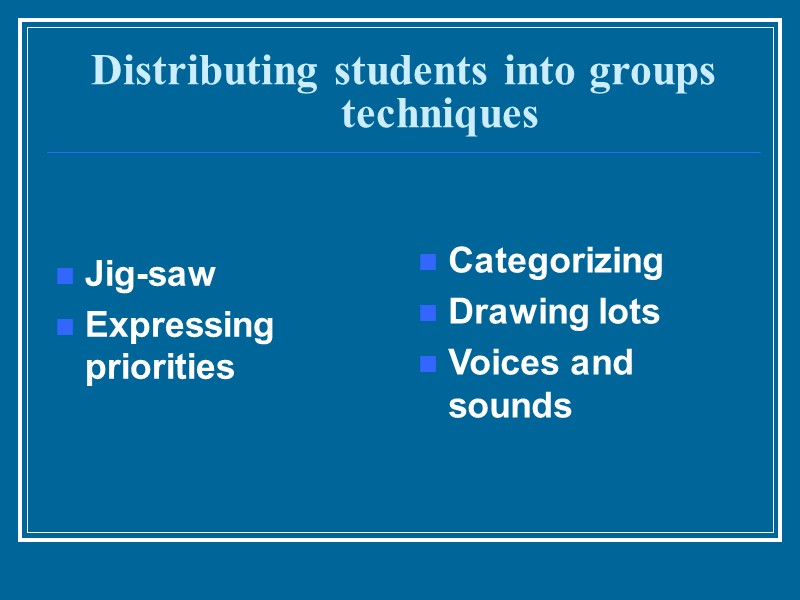
 Distributing students into groups techniques Jig-saw Expressing priorities Categorizing Drawing lots Voices and sounds
Distributing students into groups techniques Jig-saw Expressing priorities Categorizing Drawing lots Voices and sounds


 Distributing roles and responsibilities techniques Discussion Expressing priorities Listing Role-mapping Table filling Note-taking
Distributing roles and responsibilities techniques Discussion Expressing priorities Listing Role-mapping Table filling Note-taking
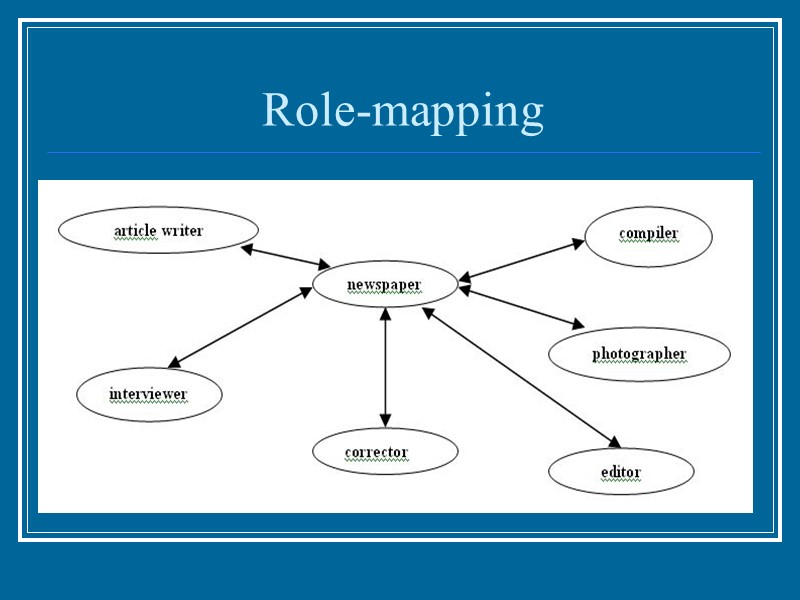
 Role-mapping
Role-mapping
 Possible Project Products Atlas Broadcast Collection Exhibition Game Guidebook Coursebook Holiday Illustrations Map Party Script System Tour Video …
Possible Project Products Atlas Broadcast Collection Exhibition Game Guidebook Coursebook Holiday Illustrations Map Party Script System Tour Video …
 Group uniting techniques Teams competitions Groupmates learning activities
Group uniting techniques Teams competitions Groupmates learning activities
 Groupmates learning activities Helping a person who cannot see Associations: if our team is a colour (music, geometric figure, a film, mood…) what colour it would be Join the ranks (according to alphabet, age, height, distance form the uni…) Finding similarities …
Groupmates learning activities Helping a person who cannot see Associations: if our team is a colour (music, geometric figure, a film, mood…) what colour it would be Join the ranks (according to alphabet, age, height, distance form the uni…) Finding similarities …
 The indicators of Teacher’s success in organizing students’ work in groups Students agree to work in groups in which they have been distributed Students agree to act roles and fulfill responsibilities they have been given Students want to help their group to achieve the goal
The indicators of Teacher’s success in organizing students’ work in groups Students agree to work in groups in which they have been distributed Students agree to act roles and fulfill responsibilities they have been given Students want to help their group to achieve the goal
 Mutual Planning Wording the aim: discussion, prioritizing, ranking, note-taking Thinking over ways of aim achievement and resources: discussion, listing, prioritising, ranking, table-filling, mind-mapping, note-taking Determining characteristics of the final product and criteria of assessment: association, listing, description
Mutual Planning Wording the aim: discussion, prioritizing, ranking, note-taking Thinking over ways of aim achievement and resources: discussion, listing, prioritising, ranking, table-filling, mind-mapping, note-taking Determining characteristics of the final product and criteria of assessment: association, listing, description
 LISTING Students are to write as many ideas as they can about the problem solution or aim achievement: to make a film about Xmas 1) To write a scenario 2) To make decorations 3) To rehearse 4) To shoot…
LISTING Students are to write as many ideas as they can about the problem solution or aim achievement: to make a film about Xmas 1) To write a scenario 2) To make decorations 3) To rehearse 4) To shoot…
 The indicators of Teacher’s success in organizing the process of mutual planning by students their (project) work in the language classroom The group of students together have formulated the aim in their own words The group of students together have described the process of aim-achievement The group of students together have determined the characteristics of their product and know exactly what they are to do
The indicators of Teacher’s success in organizing the process of mutual planning by students their (project) work in the language classroom The group of students together have formulated the aim in their own words The group of students together have described the process of aim-achievement The group of students together have determined the characteristics of their product and know exactly what they are to do
 Organization of work with information skills Organizing students’ search of information Organizing students’ processing and selection of information Organizing students’ product creation and presentation
Organization of work with information skills Organizing students’ search of information Organizing students’ processing and selection of information Organizing students’ product creation and presentation
 Organizing students’ search of information description, discussion, information transfer, interview, note-taking, questionnaire, studying resources, survey or opinion poll , prioritizing, table-filling, …
Organizing students’ search of information description, discussion, information transfer, interview, note-taking, questionnaire, studying resources, survey or opinion poll , prioritizing, table-filling, …
 Organizing students’ processing and selection of information association, mind-mapping, note-taking, making an outline, summarizing, linking, table-filling, completing, peer-editing, prioritizing, categorizing, discussion, information transfer, paraphrasing, comparing …
Organizing students’ processing and selection of information association, mind-mapping, note-taking, making an outline, summarizing, linking, table-filling, completing, peer-editing, prioritizing, categorizing, discussion, information transfer, paraphrasing, comparing …
 Organizing students’ product creation and presentation Prioritizing, discussion, compilation, materials design, publicizing …
Organizing students’ product creation and presentation Prioritizing, discussion, compilation, materials design, publicizing …
 The indicators of Teacher’s success in organizing students’ work with information The students have found the necessary information and fixed it The students have processed the chosen information and the material is gathered for making the product The product is timely created and presented to some audience
The indicators of Teacher’s success in organizing students’ work with information The students have found the necessary information and fixed it The students have processed the chosen information and the material is gathered for making the product The product is timely created and presented to some audience
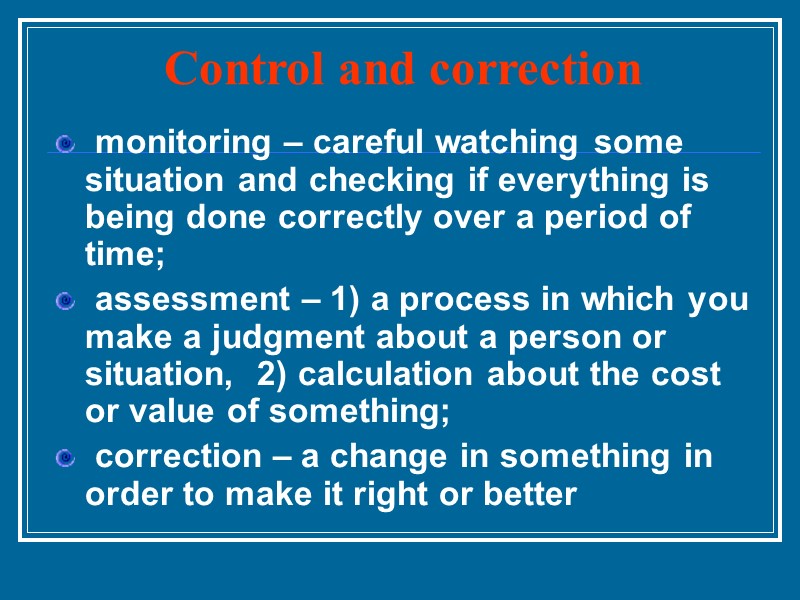
 Control and correction monitoring – careful watching some situation and checking if everything is being done correctly over a period of time; assessment – 1) a process in which you make a judgment about a person or situation, 2) calculation about the cost or value of something; correction – a change in something in order to make it right or better
Control and correction monitoring – careful watching some situation and checking if everything is being done correctly over a period of time; assessment – 1) a process in which you make a judgment about a person or situation, 2) calculation about the cost or value of something; correction – a change in something in order to make it right or better
 Principles of Monitoring continuous scientific purposeful prognostic norm-referencing
Principles of Monitoring continuous scientific purposeful prognostic norm-referencing
 Feedback giving students information about what actions have led to the necessary level of work fulfillment and visa versa
Feedback giving students information about what actions have led to the necessary level of work fulfillment and visa versa
 Formula of effective feedback (T. Russel) 1) give students the opportunity to see what they have done 2) give students the opportunity to see and realize the result of their actions 3) together with your student agree on what must be changed
Formula of effective feedback (T. Russel) 1) give students the opportunity to see what they have done 2) give students the opportunity to see and realize the result of their actions 3) together with your student agree on what must be changed
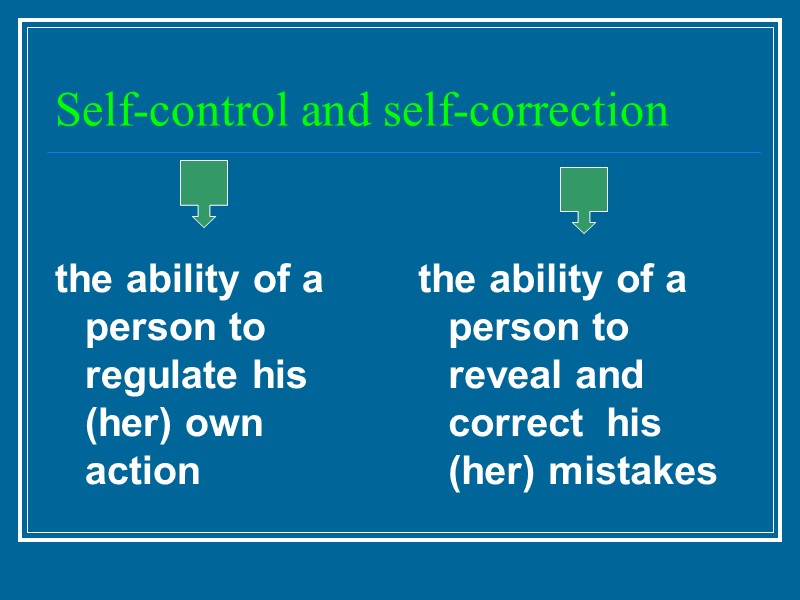
 Self-control and self-correction the ability of a person to regulate his (her) own action the ability of a person to reveal and correct his (her) mistakes
Self-control and self-correction the ability of a person to regulate his (her) own action the ability of a person to reveal and correct his (her) mistakes
 The process of self-control development (M.E. Braigina) to learn to understand and accept the teacher’s control to learn to observe and analyse the peers’ studying activity to learn to observe one’s own studying activity, its analysis, correction and assessment
The process of self-control development (M.E. Braigina) to learn to understand and accept the teacher’s control to learn to observe and analyse the peers’ studying activity to learn to observe one’s own studying activity, its analysis, correction and assessment
 Monitoring and self-correction techniques asking and answering questions table-filling observation interview comparing note-taking substitution reordering correction paraphrasing transformation
Monitoring and self-correction techniques asking and answering questions table-filling observation interview comparing note-taking substitution reordering correction paraphrasing transformation
 Assessment The process of measuring, quantifying, and/or describing aspects related to the attributes covered by the evaluation; the process of gathering information about performance, the measurement of the ability of a person or the quality or success
Assessment The process of measuring, quantifying, and/or describing aspects related to the attributes covered by the evaluation; the process of gathering information about performance, the measurement of the ability of a person or the quality or success
 To provide assessment and self-assessment Comparing Level-determination Note-taking Observation Rating Table-filling
To provide assessment and self-assessment Comparing Level-determination Note-taking Observation Rating Table-filling
 Use of English in Project Work initiating/starting the discussion/conversation/story Let me start with…First/firstly/ first of all…I wanted to talk about …The point is…I mean…Frankly speaking,…I’d like to say… developing the conversation, story Secondly/ then/ after that… Before that,…For instance/ for example… What’s more…/moreover, Actually/in fact…While this is being done we can…Meanwhile
Use of English in Project Work initiating/starting the discussion/conversation/story Let me start with…First/firstly/ first of all…I wanted to talk about …The point is…I mean…Frankly speaking,…I’d like to say… developing the conversation, story Secondly/ then/ after that… Before that,…For instance/ for example… What’s more…/moreover, Actually/in fact…While this is being done we can…Meanwhile
 Correction Aim: to stimulate correction of mistakes in the usage of the English language (grammar, vocabulary, speech, others) by students Stimulating techniques: underlining, shaking head repeating the phrase before the mistake rules revision skills drilling and practicing
Correction Aim: to stimulate correction of mistakes in the usage of the English language (grammar, vocabulary, speech, others) by students Stimulating techniques: underlining, shaking head repeating the phrase before the mistake rules revision skills drilling and practicing
 The indicators of Teacher’s success in using control and correction skills The results of monitoring are fixed in different instruments The self-corrected version of the product is prepared for presentation The students are satisfied with the assessment of the audience and the teacher
The indicators of Teacher’s success in using control and correction skills The results of monitoring are fixed in different instruments The self-corrected version of the product is prepared for presentation The students are satisfied with the assessment of the audience and the teacher
 Reflexive analysis Analysis – a careful examination of some object in order to understand it better through studying its constituents Reflexion – introspection, i.e. the process of deeply thinking about your own thoughts, feelings, qualities, behaviour
Reflexive analysis Analysis – a careful examination of some object in order to understand it better through studying its constituents Reflexion – introspection, i.e. the process of deeply thinking about your own thoughts, feelings, qualities, behaviour
 ORGANIZING REFLEXIVE ANALYSIS SKILLS To organize the process of recollection of main actions in the whole activity To stimulate students’/learners’ analysis of successful and problematic parts of work and determine one’s own progress To make students/learners draw conclusions
ORGANIZING REFLEXIVE ANALYSIS SKILLS To organize the process of recollection of main actions in the whole activity To stimulate students’/learners’ analysis of successful and problematic parts of work and determine one’s own progress To make students/learners draw conclusions
 Organizing the process of recollecting the main actions in the whole activity discussion, individual or group interview, individual or group report, listing, project documents studying, questionnairing, testing, table-filling …
Organizing the process of recollecting the main actions in the whole activity discussion, individual or group interview, individual or group report, listing, project documents studying, questionnairing, testing, table-filling …
 Stimulating students’/learners’ analysis of successful and problematic parts of work and determine one’s own progress individual or group interview, individual or group report, listing, questionnairing, counselling session, ranking, testing, …
Stimulating students’/learners’ analysis of successful and problematic parts of work and determine one’s own progress individual or group interview, individual or group report, listing, questionnairing, counselling session, ranking, testing, …
 Making students draw their own conclusions discussion, predicting, questionnairing, ranking, testing, table-filling …
Making students draw their own conclusions discussion, predicting, questionnairing, ranking, testing, table-filling …
 The indicators of Teacher’s success in organizing reflexive analysis by students of their project work results The students have described the whole process of product creation The students have determined themselves what was done successfully and what not, and why! The students have drawn conclusions for the future
The indicators of Teacher’s success in organizing reflexive analysis by students of their project work results The students have described the whole process of product creation The students have determined themselves what was done successfully and what not, and why! The students have drawn conclusions for the future
 Express your opinion about the lecture 1.What was new? 2.What was useful? 3.What did you know? 4.What don’t you need at all?
Express your opinion about the lecture 1.What was new? 2.What was useful? 3.What did you know? 4.What don’t you need at all?

