f558b4af2d2c5c958d8bec4bafc590a9.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 29

Project Management Dr Raghu Bista, NASC

Projects as… • Projects are one of the principle means by which we change our world. Whether the goal is to link Terai with Kathmandu by shortest highway, tunnel under the English channel, introduce Windows XP, develop driverless car or plan the Olympic games in Beijing, the means to achieve all these tasks remain the same: through project management. • Projects are the basic building blocks of development. Without successful project identification, preparation and implementation, developments plans are no more than wishes (Dennis A. Rondineli (1976), Project Management Quarterly, Vol VII (1), • Projects have also been the primary instruments for grant, credit, loan and technical aid to developing countries by international agencies

Projects as… • Project are the major tool for implementing and achieving the strategic goals of organisations. • Then, What is Project?

General Project Characteristics • Projects are temporary activities with a clear objectives • Projects are building blocks in the design and execution of organizational strategies • Projects are responsible for the newest and most improved products, services and organizational processes • Projects need to be completed within constraints of technical, cost, and schedule requirements • Projects are terminated upon successful completion of performance objectives.
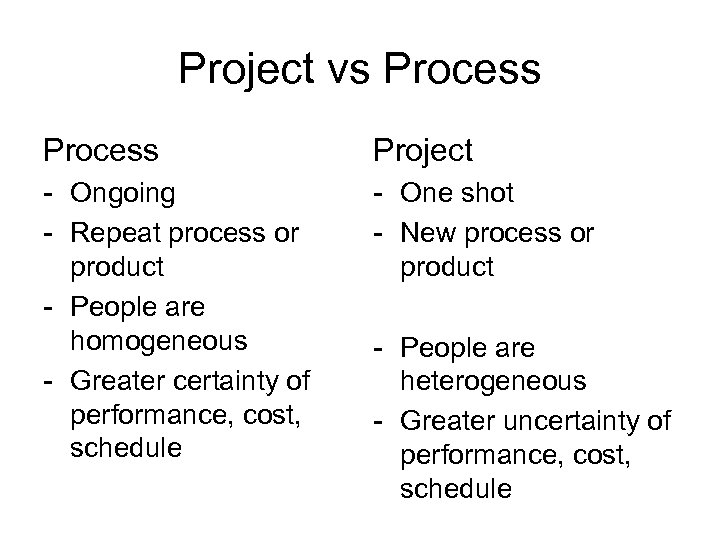
Project vs Process Project - Ongoing - Repeat process or product - People are homogeneous - Greater certainty of performance, cost, schedule - One shot - New process or product - People are heterogeneous - Greater uncertainty of performance, cost, schedule
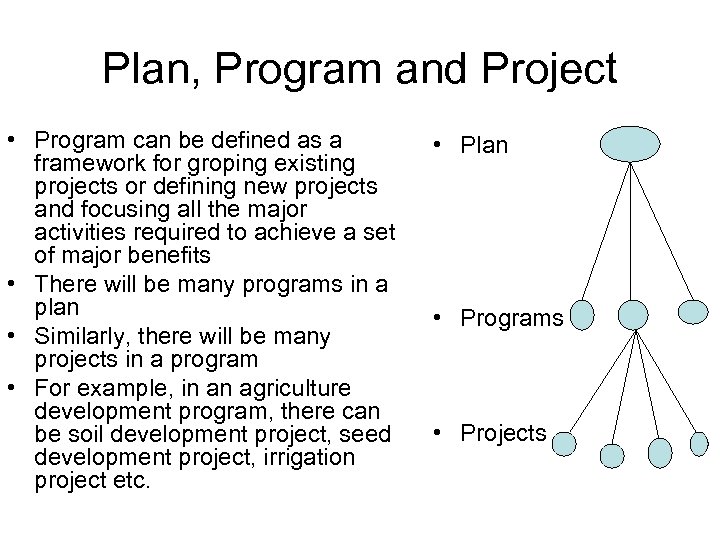
Plan, Program and Project • Program can be defined as a framework for groping existing projects or defining new projects and focusing all the major activities required to achieve a set of major benefits • There will be many programs in a plan • Similarly, there will be many projects in a program • For example, in an agriculture development program, there can be soil development project, seed development project, irrigation project etc. • Plan • Programs • Projects
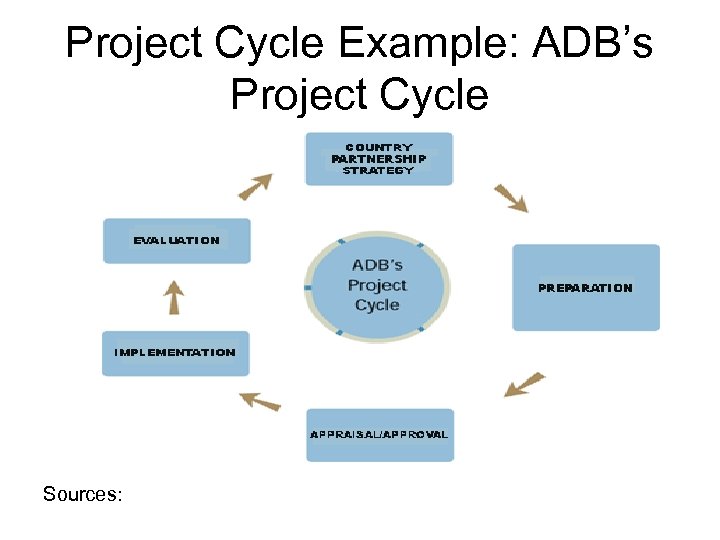
Project Cycle Example: ADB’s Project Cycle Sources:

Project and Project management • A project is a set of activities with specific objectives to be completed within time and budget and simply saying project management is the management of projects

Project management • In project every things need to be done within time and budget • Management has been defined as getting results through people • So project management is achieving successful project completion with the resources available, and the resource being time, money, materials and people.

Importance of Project Management • Project management has been a standard way for existence and progress of the organizations. Global competition, pressure of low cost, short product life cycle, fast changing customer expectations are the reasons for the organizations to adopt project management.

Project Management • • • Project studied and desiged Plan prepared Choice of project organisation Selection of project manager and assigning responsibilities Project scope finalization, Preparing project schedule and budget Hiring consultant to support the team Managing procurement functions, starting activities, and delivering outputs Monitoring and controlling Updating plan as per required Reporting

Project Manager • After completing all the paper work, a project is forwarded for implementation. So, the first task that is to give responsibility to a single person for planning implementing and completing the project. • The PM can be chosen and installed as soon as the project is selected for funding or at any earlier point that seems desirable to senior management. (Sources: J R Meredith, S. J. Mantel, 2006, project management: managerial approach, John Wiley and Sons)

Project Manager cont. . • The PM’s first set of tasks is typically to prepare a preliminary budget and schedule, to help select people to serve on the project team, to ensure that any suppliers required early in the project life are available when needed, to take care of routine details necessary to get the project moving. • As people are added to the project, plans and schedules are refined. Mechanism are developed to facilitate communication between the PM and top management, functional areas and the clients.

Functional vs Project Manager • Functional heads are usually specialist in the areas they manage. As functional managers, they are administratively responsible for deciding how something will be done, who will do it, and what resources will be devoted to accomplish the task. • The PM, new or experienced, must oversee many functional areas, each with its own specialists. Therefore, what is required is an ability to put many pieces of task together to form a coherent whole-that is , the project manager should be more skilled at synthesis. The functional manager uses the analytic approach and the PM uses the system approaches. • The functional manager is a direct, technical supervisor. The project manager is a facilitator and generalist. PM is responsible for organizing, staffing, budgeting, directing, planning, and controlling the project. In other words, The PM manages it, but the FM may affect the choice of technologies to be used by the project and the specific individuals who will do the work. • Above all a good project manager is one who can get the job done

Special Functions of Project Manager • • Planning and scheduling project activities Acquiring and motivating personnel Acquiring adequate resources Executing project as per schedule Monitoring and controlling progress Managing conflicts Reporting
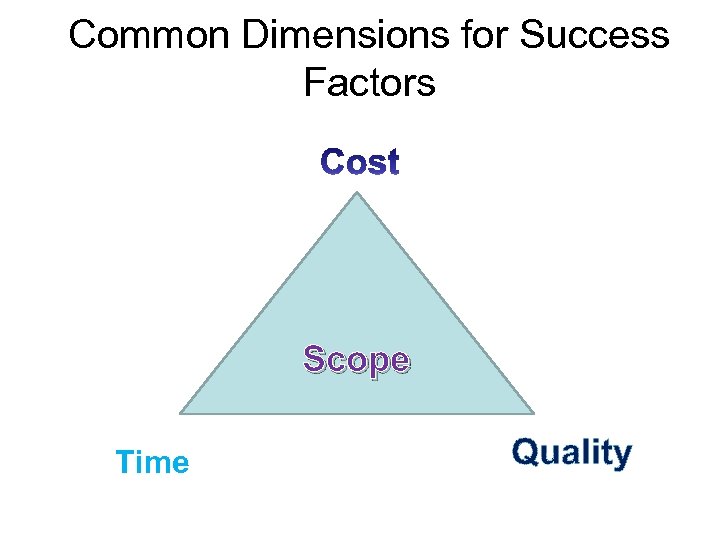
Common Dimensions for Success Factors Scope Time Quality

Cost of not Completing in time, cost, quality

Managing schedule - Prepare time schedule - Give extra care to critical activities in order to complete them in scheduled time. - Making priorities in resource allocation to critical activities in case of resource constraints - Regular monitoring and reporting - Ensuring critical activities get done on time

Schedule Awareness • The simple way to create schedule awareness is by displaying the progress achievements and target dates at visible place to remind project team about project activity deadlines and project completion time

Resource Planning • To complete project in time with minimum resource, careful planning of resource is necessary to identify the required resources • Estimating resource as per schedule • Finalize sources of supply • Acquiring resource as per required

Procurement and material Management • Effective procurement and material management are central to project success. Timely on site delivery of materials to suit the construction schedule greatly avoid time overruns. Similarly close control on procurement cost is necessary for controlling the overall cost. • Important aspects are: • make material requirement plan • set stock requirement of material • make procurement functions matching requirement plan

Managing Quality • We hear many news of under quality of our projects. If projects are not completed within desired/or planned quality, we can not assure that project will generate heavier benefits than costs. So managing quality means to assure project deliverable as per specification.

Managing Quality Cont… • • Are Inputs as per requirement? Are labour skilled as needed? Is process as per standard? Does project output as per specification?

Managing Budget - Assuring timely budget available - Making effective and efficient use of budget

Project Monitoring and Control • Project monitoring is observing or checking on project activities to identify the current status of the project, identifying deviation of the project cost, schedule and quality with the plan and identifying potential problems. A project monitoring system involves determining what data to collect; how, when, and who will collect the data, analysis of the data; and reporting current progress

Progress Monitoring and Control - Tracking actual progress monitoring - Comparing actual progress with the targets - Analyzing deviations - Taking corrective actions - Reporting progress to upper level

Project Monitoring: What data are collected? • What is the current status of the project in terms of schedule and costs? • Whether the inputs in the project are well utilized? • How much will it cost to complete the project? • When will the project be completed? • Are there potential problems that need to be addressed now? • What, who and where are the causes for cost and schedule overrun? • What did we get for the Dollars spent? • If there is cost overrun midway in the project, can we forecast the overrun at completion?

Controlling and Moving Ahead • Once we detect significant deviations from the project plan, it becomes necessary to engage in some form of corrective action to minimize or remove the deviations. Updating plan, speeding up activities, maintaining quality and moving ahead to complete project deliverables are regularly practiced.

f558b4af2d2c5c958d8bec4bafc590a9.ppt