e897afe08754fed938483865ad136187.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 43
 Project Management 1. 2 INS 509 Module Leader: Jitu Davda. Email: jitu@davda. org. uk
Project Management 1. 2 INS 509 Module Leader: Jitu Davda. Email: jitu@davda. org. uk
 Project Management 1. 2 INS 509 Revision Lecture
Project Management 1. 2 INS 509 Revision Lecture
 Project Management 1. 2 INS 509 n This revision lecture is about the essence of; Project Life Cycles ¨ Project Time Management ¨ n n Estimate Schedule Project Risk ¨ Project Quality ¨ Project Failure ¨ …
Project Management 1. 2 INS 509 n This revision lecture is about the essence of; Project Life Cycles ¨ Project Time Management ¨ n n Estimate Schedule Project Risk ¨ Project Quality ¨ Project Failure ¨ …
 Project Management 1. 2 INS 509 Project Management Life Cycle 7. 15
Project Management 1. 2 INS 509 Project Management Life Cycle 7. 15
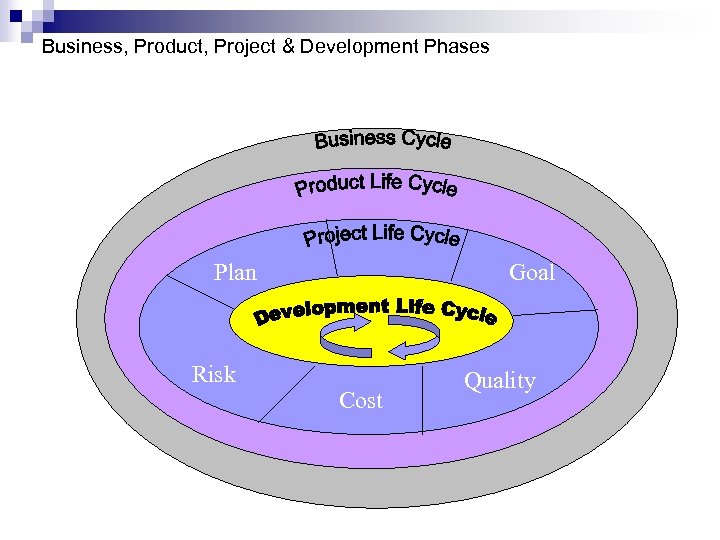 Business, Product, Project & Development Phases Plan Risk Goal Cost Quality
Business, Product, Project & Development Phases Plan Risk Goal Cost Quality
 Project Phases and the Project Life Cycle n A project life cycle is a collection of project phases that defines: What work will be performed in each phase. ¨ What deliverables will be produced and when. ¨ Who is involved in each phase. ¨ How management will control and approve work produced in each phase. ¨ n A deliverable is a product or service produced or provided as part of a project.
Project Phases and the Project Life Cycle n A project life cycle is a collection of project phases that defines: What work will be performed in each phase. ¨ What deliverables will be produced and when. ¨ Who is involved in each phase. ¨ How management will control and approve work produced in each phase. ¨ n A deliverable is a product or service produced or provided as part of a project.
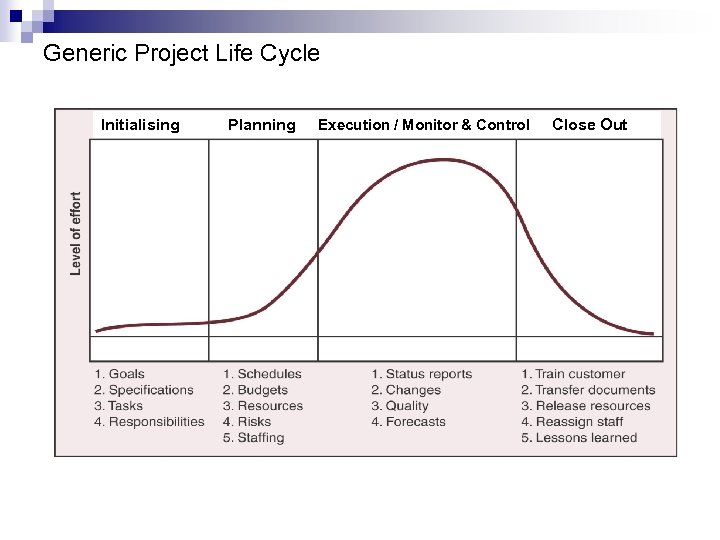 Generic Project Life Cycle Initialising Planning Execution / Monitor & Control Close Out
Generic Project Life Cycle Initialising Planning Execution / Monitor & Control Close Out
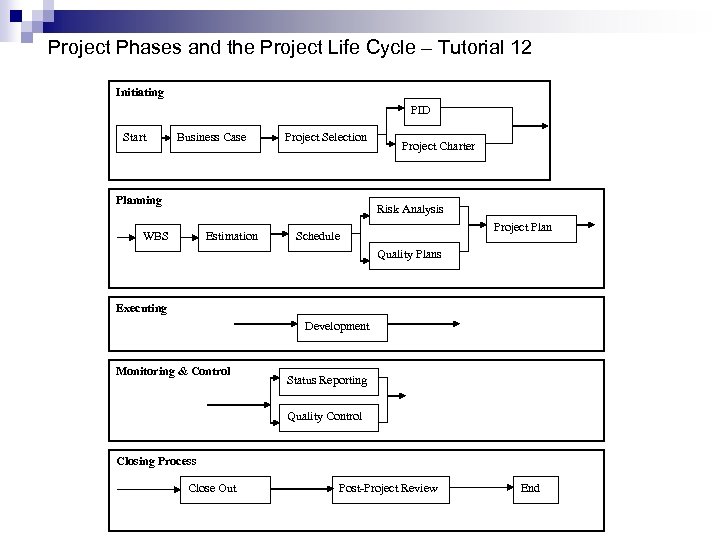 Project Phases and the Project Life Cycle – Tutorial 12 Initiating PID Start Business Case Project Selection Planning Project Charter Risk Analysis WBS Estimation Project Plan Schedule Quality Plans Executing Development Monitoring & Control Status Reporting Quality Control Closing Process Close Out Post-Project Review End
Project Phases and the Project Life Cycle – Tutorial 12 Initiating PID Start Business Case Project Selection Planning Project Charter Risk Analysis WBS Estimation Project Plan Schedule Quality Plans Executing Development Monitoring & Control Status Reporting Quality Control Closing Process Close Out Post-Project Review End
 Project Management 1. 2 INS 509 Time Management Duration Estimate
Project Management 1. 2 INS 509 Time Management Duration Estimate
 Activity Duration Estimating n Duration includes the actual amount of time spent working on an activity plus elapsed time. n n For example, even though it might take one workweek or five workdays to do the actual work, the duration estimate might be two weeks to allow extra time needed to obtain outside information or to allow for resource availability. Effort is the number of workdays or work hours required to complete a task. n A duration estimate of one day could be based on eight hours of work or eighty hours of work. n Duration relates to the time estimate, not the effort estimate. n Effort does not normally equal duration. …
Activity Duration Estimating n Duration includes the actual amount of time spent working on an activity plus elapsed time. n n For example, even though it might take one workweek or five workdays to do the actual work, the duration estimate might be two weeks to allow extra time needed to obtain outside information or to allow for resource availability. Effort is the number of workdays or work hours required to complete a task. n A duration estimate of one day could be based on eight hours of work or eighty hours of work. n Duration relates to the time estimate, not the effort estimate. n Effort does not normally equal duration. …
 Estimation. “Predictions are hard, especially about the future”, Yogi Berra Estimations are difficult for IT projects because; Software projects tend be one-off solutions. ü Initial estimates done long before detailed requirements. ü Not done by professional estimators. ü Compare to construction industry; Known and reliable metrics (e. g. bricklaying). ü Estimates against a detailed specification. ü Done by an estimator – their sole job. ü …
Estimation. “Predictions are hard, especially about the future”, Yogi Berra Estimations are difficult for IT projects because; Software projects tend be one-off solutions. ü Initial estimates done long before detailed requirements. ü Not done by professional estimators. ü Compare to construction industry; Known and reliable metrics (e. g. bricklaying). ü Estimates against a detailed specification. ü Done by an estimator – their sole job. ü …
 Estimation. Main Estimation methods; ü Direct Estimation ü ü ü Top-down. Bottom-up. Analogy. …
Estimation. Main Estimation methods; ü Direct Estimation ü ü ü Top-down. Bottom-up. Analogy. …
 Project Management 1. 2 INS 509 Time Management Scheduling
Project Management 1. 2 INS 509 Time Management Scheduling
 Project Schedule n Schedule development uses the results of all the preceding project time management processes to determine the start and end dates of project activities and of the entire project. n The resulting project schedule is often shown on a Gantt chart. n This will produce the schedule to show; The duration of the project. ¨ The critical activities of the project. ¨ The major milestones for delivery. ¨ …
Project Schedule n Schedule development uses the results of all the preceding project time management processes to determine the start and end dates of project activities and of the entire project. n The resulting project schedule is often shown on a Gantt chart. n This will produce the schedule to show; The duration of the project. ¨ The critical activities of the project. ¨ The major milestones for delivery. ¨ …
 Types of Dependencies n Mandatory dependencies are inherent in the nature of the work being performed on a project. ¨ n Discretionary dependencies are defined by the project team. ¨ n Cannot build a roof before the walls. Interview all the residents before selecting resource teams. External dependencies involve relationships between project and non-project activities. ¨ Wait for local authority approval before starting actual work. …
Types of Dependencies n Mandatory dependencies are inherent in the nature of the work being performed on a project. ¨ n Discretionary dependencies are defined by the project team. ¨ n Cannot build a roof before the walls. Interview all the residents before selecting resource teams. External dependencies involve relationships between project and non-project activities. ¨ Wait for local authority approval before starting actual work. …
 Project Management 1. 2 INS 509 Critical Path Method …
Project Management 1. 2 INS 509 Critical Path Method …
 What Does the Critical Path Really Mean? n The critical path shows the shortest time in which a project can be completed. n If one or more of the activities on the critical path takes longer than planned, the whole project schedule will slip unless the project manager takes corrective action. n It is the longest path in the network diagram. n It is also common for project stakeholders to want to shorten project schedule estimates, so you need to know what tasks are on the critical path. …
What Does the Critical Path Really Mean? n The critical path shows the shortest time in which a project can be completed. n If one or more of the activities on the critical path takes longer than planned, the whole project schedule will slip unless the project manager takes corrective action. n It is the longest path in the network diagram. n It is also common for project stakeholders to want to shorten project schedule estimates, so you need to know what tasks are on the critical path. …
 Critical Path Method ü The process for determining and optimizing the critical path. ü Non-CP tasks can start earlier or later without impacting completion date. ü Critical Path may change to another as you shorten the current. …
Critical Path Method ü The process for determining and optimizing the critical path. ü Non-CP tasks can start earlier or later without impacting completion date. ü Critical Path may change to another as you shorten the current. …
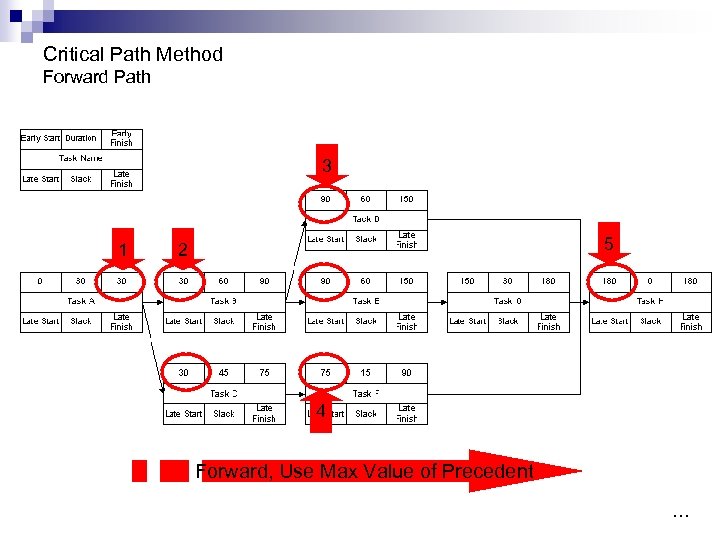 Critical Path Method Forward Path 3 1 5 2 4 Forward, Use Max Value of Precedent …
Critical Path Method Forward Path 3 1 5 2 4 Forward, Use Max Value of Precedent …
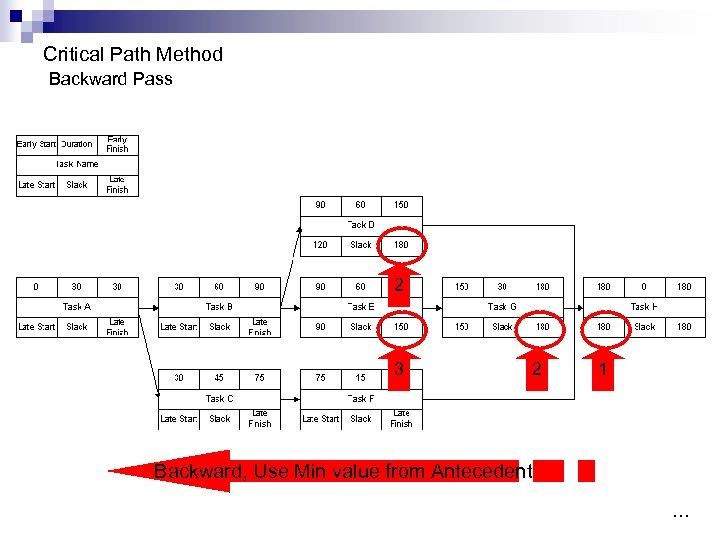 Critical Path Method Backward Pass 2 3 2 1 Backward, Use Min value from Antecedent …
Critical Path Method Backward Pass 2 3 2 1 Backward, Use Min value from Antecedent …
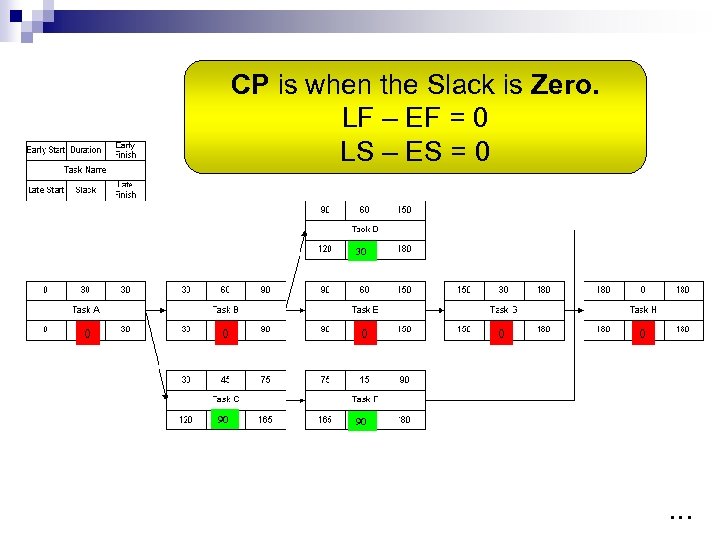 CP is when the Slack is Zero. LF – EF = 0 LS – ES = 0 30 0 90 …
CP is when the Slack is Zero. LF – EF = 0 LS – ES = 0 30 0 90 …
 Critical Path Summary; ü ü ü May be several critical paths. Critical path can change. Enables project manager to focus to important tasks. It is the shortest time a project can finish. It is the longest path in the network diagram. …
Critical Path Summary; ü ü ü May be several critical paths. Critical path can change. Enables project manager to focus to important tasks. It is the shortest time a project can finish. It is the longest path in the network diagram. …
 Project Management 2 Project Risk …
Project Management 2 Project Risk …
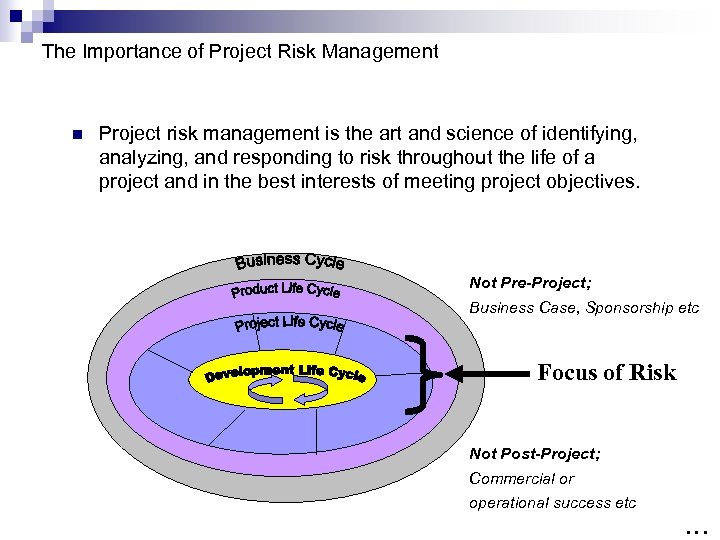 The Importance of Project Risk Management n Project risk management is the art and science of identifying, analyzing, and responding to risk throughout the life of a project and in the best interests of meeting project objectives. Not Pre-Project; Business Case, Sponsorship etc Focus of Risk Not Post-Project; Commercial or operational success etc …
The Importance of Project Risk Management n Project risk management is the art and science of identifying, analyzing, and responding to risk throughout the life of a project and in the best interests of meeting project objectives. Not Pre-Project; Business Case, Sponsorship etc Focus of Risk Not Post-Project; Commercial or operational success etc …
 Definitions of Risk n A dictionary definition of risk is “the possibility of loss or injury. ” Does not apply well to Project Management. n We have both Negative and Positive risks n Negative risk involves understanding potential problems that might occur in the project and how they might impede project success. n Negative risk is about being Proactive rather than Reactive. n Positive risks are risks that result in good things happening; sometimes called opportunities. n Goal of Risk Management is to avoid a crisis. …
Definitions of Risk n A dictionary definition of risk is “the possibility of loss or injury. ” Does not apply well to Project Management. n We have both Negative and Positive risks n Negative risk involves understanding potential problems that might occur in the project and how they might impede project success. n Negative risk is about being Proactive rather than Reactive. n Positive risks are risks that result in good things happening; sometimes called opportunities. n Goal of Risk Management is to avoid a crisis. …
 Risk Profile Risk is characterized by; ü ü ü Problem. ü A risk has materialised. Uncertainty. ü The probability of happening; (0 < x <1) Loss. ü Money, Time, Reputation, Life. Risk Exposure = Uncertainty x Loss. Risk Exposure = Probability x Impact. …
Risk Profile Risk is characterized by; ü ü ü Problem. ü A risk has materialised. Uncertainty. ü The probability of happening; (0 < x <1) Loss. ü Money, Time, Reputation, Life. Risk Exposure = Uncertainty x Loss. Risk Exposure = Probability x Impact. …
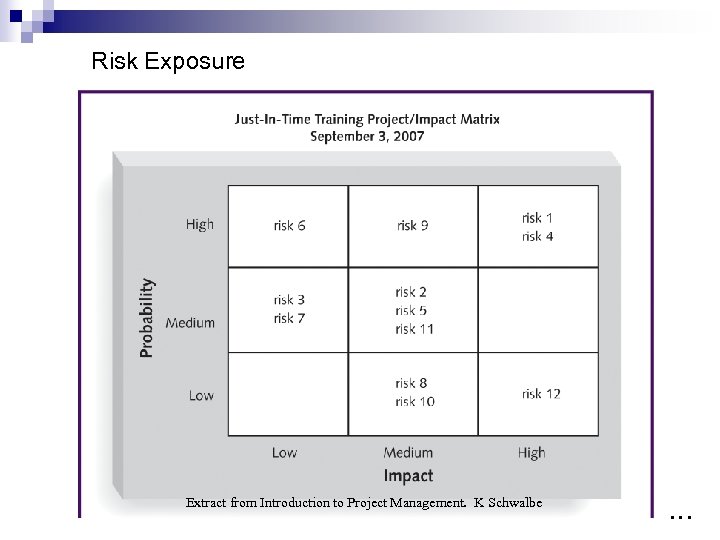 Risk Exposure Extract from Introduction to Project Management. K Schwalbe …
Risk Exposure Extract from Introduction to Project Management. K Schwalbe …
 Risk Management Planning n The main output of risk management planning is a risk management plan—a plan that documents the procedures for managing risk throughout a project. n The level of detail will vary with the needs of the project. n The Plan will contain; n Identification n Analysis n Prioritisation n Planning n Resolution n Control …
Risk Management Planning n The main output of risk management planning is a risk management plan—a plan that documents the procedures for managing risk throughout a project. n The level of detail will vary with the needs of the project. n The Plan will contain; n Identification n Analysis n Prioritisation n Planning n Resolution n Control …
 Project Risk Assessment & Control Risk is about Assessment and Control of a problem that has not happened yet! Risk Identification Risk Assessment Risk Analysis Risk Prioritisation Risk Management Risk Planning Risk Control Risk Resolution Risk Monitoring “Software Risk Management”, Boehm, 1989 …
Project Risk Assessment & Control Risk is about Assessment and Control of a problem that has not happened yet! Risk Identification Risk Assessment Risk Analysis Risk Prioritisation Risk Management Risk Planning Risk Control Risk Resolution Risk Monitoring “Software Risk Management”, Boehm, 1989 …
 Risk Identification n Important point is to IDENTIFY risks that affect the project. NOT any incident or event that COULD or MIGHT happen. n Identify risks of going away on an exotic holiday for 3 weeks? n Valid risks identification could be: n n n Risk identification is not about: n n Vaccinations, water purification, extra money, insect repellent, sun exposure, language, travel insurance etc. Car breaking down to airport, baggage lost, forgetting something, plane delays etc. Examine it under the Risk Exposure matrix. ¨ ¨ ¨ This will show impact and probability. Probability of getting a stomach bug from water is high – take action. A taxi breakdown to airport is low – live with it. …
Risk Identification n Important point is to IDENTIFY risks that affect the project. NOT any incident or event that COULD or MIGHT happen. n Identify risks of going away on an exotic holiday for 3 weeks? n Valid risks identification could be: n n n Risk identification is not about: n n Vaccinations, water purification, extra money, insect repellent, sun exposure, language, travel insurance etc. Car breaking down to airport, baggage lost, forgetting something, plane delays etc. Examine it under the Risk Exposure matrix. ¨ ¨ ¨ This will show impact and probability. Probability of getting a stomach bug from water is high – take action. A taxi breakdown to airport is low – live with it. …
 Risk Resolution Risk is managed by; ü Acceptance. No feasible counter measure or too expensive. ü e. g. critical staff, equipment, vendor, promise (keep vigilance). ü ü Avoidance. Prevent from happening. Take positive action. ü e. g. look for alternate vendors (install alarm, move house). ü ü Mitigation. Reduce the impact if it occurs. Plan for contingency. ü e. g, Monitoring, continuing assessment (make copies of valuable documents). ü ü Transfer. Passing the impact to another party. ü Outsourcing (insurance policy). ü …
Risk Resolution Risk is managed by; ü Acceptance. No feasible counter measure or too expensive. ü e. g. critical staff, equipment, vendor, promise (keep vigilance). ü ü Avoidance. Prevent from happening. Take positive action. ü e. g. look for alternate vendors (install alarm, move house). ü ü Mitigation. Reduce the impact if it occurs. Plan for contingency. ü e. g, Monitoring, continuing assessment (make copies of valuable documents). ü ü Transfer. Passing the impact to another party. ü Outsourcing (insurance policy). ü …
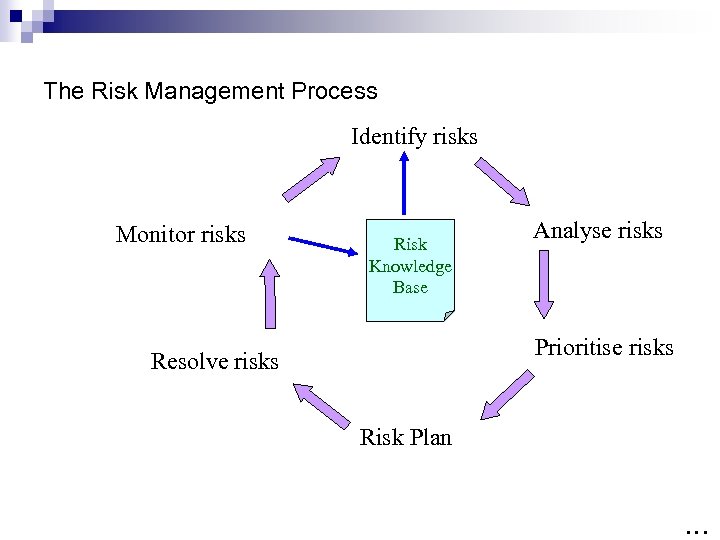 The Risk Management Process Identify risks Monitor risks Risk Knowledge Base Analyse risks Prioritise risks Resolve risks Risk Plan …
The Risk Management Process Identify risks Monitor risks Risk Knowledge Base Analyse risks Prioritise risks Resolve risks Risk Plan …
 Project Management 1. 2 INS 509 Project Quality
Project Management 1. 2 INS 509 Project Quality
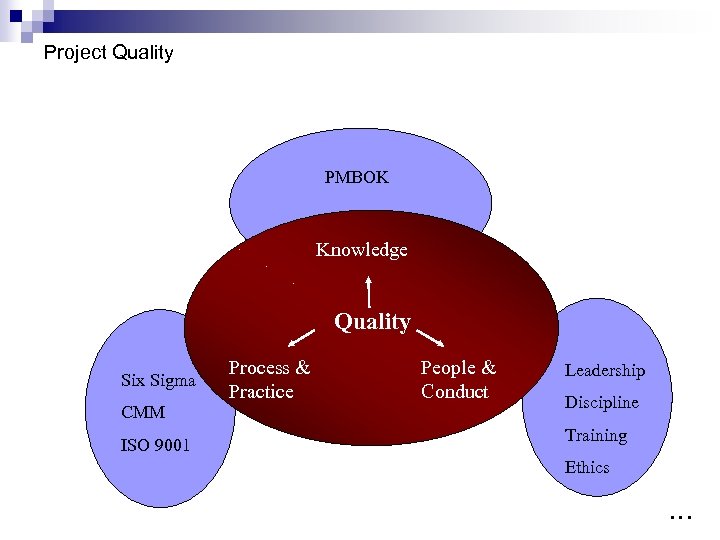 Project Quality PMBOK Knowledge Quality Six Sigma CMM ISO 9001 Process & Practice People & Conduct Leadership Discipline Training Ethics …
Project Quality PMBOK Knowledge Quality Six Sigma CMM ISO 9001 Process & Practice People & Conduct Leadership Discipline Training Ethics …
 What Is Quality? n n n A hammer is defined as an implement with a “metal head and a wooden handle”; The International Organization for Standardization (ISO) defines quality as Would a hammer with a ‘lead’ head and a ‘balsa’ handle features and characteristics of a “The totality of thedo? ? product or service that bear on its ability to satisfy specified or implied needs” (ISO 8042: 1986). Other experts define quality based on: ¨ Conformance to requirements: The project’s processes and products meet written specifications. ¨ Fitness for use: A product can be used as it was intended. …
What Is Quality? n n n A hammer is defined as an implement with a “metal head and a wooden handle”; The International Organization for Standardization (ISO) defines quality as Would a hammer with a ‘lead’ head and a ‘balsa’ handle features and characteristics of a “The totality of thedo? ? product or service that bear on its ability to satisfy specified or implied needs” (ISO 8042: 1986). Other experts define quality based on: ¨ Conformance to requirements: The project’s processes and products meet written specifications. ¨ Fitness for use: A product can be used as it was intended. …
 Quality is built in? n Influenced by the quality of process. n Determined by people committed to quality. n Quality is an inbuilt; ¨ ¨ Characteristic ¨ n Attribute ‘In the very fabric’ Quality cannot be ‘added’, ‘bought’ or ‘thought about afterwards’. …
Quality is built in? n Influenced by the quality of process. n Determined by people committed to quality. n Quality is an inbuilt; ¨ ¨ Characteristic ¨ n Attribute ‘In the very fabric’ Quality cannot be ‘added’, ‘bought’ or ‘thought about afterwards’. …
 What Is Project Quality Management? n n Project quality management ensures that the project will satisfy the needs for which it was undertaken. Processes include: ¨ Quality planning: Identifying which quality standards are relevant to the project and how to satisfy them. ¨ Quality assurance: Periodically evaluating overall project performance to ensure the project will satisfy the relevant quality standards. ¨ Quality control: Monitoring specific project results to ensure that they comply with the relevant quality standards. …
What Is Project Quality Management? n n Project quality management ensures that the project will satisfy the needs for which it was undertaken. Processes include: ¨ Quality planning: Identifying which quality standards are relevant to the project and how to satisfy them. ¨ Quality assurance: Periodically evaluating overall project performance to ensure the project will satisfy the relevant quality standards. ¨ Quality control: Monitoring specific project results to ensure that they comply with the relevant quality standards. …
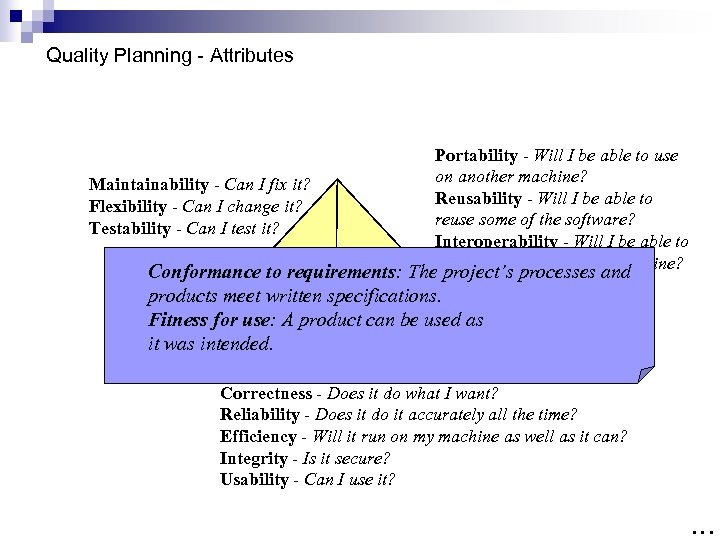 Quality Planning - Attributes Maintainability - Can I fix it? Flexibility - Can I change it? Testability - Can I test it? Portability - Will I be able to use on another machine? Reusability - Will I be able to reuse some of the software? Interoperability - Will I be able to interface it with another machine? Conformance. Revision Transition project’s processes and to requirements: The products meet written specifications. Fitness for use: A product can be used as it was intended. Operations Correctness - Does it do what I want? Reliability - Does it do it accurately all the time? Efficiency - Will it run on my machine as well as it can? Integrity - Is it secure? Usability - Can I use it? …
Quality Planning - Attributes Maintainability - Can I fix it? Flexibility - Can I change it? Testability - Can I test it? Portability - Will I be able to use on another machine? Reusability - Will I be able to reuse some of the software? Interoperability - Will I be able to interface it with another machine? Conformance. Revision Transition project’s processes and to requirements: The products meet written specifications. Fitness for use: A product can be used as it was intended. Operations Correctness - Does it do what I want? Reliability - Does it do it accurately all the time? Efficiency - Will it run on my machine as well as it can? Integrity - Is it secure? Usability - Can I use it? …
 Quality Control & Assurance Control n n Validation is are we building the right product? Verification is Are we building the product right? Assurance n Quality assurance includes all the activities related to satisfying the relevant quality standards for a project. n Another goal of quality assurance is continuous quality improvement. n A quality audit is a structured review of specific quality management activities that help identify lessons learned that could improve performance on current or future projects. …
Quality Control & Assurance Control n n Validation is are we building the right product? Verification is Are we building the product right? Assurance n Quality assurance includes all the activities related to satisfying the relevant quality standards for a project. n Another goal of quality assurance is continuous quality improvement. n A quality audit is a structured review of specific quality management activities that help identify lessons learned that could improve performance on current or future projects. …
 Project Management 1 Project Failures
Project Management 1 Project Failures
 Project Management. Avoiding Failure Important to Understand Failure at; Project Management Level Organisation Level …
Project Management. Avoiding Failure Important to Understand Failure at; Project Management Level Organisation Level …
 Project Management. Avoiding Failure The six ü deadly sins in project failure? Half-baked ideas. ü ü No, total backing. Yes, not experienced for global scope. No monitoring of vital signs. ü ü PM/ ORG Under-skilled project managers. ü ü Yes, too aggressive. Ineffective sponsorship. ü ü Yes, management convinced by industry hype. Dictated deadlines. ü ü ORG PM Yes, hoping users will adopt & functionality will improve. Failing to use a project methodology. ü No, core principles were used. READ THE CASE STUDIES FROM TUTORIAL 10 …
Project Management. Avoiding Failure The six ü deadly sins in project failure? Half-baked ideas. ü ü No, total backing. Yes, not experienced for global scope. No monitoring of vital signs. ü ü PM/ ORG Under-skilled project managers. ü ü Yes, too aggressive. Ineffective sponsorship. ü ü Yes, management convinced by industry hype. Dictated deadlines. ü ü ORG PM Yes, hoping users will adopt & functionality will improve. Failing to use a project methodology. ü No, core principles were used. READ THE CASE STUDIES FROM TUTORIAL 10 …
 Project Management 1. 2 INS 509 THE END Questions ? ? Good Luck with Revision and Exam.
Project Management 1. 2 INS 509 THE END Questions ? ? Good Luck with Revision and Exam.


