a2d866752374b98cb104f92fea03bad9.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 34
 Project: COMMUNICATION IN FOREIGN LANGUAGES Implementing innovative approaches to foreign language teaching through foreign teachers inclusion into the school curriculum FOREIGN TEACHERS’ MEETING Katja Pavlič Škerjanc, 9/12 - 2008 Operacijo delno financira Evropska unija iz Evropskega socialnega sklada ter Ministrstvo za šolstvo in šport. Operacija se izvaja v okviru Operativnega programa razvoja človeških virov v obdobju 2007 -2013, razvojne prioritete: Razvoj človeških virov in vseživljenjsko učenje; prednostne usmeritve: Izboljšanje kakovosti in učinkovitosti sistemov izobraževanja in usposabljanja.
Project: COMMUNICATION IN FOREIGN LANGUAGES Implementing innovative approaches to foreign language teaching through foreign teachers inclusion into the school curriculum FOREIGN TEACHERS’ MEETING Katja Pavlič Škerjanc, 9/12 - 2008 Operacijo delno financira Evropska unija iz Evropskega socialnega sklada ter Ministrstvo za šolstvo in šport. Operacija se izvaja v okviru Operativnega programa razvoja človeških virov v obdobju 2007 -2013, razvojne prioritete: Razvoj človeških virov in vseživljenjsko učenje; prednostne usmeritve: Izboljšanje kakovosti in učinkovitosti sistemov izobraževanja in usposabljanja.
 FOREIGN TEACHERS (of foreign languages) IN SLOVENE SCHOOLS Seeking employment: Whom to turn to? Teaching jobs? • CMEPIUS (= Centre of the Republic • Comenius language of Slovenia for Mobility and European assistants (European funding) Educational and Training programmes) • Ministry of Education and Sport, International Cooperation and European Affairs Service (bilateral in multilateral co-operation: Bronka Straus) • DSD teachers (national funding) • Austrian FL teachers (national funding) • The National Education • Foreign FL teachers in Institute, Centre for Development and European classes (national Research, Katja Pavlič Škerjanc funding) • Foreign FL teachers (European funding - ESF)
FOREIGN TEACHERS (of foreign languages) IN SLOVENE SCHOOLS Seeking employment: Whom to turn to? Teaching jobs? • CMEPIUS (= Centre of the Republic • Comenius language of Slovenia for Mobility and European assistants (European funding) Educational and Training programmes) • Ministry of Education and Sport, International Cooperation and European Affairs Service (bilateral in multilateral co-operation: Bronka Straus) • DSD teachers (national funding) • Austrian FL teachers (national funding) • The National Education • Foreign FL teachers in Institute, Centre for Development and European classes (national Research, Katja Pavlič Škerjanc funding) • Foreign FL teachers (European funding - ESF)
 ACCESS TO ELECTRONIC INFORMATION ZAVOD REPUBLIKE SLOVENIJE ZA ŠOLSTVO (The National Education Institute) http: //www. zrss. si/ Pogosto obiskane strani Tuji učitelji pri pouku tujega jezika http: //www. zrss. si/Default. asp? a=1&id=908
ACCESS TO ELECTRONIC INFORMATION ZAVOD REPUBLIKE SLOVENIJE ZA ŠOLSTVO (The National Education Institute) http: //www. zrss. si/ Pogosto obiskane strani Tuji učitelji pri pouku tujega jezika http: //www. zrss. si/Default. asp? a=1&id=908
 FOREIGN TEACHERS OF FOREIGN LANGUAGES • from a national programme run by the Ministry of Education and Sport (“Foreign language teachers in Slovenia”)… • … to a curriculum development project run by the National Education Institute and funded mostly from the European Structural Funds (Euopean Social Fund, ESF) (“Communication in Foreign Languages - Implementing innovative approaches to foreign language teaching through foreign teachers inclusion into the school curriculum”) ► KEY DIFFERENCES
FOREIGN TEACHERS OF FOREIGN LANGUAGES • from a national programme run by the Ministry of Education and Sport (“Foreign language teachers in Slovenia”)… • … to a curriculum development project run by the National Education Institute and funded mostly from the European Structural Funds (Euopean Social Fund, ESF) (“Communication in Foreign Languages - Implementing innovative approaches to foreign language teaching through foreign teachers inclusion into the school curriculum”) ► KEY DIFFERENCES
 KEY CONCEPTS School development – Pilot projects – Dissemination of results • Intercultural (communicative) competence • Authenticity (of learning goals and objectives, learning situations, assessment) • Language across the curriculum (contentbased language learning, discipline literacy development) • School curriculum (planning – implementation – monitoring – evaluation- dissemination) • Integrative curriculum (cross-curricular connections – intra- and interdisciplinary cooperation) • Cooperative teaching – Team teaching • Project approach (to teaching and learning)
KEY CONCEPTS School development – Pilot projects – Dissemination of results • Intercultural (communicative) competence • Authenticity (of learning goals and objectives, learning situations, assessment) • Language across the curriculum (contentbased language learning, discipline literacy development) • School curriculum (planning – implementation – monitoring – evaluation- dissemination) • Integrative curriculum (cross-curricular connections – intra- and interdisciplinary cooperation) • Cooperative teaching – Team teaching • Project approach (to teaching and learning)
 DEVELOPMENT - INNOVATION schools SCHOOL PROJECTS OPERATIONAL LEVEL National Education Institute TACTICAL LEVEL Ministry of Education and Sport STRATEGIC LEVEL
DEVELOPMENT - INNOVATION schools SCHOOL PROJECTS OPERATIONAL LEVEL National Education Institute TACTICAL LEVEL Ministry of Education and Sport STRATEGIC LEVEL
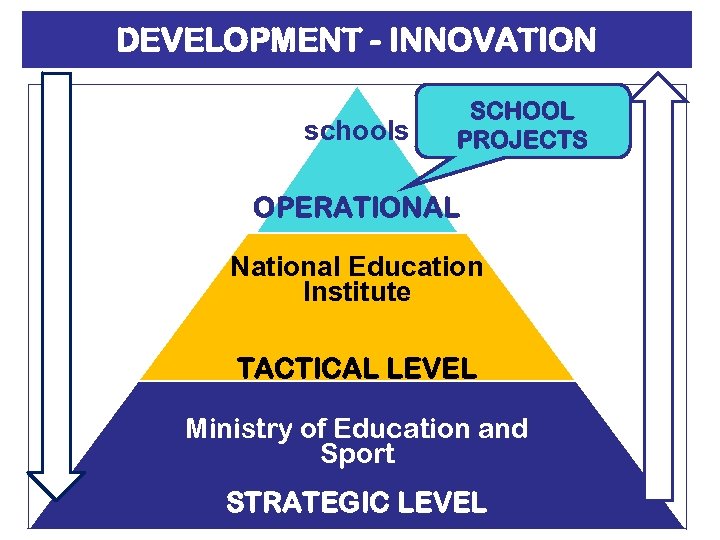
 STRATEGIC LEVEL → concepts (“white books), development strategies (strategic papers) National Education Institute → frameworks and guidelines Ministry of Education and Sport TACTICAL LEVEL Schools OPERATIONAL LEVEL → monitored and evaluated implementation, feedback on suggested solutions, dissemination of results
STRATEGIC LEVEL → concepts (“white books), development strategies (strategic papers) National Education Institute → frameworks and guidelines Ministry of Education and Sport TACTICAL LEVEL Schools OPERATIONAL LEVEL → monitored and evaluated implementation, feedback on suggested solutions, dissemination of results
 KEY DIFFERENCES • Not a programme, but a development project. • A systemic national development project, pursuing its goals through school development projects. • A European Social Fund project – strict observance of regulations, particularly reporting on activities – “acceptable evidence” (prerequisite for funding). • Schools follow the same employment procedures as for Slovene citizens – no mediation by the ministry or the NEI (mutual recognition of qualifications!)! • The foreign teacher is a co-teacher, a teaching partner, not an assistant, expected to become a vital member of the school project team; former mentors become FL coordinators. • Co-teaching follows the collaborative teaching philosophy and principles, non necessarily type A team teaching.
KEY DIFFERENCES • Not a programme, but a development project. • A systemic national development project, pursuing its goals through school development projects. • A European Social Fund project – strict observance of regulations, particularly reporting on activities – “acceptable evidence” (prerequisite for funding). • Schools follow the same employment procedures as for Slovene citizens – no mediation by the ministry or the NEI (mutual recognition of qualifications!)! • The foreign teacher is a co-teacher, a teaching partner, not an assistant, expected to become a vital member of the school project team; former mentors become FL coordinators. • Co-teaching follows the collaborative teaching philosophy and principles, non necessarily type A team teaching.
 • Idea sharing (structured & guided) • Discussion groups (guided) • Peer observation • Joint teaching activities (student projects, homework etc. ) – between classes at school level – between schools on national and international level • Teacher exchanges – between classes at school level – between schools on national and international level • Team teaching (type A and type B) COLLABORATIVE TEACHING
• Idea sharing (structured & guided) • Discussion groups (guided) • Peer observation • Joint teaching activities (student projects, homework etc. ) – between classes at school level – between schools on national and international level • Teacher exchanges – between classes at school level – between schools on national and international level • Team teaching (type A and type B) COLLABORATIVE TEACHING
 Aims and goals of the project FOREIGN TEACHERS • upgrading the quality of foreign language teaching in Slovenia by innovative approaches, based on – an enhanced authenticity of learning situations (communication with a native speaker of the target language or a non-native speaker with other FL 1 than Slovene and using the target language as a lingua franca) and – cooperative teaching in multicultural teams (Slovene & foreign teachers of foreign languages, Slovene teachers of non-language subjects & foreign teachers of foreign languages); • developing a systemic approach to foreign teachers inclusion into the Slovene educational system - piloting alternative organizational options
Aims and goals of the project FOREIGN TEACHERS • upgrading the quality of foreign language teaching in Slovenia by innovative approaches, based on – an enhanced authenticity of learning situations (communication with a native speaker of the target language or a non-native speaker with other FL 1 than Slovene and using the target language as a lingua franca) and – cooperative teaching in multicultural teams (Slovene & foreign teachers of foreign languages, Slovene teachers of non-language subjects & foreign teachers of foreign languages); • developing a systemic approach to foreign teachers inclusion into the Slovene educational system - piloting alternative organizational options
 NATIONAL PROJECT TEAM (NPT) Project manager core NPT, extended NPT, enlarged NPT SPT managers/leaders Working Groups (WG) School Project Teams (SPT) PROJECT STRUCTURE External ◄collaborators • Slovene and foreign teachers • academic experts
NATIONAL PROJECT TEAM (NPT) Project manager core NPT, extended NPT, enlarged NPT SPT managers/leaders Working Groups (WG) School Project Teams (SPT) PROJECT STRUCTURE External ◄collaborators • Slovene and foreign teachers • academic experts
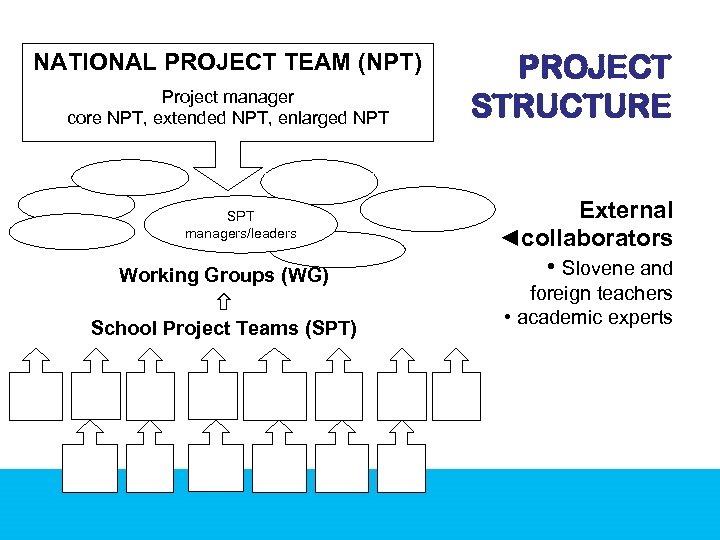
 PROJECT STRUCTURE • National Project Team (NPT) – core NPT (Katja Pavlič Škerjanc, project manager – NEI, Maja Celestina, NEI; Barbara Gregorič – financial matters, NEI; Domen Petelin – legal matters, NEI; Bronka Straus, MES) – extended NPT (core NPT + NEI foreign language advisers) – enlarged NPT (extended NPT + school project team leaders + school FL coordinators + selected foreign teachers/one per language) • School Project Teams (SPT) (3 – 5 members) – Project team leader – Foreign language coordinator – Foreign teacher – Other teachers according to the school project goals
PROJECT STRUCTURE • National Project Team (NPT) – core NPT (Katja Pavlič Škerjanc, project manager – NEI, Maja Celestina, NEI; Barbara Gregorič – financial matters, NEI; Domen Petelin – legal matters, NEI; Bronka Straus, MES) – extended NPT (core NPT + NEI foreign language advisers) – enlarged NPT (extended NPT + school project team leaders + school FL coordinators + selected foreign teachers/one per language) • School Project Teams (SPT) (3 – 5 members) – Project team leader – Foreign language coordinator – Foreign teacher – Other teachers according to the school project goals
 FOREIGN TEACHER: ROLE AND TASKS • The foreign teacher is an autonomous, independent expert, expected to contribute creatively and innovatively to the quality of foreign language teaching and the school development project. • He/She is non only an ambassador of the culture he/she comes from but also an active promoter of multiculturality and interculturality. • He/She (co)-teaches in all parts of the curriculum: – core and elective (80% of the direct instruction/teaching workload), – optional (up to 10 % of the teaching workload) and – extra-curricular activities (up to 10 % of the teaching workload). Like Slovene teachers, foreign teachers will be required to be available for work at all times when the school is open and at other such times as the principal/headteacher or governing body may reasonably direct.
FOREIGN TEACHER: ROLE AND TASKS • The foreign teacher is an autonomous, independent expert, expected to contribute creatively and innovatively to the quality of foreign language teaching and the school development project. • He/She is non only an ambassador of the culture he/she comes from but also an active promoter of multiculturality and interculturality. • He/She (co)-teaches in all parts of the curriculum: – core and elective (80% of the direct instruction/teaching workload), – optional (up to 10 % of the teaching workload) and – extra-curricular activities (up to 10 % of the teaching workload). Like Slovene teachers, foreign teachers will be required to be available for work at all times when the school is open and at other such times as the principal/headteacher or governing body may reasonably direct.
 WORK OBLIGATIONS and HOURS OF WORK • full working hours (40 hours per week) • which equals 20 teaching hours per week at a secondary school and 22 teaching hours per week at a primary school plus other obligatory working activities (see next slide) • on the basis of collaborative teaching with Slovene teachers of foreign languages and non-language subjects (favoured approaches: LAC language across the curriculum: CBLL content-based language learning, interdisciplinary teaching/learning, discipline literacy development, project-based teaching/learning etc. )
WORK OBLIGATIONS and HOURS OF WORK • full working hours (40 hours per week) • which equals 20 teaching hours per week at a secondary school and 22 teaching hours per week at a primary school plus other obligatory working activities (see next slide) • on the basis of collaborative teaching with Slovene teachers of foreign languages and non-language subjects (favoured approaches: LAC language across the curriculum: CBLL content-based language learning, interdisciplinary teaching/learning, discipline literacy development, project-based teaching/learning etc. )
 WORK OBLIGATIONS and HOURS OF WORK • preparation and lesson planning in accordance with the principles of collaborative teaching • other activities in accordance with the aims and goals of the national development project – professional development activities: participation in seminars, workshops etc. organized by NEI – development project activities: materials writing, curriculum design etc. • other obligations in accordance with the relevant legislation • possible co-operation with the National Education Institute in accordance with an agreement between the school and the NEI
WORK OBLIGATIONS and HOURS OF WORK • preparation and lesson planning in accordance with the principles of collaborative teaching • other activities in accordance with the aims and goals of the national development project – professional development activities: participation in seminars, workshops etc. organized by NEI – development project activities: materials writing, curriculum design etc. • other obligations in accordance with the relevant legislation • possible co-operation with the National Education Institute in accordance with an agreement between the school and the NEI
 A sample average weekly foreign teacher’s teaching workload • 14 teaching hours in (foreign) language teams (collaborative teaching, preferably type A team teaching) • 1 teaching hour in multidisciplinary teams (interdisciplinary teaching, foreign teacher as a language expert, collaborative teaching – team teaching) • 2 teaching hours of individulised/personalised instruction (working with students showing learning difficulties or/and gifted students) • 1 teaching hour of optional curricular activities • 2 teaching hours of extra-curricular activities A record of hours worked (preparation and other activities included!) will have to be maintained via timesheets on a daily basis!
A sample average weekly foreign teacher’s teaching workload • 14 teaching hours in (foreign) language teams (collaborative teaching, preferably type A team teaching) • 1 teaching hour in multidisciplinary teams (interdisciplinary teaching, foreign teacher as a language expert, collaborative teaching – team teaching) • 2 teaching hours of individulised/personalised instruction (working with students showing learning difficulties or/and gifted students) • 1 teaching hour of optional curricular activities • 2 teaching hours of extra-curricular activities A record of hours worked (preparation and other activities included!) will have to be maintained via timesheets on a daily basis!
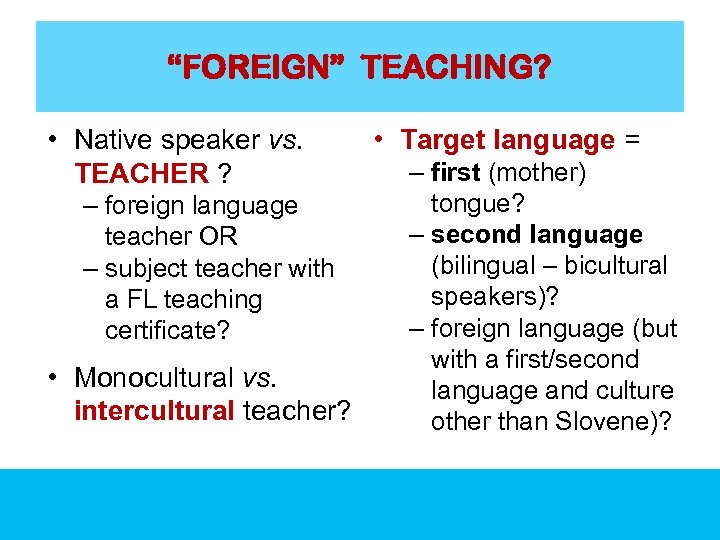 “FOREIGN” TEACHING? • Native speaker vs. TEACHER ? – foreign language teacher OR – subject teacher with a FL teaching certificate? • Monocultural vs. intercultural teacher? • Target language = – first (mother) tongue? – second language (bilingual – bicultural speakers)? – foreign language (but with a first/second language and culture other than Slovene)?
“FOREIGN” TEACHING? • Native speaker vs. TEACHER ? – foreign language teacher OR – subject teacher with a FL teaching certificate? • Monocultural vs. intercultural teacher? • Target language = – first (mother) tongue? – second language (bilingual – bicultural speakers)? – foreign language (but with a first/second language and culture other than Slovene)?
 QUALIFICATION REQUIREMENTS – PROFESSIONAL COMPETECES? TASKS foreign teacher COMPETENCES foreign teacher
QUALIFICATION REQUIREMENTS – PROFESSIONAL COMPETECES? TASKS foreign teacher COMPETENCES foreign teacher
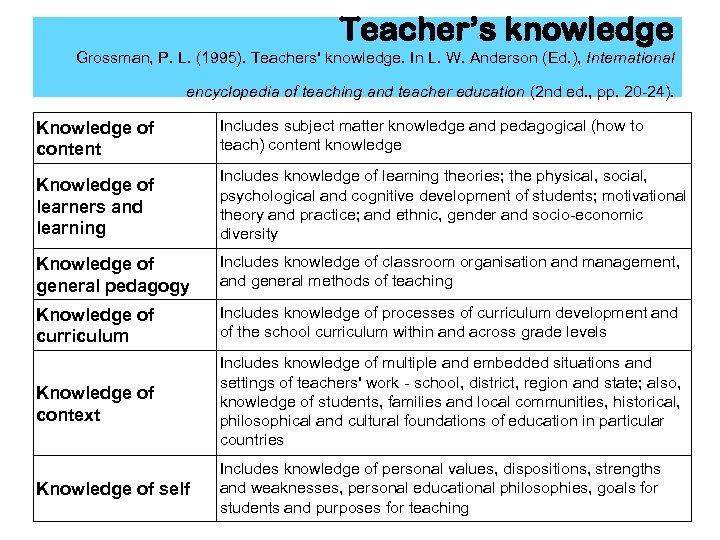
 • knowledge of content • knowledge of learners & learning • knowledge of general pedagogy • knowledge of curriculum • knowledge of context • knowledge of self (1995) ◄ TEACHER’S KNOWLEDGE Teachers should be able to: • work with information, technology and knowledge; • work with their fellow human beings – learners, colleagues and other partners in TEACHER COMPETENCES ► Common European Principles for education; Teacher Competences and • work with and in society - at Qualifications (2005) local, regional, national, European and broader global levels. http: //www. see-educoop. net/education_in/pdf/01 -en_principles_en. pdf
• knowledge of content • knowledge of learners & learning • knowledge of general pedagogy • knowledge of curriculum • knowledge of context • knowledge of self (1995) ◄ TEACHER’S KNOWLEDGE Teachers should be able to: • work with information, technology and knowledge; • work with their fellow human beings – learners, colleagues and other partners in TEACHER COMPETENCES ► Common European Principles for education; Teacher Competences and • work with and in society - at Qualifications (2005) local, regional, national, European and broader global levels. http: //www. see-educoop. net/education_in/pdf/01 -en_principles_en. pdf
 Teacher’s knowledge Grossman, P. L. (1995). Teachers' knowledge. In L. W. Anderson (Ed. ), International encyclopedia of teaching and teacher education (2 nd ed. , pp. 20 -24). Knowledge of content Includes subject matter knowledge and pedagogical (how to teach) content knowledge Knowledge of learners and learning Includes knowledge of learning theories; the physical, social, psychological and cognitive development of students; motivational theory and practice; and ethnic, gender and socio-economic diversity Knowledge of general pedagogy Includes knowledge of classroom organisation and management, and general methods of teaching Knowledge of curriculum Includes knowledge of processes of curriculum development and of the school curriculum within and across grade levels Knowledge of context Includes knowledge of multiple and embedded situations and settings of teachers' work - school, district, region and state; also, knowledge of students, families and local communities, historical, philosophical and cultural foundations of education in particular countries Knowledge of self Includes knowledge of personal values, dispositions, strengths and weaknesses, personal educational philosophies, goals for students and purposes for teaching
Teacher’s knowledge Grossman, P. L. (1995). Teachers' knowledge. In L. W. Anderson (Ed. ), International encyclopedia of teaching and teacher education (2 nd ed. , pp. 20 -24). Knowledge of content Includes subject matter knowledge and pedagogical (how to teach) content knowledge Knowledge of learners and learning Includes knowledge of learning theories; the physical, social, psychological and cognitive development of students; motivational theory and practice; and ethnic, gender and socio-economic diversity Knowledge of general pedagogy Includes knowledge of classroom organisation and management, and general methods of teaching Knowledge of curriculum Includes knowledge of processes of curriculum development and of the school curriculum within and across grade levels Knowledge of context Includes knowledge of multiple and embedded situations and settings of teachers' work - school, district, region and state; also, knowledge of students, families and local communities, historical, philosophical and cultural foundations of education in particular countries Knowledge of self Includes knowledge of personal values, dispositions, strengths and weaknesses, personal educational philosophies, goals for students and purposes for teaching
 Continuum of learning Feiman-Nemser, S. (2001). From preparation to practice: Designing a continuum to strengthen and sustain teaching. Teachers College Record, 103(6), 1013 -1055. Central tasks of learning to teach Preservice Induction 1. Examine beliefs critically in relation to vision of good teaching 1. Learn the context students, curriculum, school community 2. Develop subject matter knowledge for teaching 2. Design responsive instructional programs 3. Develop an understanding of learners, 3. Create a classroom learning and issues of learning community diversity 4. Develop the tools and 4. Develop a professional dispositions to study identity teaching Continuing professional development 1. Extend and deepen subject matter knowledge for teaching 2. Extend and refine repertoire in curriculum, instruction and assessment 3. Strengthen skills and dispositions to study and improve teaching
Continuum of learning Feiman-Nemser, S. (2001). From preparation to practice: Designing a continuum to strengthen and sustain teaching. Teachers College Record, 103(6), 1013 -1055. Central tasks of learning to teach Preservice Induction 1. Examine beliefs critically in relation to vision of good teaching 1. Learn the context students, curriculum, school community 2. Develop subject matter knowledge for teaching 2. Design responsive instructional programs 3. Develop an understanding of learners, 3. Create a classroom learning and issues of learning community diversity 4. Develop the tools and 4. Develop a professional dispositions to study identity teaching Continuing professional development 1. Extend and deepen subject matter knowledge for teaching 2. Extend and refine repertoire in curriculum, instruction and assessment 3. Strengthen skills and dispositions to study and improve teaching
 TEACHER COMPETENCES ► Common European Principles for Teacher Competences and Qualifications (2005)
TEACHER COMPETENCES ► Common European Principles for Teacher Competences and Qualifications (2005)
 TEACHER COMPETENCES ► Common European Principles for Teacher Competences and Qualifications (2005)
TEACHER COMPETENCES ► Common European Principles for Teacher Competences and Qualifications (2005)
 TEACHER COMPETENCES ► Common European Principles for Teacher Competences and Qualifications (2005)
TEACHER COMPETENCES ► Common European Principles for Teacher Competences and Qualifications (2005)
 NOVE VLOGE UČITELJA in učiteljev profesionalni razvoj New roles and professional development • posredovalec znanja svetovalec za učenje knowledge provider learning counselor • uvajalec sprememb – change agent • raziskovalec - researcher • sooblikovalec kurikula – curriculum designer • ustvarjalec učnih gradiv – materials writer • ocenjevalec/evalvator kakovosti… - evaluator • itd. – etc.
NOVE VLOGE UČITELJA in učiteljev profesionalni razvoj New roles and professional development • posredovalec znanja svetovalec za učenje knowledge provider learning counselor • uvajalec sprememb – change agent • raziskovalec - researcher • sooblikovalec kurikula – curriculum designer • ustvarjalec učnih gradiv – materials writer • ocenjevalec/evalvator kakovosti… - evaluator • itd. – etc.
 SCHOOL DEVELOPMENT PROJECTS With a development project, a school • introduces change(s) • into the usual (everyday, established) teaching and learning process(es) • in a planned and systematic way • to raise – directly or indirectly - the quality of student learning and outcomes
SCHOOL DEVELOPMENT PROJECTS With a development project, a school • introduces change(s) • into the usual (everyday, established) teaching and learning process(es) • in a planned and systematic way • to raise – directly or indirectly - the quality of student learning and outcomes
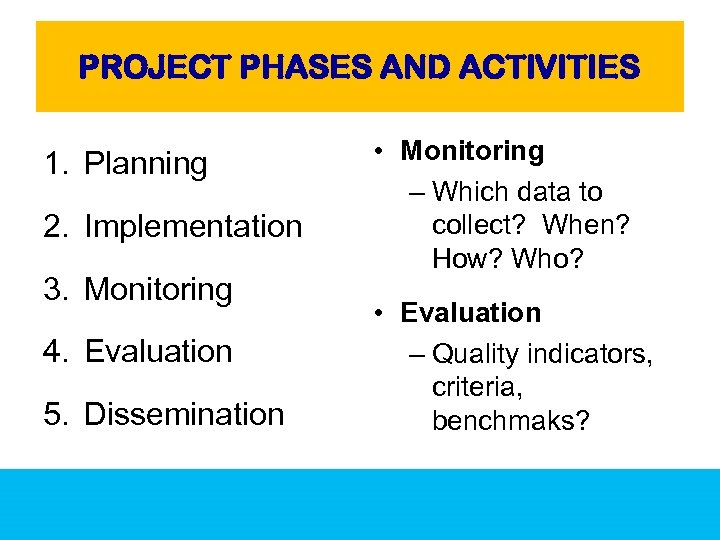 PROJECT PHASES AND ACTIVITIES 1. Planning 2. Implementation 3. Monitoring 4. Evaluation 5. Dissemination • Monitoring – Which data to collect? When? How? Who? • Evaluation – Quality indicators, criteria, benchmaks?
PROJECT PHASES AND ACTIVITIES 1. Planning 2. Implementation 3. Monitoring 4. Evaluation 5. Dissemination • Monitoring – Which data to collect? When? How? Who? • Evaluation – Quality indicators, criteria, benchmaks?
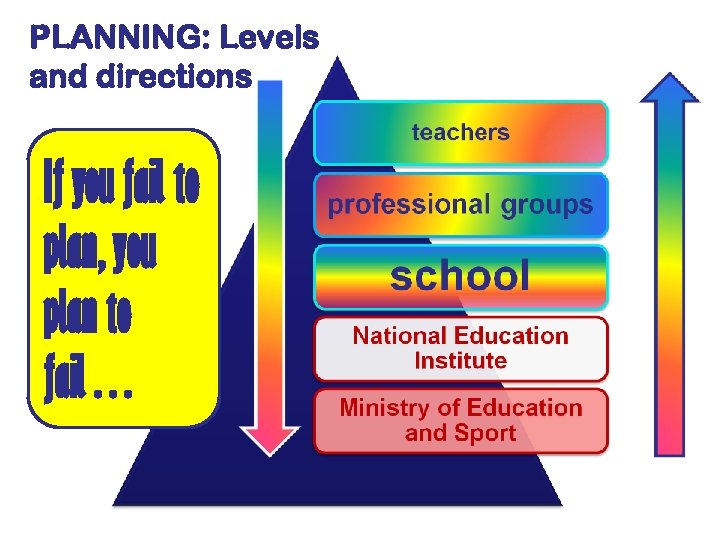 PLANNING: Levels and directions If you fail to plan, you plan to fail…
PLANNING: Levels and directions If you fail to plan, you plan to fail…
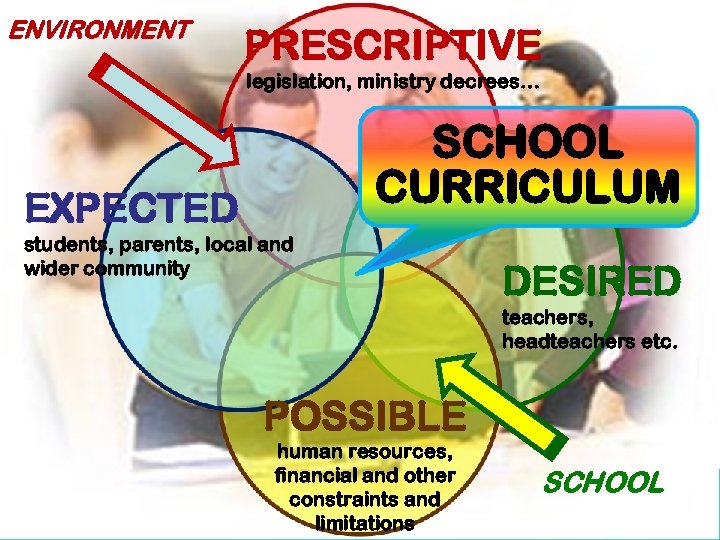 ENVIRONMENT PRESCRIPTIVE legislation, ministry decrees… SCHOOL CURRICULUM EXPECTED students, parents, local and wider community DESIRED teachers, headteachers etc. POSSIBLE human resources, financial and other constraints and limitations SCHOOL
ENVIRONMENT PRESCRIPTIVE legislation, ministry decrees… SCHOOL CURRICULUM EXPECTED students, parents, local and wider community DESIRED teachers, headteachers etc. POSSIBLE human resources, financial and other constraints and limitations SCHOOL
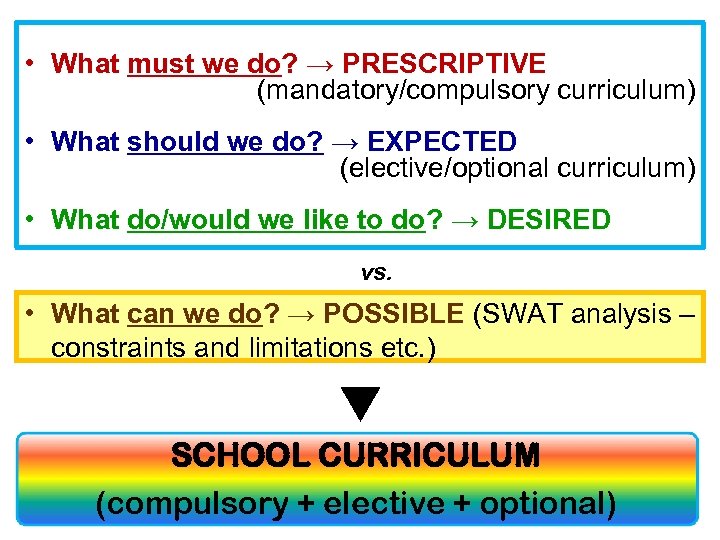 • What must we do? → PRESCRIPTIVE (mandatory/compulsory curriculum) • What should we do? → EXPECTED (elective/optional curriculum) • What do/would we like to do? → DESIRED vs. • What can we do? → POSSIBLE (SWAT analysis – constraints and limitations etc. ) SCHOOL CURRICULUM (compulsory + elective + optional)
• What must we do? → PRESCRIPTIVE (mandatory/compulsory curriculum) • What should we do? → EXPECTED (elective/optional curriculum) • What do/would we like to do? → DESIRED vs. • What can we do? → POSSIBLE (SWAT analysis – constraints and limitations etc. ) SCHOOL CURRICULUM (compulsory + elective + optional)
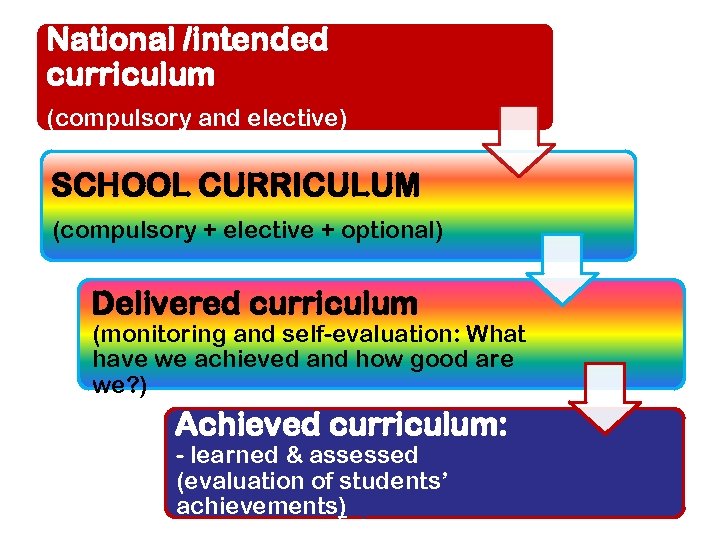 National /intended curriculum (compulsory and elective) SCHOOL CURRICULUM (compulsory + elective + optional) Delivered curriculum (monitoring and self-evaluation: What have we achieved and how good are we? ) Achieved curriculum: - learned & assessed (evaluation of students’ achievements)? )
National /intended curriculum (compulsory and elective) SCHOOL CURRICULUM (compulsory + elective + optional) Delivered curriculum (monitoring and self-evaluation: What have we achieved and how good are we? ) Achieved curriculum: - learned & assessed (evaluation of students’ achievements)? )
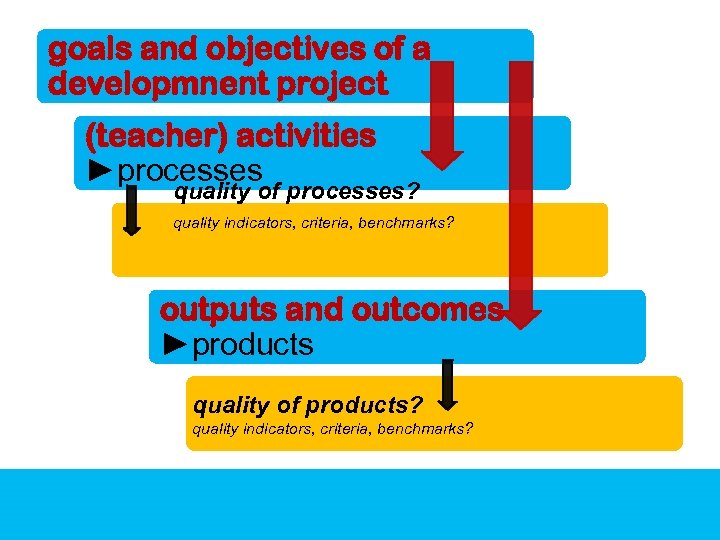 goals and objectives of a developmnent project (teacher) activities ►processes quality of processes? quality indicators, criteria, benchmarks? outputs and outcomes ►products quality of products? quality indicators, criteria, benchmarks?
goals and objectives of a developmnent project (teacher) activities ►processes quality of processes? quality indicators, criteria, benchmarks? outputs and outcomes ►products quality of products? quality indicators, criteria, benchmarks?
 NAČRT - PLAN izvajanja (implementation), spremljanja (monitoring) in evalviranja (evaluation) 1. Cilji - goals 2. Pričakovani dosežki – expected outcomes 3. Kazalniki kakovosti dosežkov (kvantitativni in kvalitativni) – product quality indicators • Kriteriji in merili ocenjevanja kakovosti 4. Dejavnosti za doseganje ciljev - activities 5. Kazalniki kakovosti procesov (kvantitativni in kvalitativni) – process quality indicators • Kriteriji in merili ocenjevanja kakovosti 6. Omejitve in tveganja – limitations and constraints • Načini odpravljanja omejitev in zmanjševanja tveganj 7. Nujni pogoji – necessary conditions
NAČRT - PLAN izvajanja (implementation), spremljanja (monitoring) in evalviranja (evaluation) 1. Cilji - goals 2. Pričakovani dosežki – expected outcomes 3. Kazalniki kakovosti dosežkov (kvantitativni in kvalitativni) – product quality indicators • Kriteriji in merili ocenjevanja kakovosti 4. Dejavnosti za doseganje ciljev - activities 5. Kazalniki kakovosti procesov (kvantitativni in kvalitativni) – process quality indicators • Kriteriji in merili ocenjevanja kakovosti 6. Omejitve in tveganja – limitations and constraints • Načini odpravljanja omejitev in zmanjševanja tveganj 7. Nujni pogoji – necessary conditions
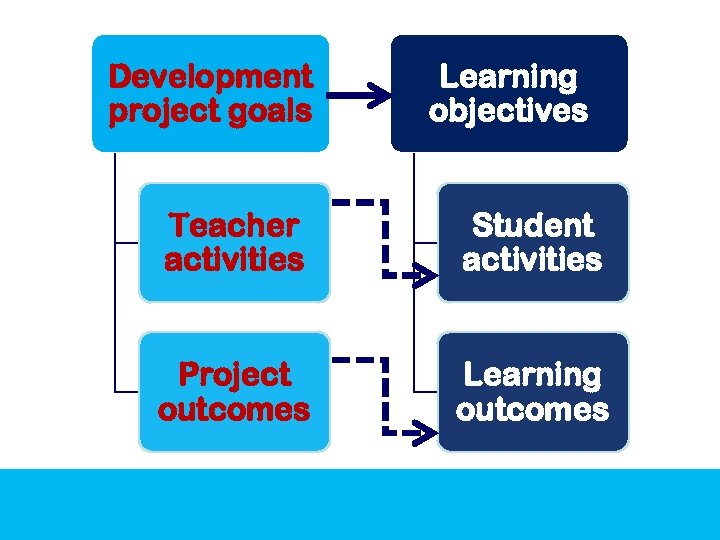 Development project goals Learning objectives Teacher activities Student activities Project outcomes Learning outcomes
Development project goals Learning objectives Teacher activities Student activities Project outcomes Learning outcomes


