f91bfc1d38459e9d6a28e3d892782b34.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 35
 Progressivism in the West, 1890 -1920
Progressivism in the West, 1890 -1920
 Origins of the Progressive Movement n Reaction to “extremes” of modern life n Urbanization n Industrialization n Labor conflict n Environmental exploitation n Immigration n Citizenship and rights n Social “problems”
Origins of the Progressive Movement n Reaction to “extremes” of modern life n Urbanization n Industrialization n Labor conflict n Environmental exploitation n Immigration n Citizenship and rights n Social “problems”
 Characteristics of Progressivism n Middle class morality n “Scientific” expertise and organizational management n Order and modernization n Assimilation n Federal role n Christian action AND humanitarianism n Professionalization of work n Organizational impulse
Characteristics of Progressivism n Middle class morality n “Scientific” expertise and organizational management n Order and modernization n Assimilation n Federal role n Christian action AND humanitarianism n Professionalization of work n Organizational impulse
 The Economic Extremes n Corporate control of n n n n industry & resources Rockefeller & Standard Oil (1911) Carnegie U. S. Steel Weyerhauser “Big Four” Railroads Political influence Anti-democratic
The Economic Extremes n Corporate control of n n n n industry & resources Rockefeller & Standard Oil (1911) Carnegie U. S. Steel Weyerhauser “Big Four” Railroads Political influence Anti-democratic
 Standard Oil, 1906
Standard Oil, 1906
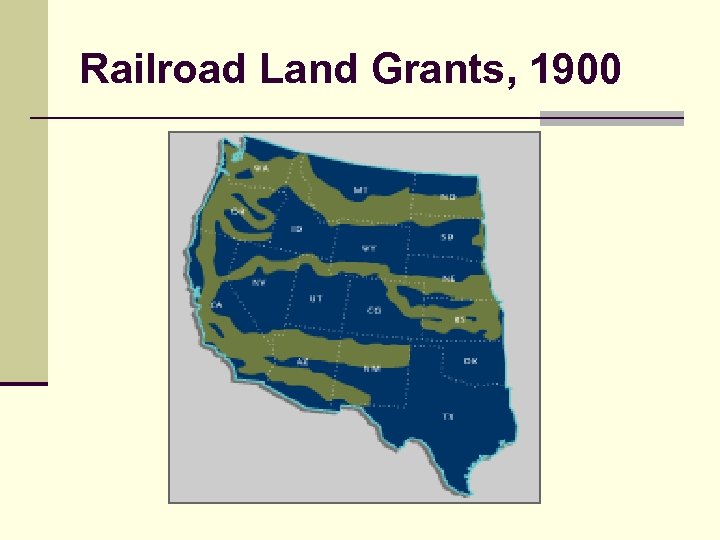 Railroad Land Grants, 1900
Railroad Land Grants, 1900
 The Economic Extremes n Western Federation of Miners, Butte, MT, 1892 n By 1901: A socialist union n Health, pay, working conditions, daily self -help and community support
The Economic Extremes n Western Federation of Miners, Butte, MT, 1892 n By 1901: A socialist union n Health, pay, working conditions, daily self -help and community support
 International Workers of the World n 1905 in Chicago and West n All workers, free speech, ACLU, justice n Self-Conscious creation of a working class n Ethnic and nationalistic divisions, identities n “Skilled vs. unskilled” workers, mobile vs. fixed
International Workers of the World n 1905 in Chicago and West n All workers, free speech, ACLU, justice n Self-Conscious creation of a working class n Ethnic and nationalistic divisions, identities n “Skilled vs. unskilled” workers, mobile vs. fixed
 Western Timber Industry n 1917: Idaho and WA n Migrant sedentary workers n World War I n National Guard n Negotiated 8 hr work day n Jailed union leaders n Criminalized unions
Western Timber Industry n 1917: Idaho and WA n Migrant sedentary workers n World War I n National Guard n Negotiated 8 hr work day n Jailed union leaders n Criminalized unions
 Copper Mining n Phelps-Dodge n “Modern generation” of corporations n Ethnic & racial divide and conquer n 1917 strike by unions, Jerome and Bisbee n 1, 200 deported
Copper Mining n Phelps-Dodge n “Modern generation” of corporations n Ethnic & racial divide and conquer n 1917 strike by unions, Jerome and Bisbee n 1, 200 deported
 Forced March from Bisbee, AZ
Forced March from Bisbee, AZ
 Free Mother Jones n Trinidad, Colorado n 1914 strike against Colorado Fuel and Iron Corporation n Threw Jones in jail n Women protested
Free Mother Jones n Trinidad, Colorado n 1914 strike against Colorado Fuel and Iron Corporation n Threw Jones in jail n Women protested
 Ludlow Massacre n Ludlow, CO 1917 n Rockefeller Coal Mines n Greek, Slavic, Italian miners and women
Ludlow Massacre n Ludlow, CO 1917 n Rockefeller Coal Mines n Greek, Slavic, Italian miners and women
 Continued n Militia attacked tents & killed 39 n 11 women & children died n Survivors deported
Continued n Militia attacked tents & killed 39 n 11 women & children died n Survivors deported
 Ludlow Refugees
Ludlow Refugees
 Populism: Agrarian Precursor to Progressivism n Corporate domination n Political apathy n Agrarian discontent n The Grange n Farmers Alliances n Populist Party n Democratic and community oriented
Populism: Agrarian Precursor to Progressivism n Corporate domination n Political apathy n Agrarian discontent n The Grange n Farmers Alliances n Populist Party n Democratic and community oriented
 Western Populists n Rural cooperatives n Local control over resources n Silver and tariffs n Jerry Simpson n Mary Elizabeth Lease n Omaha Platform n William Jennings Bryan
Western Populists n Rural cooperatives n Local control over resources n Silver and tariffs n Jerry Simpson n Mary Elizabeth Lease n Omaha Platform n William Jennings Bryan
 Populist Library, KS
Populist Library, KS
 Confluence of Trends & Changes n Corporate domination of resources n Control over political life n Political corruption n Economic inequalities n Labor unions and radicalism n Massive immigration n Mexican Revolution n Feeling that country is out of control
Confluence of Trends & Changes n Corporate domination of resources n Control over political life n Political corruption n Economic inequalities n Labor unions and radicalism n Massive immigration n Mexican Revolution n Feeling that country is out of control
 Progressive Causes n Statehood n Direct election of Senators n 1913 Income Tax n Referendum, Initiative, n n Recall Secret Ballot Child labor laws Contracts Work-hours n Frank Norris, NEB
Progressive Causes n Statehood n Direct election of Senators n 1913 Income Tax n Referendum, Initiative, n n Recall Secret Ballot Child labor laws Contracts Work-hours n Frank Norris, NEB
 Women and Progressivism n Western states surpassed eastern states in female voting rights n State laws allowed suffrage in WY 1869; UT 1870; CO 1893; ID 1896; WA 1910; CA 1911; AZ 1912; KA 1912; NV 1914; MT 1914; OR 1913 n Why? UT wanted more women to gain political influence for Mormons n Middle Class women’s groups such as the WCTU pressed for rights n “Frontier Thesis” n
Women and Progressivism n Western states surpassed eastern states in female voting rights n State laws allowed suffrage in WY 1869; UT 1870; CO 1893; ID 1896; WA 1910; CA 1911; AZ 1912; KA 1912; NV 1914; MT 1914; OR 1913 n Why? UT wanted more women to gain political influence for Mormons n Middle Class women’s groups such as the WCTU pressed for rights n “Frontier Thesis” n
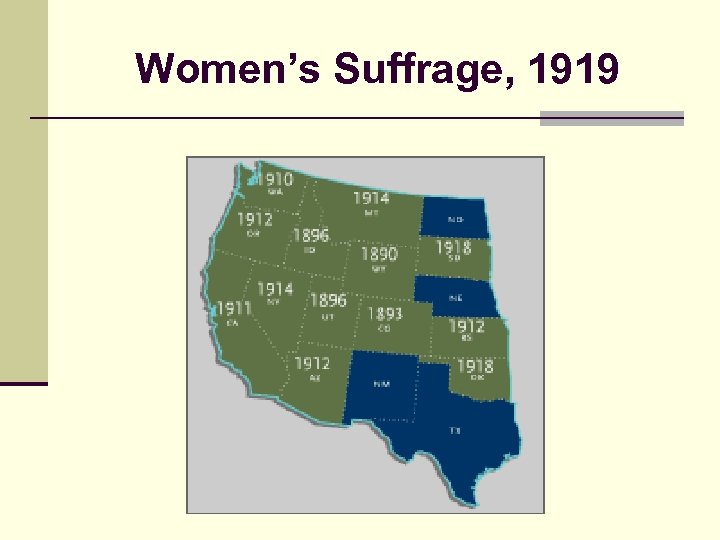 Women’s Suffrage, 1919
Women’s Suffrage, 1919
 Women Progressives Abigail Scott Duniway (OR): Agrarian reformer in 1870 s-1910 s. Divorce reforms, property rights, educational reform, working class women, suffrage, publisher n Caroline Church Nichols (CO): Published newspaper Colorado Antelope 1890 s n Jeanette Rankin (MT): first woman elected to the U. S. Congress in 1917 n Nellie Ross (WY) and Bertha Landes (TX) first female governors in 1925 n
Women Progressives Abigail Scott Duniway (OR): Agrarian reformer in 1870 s-1910 s. Divorce reforms, property rights, educational reform, working class women, suffrage, publisher n Caroline Church Nichols (CO): Published newspaper Colorado Antelope 1890 s n Jeanette Rankin (MT): first woman elected to the U. S. Congress in 1917 n Nellie Ross (WY) and Bertha Landes (TX) first female governors in 1925 n
 Women’s Suffrage n Nineteenth Amendment n 1920 passed n Full voting rights accorded to all men n Susan B. Anthony
Women’s Suffrage n Nineteenth Amendment n 1920 passed n Full voting rights accorded to all men n Susan B. Anthony
 Progressives in the West n Controlled senate and house seats n Governors n 1910: Nebraska, Kansas, South Dakota were n n n dominated by Republican Progressives Not anti-business; weary of unions “Efficiency” and “good government” Ambivalence towards “open” or “closed” shop California: Union Labor Party, moderates Dependency on the federal government as counterweight to corporate dominance
Progressives in the West n Controlled senate and house seats n Governors n 1910: Nebraska, Kansas, South Dakota were n n n dominated by Republican Progressives Not anti-business; weary of unions “Efficiency” and “good government” Ambivalence towards “open” or “closed” shop California: Union Labor Party, moderates Dependency on the federal government as counterweight to corporate dominance
 Western Progressives n Hiram Johnson: Reforms in California n Referendum, Recall, Initiative n Big Four n Prohibition across the West by 1915 n 18 th Amendment in 1920 n Unpredictable voting record on national elections n Oregon System: dozens of political candidates and 126 propositions in 1914 n Seattle: City Manager and Commission
Western Progressives n Hiram Johnson: Reforms in California n Referendum, Recall, Initiative n Big Four n Prohibition across the West by 1915 n 18 th Amendment in 1920 n Unpredictable voting record on national elections n Oregon System: dozens of political candidates and 126 propositions in 1914 n Seattle: City Manager and Commission
 Progressivism & Race n White male sense of chaos & disorganization due to suffrage, immigration, class oppression n Limited rights of non-white groups to create “order” and control resources and politics n South Texas: 1902 -1918 poll taxes, white primary, segregated education n Progressive newspapers view of Mexicans in 1913, “a class of foreigners who claim American citizenship but who are as ignorant of things American as a mule. ”
Progressivism & Race n White male sense of chaos & disorganization due to suffrage, immigration, class oppression n Limited rights of non-white groups to create “order” and control resources and politics n South Texas: 1902 -1918 poll taxes, white primary, segregated education n Progressive newspapers view of Mexicans in 1913, “a class of foreigners who claim American citizenship but who are as ignorant of things American as a mule. ”
 Progressivism and the Environment n Natural resources n Exploitation n Public use and access n Conservation n Preservation
Progressivism and the Environment n Natural resources n Exploitation n Public use and access n Conservation n Preservation
 Hetchy, 1913 n John Muir n Gifford Pinchot n Hetch-Hetchy, Yosemite Valley n Preserve or flood & use as reservoir for cities? n Flooded it…
Hetchy, 1913 n John Muir n Gifford Pinchot n Hetch-Hetchy, Yosemite Valley n Preserve or flood & use as reservoir for cities? n Flooded it…
 National Association for the Advancement of Colored People n 1908 n Segregation n Voting rights n Lawsuits n Elites n Strong in LA, SF, Seattle, Portland
National Association for the Advancement of Colored People n 1908 n Segregation n Voting rights n Lawsuits n Elites n Strong in LA, SF, Seattle, Portland
 Society for American Indians n Multi-tribal, national, bi-racial n 1911 established n BIA and employment n Citizenship: 1924 n Peyote n Language n “Traditionalism” n Education n Self-determination
Society for American Indians n Multi-tribal, national, bi-racial n 1911 established n BIA and employment n Citizenship: 1924 n Peyote n Language n “Traditionalism” n Education n Self-determination
 League of United Latin American Citizens n Corpus Christi 1929 n Origins in self-defense n n against white supremacist groups in Texas Equal opportunities in business, education Voting rights and civil rights Self-help and selfdetermination Mexican-American
League of United Latin American Citizens n Corpus Christi 1929 n Origins in self-defense n n against white supremacist groups in Texas Equal opportunities in business, education Voting rights and civil rights Self-help and selfdetermination Mexican-American
 LULAC Meeting, 1929
LULAC Meeting, 1929
 Japanese American Citizens League n Established 1929 to combat racism & citizenship laws n Fought the “Sons of the Golden West” and Japanese Exclusion League n Obtained citizenship for 500 Japanese soldiers who fought for the U. S. in WW I
Japanese American Citizens League n Established 1929 to combat racism & citizenship laws n Fought the “Sons of the Golden West” and Japanese Exclusion League n Obtained citizenship for 500 Japanese soldiers who fought for the U. S. in WW I
 Conclusions n Suffrage was one of the biggest differences n Concentration of corporate power n Federal influence on the west n Less “ethnic politics” n Urban, rural n Mixed relations with parties n Influence of the Populist Party n Environmental aspects of Progressivism
Conclusions n Suffrage was one of the biggest differences n Concentration of corporate power n Federal influence on the west n Less “ethnic politics” n Urban, rural n Mixed relations with parties n Influence of the Populist Party n Environmental aspects of Progressivism


