9b20eececeb26e488cfd42662976fd54.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 34
 Progressive Era
Progressive Era
 17 G. Progressive Era - period from 1898 to 1917 when reformers won many changes to improve American life Progressives believed that the public interest should guide all government actions.
17 G. Progressive Era - period from 1898 to 1917 when reformers won many changes to improve American life Progressives believed that the public interest should guide all government actions.
 Progressive Reforms 13. Problem: Monopolies and Trusts have an unfair advantage over other businesses and increase the cost to consumers Reform: Sherman Anti-Trust Act- outlawed monopolies and gave the government the power to break them up
Progressive Reforms 13. Problem: Monopolies and Trusts have an unfair advantage over other businesses and increase the cost to consumers Reform: Sherman Anti-Trust Act- outlawed monopolies and gave the government the power to break them up
 Progressive Reforms 17 D. Problem: Political bosses chose the candidates for each party for elections Reform: Primaries were adopted nationwide in which voters could choose their party’s candidate from among several people
Progressive Reforms 17 D. Problem: Political bosses chose the candidates for each party for elections Reform: Primaries were adopted nationwide in which voters could choose their party’s candidate from among several people
 Progressive Reforms 17 E. Problem: Poor Americans felt they were paying an unfair share of taxes (tariffs and excise taxes) Reform: 16 th Amendment (1913) – gave Congress the power to impose an income tax
Progressive Reforms 17 E. Problem: Poor Americans felt they were paying an unfair share of taxes (tariffs and excise taxes) Reform: 16 th Amendment (1913) – gave Congress the power to impose an income tax
 Progressive Reforms 17 D. Problem: US senators were chosen by state legislatures that were controlled by big business and monopolies 17 th Amendment (1913) – gave voters the right to directly elect U. S. Senators, took it away from state legislature (controlled by monopolies)
Progressive Reforms 17 D. Problem: US senators were chosen by state legislatures that were controlled by big business and monopolies 17 th Amendment (1913) – gave voters the right to directly elect U. S. Senators, took it away from state legislature (controlled by monopolies)
 Political Reforms Problem: State legislatures were not responsive to the wished of the people Reforms: 17 A. Initiatives Process in which certain citizens propose a new law directly on the ballot 17 B. Referendums Process that allows citizens to approve or reject a law passed by a legislature
Political Reforms Problem: State legislatures were not responsive to the wished of the people Reforms: 17 A. Initiatives Process in which certain citizens propose a new law directly on the ballot 17 B. Referendums Process that allows citizens to approve or reject a law passed by a legislature
 Political Reforms 17 C. Problem: Government officials were not held accountable for corruption Reform: Recalls allow voters to remove an elected official from office
Political Reforms 17 C. Problem: Government officials were not held accountable for corruption Reform: Recalls allow voters to remove an elected official from office
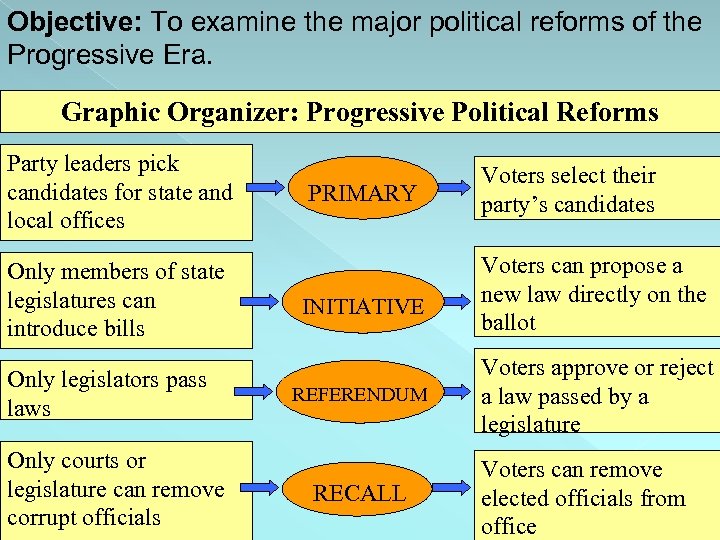 Objective: To examine the major political reforms of the Progressive Era. Graphic Organizer: Progressive Political Reforms Party leaders pick candidates for state and local offices Only members of state legislatures can introduce bills Only legislators pass laws Only courts or legislature can remove corrupt officials PRIMARY INITIATIVE REFERENDUM RECALL Voters select their party’s candidates Voters can propose a new law directly on the ballot Voters approve or reject a law passed by a legislature Voters can remove elected officials from office
Objective: To examine the major political reforms of the Progressive Era. Graphic Organizer: Progressive Political Reforms Party leaders pick candidates for state and local offices Only members of state legislatures can introduce bills Only legislators pass laws Only courts or legislature can remove corrupt officials PRIMARY INITIATIVE REFERENDUM RECALL Voters select their party’s candidates Voters can propose a new law directly on the ballot Voters approve or reject a law passed by a legislature Voters can remove elected officials from office
 Women’s Suffrage Movement to give women the right to vote Started by Susan B Anthony and Elizabeth Cady Stanton Sojourner Truth a former slave a key abolitionist also campaigned for Women’s Suffrage in her famous speech “Ain’t I a Women”
Women’s Suffrage Movement to give women the right to vote Started by Susan B Anthony and Elizabeth Cady Stanton Sojourner Truth a former slave a key abolitionist also campaigned for Women’s Suffrage in her famous speech “Ain’t I a Women”
 Push for a Constitutional Amendment Alice Paul formed the National Woman’s Party (NWP) NWP organized protests around the nation in support of women’s suffrage
Push for a Constitutional Amendment Alice Paul formed the National Woman’s Party (NWP) NWP organized protests around the nation in support of women’s suffrage
 In front of the Geneva Headquarters of the National Woman's Party. (Alice Paul, second from the left)
In front of the Geneva Headquarters of the National Woman's Party. (Alice Paul, second from the left)
 On March 3, 1913, charismatic and devoted women's suffrage leader Alice Paul organized a massive suffrage parade down Pennsylvania Avenue the day before President Woodrow Wilson's inauguration.
On March 3, 1913, charismatic and devoted women's suffrage leader Alice Paul organized a massive suffrage parade down Pennsylvania Avenue the day before President Woodrow Wilson's inauguration.
 Women's suffrage protest in front of the White House, February 1917
Women's suffrage protest in front of the White House, February 1917
 19 th Amendment and Tennessee 18. Gov. Al Roberts- TN governor, called special legislation session to vote on 19 th amendment 18 c Josephine A. Pearson- leader of the anti-suffrage movement in TN, she had promised her dying mother she would fight women’s suffrage if it came to TN for ratification 18 A. Anne Dallas Dudley - President of the Tennessee Equal Suffrage Association , Vice president of the NAWSA, led campaign for 19 th amendment in TN 18 B. Harry Burn – casted deciding vote in TN legislature, originally going to vote against amendment but got letter from his mama asking him to vote for it 18 D. Tennessee was the perfect 36 because it the 36 th (final state needed) to ratify the amendment
19 th Amendment and Tennessee 18. Gov. Al Roberts- TN governor, called special legislation session to vote on 19 th amendment 18 c Josephine A. Pearson- leader of the anti-suffrage movement in TN, she had promised her dying mother she would fight women’s suffrage if it came to TN for ratification 18 A. Anne Dallas Dudley - President of the Tennessee Equal Suffrage Association , Vice president of the NAWSA, led campaign for 19 th amendment in TN 18 B. Harry Burn – casted deciding vote in TN legislature, originally going to vote against amendment but got letter from his mama asking him to vote for it 18 D. Tennessee was the perfect 36 because it the 36 th (final state needed) to ratify the amendment
 Letter from Burn’s mother Dear Son: Hurrah and vote for suffrage! Don't keep them in doubt! I notice some of the speeches against. They were bitter. I have been watching to see how you stood, but have noticed anything yet. Don't forget to be a good boy and help Mrs. Catt put the "rat" in ratification. Your mother Anti-suffragists became very enraged when they discovered the news of Burn's decision. There is an apocryphal story that after the vote was ratified, angry anti-suffragists chased Burn through the Tennessee Legislature Hall, and Burn was forced to conceal himself for a short time until the tense situation had been defused
Letter from Burn’s mother Dear Son: Hurrah and vote for suffrage! Don't keep them in doubt! I notice some of the speeches against. They were bitter. I have been watching to see how you stood, but have noticed anything yet. Don't forget to be a good boy and help Mrs. Catt put the "rat" in ratification. Your mother Anti-suffragists became very enraged when they discovered the news of Burn's decision. There is an apocryphal story that after the vote was ratified, angry anti-suffragists chased Burn through the Tennessee Legislature Hall, and Burn was forced to conceal himself for a short time until the tense situation had been defused
 Muckrakers Named by President Teddy Roosevelt Journalist who uncovered wrongdoing in politics and business Raked through the mud to expose the truth to the public
Muckrakers Named by President Teddy Roosevelt Journalist who uncovered wrongdoing in politics and business Raked through the mud to expose the truth to the public
 16 A. Muckrakers and Reformers Problem: Government controlled by big business and special interests, not responsive to the will of the people Muckraker: Robert La Follette, governor of Wisconsin, latter a US Senator Reform: Founder of the Progressive Movement, made Wisconsin a “laboratory of democracy”, first state to enact progressive reforms (primaries, recall, etc. )
16 A. Muckrakers and Reformers Problem: Government controlled by big business and special interests, not responsive to the will of the people Muckraker: Robert La Follette, governor of Wisconsin, latter a US Senator Reform: Founder of the Progressive Movement, made Wisconsin a “laboratory of democracy”, first state to enact progressive reforms (primaries, recall, etc. )
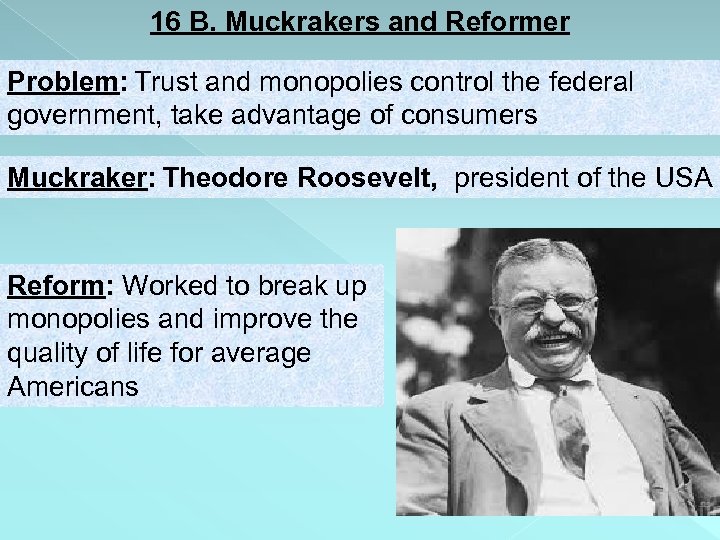 16 B. Muckrakers and Reformer Problem: Trust and monopolies control the federal government, take advantage of consumers Muckraker: Theodore Roosevelt, president of the USA Reform: Worked to break up monopolies and improve the quality of life for average Americans
16 B. Muckrakers and Reformer Problem: Trust and monopolies control the federal government, take advantage of consumers Muckraker: Theodore Roosevelt, president of the USA Reform: Worked to break up monopolies and improve the quality of life for average Americans
 16 C. Muckrakers and Reformers Problem: Unfair business practices by Standard Oil and other trusts. Muckraker: Ida Tarbell, journalist for Mc. Clures Reform: Her stories led to demands for tighter control of trusts. Sherman Ant-trust Act outlawed monopolies
16 C. Muckrakers and Reformers Problem: Unfair business practices by Standard Oil and other trusts. Muckraker: Ida Tarbell, journalist for Mc. Clures Reform: Her stories led to demands for tighter control of trusts. Sherman Ant-trust Act outlawed monopolies
 16 D. Muckrakers and Reformers Problem: Corruption in government, political bosses, crime and other safety problems in cities Muckraker: Lincoln Steffens, wrote The Shame of Cities Reform: His book led to the election of progressives who worked to fixed the problems described in his book
16 D. Muckrakers and Reformers Problem: Corruption in government, political bosses, crime and other safety problems in cities Muckraker: Lincoln Steffens, wrote The Shame of Cities Reform: His book led to the election of progressives who worked to fixed the problems described in his book
 16 E. Muckrakers and Reformers Problem: Filthy, unsanitary conditions in the meatpacking industry. Muckraker: Upton Sinclair, author of The Jungle Reform: Laws were passed to improve meat inspection. Food and Drug Administration (FDA)
16 E. Muckrakers and Reformers Problem: Filthy, unsanitary conditions in the meatpacking industry. Muckraker: Upton Sinclair, author of The Jungle Reform: Laws were passed to improve meat inspection. Food and Drug Administration (FDA)
 Reforms caused by The Jungle 19 D. Meat Inspection Act- Forced meat packers to allow more inspection of their meat 19 C. Pure Food and Drug Act- Ingredients were required on all food and drug items Food and Drug Administration. Government agency that oversaw the implementation of the reforms
Reforms caused by The Jungle 19 D. Meat Inspection Act- Forced meat packers to allow more inspection of their meat 19 C. Pure Food and Drug Act- Ingredients were required on all food and drug items Food and Drug Administration. Government agency that oversaw the implementation of the reforms
 Domestic Accomplishments of TR 19 A. Square Deal- Roosevelt program that promised Americans a nation where everyone would have an equal chance to succeed.
Domestic Accomplishments of TR 19 A. Square Deal- Roosevelt program that promised Americans a nation where everyone would have an equal chance to succeed.
 19 B. “trust-busting”- · Roosevelt felt that the government should keep an eye on all trusts and control or break up bad trusts (monopolies).
19 B. “trust-busting”- · Roosevelt felt that the government should keep an eye on all trusts and control or break up bad trusts (monopolies).
 19 E. Support for Conservation Named Gifford Pinchot first chief of US Forrest Service (efficiency movement) Added new federally protected land (national parks, national forests and national monuments)
19 E. Support for Conservation Named Gifford Pinchot first chief of US Forrest Service (efficiency movement) Added new federally protected land (national parks, national forests and national monuments)
 William Howard Taft
William Howard Taft
 Candidates - 1912 Presidential Election Republican Party Progressive Party (Bull Moose Party) + William Howard Taft Democratic Party = Theodore Roosevelt Woodrow Wilson
Candidates - 1912 Presidential Election Republican Party Progressive Party (Bull Moose Party) + William Howard Taft Democratic Party = Theodore Roosevelt Woodrow Wilson
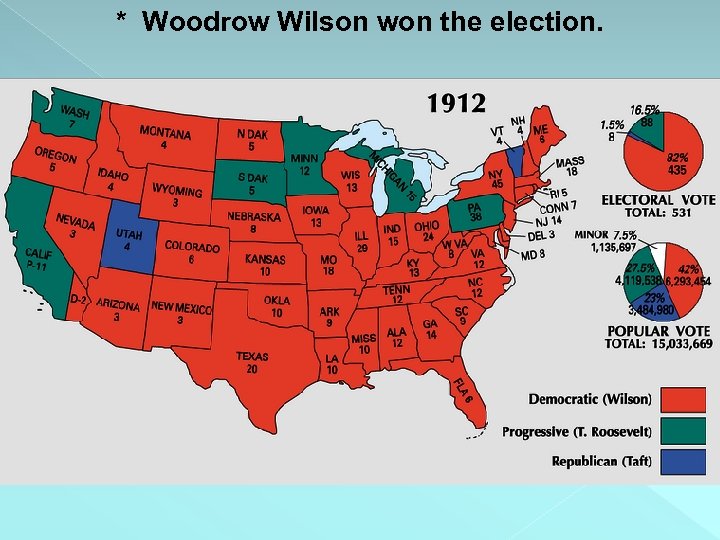 * Woodrow Wilson won the election.
* Woodrow Wilson won the election.
 Woodrow Wilson
Woodrow Wilson
 19 A. Wilson’s New Freedom Wilson’s promise of significant reforms that would result in for greater economic opportunity for all while ensuring the tradition of limited government Three Areas of New Freedom 1. Tariffs 2. Banking 3. Business
19 A. Wilson’s New Freedom Wilson’s promise of significant reforms that would result in for greater economic opportunity for all while ensuring the tradition of limited government Three Areas of New Freedom 1. Tariffs 2. Banking 3. Business
 President Woodrow Wilson’s New Freedom Policy / Act 19 B. Underwood Tariff 19 C. Federal Reserve Act Purpose Imposed federal income tax and drastically lowered tariffs (tax on imports) Regulated banking and currency, controlled the money supply and interest rates
President Woodrow Wilson’s New Freedom Policy / Act 19 B. Underwood Tariff 19 C. Federal Reserve Act Purpose Imposed federal income tax and drastically lowered tariffs (tax on imports) Regulated banking and currency, controlled the money supply and interest rates
 President Woodrow Wilson’s New Freedom Policy / Act 19 D. Clayton Antitrust Act Federal Trade Commission Purpose Amended the Sherman Anti-trust Act by defining and preventing the actions and policies that made a company a monopoly, goal was to stop monopoles before they were created Government agency created to promote consumer protection and eliminate anticompetitive business practices
President Woodrow Wilson’s New Freedom Policy / Act 19 D. Clayton Antitrust Act Federal Trade Commission Purpose Amended the Sherman Anti-trust Act by defining and preventing the actions and policies that made a company a monopoly, goal was to stop monopoles before they were created Government agency created to promote consumer protection and eliminate anticompetitive business practices


