937838b84b2a99c28fde82571a09534b.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 23

PROGRESSIVE AMERICA Unit VB AP United States History

Fundamental Question ► To what extent was the progressive movement “progressive”?

Solving the Problems of the Gilded Age ► Massive industrialization, production, and urbanization led to a wide variety of issues and problems or an expanding of existing concerns § § Political ineptitude Social inequalities Economical gaps Culture clashes ► Certain individuals and groups strongly pursued causes to improve America’s conditions and led the way for further government intervention

Progressivism (1900 -1920) ► Reformers destined to solve the many issues through a pragmatic approach § Experiment for improvement ► Most Progressives came from the urban middle- class ► Progressives charged with Christian values and morality ► American ideals seemed antiquated and needed changes or modifications § The American character should change/evolve with society

Development of Progressives Industrialization, commercialism, and urbanization exacerbated social, political, and economic problems and issues ► Expansion of the middle-class who were educated and understood the conditions ► § Whereas upper-class preferred status quo and lower-class enveloped in conditions ► ► ► Laissez-faire and limited government proved ineffective and socialism and anarchism proved too radical Inspired by Social Gospel and Gospel of Wealth to solve problems affecting society through promotion of Christian values Fueled by historic idealistic pursuits such as Jeffersonianism, Jacksonian democracy, and Populism Initiatives and referendums at municipal and state levels spread notice of issues in hopes of making them national Use of scientific research and statistics supported Progressive initiatives to justify and reason for change/modification

Progressives and Democracy ► Promotion of democracy by pursuing policies and initiatives to expand the people’s voice § In order to limit the corruption and influence of patronage, political machines, and big business ► Secret ballots (Australian ballot) § § ► Polling places inundated with corrupt tactics All candidates printed on ballots Vote in privacy at assigned polling place Established in all states by 1891 Direct primaries § Eliminate practice of electing candidates through political bosses § Not thoroughly effective ► Direct election of Senators § Eliminate patronage practice with state legislators selecting candidates § Seventeenth Amendment (1913) § Most Southern states did not ratify due to belief in limiting states’ rights ► Initiatives, referendums, and recalls § Way of persuading legislatures to seriously consider and adhere to issues

States Not Ratifying 17 th Amendment ► Alabama, Kentucky, Mississippi, Virginia, South Carolina, Georgia, Maryland, Rhode Island, Florida, Utah*

Progressive Social Initiatives and Developments ► Settlement Houses and YMCA § § § ► Blue Laws § ► From idealistic reformers to professional social workers Provide shelters, constructive leisure activities, education Hull House in Chicago and Jane Addams Regulating morality at the local and state levels Temperance to Prohibition § § Support for prohibition more from rural reformers than urban reformers Eighteenth Amendment (1919) and Volsteadt Act prohibited manufacturing and sale of alcohol ► Connecticut and Rhode Island rejected it ► Education § § § ► Comprehensive and compulsory education Teachers based on merit and professionalism Educational reform varied from location Labor Unions § AFL worked better for labor reforms ► Workers’ compensation, minimum wages, improved conditions § Industrial Workers of the World (IWW) aka Wobblies ► Direct action use of general strikes ► Socialists, anarchists, immigrants

Progressives and Minorities ► Blacks and Civil Rights § § Whether exploited through sharecropping or publicly segregated, blacks suffered inequities and Progressives tended to ignore their plight By 1900, 90% blacks in South; Great Migration to cities and the North ► National Urban League (1911) § § W. E. B Du Bois – demand for civil rights for progress Booker T. Washington – economic opportunity for progress ► President of Tuskegee University ► Up From Slavery and White House dinner § ► Niagara Movement to NAACP (1908) Women’s Suffrage Movement § § Younger women rose up for women reform and suffrage Suffrage gains at the state levels and changed to national suffrage movement National American Woman Suffrage Association (NAWSA) (1900) – Carrie Catt Stronger tactics – Alice Paul and Lucy Burns AND National Women’s Party (NWP, 1916) ► Picketing, parades, hunger strikes ► Silent Sentinels § Nineteenth Amendment (1920) ► League of Women Voters for female efficacy ► Immigrants § § Gilded Age: Chinese Exclusion Act (1882), 1882 Immigration Act excluded “lunatics, ” Anarchist Exclusion Act (1903) Naturalization Act of 1906 required English for citizenship Dillingham Commission (1907 -1911) ► Southern and Eastern Europeans threatened American character ► Recommended literacy requirements § Immigration Act of 1917 ► Extended list of “undesirables” ► Asiatic Barred Zone

States Delaying Ratification of the 19 th Amendment ► Maryland (1941), Virginia (1952), Alabama (1953), Florida (1969), South Carolina (1969), Georgia (1970), Louisiana (1970), North Carolina (1971), Mississippi (1984)

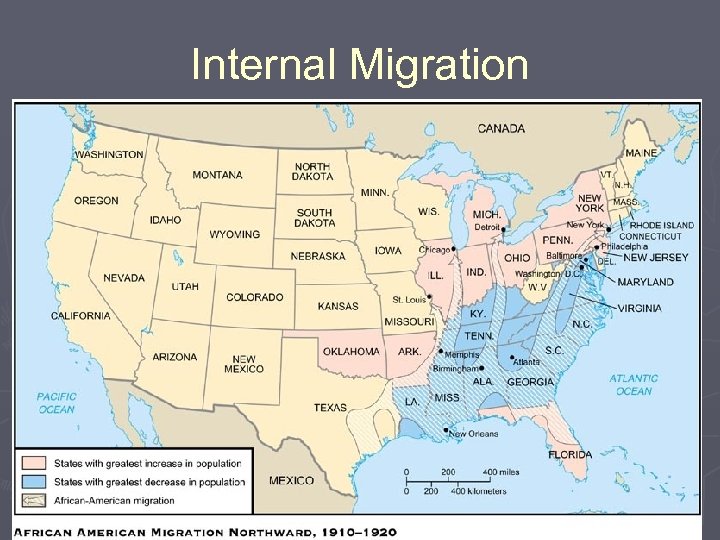
Internal Migration
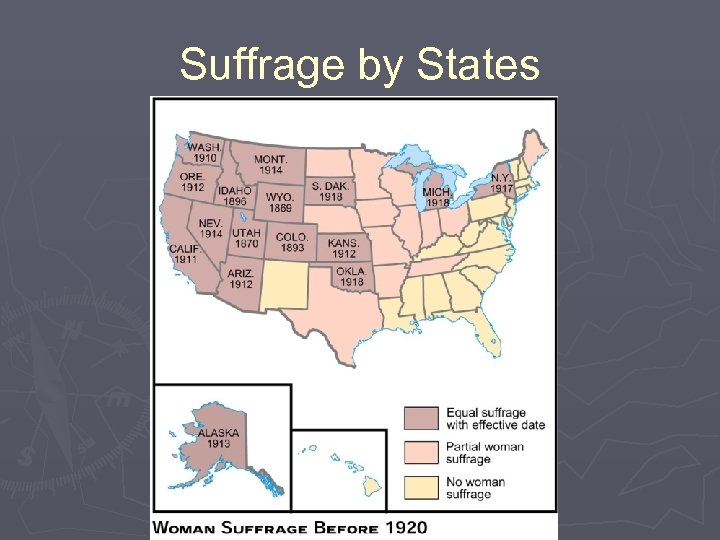
Suffrage by States
Migration

Muckrakers ► ► ► Journalists and authors investigated and probed the “dirty side” of politics, economics, and society by combining research with sensationalism Originated with attacks on the Standard Oil Company Targets included: monopolies/trusts (steel, oil), corporations (railroads), political bosses and machines, poor living and working conditions (tenements) Informed public and aroused feelings against corruption and poor conditions Led to more and new government regulations and enforcement; development of public relations by businesses Upton Sinclair’s The Jungle

Local Political Reform ► Political bosses and local businesses forged corrupt allegiances ► Cities asserted more control and regulation of public utilities ► Commissioners and city councils popularly elected; city managers ► Progressive mayors: Toledo’s Samuel Jones and Cleveland’s Tom Johnson

State Political Reform ► More and more states assumed progressive reforms § Direct primaries, business regulations, tax reforms, suffrage, temperance ► Wisconsin’s Robert La. Follette’s “Wisconsin Idea” ► As more states became progressive, reformers began to pursue initiatives on a national level

Roosevelt and Progressives (19011908) ► Square Deal § Favored fairness and national welfare § Domestic “Big-Stick” ► Trust-Busting § Enforce Sherman Anti-Trust Act § Good trusts and bad trusts ► National Regulation § Elkins Act and Hepburn Act strengthened ICC over railroads § Pure Food and Drug Act § Meat Inspection Act ► Conservation § Forest Reserve Act § Newlands Reclamation Act § Gifford Pinchot and National Conservation Commission
National Parks

Taft and the Progressives (19081912) ► Trust-busted more than Roosevelt ► Set aside lands for conservation ► Mann-Elkins Act § Increased powers of ICC over communications and railroads ► Sixteenth Amendment § Federal income tax

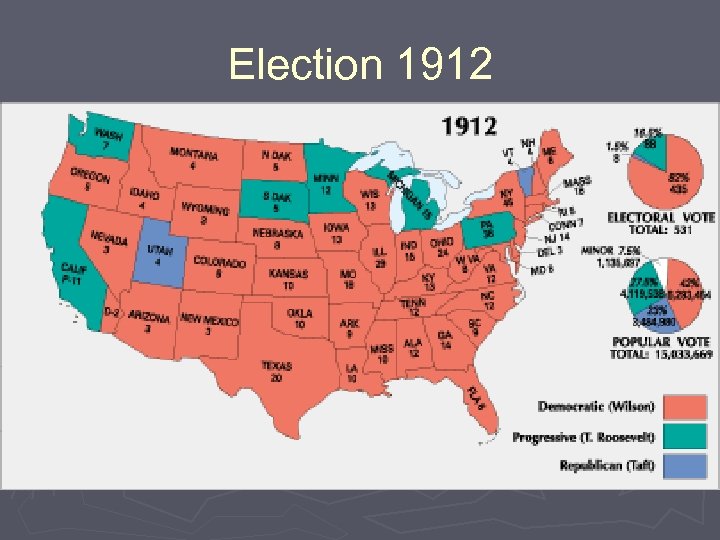
Election of 1912 ► Taft’s policies lead to a split in the Republican Party § Conservative Republicans and Progressive Republicans (Insurgents) ► Bull Moose Party and Roosevelt § New Nationalism – executive regulations of industries and social justice ► Democrat Woodrow Wilson § New Freedom – regulate business but promote competition and small businesses ► Socialist Party of America and Eugene V. Debs § Radical reforms ► Woodrow Wilson defeated Roosevelt as the Republicans were split
Election 1912

Woodrow Wilson and Progressives (1912 -1920) ► ► ► Business Regulation § Clayton Antitrust Act § Federal Trade Commission ► Regulate unfair practices in most industries Federal Reserve § Banks’ bank § Federal Reserve Board dictated monetary policy § 12 national financial districts Federal Farm Loan Act § Low interest loans from federal banks Child Labor Act (1916) § Prohibited interstate shipment of products made with children under 14 § Found unconstitutional Underwood Tariff § Lowered tariffs and increased income tax
937838b84b2a99c28fde82571a09534b.ppt