bd41721b29e9ecd2dea4bb4b19d05404.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 25

Programming Web Pages with Java. Script

Objectives Explore the Document Object Model Access elements and properties using Java. Script Create statements Store and access data in variables HTML 5 and CSS 3 – Illustrated, 2 nd Edition 2

Objectives (continued) Create a function Add an event listener Change CSS with Java. Script Create an if statement HTML 5 and CSS 3 – Illustrated, 2 nd Edition 3
Explore the Document Object Model Java. Script: the most widely used programming language for modern web browsers Document Object Model (DOM): standardized way of referring to parts of a web page Ø Creates a hierarchical arrangement known as a DOM tree Ø Each part of HTML document represented by a node HTML 5 and CSS 3 – Illustrated, 2 nd Edition 4
Explore the Document Object Model (continued) Object: HTML element in DOM Ø Specific object must be identified in order to manipulate it using Java. Script Property: piece of a standard set of information associated with DOM node Ø Attributes are considered their own nodes and are associated with their own properties HTML 5 and CSS 3 – Illustrated, 2 nd Edition 5

Explore the Document Object Model (continued) Method: action that can be performed for a node Ø Method names are followed by parentheses between which you specify information specific to the method Ø query. Selector() method lets you access any HTML element by specifying a CSS selector • Example: query. Selector("#nameinput") selects the element with the id value nameinput HTML 5 and CSS 3 – Illustrated, 2 nd Edition 6
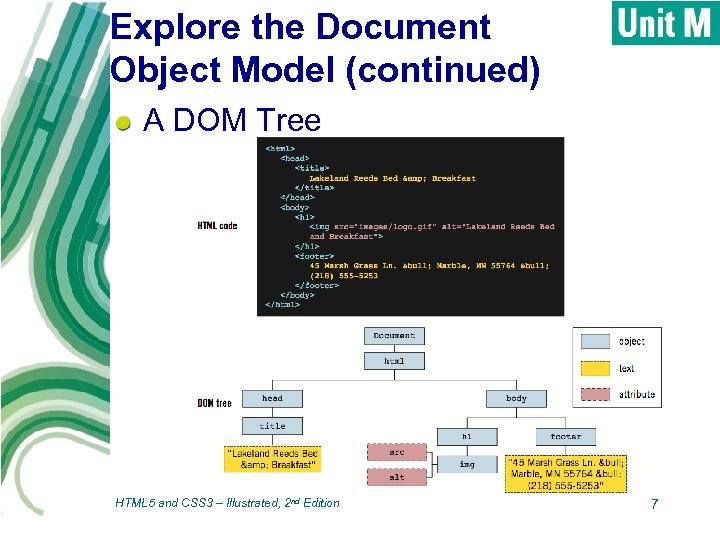
Explore the Document Object Model (continued) A DOM Tree HTML 5 and CSS 3 – Illustrated, 2 nd Edition 7

Access Elements and Properties Using Java. Script query. Selector() method lets you reference objects and properties Ø query. Selector() is a child of the Document object To use a method, specify its parent object, a period, and method name: document. query. Selector() HTML 5 and CSS 3 – Illustrated, 2 nd Edition 8

Access Elements and Properties Using Java. Script (continued) Specify CSS selector within parentheses of method to reference an object Ø To select the aside element: document. query. Selector("aside") To access a property, add dot and property name after method: document. query. Selector("aside"). text. Content HTML 5 and CSS 3 – Illustrated, 2 nd Edition 9

Access Elements and Properties Using Java. Script (continued) Console: part of developer tools in modern browsers; can be used to enter test code and view error messages related to Java. Script The browser console in Chrome: HTML 5 and CSS 3 – Illustrated, 2 nd Edition 10

Create Statements Statement: a Java. Script instruction that performs an action: Assignment operator (=): Part of a statement that lets you assign a new property value Ø Code on left of = accesses property Ø Code on right of = specifies new value • often enclosed in quotes HTML 5 and CSS 3 – Illustrated, 2 nd Edition 11

Create Statements (continued) Every Java. Script statement ends with a semicolon (; ) Statements created in external Java. Script file Ø Text file with. js extension Ø Referenced within HTML document using script element HTML 5 and CSS 3 – Illustrated, 2 nd Edition 12
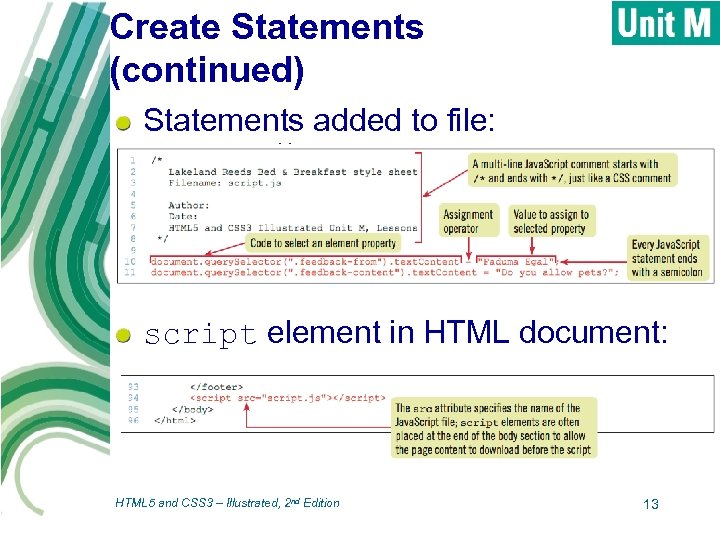
Create Statements (continued) Statements added to file: script element in HTML document: HTML 5 and CSS 3 – Illustrated, 2 nd Edition 13

Store and Access Data in Variables: Stored values you can access with a name you specify Ø Can store many types of information Ø Create with var keyword followed by name, equal sign, and value: HTML 5 and CSS 3 – Illustrated, 2 nd Edition 14
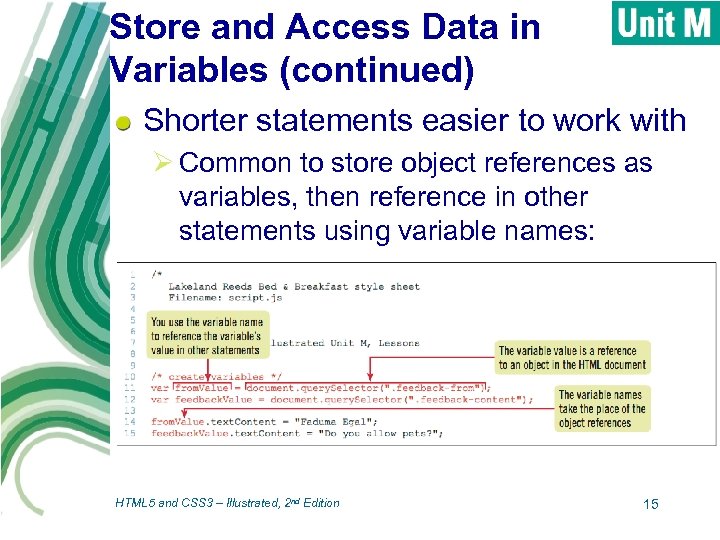
Store and Access Data in Variables (continued) Shorter statements easier to work with Ø Common to store object references as variables, then reference in other statements using variable names: HTML 5 and CSS 3 – Illustrated, 2 nd Edition 15
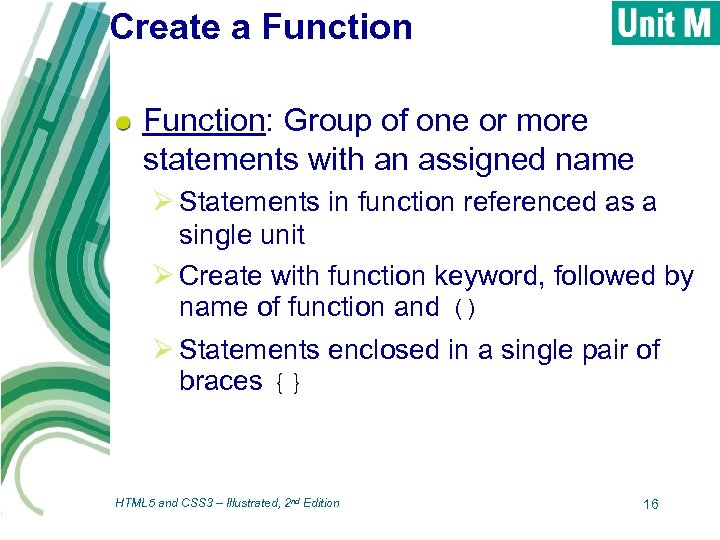
Create a Function: Group of one or more statements with an assigned name Ø Statements in function referenced as a single unit Ø Create with function keyword, followed by name of function and () Ø Statements enclosed in a single pair of braces {} HTML 5 and CSS 3 – Illustrated, 2 nd Edition 16
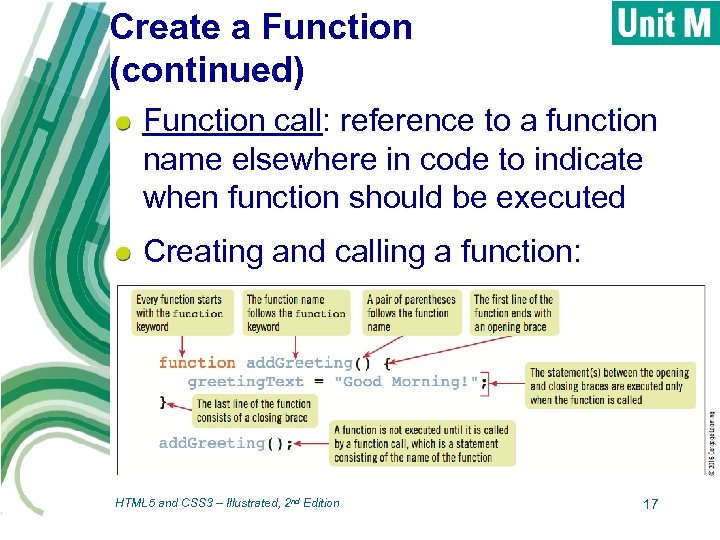
Create a Function (continued) Function call: reference to a function name elsewhere in code to indicate when function should be executed Creating and calling a function: HTML 5 and CSS 3 – Illustrated, 2 nd Edition 17

Add an Event Listener Events: actions commonly performed on a web page Ø Can write Java. Script that responds to events Commonly used events: HTML 5 and CSS 3 – Illustrated, 2 nd Edition 18

Add an Event Listener (continued) Event listener: a statement that specifies an object, an event, and function to call in response to event HTML 5 and CSS 3 – Illustrated, 2 nd Edition 19
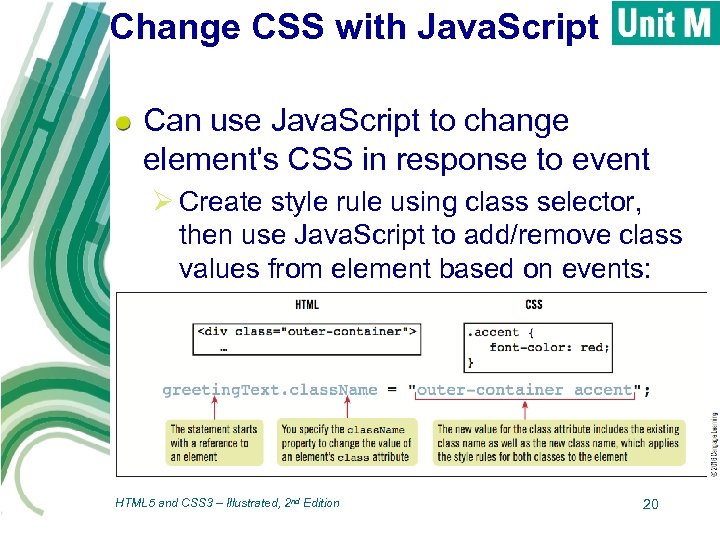
Change CSS with Java. Script Can use Java. Script to change element's CSS in response to event Ø Create style rule using class selector, then use Java. Script to add/remove class values from element based on events: HTML 5 and CSS 3 – Illustrated, 2 nd Edition 20

Create an if Statement operators: symbols to compare or change values of multiple objects or properties Ø assignment operator (=) Ø comparison operators: determine whether 2 values same or different if statement: compares 2 values; if result is true, statements are executed HTML 5 and CSS 3 – Illustrated, 2 nd Edition 21
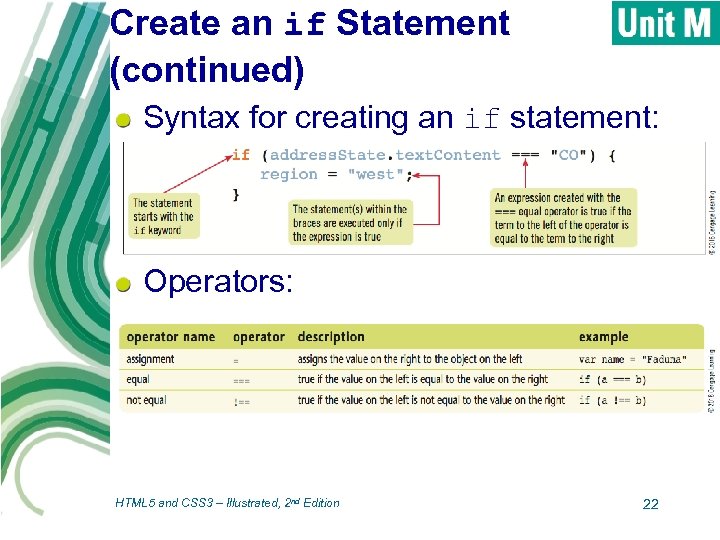
Create an if Statement (continued) Syntax for creating an if statement: Operators: HTML 5 and CSS 3 – Illustrated, 2 nd Edition 22
Summary DOM is a standardized way of referring to parts of a web page The query. Selector() method lets you reference objects and properties Script code is created by combining DOM objects, properties, and methods A statement is a Java. Script instruction that performs an action HTML 5 and CSS 3 – Illustrated, 2 nd Edition 23

Summary (continued) The assignment operator lets you assign a new property value Variables are stored values you can access with a name you specify A function is a group of one or more statements with an assigned name A function must be called for its statements to be executed HTML 5 and CSS 3 – Illustrated, 2 nd Edition 24

Summary (continued) An event listener is a statement that specifies an object, an event, and function to call in response to event You can use Java. Script to change the CSS for an element in response to an event An if statement compares 2 values and executes statements only if the comparison result is true HTML 5 and CSS 3 – Illustrated, 2 nd Edition 25
bd41721b29e9ecd2dea4bb4b19d05404.ppt