18e1309f3ff24262eff11d614471fa26.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 55
 Programming Thinking and Method (1) Zhao Hai 赵海 Department of Computer Science and Engineering Shanghai Jiao Tong University zhaohai@cs. sjtu. edu. cn
Programming Thinking and Method (1) Zhao Hai 赵海 Department of Computer Science and Engineering Shanghai Jiao Tong University zhaohai@cs. sjtu. edu. cn
 Outline • Introduction to Computer Science (CS) • Introduction to Python
Outline • Introduction to Computer Science (CS) • Introduction to Python
 Introduction to CS • What is Computer Science? Ø It is not the study of computers. Ø “Computers are to computer science what telescopes are to astronomy. ” – E. Dijkstra (May 11, 1930 – August 6, 2002) - He is a Dutch computer scientist and received the Turing Award for fundamental contributions to developing programming languages in 1972.
Introduction to CS • What is Computer Science? Ø It is not the study of computers. Ø “Computers are to computer science what telescopes are to astronomy. ” – E. Dijkstra (May 11, 1930 – August 6, 2002) - He is a Dutch computer scientist and received the Turing Award for fundamental contributions to developing programming languages in 1972.
 Introduction to CS - List of well-known computer scientists (http: //en. wikipedia. org/wiki/List_of_computer_scientists#U) Ø “Computer science is the study of the foundations of information and computation and their implementation and application in computer systems. ” – Wikipedia Ø It combines science, engineering, and mathematics into a unique and powerful field.
Introduction to CS - List of well-known computer scientists (http: //en. wikipedia. org/wiki/List_of_computer_scientists#U) Ø “Computer science is the study of the foundations of information and computation and their implementation and application in computer systems. ” – Wikipedia Ø It combines science, engineering, and mathematics into a unique and powerful field.
 Introduction to CS Areas of Computer Science Ø Four areas that it considers crucial to the discipline of computer science: theory of computation, algorithms and data structures, programming methodology and languages, and computer elements and architecture.
Introduction to CS Areas of Computer Science Ø Four areas that it considers crucial to the discipline of computer science: theory of computation, algorithms and data structures, programming methodology and languages, and computer elements and architecture.
 Introduction to CS Ø Theory of computation - focus on answering fundamental questions about what can be computed and what amount of resources are required to perform those computations. For example,
Introduction to CS Ø Theory of computation - focus on answering fundamental questions about what can be computed and what amount of resources are required to perform those computations. For example,
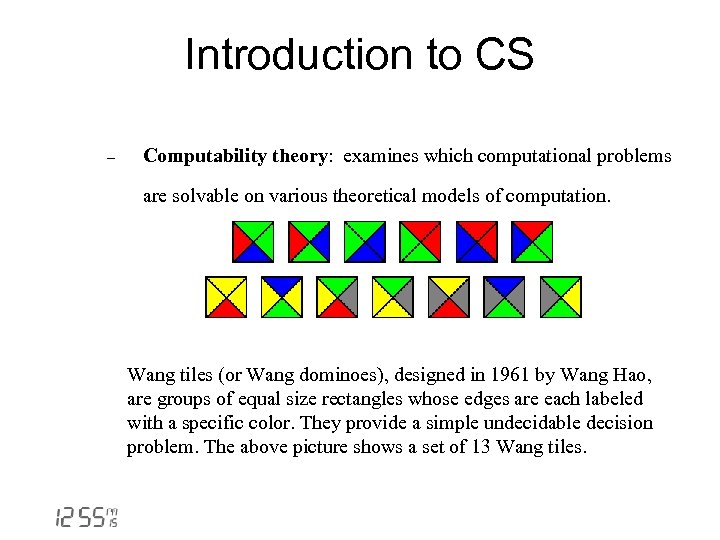 Introduction to CS - Computability theory: examines which computational problems are solvable on various theoretical models of computation. Wang tiles (or Wang dominoes), designed in 1961 by Wang Hao, are groups of equal size rectangles whose edges are each labeled with a specific color. They provide a simple undecidable decision problem. The above picture shows a set of 13 Wang tiles.
Introduction to CS - Computability theory: examines which computational problems are solvable on various theoretical models of computation. Wang tiles (or Wang dominoes), designed in 1961 by Wang Hao, are groups of equal size rectangles whose edges are each labeled with a specific color. They provide a simple undecidable decision problem. The above picture shows a set of 13 Wang tiles.
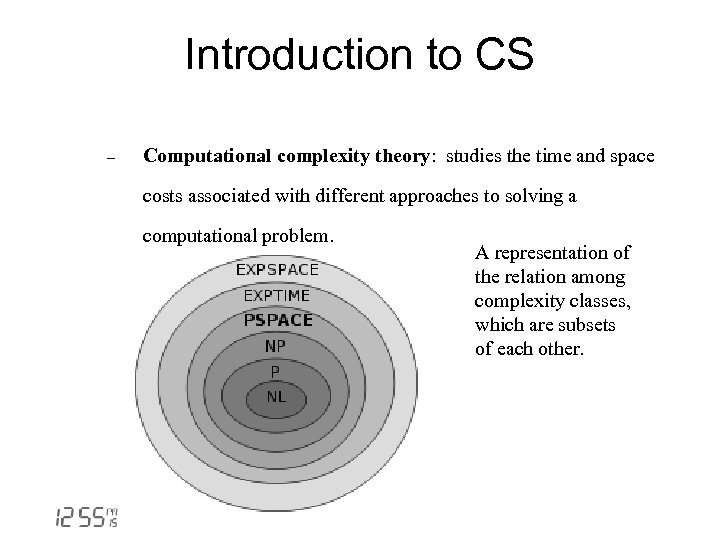 Introduction to CS - Computational complexity theory: studies the time and space costs associated with different approaches to solving a computational problem. A representation of the relation among complexity classes, which are subsets of each other.
Introduction to CS - Computational complexity theory: studies the time and space costs associated with different approaches to solving a computational problem. A representation of the relation among complexity classes, which are subsets of each other.
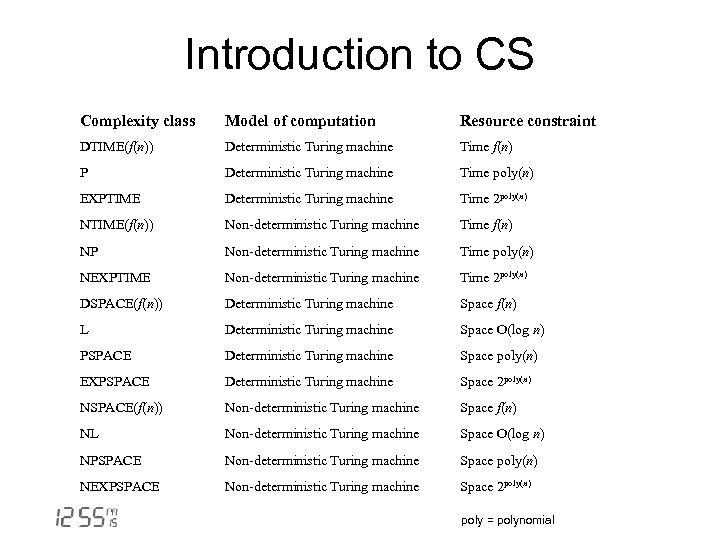 Introduction to CS Complexity class Model of computation Resource constraint DTIME(f(n)) Deterministic Turing machine Time f(n) P Deterministic Turing machine Time poly(n) EXPTIME Deterministic Turing machine Time 2 poly(n) NTIME(f(n)) Non-deterministic Turing machine Time f(n) NP Non-deterministic Turing machine Time poly(n) NEXPTIME Non-deterministic Turing machine Time 2 poly(n) DSPACE(f(n)) Deterministic Turing machine Space f(n) L Deterministic Turing machine Space O(log n) PSPACE Deterministic Turing machine Space poly(n) EXPSPACE Deterministic Turing machine Space 2 poly(n) NSPACE(f(n)) Non-deterministic Turing machine Space f(n) NL Non-deterministic Turing machine Space O(log n) NPSPACE Non-deterministic Turing machine Space poly(n) NEXPSPACE Non-deterministic Turing machine Space 2 poly(n) poly = polynomial
Introduction to CS Complexity class Model of computation Resource constraint DTIME(f(n)) Deterministic Turing machine Time f(n) P Deterministic Turing machine Time poly(n) EXPTIME Deterministic Turing machine Time 2 poly(n) NTIME(f(n)) Non-deterministic Turing machine Time f(n) NP Non-deterministic Turing machine Time poly(n) NEXPTIME Non-deterministic Turing machine Time 2 poly(n) DSPACE(f(n)) Deterministic Turing machine Space f(n) L Deterministic Turing machine Space O(log n) PSPACE Deterministic Turing machine Space poly(n) EXPSPACE Deterministic Turing machine Space 2 poly(n) NSPACE(f(n)) Non-deterministic Turing machine Space f(n) NL Non-deterministic Turing machine Space O(log n) NPSPACE Non-deterministic Turing machine Space poly(n) NEXPSPACE Non-deterministic Turing machine Space 2 poly(n) poly = polynomial
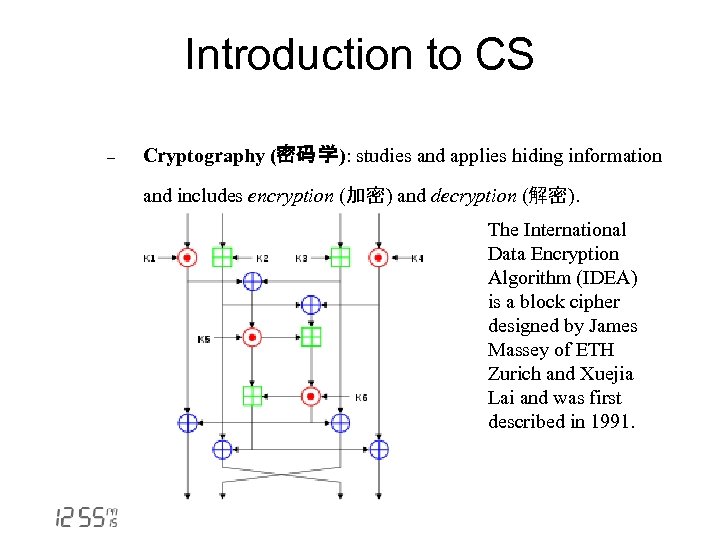 Introduction to CS - Cryptography (密码 学): studies and applies hiding information and includes encryption (加密) and decryption (解密). The International Data Encryption Algorithm (IDEA) is a block cipher designed by James Massey of ETH Zurich and Xuejia Lai and was first described in 1991.
Introduction to CS - Cryptography (密码 学): studies and applies hiding information and includes encryption (加密) and decryption (解密). The International Data Encryption Algorithm (IDEA) is a block cipher designed by James Massey of ETH Zurich and Xuejia Lai and was first described in 1991.
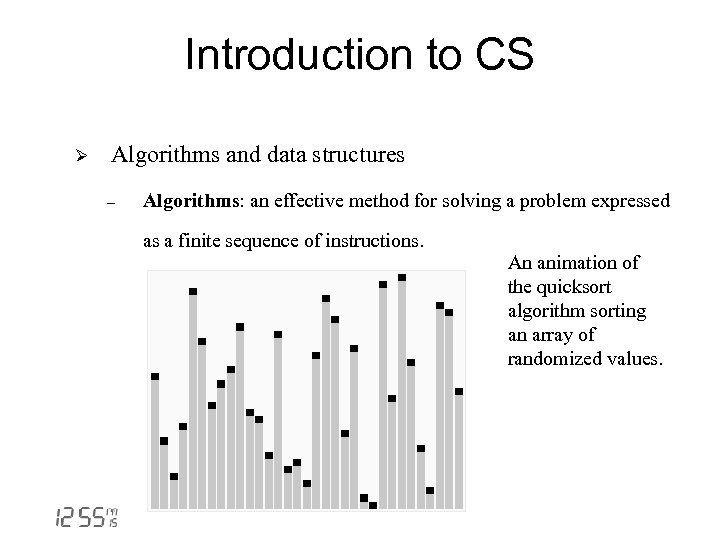 Introduction to CS Ø Algorithms and data structures - Algorithms: an effective method for solving a problem expressed as a finite sequence of instructions. An animation of the quicksort algorithm sorting an array of randomized values.
Introduction to CS Ø Algorithms and data structures - Algorithms: an effective method for solving a problem expressed as a finite sequence of instructions. An animation of the quicksort algorithm sorting an array of randomized values.
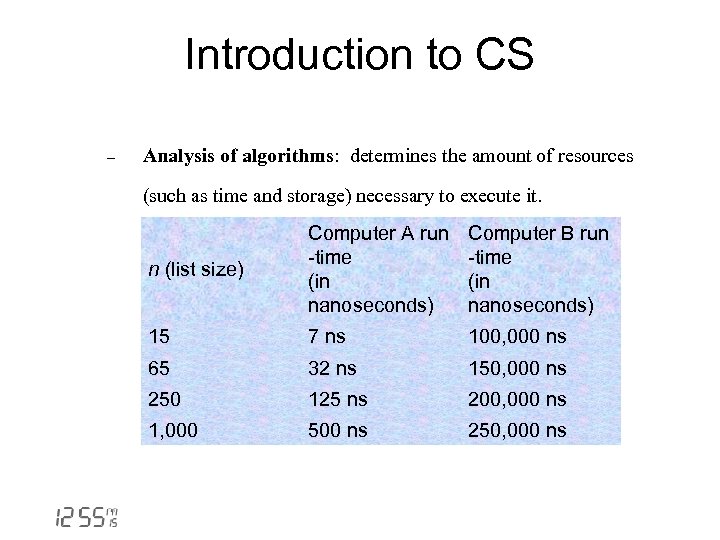 Introduction to CS - Analysis of algorithms: determines the amount of resources (such as time and storage) necessary to execute it. n (list size) Computer A run -time (in nanoseconds) Computer B run -time (in nanoseconds) 15 7 ns 100, 000 ns 65 32 ns 150, 000 ns 250 125 ns 200, 000 ns 1, 000 500 ns 250, 000 ns
Introduction to CS - Analysis of algorithms: determines the amount of resources (such as time and storage) necessary to execute it. n (list size) Computer A run -time (in nanoseconds) Computer B run -time (in nanoseconds) 15 7 ns 100, 000 ns 65 32 ns 150, 000 ns 250 125 ns 200, 000 ns 1, 000 500 ns 250, 000 ns
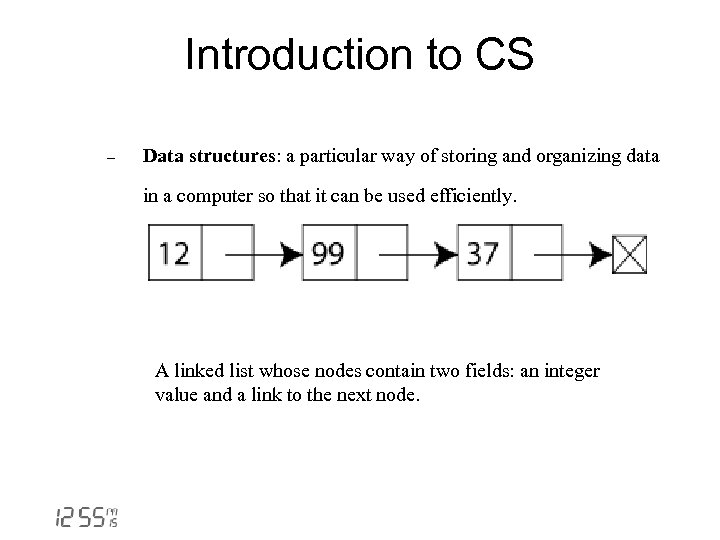 Introduction to CS - Data structures: a particular way of storing and organizing data in a computer so that it can be used efficiently. A linked list whose nodes contain two fields: an integer value and a link to the next node.
Introduction to CS - Data structures: a particular way of storing and organizing data in a computer so that it can be used efficiently. A linked list whose nodes contain two fields: an integer value and a link to the next node.
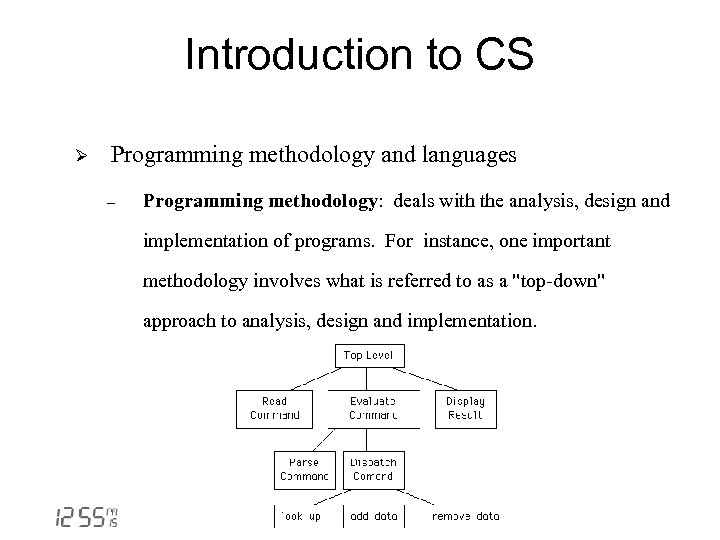 Introduction to CS Ø Programming methodology and languages - Programming methodology: deals with the analysis, design and implementation of programs. For instance, one important methodology involves what is referred to as a "top-down" approach to analysis, design and implementation.
Introduction to CS Ø Programming methodology and languages - Programming methodology: deals with the analysis, design and implementation of programs. For instance, one important methodology involves what is referred to as a "top-down" approach to analysis, design and implementation.
 Introduction to CS - Programming languages: a formal language endowed with semantics that can be utilized to control the behavior of a machine, particularly a computer, to perform specific tasks.
Introduction to CS - Programming languages: a formal language endowed with semantics that can be utilized to control the behavior of a machine, particularly a computer, to perform specific tasks.
 Introduction to CS For example, in 2008 the 10 most cited programming languages are (in alphabetical order): C, C++, C#, Java. Script, Perl, PHP, Python, Ruby, and SQL.
Introduction to CS For example, in 2008 the 10 most cited programming languages are (in alphabetical order): C, C++, C#, Java. Script, Perl, PHP, Python, Ruby, and SQL.
 Introduction to CS Ø Computer elements and architecture - Digital logic: may be divided into two classes: combinational logic, in which the logical outputs are determined by the logical function being performed and the logical input states at that particular moment; and sequential logic, in which the outputs also depend on the prior states of those outputs. Both classes of logic are used extensively in all digital computers.
Introduction to CS Ø Computer elements and architecture - Digital logic: may be divided into two classes: combinational logic, in which the logical outputs are determined by the logical function being performed and the logical input states at that particular moment; and sequential logic, in which the outputs also depend on the prior states of those outputs. Both classes of logic are used extensively in all digital computers.
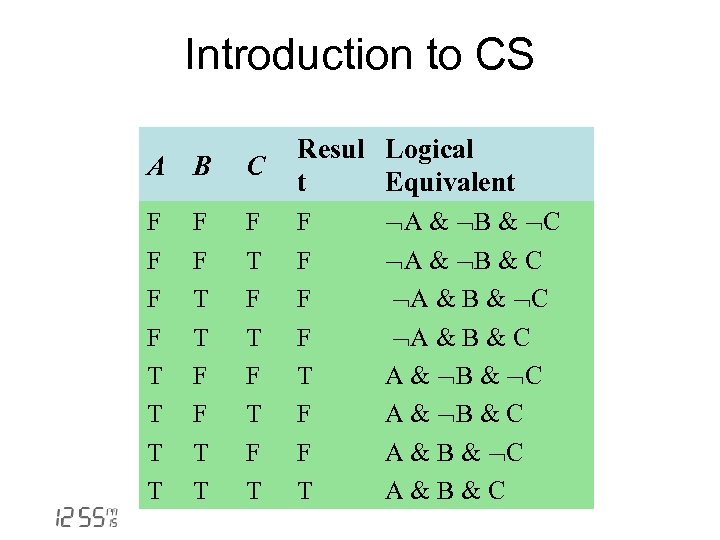 Introduction to CS A B C Resul Logical t Equivalent F F T T F T F T F F T T F F T T A & B & C A & B & C
Introduction to CS A B C Resul Logical t Equivalent F F T T F T F T F F T T F F T T A & B & C A & B & C
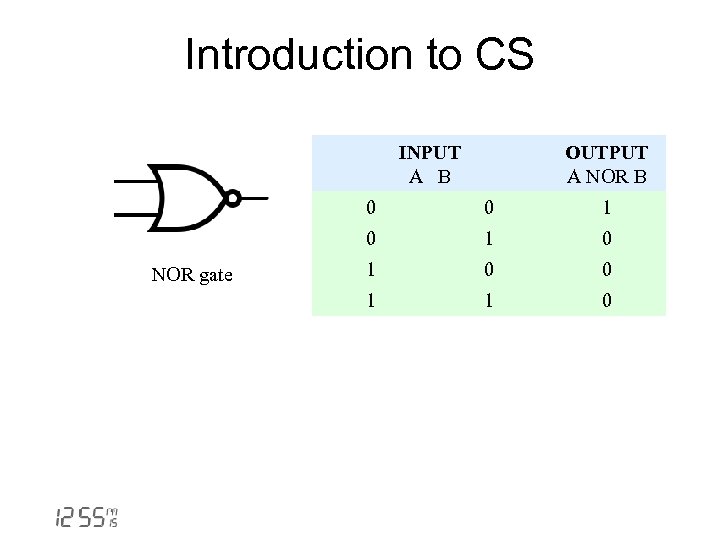 Introduction to CS INPUT A B OUTPUT A NOR B 0 1 0 NOR gate 0 1 0 0 1 1 0
Introduction to CS INPUT A B OUTPUT A NOR B 0 1 0 NOR gate 0 1 0 0 1 1 0
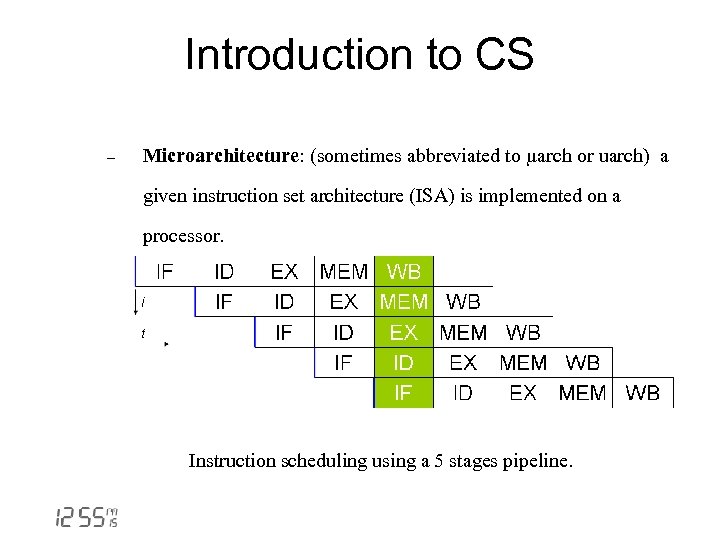 Introduction to CS - Microarchitecture: (sometimes abbreviated to µarch or uarch) a given instruction set architecture (ISA) is implemented on a processor. Instruction scheduling using a 5 stages pipeline.
Introduction to CS - Microarchitecture: (sometimes abbreviated to µarch or uarch) a given instruction set architecture (ISA) is implemented on a processor. Instruction scheduling using a 5 stages pipeline.
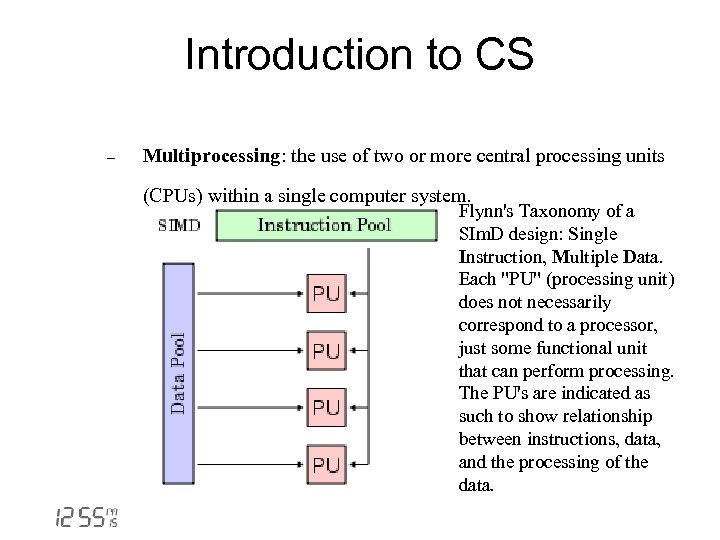 Introduction to CS - Multiprocessing: the use of two or more central processing units (CPUs) within a single computer system. Flynn's Taxonomy of a SIm. D design: Single Instruction, Multiple Data. Each "PU" (processing unit) does not necessarily correspond to a processor, just some functional unit that can perform processing. The PU's are indicated as such to show relationship between instructions, data, and the processing of the data.
Introduction to CS - Multiprocessing: the use of two or more central processing units (CPUs) within a single computer system. Flynn's Taxonomy of a SIm. D design: Single Instruction, Multiple Data. Each "PU" (processing unit) does not necessarily correspond to a processor, just some functional unit that can perform processing. The PU's are indicated as such to show relationship between instructions, data, and the processing of the data.
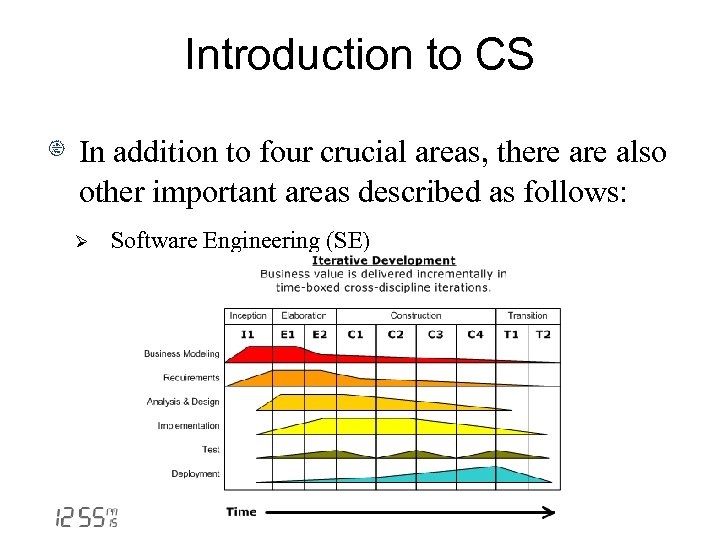 Introduction to CS In addition to four crucial areas, there also other important areas described as follows: Ø Software Engineering (SE)
Introduction to CS In addition to four crucial areas, there also other important areas described as follows: Ø Software Engineering (SE)
 Introduction to CS Ø Artificial Intelligence (AI) Machine Learning Natural Language Processing
Introduction to CS Ø Artificial Intelligence (AI) Machine Learning Natural Language Processing
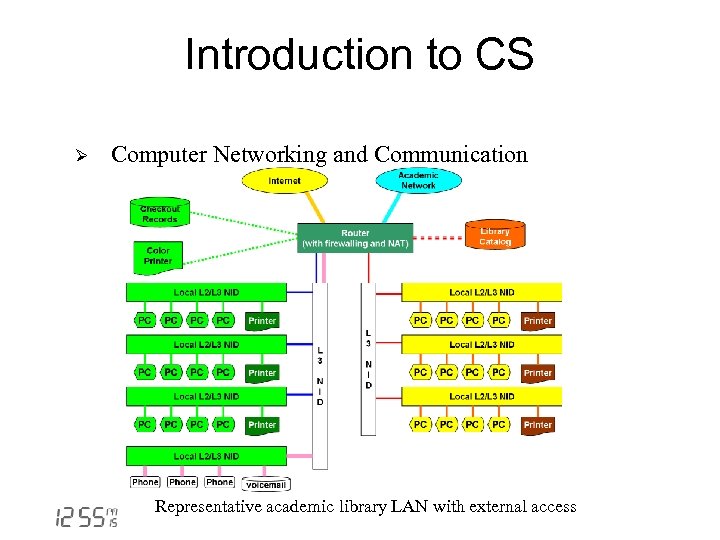 Introduction to CS Ø Computer Networking and Communication Representative academic library LAN with external access
Introduction to CS Ø Computer Networking and Communication Representative academic library LAN with external access
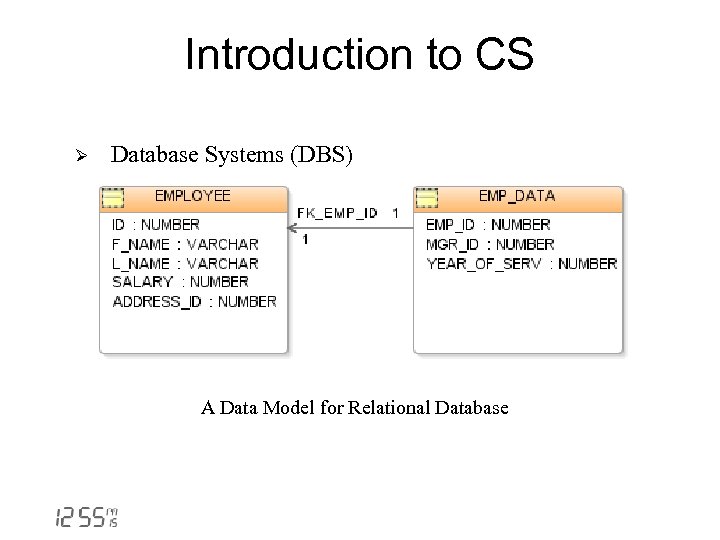 Introduction to CS Ø Database Systems (DBS) A Data Model for Relational Database
Introduction to CS Ø Database Systems (DBS) A Data Model for Relational Database
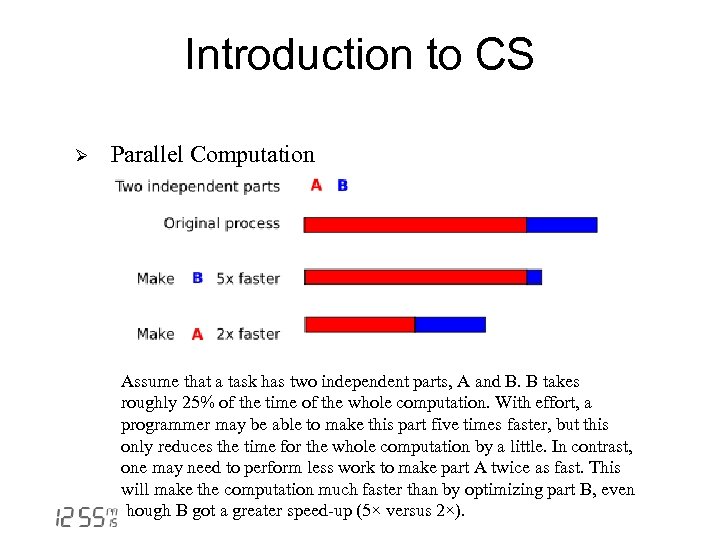 Introduction to CS Ø Parallel Computation Assume that a task has two independent parts, A and B. B takes roughly 25% of the time of the whole computation. With effort, a programmer may be able to make this part five times faster, but this only reduces the time for the whole computation by a little. In contrast, one may need to perform less work to make part A twice as fast. This will make the computation much faster than by optimizing part B, even though B got a greater speed-up (5× versus 2×).
Introduction to CS Ø Parallel Computation Assume that a task has two independent parts, A and B. B takes roughly 25% of the time of the whole computation. With effort, a programmer may be able to make this part five times faster, but this only reduces the time for the whole computation by a little. In contrast, one may need to perform less work to make part A twice as fast. This will make the computation much faster than by optimizing part B, even though B got a greater speed-up (5× versus 2×).
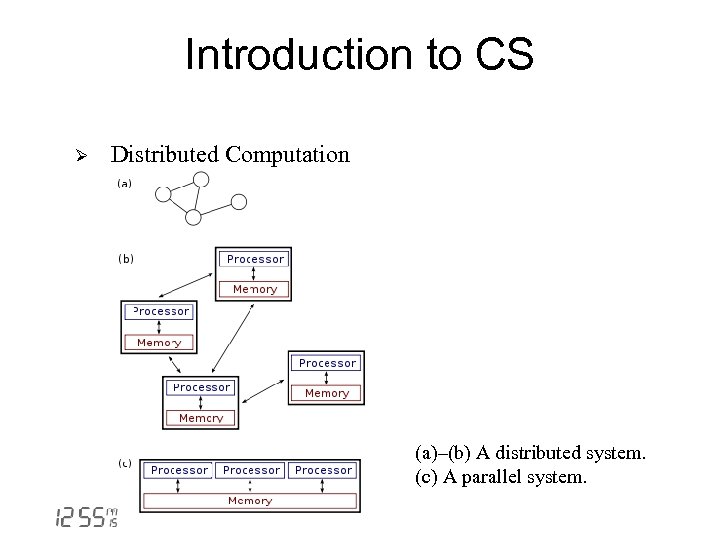 Introduction to CS Ø Distributed Computation (a)–(b) A distributed system. (c) A parallel system.
Introduction to CS Ø Distributed Computation (a)–(b) A distributed system. (c) A parallel system.
 Introduction to CS Ø Computer-Human Interaction Wacom Pen Tablet with Pen and mouse, Intuos 3 A 5
Introduction to CS Ø Computer-Human Interaction Wacom Pen Tablet with Pen and mouse, Intuos 3 A 5
 Introduction to CS Ø Computer Graphics A 3 D projection of a 5 -cell performing a double rotation about two orthogonal planes.
Introduction to CS Ø Computer Graphics A 3 D projection of a 5 -cell performing a double rotation about two orthogonal planes.
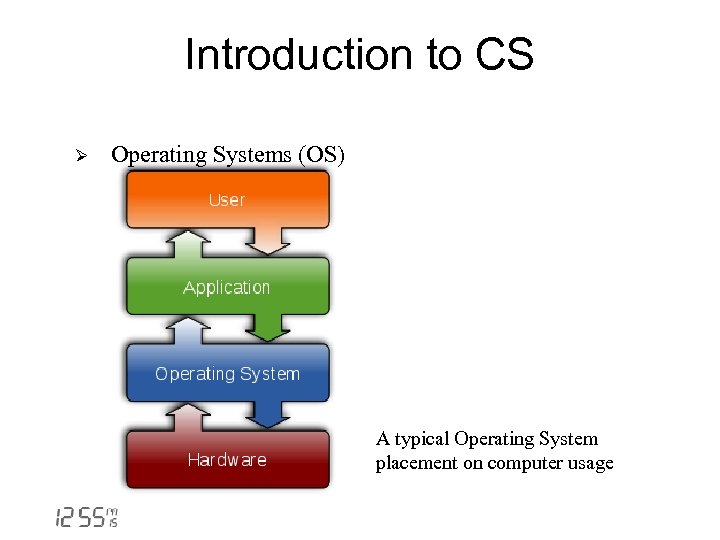 Introduction to CS Ø Operating Systems (OS) A typical Operating System placement on computer usage
Introduction to CS Ø Operating Systems (OS) A typical Operating System placement on computer usage
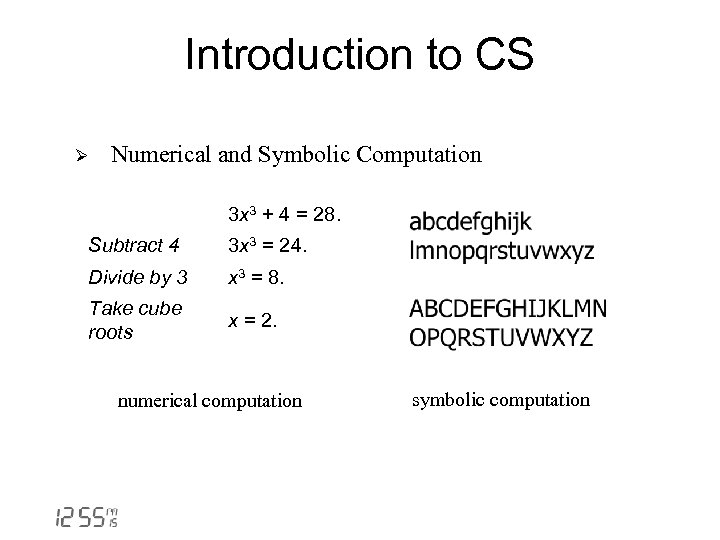 Introduction to CS Ø Numerical and Symbolic Computation 3 x 3 + 4 = 28. Subtract 4 3 x 3 = 24. Divide by 3 x 3 = 8. Take cube roots x = 2. numerical computation symbolic computation
Introduction to CS Ø Numerical and Symbolic Computation 3 x 3 + 4 = 28. Subtract 4 3 x 3 = 24. Divide by 3 x 3 = 8. Take cube roots x = 2. numerical computation symbolic computation
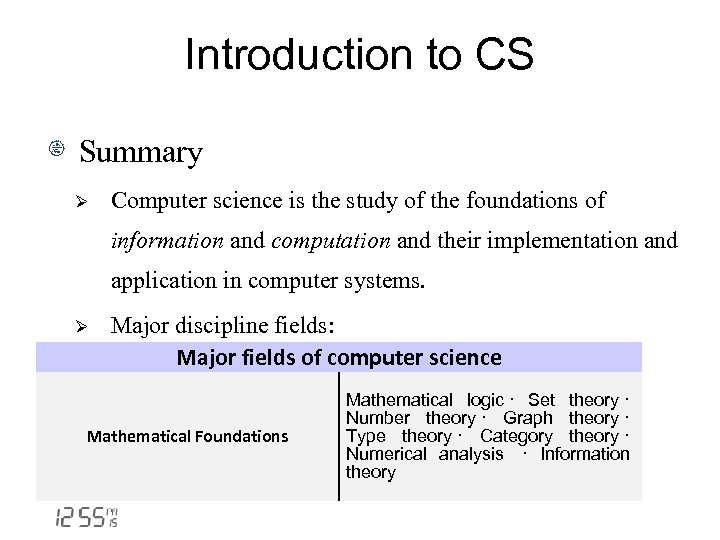 Introduction to CS Summary Ø Computer science is the study of the foundations of information and computation and their implementation and application in computer systems. Ø Major discipline fields: Major fields of computer science Mathematical Foundations Mathematical logic · Set theory · Number theory · Graph theory · Type theory · Category theory · Numerical analysis · Information theory
Introduction to CS Summary Ø Computer science is the study of the foundations of information and computation and their implementation and application in computer systems. Ø Major discipline fields: Major fields of computer science Mathematical Foundations Mathematical logic · Set theory · Number theory · Graph theory · Type theory · Category theory · Numerical analysis · Information theory
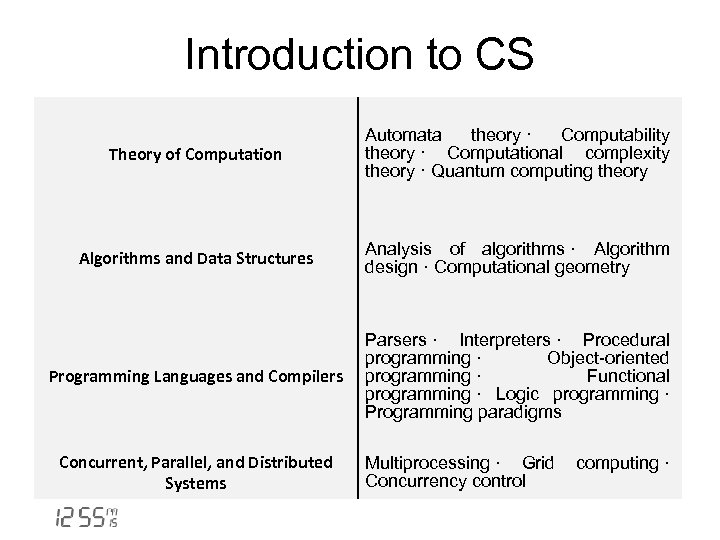 Introduction to CS Theory of Computation Automata theory · Computability theory · Computational complexity theory · Quantum computing theory Algorithms and Data Structures Analysis of algorithms · Algorithm design · Computational geometry Programming Languages and Compilers Parsers · Interpreters · Procedural programming · Object-oriented programming · Functional programming · Logic programming · Programming paradigms Concurrent, Parallel, and Distributed Systems Multiprocessing · Grid computing · Concurrency control
Introduction to CS Theory of Computation Automata theory · Computability theory · Computational complexity theory · Quantum computing theory Algorithms and Data Structures Analysis of algorithms · Algorithm design · Computational geometry Programming Languages and Compilers Parsers · Interpreters · Procedural programming · Object-oriented programming · Functional programming · Logic programming · Programming paradigms Concurrent, Parallel, and Distributed Systems Multiprocessing · Grid computing · Concurrency control
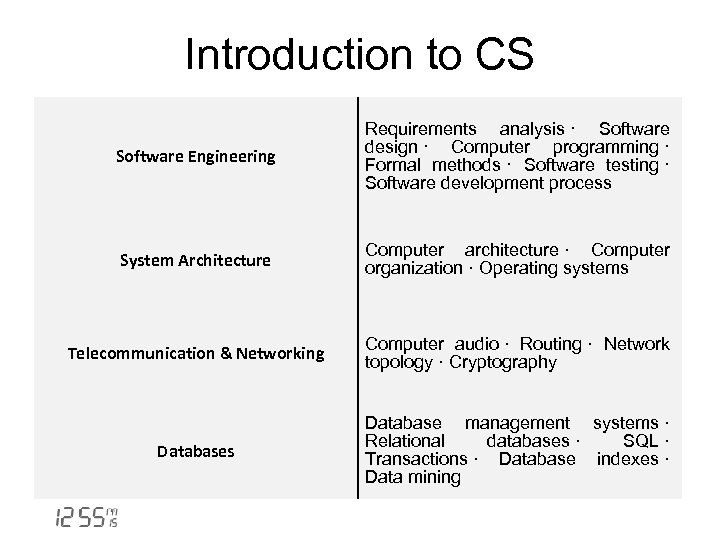 Introduction to CS Software Engineering Requirements analysis · Software design · Computer programming · Formal methods · Software testing · Software development process System Architecture Computer architecture · Computer organization · Operating systems Telecommunication & Networking Computer audio · Routing · Network topology · Cryptography Databases Database management systems · Relational databases · SQL · Transactions · Database indexes · Data mining
Introduction to CS Software Engineering Requirements analysis · Software design · Computer programming · Formal methods · Software testing · Software development process System Architecture Computer architecture · Computer organization · Operating systems Telecommunication & Networking Computer audio · Routing · Network topology · Cryptography Databases Database management systems · Relational databases · SQL · Transactions · Database indexes · Data mining
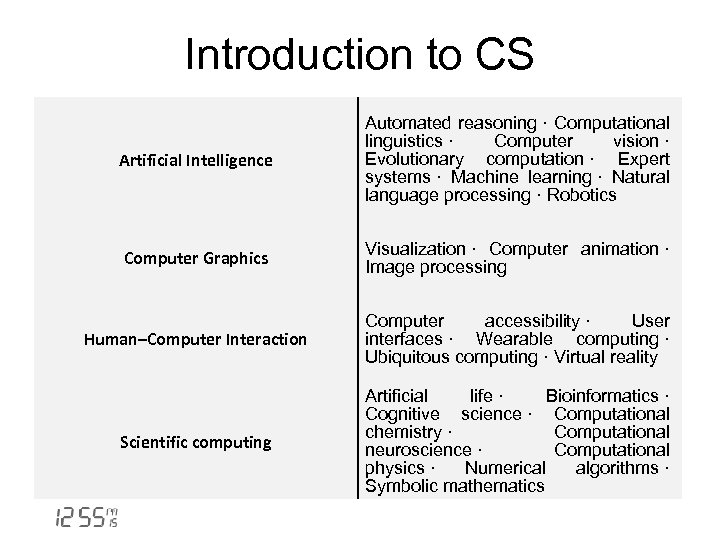 Introduction to CS Artificial Intelligence Automated reasoning · Computational linguistics · Computer vision · Evolutionary computation · Expert systems · Machine learning · Natural language processing · Robotics Computer Graphics Visualization · Computer animation · Image processing Human–Computer Interaction Computer accessibility · User interfaces · Wearable computing · Ubiquitous computing · Virtual reality Scientific computing Artificial life · Bioinformatics · Cognitive science · Computational chemistry · Computational neuroscience · Computational physics · Numerical algorithms · Symbolic mathematics
Introduction to CS Artificial Intelligence Automated reasoning · Computational linguistics · Computer vision · Evolutionary computation · Expert systems · Machine learning · Natural language processing · Robotics Computer Graphics Visualization · Computer animation · Image processing Human–Computer Interaction Computer accessibility · User interfaces · Wearable computing · Ubiquitous computing · Virtual reality Scientific computing Artificial life · Bioinformatics · Cognitive science · Computational chemistry · Computational neuroscience · Computational physics · Numerical algorithms · Symbolic mathematics
 Introduction to CS Reference Nell Dale, John Lewis. Computer Science Illuminated. Jones and Bartlett Publishers. 2002. ISBN 0 -7637 -1760 -6. http: //202. 120. 38. 156/PTM-Python/
Introduction to CS Reference Nell Dale, John Lewis. Computer Science Illuminated. Jones and Bartlett Publishers. 2002. ISBN 0 -7637 -1760 -6. http: //202. 120. 38. 156/PTM-Python/
 Introduction to Python What is Python Programming Language? Ø Python is a general-purpose high-level programming language whose design philosophy emphasizes code readability. Ø Python supports multiple programming paradigms, primarily but not limited to object oriented, imperative and, to a lesser extent, functional programming styles.
Introduction to Python What is Python Programming Language? Ø Python is a general-purpose high-level programming language whose design philosophy emphasizes code readability. Ø Python supports multiple programming paradigms, primarily but not limited to object oriented, imperative and, to a lesser extent, functional programming styles.
 Introduction to Python Ø Python aims to combine "remarkable power with very clear syntax", and its standard library is large and comprehensive. Ø Its use of indentation for block delimiters is unusual among popular programming languages.
Introduction to Python Ø Python aims to combine "remarkable power with very clear syntax", and its standard library is large and comprehensive. Ø Its use of indentation for block delimiters is unusual among popular programming languages.
 Introduction to Python Development of Python Ø Python was conceived in the late 1980 s and its implementation was started in December 1989 by Guido van Rossum at CWI (Centrum Wiskunde & Informatica) in the Netherlands.
Introduction to Python Development of Python Ø Python was conceived in the late 1980 s and its implementation was started in December 1989 by Guido van Rossum at CWI (Centrum Wiskunde & Informatica) in the Netherlands.
 Introduction to Python Ø Python 2. 0 was released on 16 October 2000, with many major new features including a full garbage collector and support for Unicode. Ø Python 3. 0, a major, backwards-incompatible release with Python 2. x, was released on 3 December 2008 after a long period of testing. Ø Many of its major features have been backported to the backwards-compatible Python 2. 7.
Introduction to Python Ø Python 2. 0 was released on 16 October 2000, with many major new features including a full garbage collector and support for Unicode. Ø Python 3. 0, a major, backwards-incompatible release with Python 2. x, was released on 3 December 2008 after a long period of testing. Ø Many of its major features have been backported to the backwards-compatible Python 2. 7.
 Introduction to Python Advantages of Python Ø Ø It's Object-Oriented: Python is an object-oriented language, from the ground up. Its class model supports advanced notions such as polymorphism, operator overloading, and multiple inheritance. It's Free: Python is freeware — something which has lately been come to be called open source software.
Introduction to Python Advantages of Python Ø Ø It's Object-Oriented: Python is an object-oriented language, from the ground up. Its class model supports advanced notions such as polymorphism, operator overloading, and multiple inheritance. It's Free: Python is freeware — something which has lately been come to be called open source software.
 Introduction to Python Ø It's Portable: Python is written in portable ANSI C, and compiles and runs on virtually every major platform in use today. Ø It's Powerful: Its tool set places it between traditional scripting languages (such as Tcl, Scheme, and Perl), and systems languages (such as C, C++, and Java).
Introduction to Python Ø It's Portable: Python is written in portable ANSI C, and compiles and runs on virtually every major platform in use today. Ø It's Powerful: Its tool set places it between traditional scripting languages (such as Tcl, Scheme, and Perl), and systems languages (such as C, C++, and Java).
 Introduction to Python Ø It's Mixable: Python programs can be easily "glued" to components written in other languages. Ø It's Easy to Use: as with other interpreted languages, Python executes programs immediately, which makes for both an interactive programming experience and rapid turnaround after program changes.
Introduction to Python Ø It's Mixable: Python programs can be easily "glued" to components written in other languages. Ø It's Easy to Use: as with other interpreted languages, Python executes programs immediately, which makes for both an interactive programming experience and rapid turnaround after program changes.
 Introduction to Python Ø It's Easy to Learn: In fact, you can expect to be coding significant Python programs in a matter of days (and perhaps in just hours, if you're already an experienced programmer).
Introduction to Python Ø It's Easy to Learn: In fact, you can expect to be coding significant Python programs in a matter of days (and perhaps in just hours, if you're already an experienced programmer).
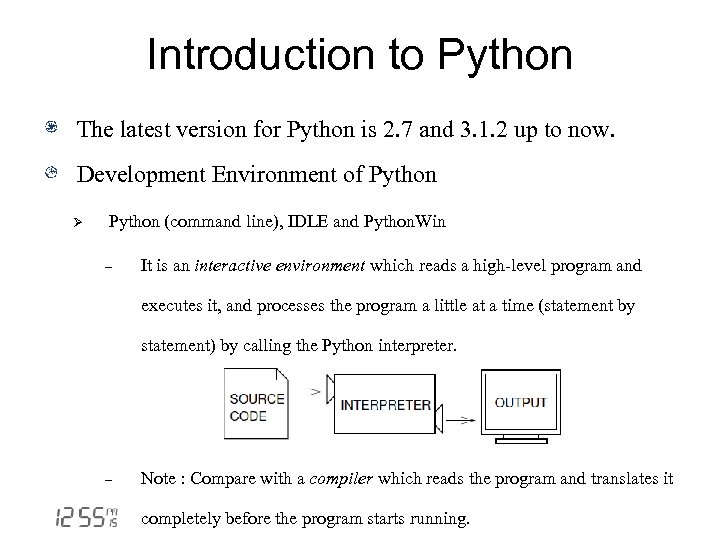 Introduction to Python The latest version for Python is 2. 7 and 3. 1. 2 up to now. Development Environment of Python Ø Python (command line), IDLE and Python. Win - It is an interactive environment which reads a high-level program and executes it, and processes the program a little at a time (statement by statement) by calling the Python interpreter. - Note : Compare with a compiler which reads the program and translates it completely before the program starts running.
Introduction to Python The latest version for Python is 2. 7 and 3. 1. 2 up to now. Development Environment of Python Ø Python (command line), IDLE and Python. Win - It is an interactive environment which reads a high-level program and executes it, and processes the program a little at a time (statement by statement) by calling the Python interpreter. - Note : Compare with a compiler which reads the program and translates it completely before the program starts running.
 Introduction to Python - Python under Windows
Introduction to Python - Python under Windows
 Introduction to Python The First Example (interactive mode) Ø Run Python (command line) and then see system information: Python 3. 1. 2 (r 312: 79149, Mar 20 2010, 22: 55: 39) [MSC v. 1500 64 bit (AMD 64)] on win 32 Type “help”, “copyright”, “credits” or “license” for more information. >>> Ø Input a statement after the prompt symbol and return: >>> print (“Hello, Everybody!”)
Introduction to Python The First Example (interactive mode) Ø Run Python (command line) and then see system information: Python 3. 1. 2 (r 312: 79149, Mar 20 2010, 22: 55: 39) [MSC v. 1500 64 bit (AMD 64)] on win 32 Type “help”, “copyright”, “credits” or “license” for more information. >>> Ø Input a statement after the prompt symbol and return: >>> print (“Hello, Everybody!”)
 Introduction to Python Ø The string is displayed on the screen: Hello, Everybody!
Introduction to Python Ø The string is displayed on the screen: Hello, Everybody!
 Introduction to Python The Second Example (module or script mode) Ø A module file is a text file, and you can create one using any environment for editing text. The. py extension of the text file indicates that this is a Python module. Ø The advantages of module or script mode is that we can saved it on a disk so that it can be used over and over again. On the other hand, it can be run like a compiled program. Especially it is suitable for large program.
Introduction to Python The Second Example (module or script mode) Ø A module file is a text file, and you can create one using any environment for editing text. The. py extension of the text file indicates that this is a Python module. Ø The advantages of module or script mode is that we can saved it on a disk so that it can be used over and over again. On the other hand, it can be run like a compiled program. Especially it is suitable for large program.
 Introduction to Python Ø A module file called chaos. py is shown as follows. Ø Chaos theory (混沌理论) is a field of study in mathematics, physics, economics and philosophy studying the behavior of dynamical systems that are highly sensitive to initial conditions.
Introduction to Python Ø A module file called chaos. py is shown as follows. Ø Chaos theory (混沌理论) is a field of study in mathematics, physics, economics and philosophy studying the behavior of dynamical systems that are highly sensitive to initial conditions.
 Introduction to Python # File: chaos. py # A simple program illustrating chaotic behavior. def main(): print ("This program illustrates a chaotic function“) x = input("Enter a number between 0 and 1: ") for i in range(10): x = 3. 9 * x * (1 - x) print (x) main()
Introduction to Python # File: chaos. py # A simple program illustrating chaotic behavior. def main(): print ("This program illustrates a chaotic function“) x = input("Enter a number between 0 and 1: ") for i in range(10): x = 3. 9 * x * (1 - x) print (x) main()
 Introduction to Python Ø You can use Run or Import function under Python. Win, and then select a module’s file name (chaos. py). Ø The running result is shown on the screen: This program illustrates a chaotic function Enter a number between 0: . 25 0. 73125 0. 76644140625 0. 698135010439 0. 82189581879 0. 570894019197
Introduction to Python Ø You can use Run or Import function under Python. Win, and then select a module’s file name (chaos. py). Ø The running result is shown on the screen: This program illustrates a chaotic function Enter a number between 0: . 25 0. 73125 0. 76644140625 0. 698135010439 0. 82189581879 0. 570894019197
 Introduction to Python 0. 955398748364 0. 166186721954 0. 540417912062 0. 9686289303 0. 118509010176
Introduction to Python 0. 955398748364 0. 166186721954 0. 540417912062 0. 9686289303 0. 118509010176
 Introduction to Python Summary Ø Python is a general-purpose high-level programming language. Ø Python supports multiple programming paradigms, primarily but not limited to object oriented, imperative, and functional programming styles. Ø Python aims to combine "remarkable power with very clear syntax", and its standard library is large and comprehensive.
Introduction to Python Summary Ø Python is a general-purpose high-level programming language. Ø Python supports multiple programming paradigms, primarily but not limited to object oriented, imperative, and functional programming styles. Ø Python aims to combine "remarkable power with very clear syntax", and its standard library is large and comprehensive.
 Introduction to Python Ø Its use of indentation for block delimiters is unusual among popular programming languages. Ø Python was conceived in the late 1980 s and its implementation was started in December 1989 by Guido van Rossum at CWI in the Netherlands. Ø Python’s advantages include object-oriented, free, portable, powerful, mixable, easy to use, and easy to learn properties. Ø Python. Win 2. 6. 4 is a perfect development environment for Python under Windows.
Introduction to Python Ø Its use of indentation for block delimiters is unusual among popular programming languages. Ø Python was conceived in the late 1980 s and its implementation was started in December 1989 by Guido van Rossum at CWI in the Netherlands. Ø Python’s advantages include object-oriented, free, portable, powerful, mixable, easy to use, and easy to learn properties. Ø Python. Win 2. 6. 4 is a perfect development environment for Python under Windows.


