aedb66d9d20f882d725a51c9d6309595.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 32
 Programming the Grid with Components Madhu Govindaraju Aleksander Slominski Dennis Gannon Sriram Krishnan Extreme! Computing Lab, Dept. of Computer Science, Indiana University 1
Programming the Grid with Components Madhu Govindaraju Aleksander Slominski Dennis Gannon Sriram Krishnan Extreme! Computing Lab, Dept. of Computer Science, Indiana University 1
 Outline • Software Components • XCAT – – Component and Services model Web Services Programming model OGSI Extreme! Computing Lab, Dept. of Computer Science, Indiana University 2
Outline • Software Components • XCAT – – Component and Services model Web Services Programming model OGSI Extreme! Computing Lab, Dept. of Computer Science, Indiana University 2
 Software Components • Analogy with hardware • Standard design paradigm for app development • Goal: to build applications by composition of well tested and well behaved subsystems (components). – simplify application design process – promote code reusability – plug and play Extreme! Computing Lab, Dept. of Computer Science, Indiana University 3
Software Components • Analogy with hardware • Standard design paradigm for app development • Goal: to build applications by composition of well tested and well behaved subsystems (components). – simplify application design process – promote code reusability – plug and play Extreme! Computing Lab, Dept. of Computer Science, Indiana University 3
 Component Architecture • A Component Architecture consists of two parts: – Components • software objects that implement a set of required behaviors – Frameworks • A runtime environment • A set of services used by components Extreme! Computing Lab, Dept. of Computer Science, Indiana University 4
Component Architecture • A Component Architecture consists of two parts: – Components • software objects that implement a set of required behaviors – Frameworks • A runtime environment • A set of services used by components Extreme! Computing Lab, Dept. of Computer Science, Indiana University 4
 Industry Standards • COM/DCOM – interoperability for Microsoft applications • Java Beans, Enterprise Java Beans (EJB) – Java based desktop and enterprise applications • OMG CORBA Component Model (CCM) – language neutral superset of EJB Extreme! Computing Lab, Dept. of Computer Science, Indiana University 5
Industry Standards • COM/DCOM – interoperability for Microsoft applications • Java Beans, Enterprise Java Beans (EJB) – Java based desktop and enterprise applications • OMG CORBA Component Model (CCM) – language neutral superset of EJB Extreme! Computing Lab, Dept. of Computer Science, Indiana University 5
 Academic Research • Sci. Run from Utah – scalable parallel applications and viz • Webflow from Syracuse – graphical composition palette • CCAT and XCAT from Indiana University – framework for Grid based applications Extreme! Computing Lab, Dept. of Computer Science, Indiana University 6
Academic Research • Sci. Run from Utah – scalable parallel applications and viz • Webflow from Syracuse – graphical composition palette • CCAT and XCAT from Indiana University – framework for Grid based applications Extreme! Computing Lab, Dept. of Computer Science, Indiana University 6
 CCA: Common Component Architecture § CCA: Initiative to define minimal specification for scientific components § Department of Energy (National Labs) § Few universities § Aim: build components for high performance computing § Draws ideas from CCM and other models as a baseline § Targeting § Parallel § Distributed Extreme! Computing Lab, Dept. of Computer Science, Indiana University 7
CCA: Common Component Architecture § CCA: Initiative to define minimal specification for scientific components § Department of Energy (National Labs) § Few universities § Aim: build components for high performance computing § Draws ideas from CCM and other models as a baseline § Targeting § Parallel § Distributed Extreme! Computing Lab, Dept. of Computer Science, Indiana University 7
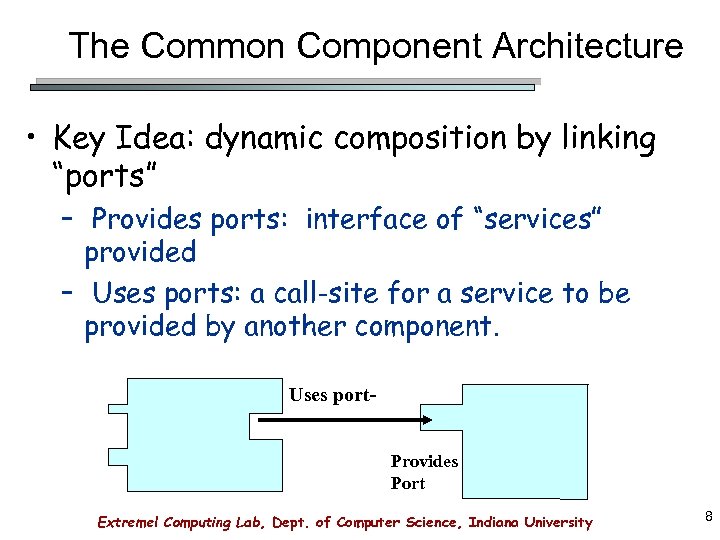 The Common Component Architecture • Key Idea: dynamic composition by linking “ports” – Provides ports: interface of “services” provided – Uses ports: a call-site for a service to be provided by another component. Uses port. Provides Port Extreme! Computing Lab, Dept. of Computer Science, Indiana University 8
The Common Component Architecture • Key Idea: dynamic composition by linking “ports” – Provides ports: interface of “services” provided – Uses ports: a call-site for a service to be provided by another component. Uses port. Provides Port Extreme! Computing Lab, Dept. of Computer Science, Indiana University 8
 What is new about CCA? • Minimal specification • Envision connections as dynamic – Can add, remove and connect ports at run-time • Tailored to build Problem Solving Environments – End user manipulates connections • Not specific to any underlying distributed object model • Notion of collective ports – logically one connection – implementation: multiple network connections Extreme! Computing Lab, Dept. of Computer Science, Indiana University 9
What is new about CCA? • Minimal specification • Envision connections as dynamic – Can add, remove and connect ports at run-time • Tailored to build Problem Solving Environments – End user manipulates connections • Not specific to any underlying distributed object model • Notion of collective ports – logically one connection – implementation: multiple network connections Extreme! Computing Lab, Dept. of Computer Science, Indiana University 9
 Components on the Grid: Issues • • • Discovering static information about components Launching components Discovering references for running instances Communication protocols Messages and Events Authentication and Authorization Encapsulating legacy applications Efficient scheduling Run-time environment Extreme! Computing Lab, Dept. of Computer Science, Indiana University 10
Components on the Grid: Issues • • • Discovering static information about components Launching components Discovering references for running instances Communication protocols Messages and Events Authentication and Authorization Encapsulating legacy applications Efficient scheduling Run-time environment Extreme! Computing Lab, Dept. of Computer Science, Indiana University 10
 Grid Programming Model: Needs • Need a set of APIs, protocols, libraries and tools that allow access to Grid resources • Examples: Globus, Condor – provide infrastructure – do not provide programming model • What is missing? – How can we make it easier to “program” the Grid? Extreme! Computing Lab, Dept. of Computer Science, Indiana University 11
Grid Programming Model: Needs • Need a set of APIs, protocols, libraries and tools that allow access to Grid resources • Examples: Globus, Condor – provide infrastructure – do not provide programming model • What is missing? – How can we make it easier to “program” the Grid? Extreme! Computing Lab, Dept. of Computer Science, Indiana University 11
 XCAT • Implementation of the CCA specification • Designed for distributed applications • Allows creation of Grid application from components • Wraps Grid Services as components • Test-bed for CCA – Is there an alternative to OMG IDL? Extreme! Computing Lab, Dept. of Computer Science, Indiana University 12
XCAT • Implementation of the CCA specification • Designed for distributed applications • Allows creation of Grid application from components • Wraps Grid Services as components • Test-bed for CCA – Is there an alternative to OMG IDL? Extreme! Computing Lab, Dept. of Computer Science, Indiana University 12
 Component Communication • How do components communicate? – Use Remote Procedure Call (RPC) Mechanism • XCAT uses SOAP 1. 1 • XCAT ports can serve as web services – Events/Messages • Objects encoded as XML documents Extreme! Computing Lab, Dept. of Computer Science, Indiana University 13
Component Communication • How do components communicate? – Use Remote Procedure Call (RPC) Mechanism • XCAT uses SOAP 1. 1 • XCAT ports can serve as web services – Events/Messages • Objects encoded as XML documents Extreme! Computing Lab, Dept. of Computer Science, Indiana University 13
 XCAT Services Architecture • Default services for all components • XCAT services – Directory • locate components based on port types and other attributes – Registry • locate running instances of components – Creation • create running instance of a component – Connection • connect ports of two running instances – Events • publish/subscribe framework for messages Extreme! Computing Lab, Dept. of Computer Science, Indiana University 14
XCAT Services Architecture • Default services for all components • XCAT services – Directory • locate components based on port types and other attributes – Registry • locate running instances of components – Creation • create running instance of a component – Connection • connect ports of two running instances – Events • publish/subscribe framework for messages Extreme! Computing Lab, Dept. of Computer Science, Indiana University 14
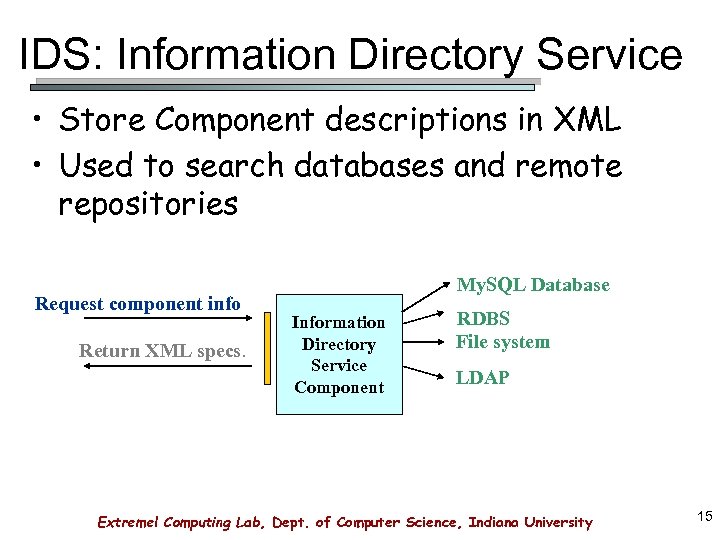 IDS: Information Directory Service • Store Component descriptions in XML • Used to search databases and remote repositories Request component info Return XML specs. My. SQL Database Information Directory Service Component RDBS File system LDAP Extreme! Computing Lab, Dept. of Computer Science, Indiana University 15
IDS: Information Directory Service • Store Component descriptions in XML • Used to search databases and remote repositories Request component info Return XML specs. My. SQL Database Information Directory Service Component RDBS File system LDAP Extreme! Computing Lab, Dept. of Computer Science, Indiana University 15
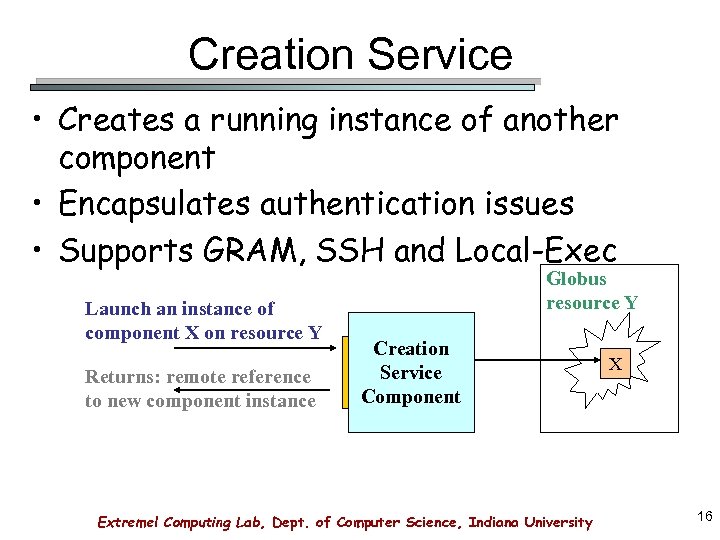 Creation Service • Creates a running instance of another component • Encapsulates authentication issues • Supports GRAM, SSH and Local-Exec Launch an instance of component X on resource Y Returns: remote reference to new component instance Globus resource Y Creation Service Component Extreme! Computing Lab, Dept. of Computer Science, Indiana University X 16
Creation Service • Creates a running instance of another component • Encapsulates authentication issues • Supports GRAM, SSH and Local-Exec Launch an instance of component X on resource Y Returns: remote reference to new component instance Globus resource Y Creation Service Component Extreme! Computing Lab, Dept. of Computer Science, Indiana University X 16
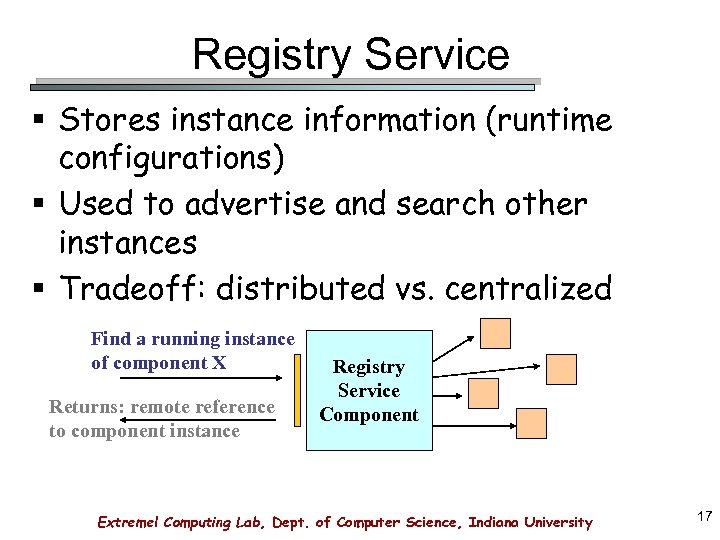 Registry Service § Stores instance information (runtime configurations) § Used to advertise and search other instances § Tradeoff: distributed vs. centralized Find a running instance of component X Returns: remote reference to component instance Registry Service Component Extreme! Computing Lab, Dept. of Computer Science, Indiana University 17
Registry Service § Stores instance information (runtime configurations) § Used to advertise and search other instances § Tradeoff: distributed vs. centralized Find a running instance of component X Returns: remote reference to component instance Registry Service Component Extreme! Computing Lab, Dept. of Computer Science, Indiana University 17
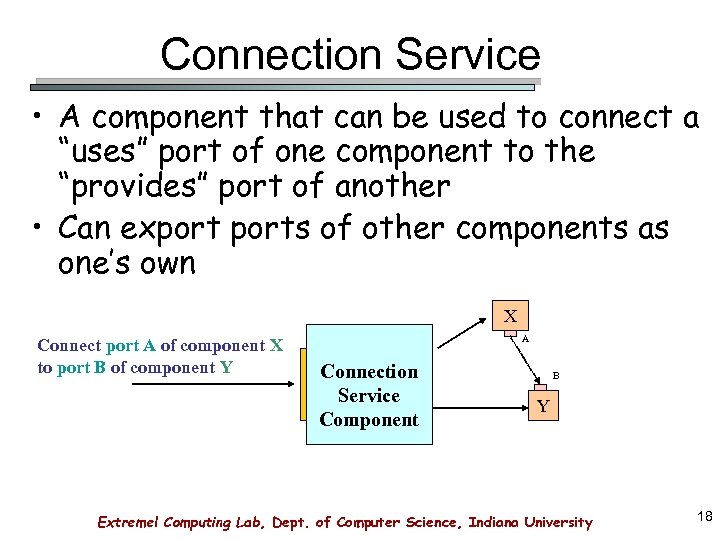 Connection Service • A component that can be used to connect a “uses” port of one component to the “provides” port of another • Can exports of other components as one’s own X Connect port A of component X to port B of component Y A Connection Service Component B Y Extreme! Computing Lab, Dept. of Computer Science, Indiana University 18
Connection Service • A component that can be used to connect a “uses” port of one component to the “provides” port of another • Can exports of other components as one’s own X Connect port A of component X to port B of component Y A Connection Service Component B Y Extreme! Computing Lab, Dept. of Computer Science, Indiana University 18
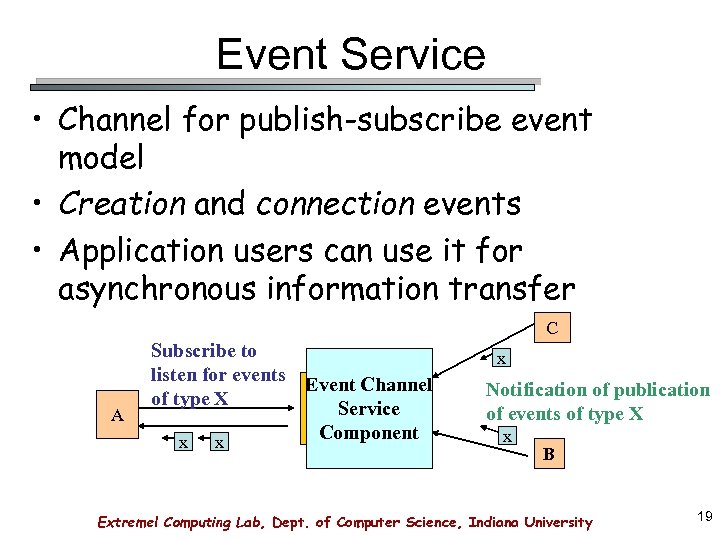 Event Service • Channel for publish-subscribe event model • Creation and connection events • Application users can use it for asynchronous information transfer C A Subscribe to listen for events Event Channel of type X Service Component x x x Notification of publication of events of type X x B Extreme! Computing Lab, Dept. of Computer Science, Indiana University 19
Event Service • Channel for publish-subscribe event model • Creation and connection events • Application users can use it for asynchronous information transfer C A Subscribe to listen for events Event Channel of type X Service Component x x x Notification of publication of events of type X x B Extreme! Computing Lab, Dept. of Computer Science, Indiana University 19
 Features of Events • Event/Notification Services are an essential part of all distributed systems • Application Events – “I am done. ” “I just wrote to a file, ” “here is a result. ” • Event Publishers & Listeners – Some Listeners subscribe, others poll – Must have persistent event channels • record events for later analysis • application history logs • allow for retrieval in chunks Extreme! Computing Lab, Dept. of Computer Science, Indiana University 20
Features of Events • Event/Notification Services are an essential part of all distributed systems • Application Events – “I am done. ” “I just wrote to a file, ” “here is a result. ” • Event Publishers & Listeners – Some Listeners subscribe, others poll – Must have persistent event channels • record events for later analysis • application history logs • allow for retrieval in chunks Extreme! Computing Lab, Dept. of Computer Science, Indiana University 20
 XCAT: Other Features • Security: – – Every remote method call is intercepted port, method and parameter level authentication based on SSL authorization based on simple ACL • Component Handle: – in XML and can be converted to WSDL – GSH /GSR • Exceptions – Supports throw and catch across components Extreme! Computing Lab, Dept. of Computer Science, Indiana University 21
XCAT: Other Features • Security: – – Every remote method call is intercepted port, method and parameter level authentication based on SSL authorization based on simple ACL • Component Handle: – in XML and can be converted to WSDL – GSH /GSR • Exceptions – Supports throw and catch across components Extreme! Computing Lab, Dept. of Computer Science, Indiana University 21
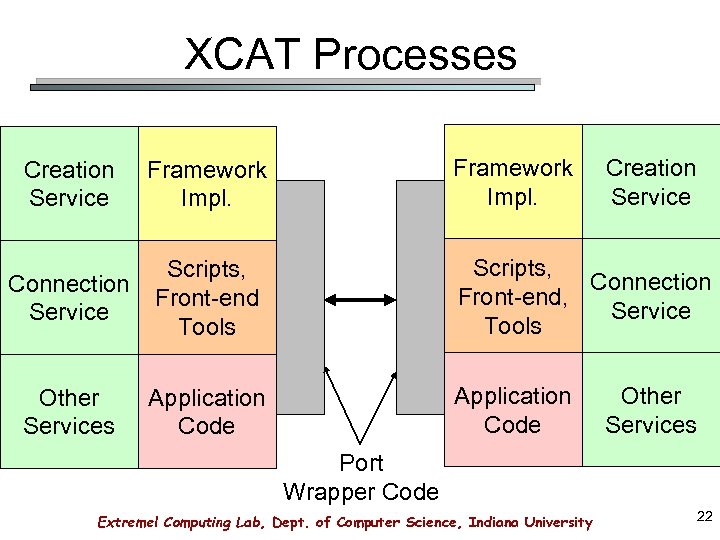 XCAT Processes Framework Impl. Creation Service Framework Impl. Connection Service Scripts, Front-end Tools Scripts, Connection Front-end, Service Tools Other Services Application Code Other Services Port Wrapper Code Extreme! Computing Lab, Dept. of Computer Science, Indiana University 22
XCAT Processes Framework Impl. Creation Service Framework Impl. Connection Service Scripts, Front-end Tools Scripts, Connection Front-end, Service Tools Other Services Application Code Other Services Port Wrapper Code Extreme! Computing Lab, Dept. of Computer Science, Indiana University 22
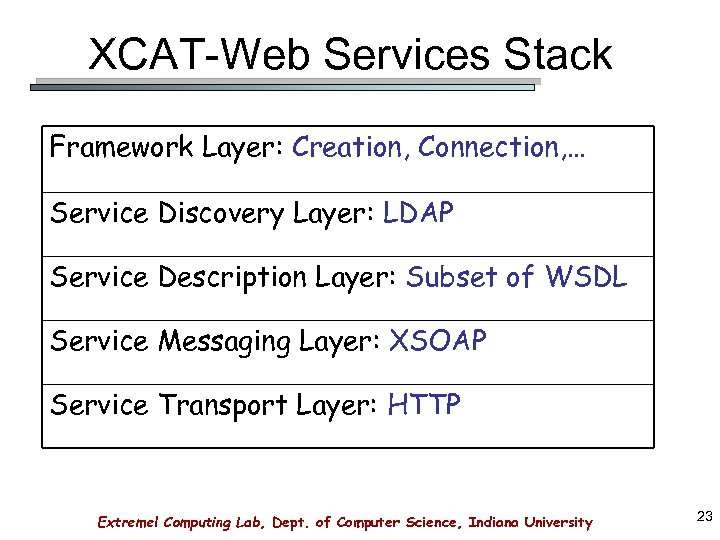 XCAT-Web Services Stack Framework Layer: Creation, Connection, … Service Discovery Layer: LDAP Service Description Layer: Subset of WSDL Service Messaging Layer: XSOAP Service Transport Layer: HTTP Extreme! Computing Lab, Dept. of Computer Science, Indiana University 23
XCAT-Web Services Stack Framework Layer: Creation, Connection, … Service Discovery Layer: LDAP Service Description Layer: Subset of WSDL Service Messaging Layer: XSOAP Service Transport Layer: HTTP Extreme! Computing Lab, Dept. of Computer Science, Indiana University 23
 XCAT Programming: Examples • Builder: A tool used to select and link components together • Builder Options – Swing based GUI – Jython scripting – Portal • XCAT – Jython scripting Extreme! Computing Lab, Dept. of Computer Science, Indiana University 24
XCAT Programming: Examples • Builder: A tool used to select and link components together • Builder Options – Swing based GUI – Jython scripting – Portal • XCAT – Jython scripting Extreme! Computing Lab, Dept. of Computer Science, Indiana University 24
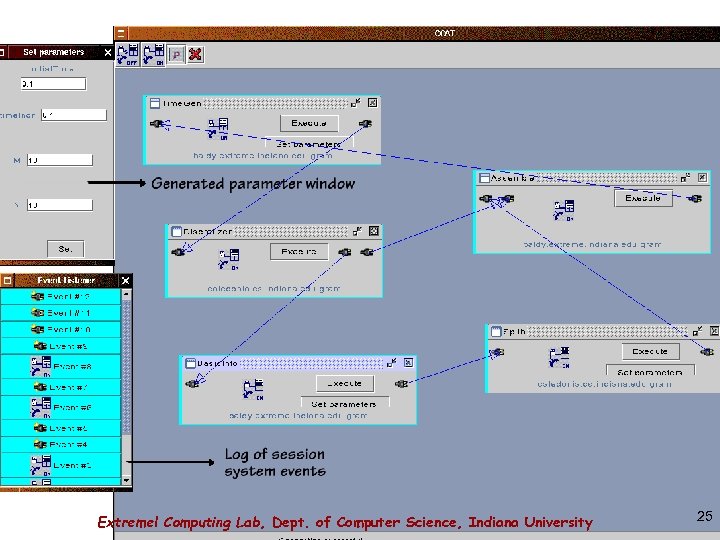 CCAT Gui image Extreme! Computing Lab, Dept. of Computer Science, Indiana University 25
CCAT Gui image Extreme! Computing Lab, Dept. of Computer Science, Indiana University 25
 Scripting XCAT Applications import xcat string. Dump = xcat. create. Component(‘String. Dump’) printer = xcat. create. Component(‘Printer’) xcat. set. Creation. Mechanism(string. Dump, ‘gram’) xcat. set. Creation. Mechanism(printer, ‘ssh’) xcat. set. Machine. Name(string. Dump, “exodus”) xcat. set. Machine. Name(printer, “rainier”) Extreme! Computing Lab, Dept. of Computer Science, Indiana University 26
Scripting XCAT Applications import xcat string. Dump = xcat. create. Component(‘String. Dump’) printer = xcat. create. Component(‘Printer’) xcat. set. Creation. Mechanism(string. Dump, ‘gram’) xcat. set. Creation. Mechanism(printer, ‘ssh’) xcat. set. Machine. Name(string. Dump, “exodus”) xcat. set. Machine. Name(printer, “rainier”) Extreme! Computing Lab, Dept. of Computer Science, Indiana University 26
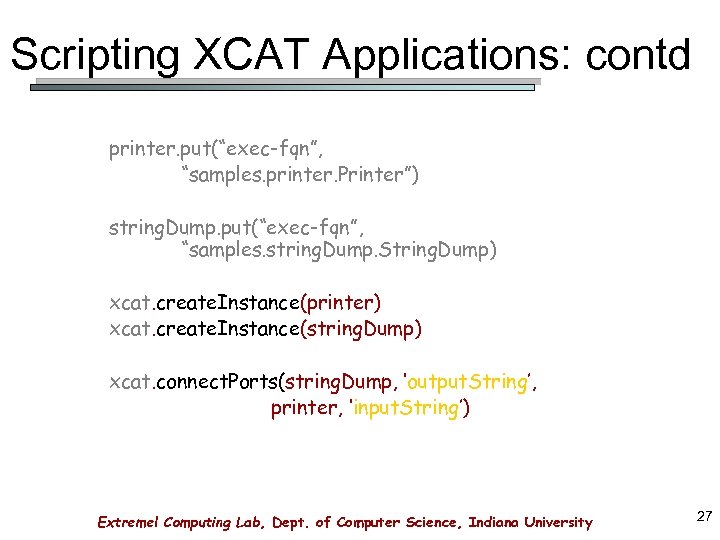 Scripting XCAT Applications: contd printer. put(“exec-fqn”, “samples. printer. Printer”) string. Dump. put(“exec-fqn”, “samples. string. Dump. String. Dump) xcat. create. Instance(printer) xcat. create. Instance(string. Dump) xcat. connect. Ports(string. Dump, ‘output. String’, printer, ‘input. String’) Extreme! Computing Lab, Dept. of Computer Science, Indiana University 27
Scripting XCAT Applications: contd printer. put(“exec-fqn”, “samples. printer. Printer”) string. Dump. put(“exec-fqn”, “samples. string. Dump. String. Dump) xcat. create. Instance(printer) xcat. create. Instance(string. Dump) xcat. connect. Ports(string. Dump, ‘output. String’, printer, ‘input. String’) Extreme! Computing Lab, Dept. of Computer Science, Indiana University 27
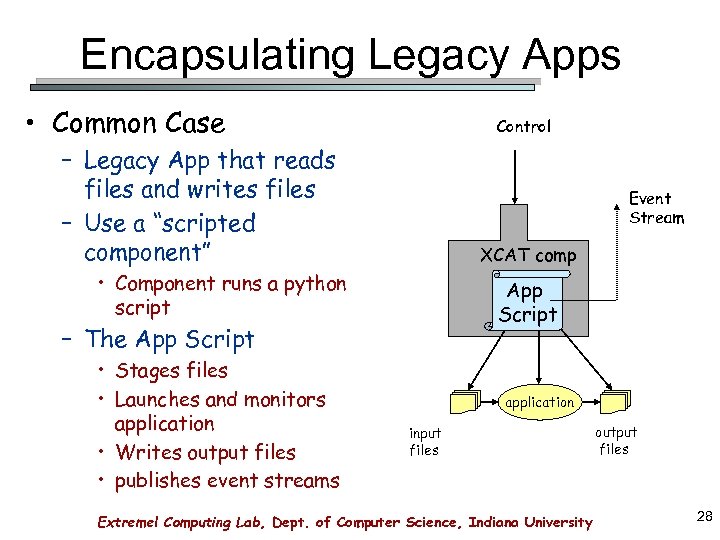 Encapsulating Legacy Apps • Common Case Control – Legacy App that reads files and writes files – Use a “scripted component” Event Stream XCAT comp • Component runs a python script App Script – The App Script • Stages files • Launches and monitors application • Writes output files • publishes event streams application input files Extreme! Computing Lab, Dept. of Computer Science, Indiana University output files 28
Encapsulating Legacy Apps • Common Case Control – Legacy App that reads files and writes files – Use a “scripted component” Event Stream XCAT comp • Component runs a python script App Script – The App Script • Stages files • Launches and monitors application • Writes output files • publishes event streams application input files Extreme! Computing Lab, Dept. of Computer Science, Indiana University output files 28
 Scripting Grid Computations • Grid Scripts are executable documents that – Orchestrate Computations • • • Select resources Supply application parameters and launch remote jobs Subscribe to event streams Create components Connect components Extreme! Computing Lab, Dept. of Computer Science, Indiana University 29
Scripting Grid Computations • Grid Scripts are executable documents that – Orchestrate Computations • • • Select resources Supply application parameters and launch remote jobs Subscribe to event streams Create components Connect components Extreme! Computing Lab, Dept. of Computer Science, Indiana University 29
 Composition Using Components • Two ways of composing applications – Composition in space: • one component/service directly invokes the services of another – Composition in time: • A workflow engine schedules tasks that involve accessing remote services and responding to events Extreme! Computing Lab, Dept. of Computer Science, Indiana University 30
Composition Using Components • Two ways of composing applications – Composition in space: • one component/service directly invokes the services of another – Composition in time: • A workflow engine schedules tasks that involve accessing remote services and responding to events Extreme! Computing Lab, Dept. of Computer Science, Indiana University 30
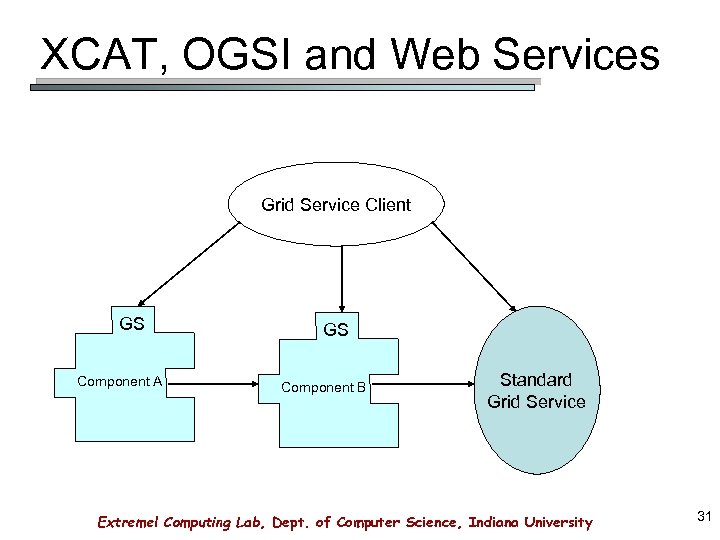 XCAT, OGSI and Web Services Grid Service Client GS Component A GS Component B Standard Grid Service Extreme! Computing Lab, Dept. of Computer Science, Indiana University 31
XCAT, OGSI and Web Services Grid Service Client GS Component A GS Component B Standard Grid Service Extreme! Computing Lab, Dept. of Computer Science, Indiana University 31
 XCAT and OGSI compliance • Add a Grid. Service port to each component • Merge component handle with GSH/GSR • OGSI messaging is non-reliable push model – XCAT has a reliable, persistent model • OGSI has factory port. Type for instantiating new services – XCAT has an extended distributed factory model Extreme! Computing Lab, Dept. of Computer Science, Indiana University 32
XCAT and OGSI compliance • Add a Grid. Service port to each component • Merge component handle with GSH/GSR • OGSI messaging is non-reliable push model – XCAT has a reliable, persistent model • OGSI has factory port. Type for instantiating new services – XCAT has an extended distributed factory model Extreme! Computing Lab, Dept. of Computer Science, Indiana University 32


