16951801094811f43849c5139b474630.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 23
Programming Scientific and Distributed Workflow with Triana Services Matthew Shields, GGF 10 Workflow Workshop, 9 th March
Presentation Outline Triana Overview Triana services and their distribution Distribution policies The GAP interface and its relation to the Gridlab GAT Scientific Workflow Binary Inspiral Algorithm Example Dynamic Distributed Workflow Service Composition on the Grid Service Usage, dynamically distributing a Triana workflow Conclusion Matthew Shields, Cardiff University
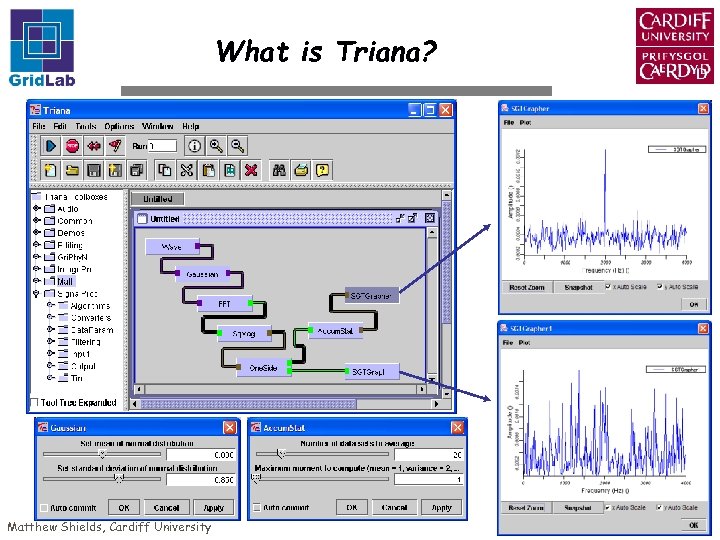
What is Triana? Matthew Shields, Cardiff University
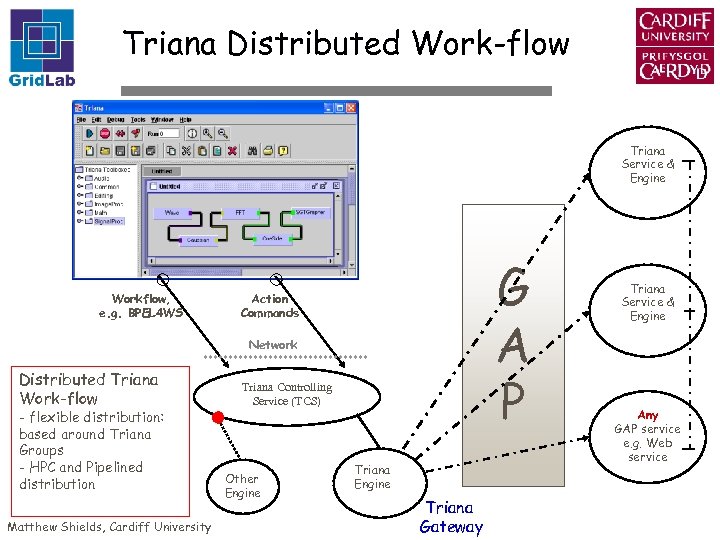
Triana Distributed Work-flow Triana Service & Engine Workflow, e. g. BPEL 4 WS G A P Action Commands Network Distributed Triana Work-flow - flexible distribution: based around Triana Groups - HPC and Pipelined distribution Matthew Shields, Cardiff University Triana Controlling Service (TCS) Other Engine Triana Gateway Triana Service & Engine Any GAP service e. g. Web service
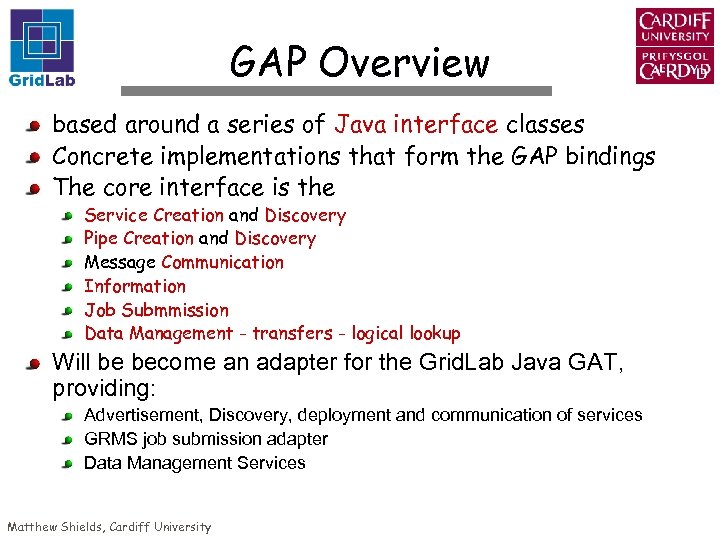
GAP Overview based around a series of Java interface classes Concrete implementations that form the GAP bindings The core interface is the Service Creation and Discovery Pipe Creation and Discovery Message Communication Information Job Submmission Data Management - transfers - logical lookup Will be become an adapter for the Grid. Lab Java GAT, providing: Advertisement, Discovery, deployment and communication of services GRMS job submission adapter Data Management Services Matthew Shields, Cardiff University
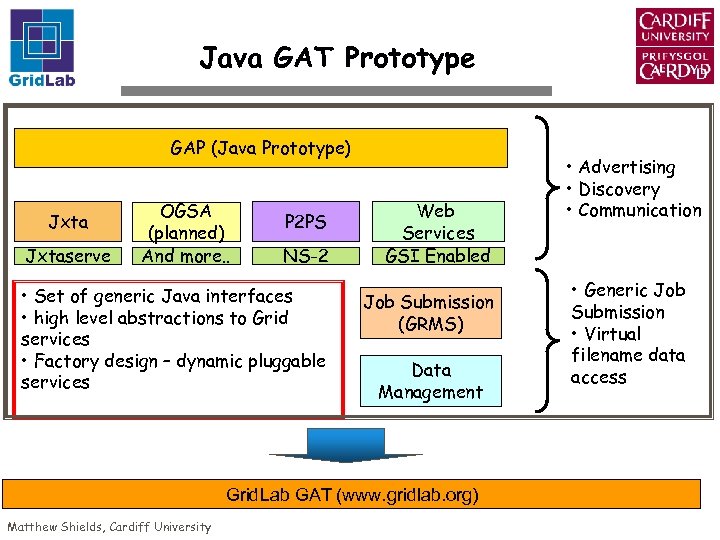
Java GAT Prototype GAP (Java Prototype) Jxtaserve OGSA (planned) And more. . P 2 PS NS-2 • Set of generic Java interfaces • high level abstractions to Grid services • Factory design – dynamic pluggable services Web Services GSI Enabled Job Submission (GRMS) Data Management Grid. Lab GAT (www. gridlab. org) Matthew Shields, Cardiff University • Advertising • Discovery • Communication • Generic Job Submission • Virtual filename data access
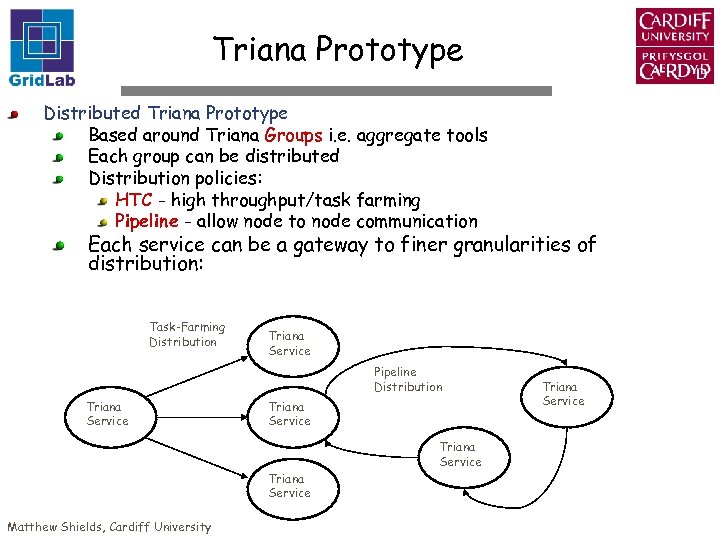
Triana Prototype Distributed Triana Prototype Based around Triana Groups i. e. aggregate tools Each group can be distributed Distribution policies: HTC - high throughput/task farming Pipeline - allow node to node communication Each service can be a gateway to finer granularities of distribution: Task-Farming Distribution Triana Service Pipeline Distribution Triana Service Matthew Shields, Cardiff University Triana Service
Triana Workflow Triana is inherently flow based Data flow - data arriving at component triggers execution Control flow - control commands trigger execution Decentralised execution Data or Control messages sent along communication “pipes” from sender to receiver causes receiver to execute Synchronous or Asynchronous messaging (Implementation dependant) Multiple inputs can block or trigger immediately (Component designer defined) Matthew Shields, Cardiff University
Components and Definitions Component is unit of execution Components are defined in XML files: Naming information Input and output ports Parameter information Why Components? To simplify the application design process and to speed up application development The component model provides an infrastructure for the interaction of components Matthew Shields, Cardiff University
Taskgraph Internal object based workflow graph representation Taskgraph - DAG Tasks Connections External XML representation Simple XML syntax List of participating Task definitions Parent/Child connection Hierarchical (Compound components) Alternative Languages & Syntax e. g. BPEL 4 WS Available through pluggable readers & writers. Matthew Shields, Cardiff University
Workflow No explicit language support for control constructs Loops and execution branching handled by components Loop component - controls loop over sub-workflow Logical component - control workflow branching Unlike BPEL 4 WS or similar Flexibility of control - constraint based loops etc… Matthew Shields, Cardiff University
Distributing Triana Workflow Deploying Remote Services on Resources Service application installation Service execution Service discovery Mapping tasks or groups of tasks to Services Workflow rewiring, XML definition for connections modified for remote location - sub-workflows duplicated Data distribution, annotated sub-sections of taskgraph passed to resources Matthew Shields, Cardiff University

GEO 600 Inspiral Search Background Compact binary stars orbiting each other in a close orbit among the most powerful sources of gravitational waves As the orbital radius decreases a characteristic chirp waveform is produced - amplitude and frequency increase with time until eventually the two bodies merge together Computing Need 10 Gigaflops to keep up with real time data (modest search. . ) Data 8 k. Hz in 24 -bit resolution (stored in 4 bytes) -> Signal contained within 1 k. Hz = 2000 samples/second divided into chunks of 15 minutes in duration (i. e. 900 seconds) = 8 MB Algorithm Data is transmitted to a node Node initialises i. e. generates its templates (around 10000) fast correlates its templates with data Matthew Shields, Cardiff University
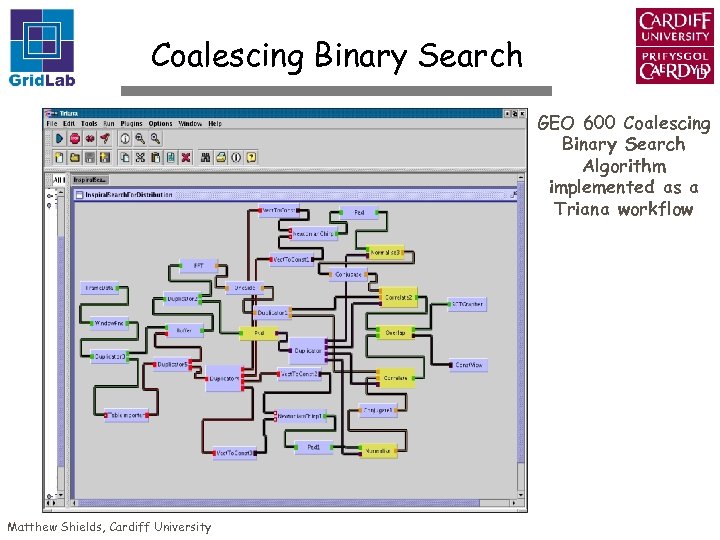
Coalescing Binary Search GEO 600 Coalescing Binary Search Algorithm implemented as a Triana workflow Matthew Shields, Cardiff University
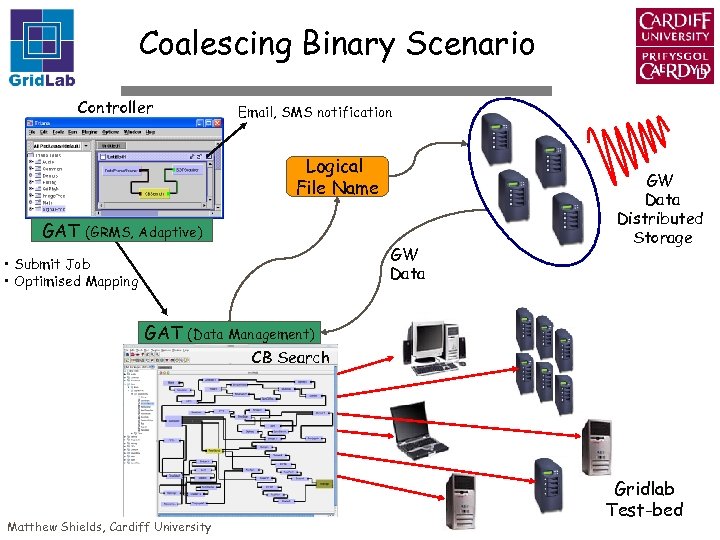
Coalescing Binary Scenario Controller Email, SMS notification Logical File Name GAT (GRMS, Adaptive) GW Data • Submit Job • Optimised Mapping GAT GW Data Distributed Storage (Data Management) CB Search Matthew Shields, Cardiff University Gridlab Test-bed
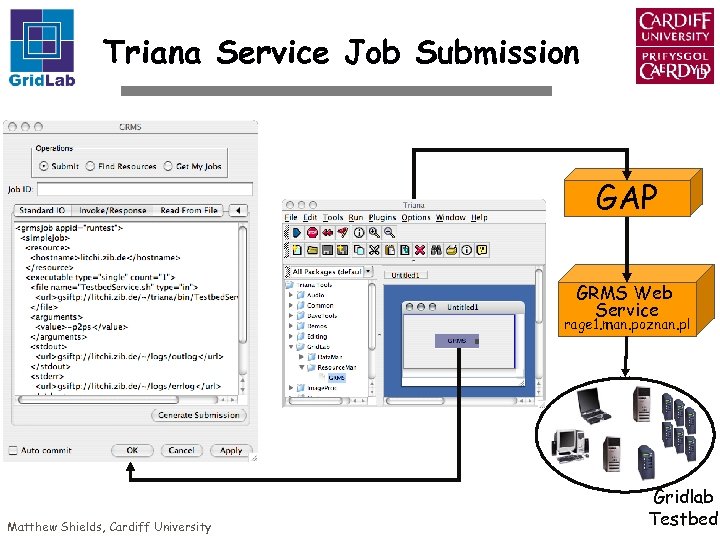
Triana Service Job Submission GAP GRMS Web Service rage 1. man. poznan. pl Matthew Shields, Cardiff University Gridlab Testbed

Triana GRMS Component Front end to Grid. Lab GRMS Web Service Job Submission Service - interfaces with GRAM GAP Web Service binding + GSI Authentication Java Co. G Kit X 509 Certificate handling Axis authentication & communication GRMS executes applications on Grid. Lab Testbed Heterogeneous hardware platforms Default software - Globus 2. 4, GSISSH, cc, cvs, c++, F 90, make, perl, mpicc Matthew Shields, Cardiff University
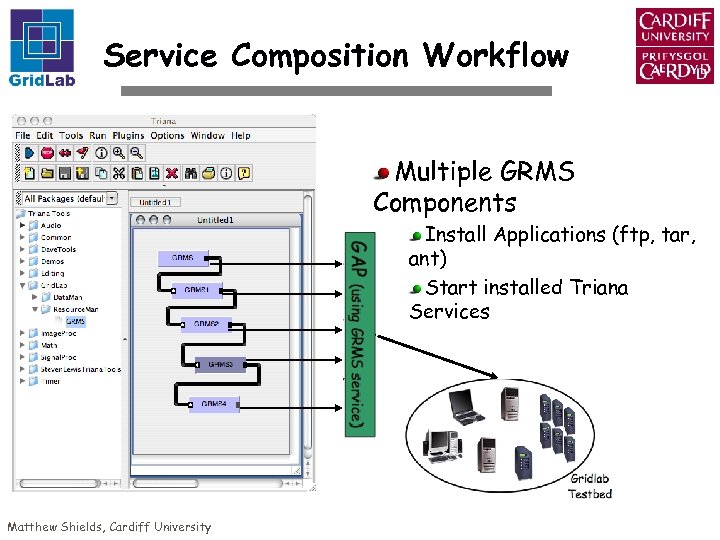
Service Composition Workflow Multiple GRMS Components Install Applications (ftp, tar, ant) Start installed Triana Services Matthew Shields, Cardiff University
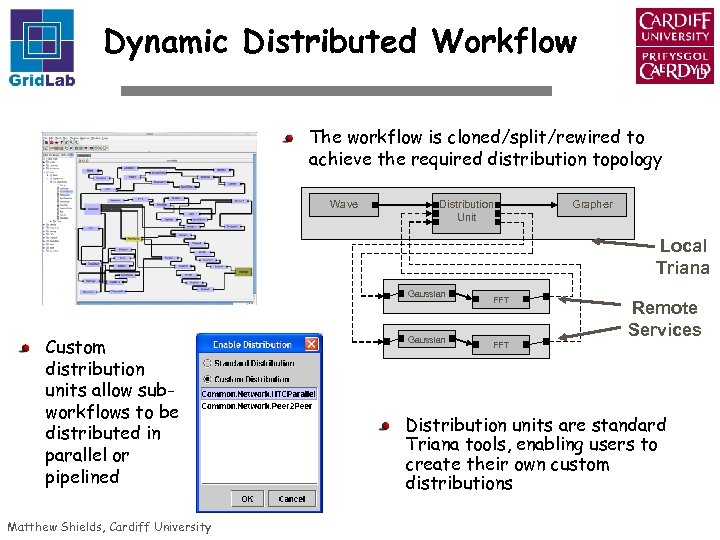
Dynamic Distributed Workflow The workflow is cloned/split/rewired to achieve the required distribution topology Wave Distribution Unit Grapher Local Triana Gaussian Custom distribution units allow subworkflows to be distributed in parallel or pipelined Matthew Shields, Cardiff University Gaussian FFT Remote Services FFT Distribution units are standard Triana tools, enabling users to create their own custom distributions
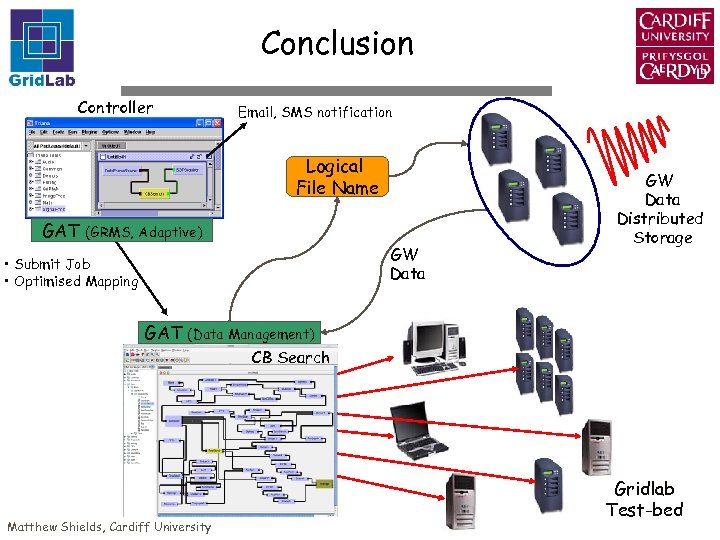
Conclusion Controller Email, SMS notification Logical File Name GAT (GRMS, Adaptive) GW Data • Submit Job • Optimised Mapping GAT GW Data Distributed Storage (Data Management) CB Search Matthew Shields, Cardiff University Gridlab Test-bed
Conclusion Shown three distinct workflows Service composition workflow to submit grid jobs that deploys multiple Triana Services on remote resources Local scientific workflow representing the algorithm Dynamic distributed workflow - rewire local workflow for data parallelism across multiple Triana Services GAP API Web Service binding + GSI - Grid Job Submission P 2 PS binding - service discovery + service communication Combined to perform parallel scientific computation Matthew Shields, Cardiff University

Thanks ! The Astronomers: Prof. B Sathyaprakash, David Churches, Roger Philp and Craig Robinson The Triana team: Ian Wang, Andrew Harrison, Omer Rana, Diem Lam and Shalil Majithia All the partners in the Grid. Lab project Matthew Shields, Cardiff University
Thanks ! Information & Software http: //www. trianacode. org/ http: //www. gridlab. org/ Matthew Shields, Cardiff University
16951801094811f43849c5139b474630.ppt