348766118a4a8ededd55087e478dfdc1.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 19
 Programme assessment design: How might technology help? Dr Greg Benfield Oxford Centre for Staff and Learning Development
Programme assessment design: How might technology help? Dr Greg Benfield Oxford Centre for Staff and Learning Development
 Oxford Centre for Staff and Learning Development Landscape: social software An ‘”underworld” of digital communication among learners’ (LEX, Creanor et al 2006) Google and Wikipedia preferred information search & retrieval tools (LXP, Conole et al 2006) “The concept of ‘time’ is changing – both in terms of expectation of information and results on demand. There is evidence of a fragmentation of the learning timetable” (LXP, Conole et al 2006) ©BBC http: //news. bbc. co. uk/1/hi/ technology/3830527. stm
Oxford Centre for Staff and Learning Development Landscape: social software An ‘”underworld” of digital communication among learners’ (LEX, Creanor et al 2006) Google and Wikipedia preferred information search & retrieval tools (LXP, Conole et al 2006) “The concept of ‘time’ is changing – both in terms of expectation of information and results on demand. There is evidence of a fragmentation of the learning timetable” (LXP, Conole et al 2006) ©BBC http: //news. bbc. co. uk/1/hi/ technology/3830527. stm
 Oxford Centre for Staff and Learning Development “technologically adept and had integrated ICT into their lives (JISC 2007: 10) “student respondents [are] immersed in technology ownership and use and impatient with instructors who don’t have adequate technical skills” (Salaway et al 2007: 5) Immersed in technology ©BBC http: //news. bbc. co. uk/1/hi/ technology/3830527. stm
Oxford Centre for Staff and Learning Development “technologically adept and had integrated ICT into their lives (JISC 2007: 10) “student respondents [are] immersed in technology ownership and use and impatient with instructors who don’t have adequate technical skills” (Salaway et al 2007: 5) Immersed in technology ©BBC http: //news. bbc. co. uk/1/hi/ technology/3830527. stm
 Oxford Centre for Staff and Learning Development Assessment and feedback Formative use of CAA stands out as a rare application of e-learning leading to measurable impact on student performance (Sharpe et al 2006)
Oxford Centre for Staff and Learning Development Assessment and feedback Formative use of CAA stands out as a rare application of e-learning leading to measurable impact on student performance (Sharpe et al 2006)
 Oxford Centre for Staff and Learning Development Scenarios 1. VLE supporting self directed study in financial accounting 2. Automated assessments in life sciences 3. Personal response systems supporting discussion of problems in engineering Sharpe, R. , Benfield, G. , Roberts, G. & Francis, R. (2006) The undergraduate experience of blended e-learning: a review of UK literature and practice undertaken for the Higher Education Academy. At http: //www. heacademy. ac. uk/4884. htm
Oxford Centre for Staff and Learning Development Scenarios 1. VLE supporting self directed study in financial accounting 2. Automated assessments in life sciences 3. Personal response systems supporting discussion of problems in engineering Sharpe, R. , Benfield, G. , Roberts, G. & Francis, R. (2006) The undergraduate experience of blended e-learning: a review of UK literature and practice undertaken for the Higher Education Academy. At http: //www. heacademy. ac. uk/4884. htm
 Oxford Centre for Staff and Learning Development Scenario 1: Newcastle Business School Background • 600 undergraduate students • Needed efficient management of self-directed study • Student diversity • Student expectations of flexibility
Oxford Centre for Staff and Learning Development Scenario 1: Newcastle Business School Background • 600 undergraduate students • Needed efficient management of self-directed study • Student diversity • Student expectations of flexibility
 Oxford Centre for Staff and Learning Development Scenario 1: Newcastle Business School Background • 600 undergraduate students • Needed efficient management of self-directed study • Student diversity • Student expectations of flexibility An approach to the problem • Online resources • Weekly directed study tasks • Answers on timed release • Formative self- assessment quizzes
Oxford Centre for Staff and Learning Development Scenario 1: Newcastle Business School Background • 600 undergraduate students • Needed efficient management of self-directed study • Student diversity • Student expectations of flexibility An approach to the problem • Online resources • Weekly directed study tasks • Answers on timed release • Formative self- assessment quizzes
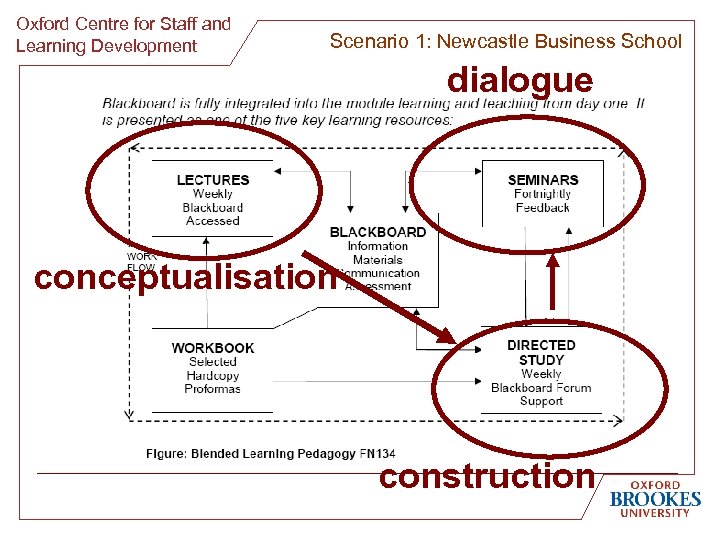 Oxford Centre for Staff and Learning Development Scenario 1: Newcastle Business School dialogue conceptualisation construction
Oxford Centre for Staff and Learning Development Scenario 1: Newcastle Business School dialogue conceptualisation construction
 Oxford Centre for Staff and Learning Development What the students said Survey responses from 200 students Ø Most agreed Blackboard helped them study Ø Most used it weekly Ø High usage of content and quizzes, less of discussions Students valued Ø Access to learner materials Ø Greater independence Ø Time saving Ø More convenient
Oxford Centre for Staff and Learning Development What the students said Survey responses from 200 students Ø Most agreed Blackboard helped them study Ø Most used it weekly Ø High usage of content and quizzes, less of discussions Students valued Ø Access to learner materials Ø Greater independence Ø Time saving Ø More convenient
 Oxford Centre for Staff and Learning Development Scenario 2: Life Sciences at Dundee Background • 1 st year introductory lecture based course • Lecture notes on web since 2002 • High failure rate • Poor turnaround time for assignments • Inconsistency in quality of feedback and marking
Oxford Centre for Staff and Learning Development Scenario 2: Life Sciences at Dundee Background • 1 st year introductory lecture based course • Lecture notes on web since 2002 • High failure rate • Poor turnaround time for assignments • Inconsistency in quality of feedback and marking
 Oxford Centre for Staff and Learning Development Scenario 2: Life Sciences at Dundee Background • 1 st year introductory lecture based course • Lecture notes on web since 2002 • High failure rate • Poor turnaround time for assignments • Inconsistency in quality of feedback and marking An approach to the problem • Computer-aided assessment (CAA)
Oxford Centre for Staff and Learning Development Scenario 2: Life Sciences at Dundee Background • 1 st year introductory lecture based course • Lecture notes on web since 2002 • High failure rate • Poor turnaround time for assignments • Inconsistency in quality of feedback and marking An approach to the problem • Computer-aided assessment (CAA)
 Oxford Centre for Staff and Learning Development Evaluation • No negative feedback regarding the use of CAA • 99% of those who responded said the online tutorials improved their understanding of the topics covered • 93% felt that the marks awarded were appropriate • “The ability to re-do tests and assignments again once you have already done it is good. It enables you to continue learning the more you try it. ” • The overall module pass rate rose from 73% to 93%.
Oxford Centre for Staff and Learning Development Evaluation • No negative feedback regarding the use of CAA • 99% of those who responded said the online tutorials improved their understanding of the topics covered • 93% felt that the marks awarded were appropriate • “The ability to re-do tests and assignments again once you have already done it is good. It enables you to continue learning the more you try it. ” • The overall module pass rate rose from 73% to 93%.
 Oxford Centre for Staff and Learning Development Scenario 3: Engineering at Strathclyde Background • Weak conceptual understanding • Insufficient interaction and discussion in class • Low student motivation An approach to the problem • Personal response system in class • Question and answer with discussion/defence of answers.
Oxford Centre for Staff and Learning Development Scenario 3: Engineering at Strathclyde Background • Weak conceptual understanding • Insufficient interaction and discussion in class • Low student motivation An approach to the problem • Personal response system in class • Question and answer with discussion/defence of answers.
 Oxford Centre for Staff and Learning Development Scenario 3: Engineering at Strathclyde Evaluation Ø 74% of students agreed that in comparison with traditional lecture classes, the teaching methods used here were more effective in helping them to acquire an understanding of fundamental engineering concepts. Ø 95% agreed that I am more actively involved in PRS than traditional classes In focus groups students attributed their understanding to Ø being active in class Ø having time to think, reflect and discuss Ø discussion with other students in peer groups.
Oxford Centre for Staff and Learning Development Scenario 3: Engineering at Strathclyde Evaluation Ø 74% of students agreed that in comparison with traditional lecture classes, the teaching methods used here were more effective in helping them to acquire an understanding of fundamental engineering concepts. Ø 95% agreed that I am more actively involved in PRS than traditional classes In focus groups students attributed their understanding to Ø being active in class Ø having time to think, reflect and discuss Ø discussion with other students in peer groups.
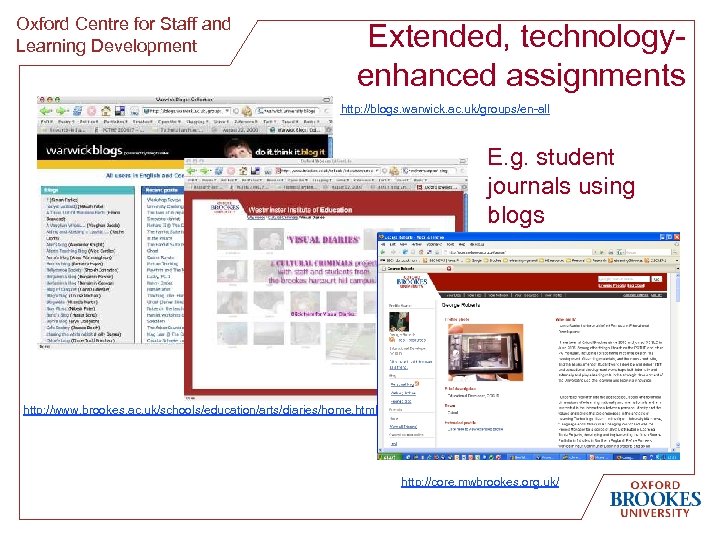 Oxford Centre for Staff and Learning Development Extended, technologyenhanced assignments http: //blogs. warwick. ac. uk/groups/en-all E. g. student journals using blogs http: //www. brookes. ac. uk/schools/education/arts/diaries/home. html! http: //core. mwbrookes. org. uk/
Oxford Centre for Staff and Learning Development Extended, technologyenhanced assignments http: //blogs. warwick. ac. uk/groups/en-all E. g. student journals using blogs http: //www. brookes. ac. uk/schools/education/arts/diaries/home. html! http: //core. mwbrookes. org. uk/
 Oxford Centre for Staff and Learning Development …. or e-portfolios http: //elgg. net/
Oxford Centre for Staff and Learning Development …. or e-portfolios http: //elgg. net/
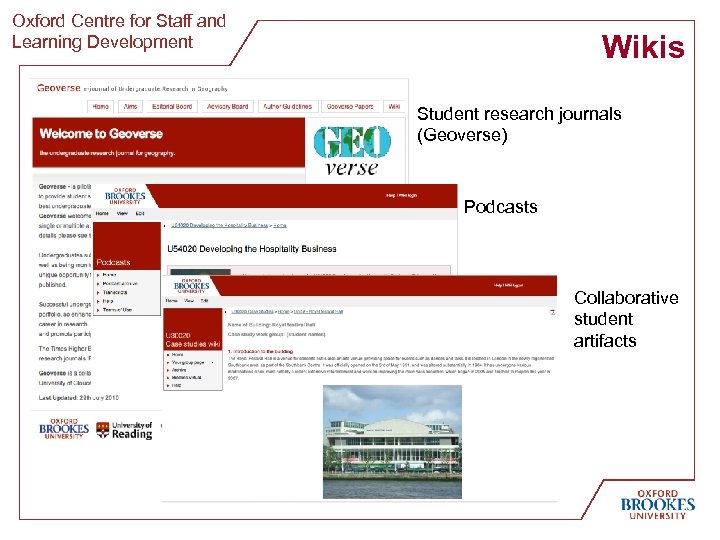 Oxford Centre for Staff and Learning Development Wikis Student research journals (Geoverse) Podcasts Collaborative student artifacts
Oxford Centre for Staff and Learning Development Wikis Student research journals (Geoverse) Podcasts Collaborative student artifacts
 Oxford Centre for Staff and Learning Development References Biggs, J. (2003). Teaching for Quality Learning at University Second Edition. Maidenhead, Open University Press. Browne, T. and Jenkins, M. (2003). 'VLE surveys: a longitudinal perspective between March 2001 and March 2003 for Higher Education in the United Kingdom. ' UCISA. online http: //www. ucisa. ac. uk/groups/tlig/vle 2003. pdf, accessed 12 November 2003 Catley, P (2005). ‘One Lecturer's Experience of Blending E-learning with Traditional Teaching or How to Improve Retention and Progression by Engaging Students’. Brookes e. Journal of Learning and Teaching, 1(2) online at http: //www. brookes. ac. uk/publications/bejlt/volume 1 issue 2/academic/catley 05_1. html! Collis, B. & Moonen, J. (2005). An On-Going Journey: Technology as a Learning Workbench. [Online] at http: //bettycollisjefmoonen. nl/Book-Learning-Workbench-V 2. pdf Conole, G. , De Laat, M. , Dillon, T. and Darby, J. (2006, November 2006). "JISC LXP: Student Experiences of Technologies Draft Final Report. " November 2006. [Online] Retrieved 20 Nov, 2006, from http: //www. jisc. ac. uk/media/documents/lxp_project_final_report_nov_06. pdf. Creanor, L. , Trinder, K. , Gowan, D. and Howells, C. (2006, August 2006). "LEX: The Learner Experience of e-Learning Final Project Report August 2006. " [Online] Retrieved 2 November, 2006, from http: //www. jisc. ac. uk/uploaded_documents/LEX%20 Final%20 Report_August 06. pdf Df. ES (2005) 'Harnessing Technology: Transforming learning and children's services'. Online at http: //www. dfes. gov. uk/publications/e-strategy/ HEFCE (2005). HEFCE strategy for e-learning, online at http: //www. hefce. ac. uk/pubs/hefce/2005/05_12/ JISC (2003). 'Virtual and Managed Learning Environments. ' Joint Information Systems Committee. online at http: //www. jisc. ac. uk/index. cfm? name=issue_vle_mle , accessed 25 August 2005. JISC (2004). Effective Practice with e-Learning: A good practice guide in designing for e-Learning. Bristol, JISC. Online at http: //www. jisc. ac. uk/uploaded_documents/jisc%20 effective%20 practice 3. pdf
Oxford Centre for Staff and Learning Development References Biggs, J. (2003). Teaching for Quality Learning at University Second Edition. Maidenhead, Open University Press. Browne, T. and Jenkins, M. (2003). 'VLE surveys: a longitudinal perspective between March 2001 and March 2003 for Higher Education in the United Kingdom. ' UCISA. online http: //www. ucisa. ac. uk/groups/tlig/vle 2003. pdf, accessed 12 November 2003 Catley, P (2005). ‘One Lecturer's Experience of Blending E-learning with Traditional Teaching or How to Improve Retention and Progression by Engaging Students’. Brookes e. Journal of Learning and Teaching, 1(2) online at http: //www. brookes. ac. uk/publications/bejlt/volume 1 issue 2/academic/catley 05_1. html! Collis, B. & Moonen, J. (2005). An On-Going Journey: Technology as a Learning Workbench. [Online] at http: //bettycollisjefmoonen. nl/Book-Learning-Workbench-V 2. pdf Conole, G. , De Laat, M. , Dillon, T. and Darby, J. (2006, November 2006). "JISC LXP: Student Experiences of Technologies Draft Final Report. " November 2006. [Online] Retrieved 20 Nov, 2006, from http: //www. jisc. ac. uk/media/documents/lxp_project_final_report_nov_06. pdf. Creanor, L. , Trinder, K. , Gowan, D. and Howells, C. (2006, August 2006). "LEX: The Learner Experience of e-Learning Final Project Report August 2006. " [Online] Retrieved 2 November, 2006, from http: //www. jisc. ac. uk/uploaded_documents/LEX%20 Final%20 Report_August 06. pdf Df. ES (2005) 'Harnessing Technology: Transforming learning and children's services'. Online at http: //www. dfes. gov. uk/publications/e-strategy/ HEFCE (2005). HEFCE strategy for e-learning, online at http: //www. hefce. ac. uk/pubs/hefce/2005/05_12/ JISC (2003). 'Virtual and Managed Learning Environments. ' Joint Information Systems Committee. online at http: //www. jisc. ac. uk/index. cfm? name=issue_vle_mle , accessed 25 August 2005. JISC (2004). Effective Practice with e-Learning: A good practice guide in designing for e-Learning. Bristol, JISC. Online at http: //www. jisc. ac. uk/uploaded_documents/jisc%20 effective%20 practice 3. pdf
 Oxford Centre for Staff and Learning Development References cont’d JISC (2005). Innovative Practice with e-Learning. Bristol, JISC. Online at http: //www. jisc. ac. uk/uploaded_documents/publication_txt. pdf JISC. (2007). "Student Expectations Study: Key findings from online research and discussion evenings held in June 2007 for the Joint Information Systems Committee. " [Online] Retrieved 10 September, 2007, from http: //www. jisc. ac. uk/media/documents/publications/studentexpectations. pdf Laurillard, D. (1993). Rethinking University Teaching-A framework for the effective use of educational technology. New York, Routledge. Laurillard, D. (2002). Rethinking University Teaching-a conversational framework for the effective use of educational technology. London, Routledge. Farmer. Mayes, T and de Freitas, S. (2004) Review of e-learning theories, frameworks and models. JISC. Online at http: //www. jisc. ac. uk/uploaded_documents/Stage%202%20 Learning%20 Models%20(Version%2 01). pdf Sharpe, R, Benfield, G, Roberts, G and Francis, R (2006). "The undergraduate experience of blended e-learning: a review of UK literature and practice undertaken for the Higher Education Academy. " Retrieved 3 October, 2006, from http: //www. heacademy. ac. uk/research/Sharpe_Benfield_Roberts_Francis. pdf Salaway, G. , Caruso, J. B. and Nelson, M. R. (2007). "The ECAR Study of Undergraduate Students and Information Technology, 2007. " [Online] Retrieved 9 October, 2007, from http: //www. educause. edu/ir/library/pdf/ers 0706/rs/ERS 0706 w. pdf
Oxford Centre for Staff and Learning Development References cont’d JISC (2005). Innovative Practice with e-Learning. Bristol, JISC. Online at http: //www. jisc. ac. uk/uploaded_documents/publication_txt. pdf JISC. (2007). "Student Expectations Study: Key findings from online research and discussion evenings held in June 2007 for the Joint Information Systems Committee. " [Online] Retrieved 10 September, 2007, from http: //www. jisc. ac. uk/media/documents/publications/studentexpectations. pdf Laurillard, D. (1993). Rethinking University Teaching-A framework for the effective use of educational technology. New York, Routledge. Laurillard, D. (2002). Rethinking University Teaching-a conversational framework for the effective use of educational technology. London, Routledge. Farmer. Mayes, T and de Freitas, S. (2004) Review of e-learning theories, frameworks and models. JISC. Online at http: //www. jisc. ac. uk/uploaded_documents/Stage%202%20 Learning%20 Models%20(Version%2 01). pdf Sharpe, R, Benfield, G, Roberts, G and Francis, R (2006). "The undergraduate experience of blended e-learning: a review of UK literature and practice undertaken for the Higher Education Academy. " Retrieved 3 October, 2006, from http: //www. heacademy. ac. uk/research/Sharpe_Benfield_Roberts_Francis. pdf Salaway, G. , Caruso, J. B. and Nelson, M. R. (2007). "The ECAR Study of Undergraduate Students and Information Technology, 2007. " [Online] Retrieved 9 October, 2007, from http: //www. educause. edu/ir/library/pdf/ers 0706/rs/ERS 0706 w. pdf


