caea6ddf044d63181831ea427e69892a.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 11
 Programma Erasmus+ KA 2 - Partenariati Strategici tra scuole per lo scambio di buone pratiche Durata: 3 anni (2016 -2017 -2018) Titolo del progetto Unissons nos cœurs sans frontières
Programma Erasmus+ KA 2 - Partenariati Strategici tra scuole per lo scambio di buone pratiche Durata: 3 anni (2016 -2017 -2018) Titolo del progetto Unissons nos cœurs sans frontières
 Who are the Italians? A brief history of Italy
Who are the Italians? A brief history of Italy
 All the events happened during several centuries of history and all the populations who lived in the territory led to the development of our country, Italy. The most important historical periods are: pre-Roman era, the Middle Ages, the Reinassance and current age.
All the events happened during several centuries of history and all the populations who lived in the territory led to the development of our country, Italy. The most important historical periods are: pre-Roman era, the Middle Ages, the Reinassance and current age.
 Pre-Roman Era Before Roman Era Italy was divided into many regions. The Etruscan civilization colonized the current Campania and Emilia-Romagna, while Greek conquered Sicily and part of the South Italy. Some of the regions in the centre and in the north of Italy were inhabited by Sunnis, Ligurians and Umbri people.
Pre-Roman Era Before Roman Era Italy was divided into many regions. The Etruscan civilization colonized the current Campania and Emilia-Romagna, while Greek conquered Sicily and part of the South Italy. Some of the regions in the centre and in the north of Italy were inhabited by Sunnis, Ligurians and Umbri people.
 Roman Era Roman era lasted for about seven centuries. Rome promoted a process of cultural, ethnic, lingual, religious and juridical unification which laid the foundations for the development of Italian people. Romans were important for their artworks and infrastructural works and famous for the Colosseum and the aqueducts.
Roman Era Roman era lasted for about seven centuries. Rome promoted a process of cultural, ethnic, lingual, religious and juridical unification which laid the foundations for the development of Italian people. Romans were important for their artworks and infrastructural works and famous for the Colosseum and the aqueducts.
 The Middle Ages At the beginning of the Middle Ages Italy had to face the invasions of barbarians, but this dark period was followed by rebirth. Between the XI and XII century Italy started to outline its borders thanks to the inception of municipalities. Soon after an artistic and literal culture prospered in the Reign of Sicily which included the South of Italy. Later, in the period of Signoria, humanism spreaded and with it people tried to recover the ancient values of classical style.
The Middle Ages At the beginning of the Middle Ages Italy had to face the invasions of barbarians, but this dark period was followed by rebirth. Between the XI and XII century Italy started to outline its borders thanks to the inception of municipalities. Soon after an artistic and literal culture prospered in the Reign of Sicily which included the South of Italy. Later, in the period of Signoria, humanism spreaded and with it people tried to recover the ancient values of classical style.
 The Renaissance From the 11 th century on, Italian cities began to grow rapidly in independence and importance. They became centres of political life, banking, and foreign trade. Some became wealthy, and many, including Florence, Rome, Genoa, Milan, Pisa, Siena and Venice, grew into nearly independent city states. Each had its own foreign policy and political life. During the 14 th and 15 th centuries, some Italian city -states ranked among the most important powers of Europe. They helped the development of Renaissance which began in Florence in the 14 th century and led to a flourishing of the arts, literature, music, and science. The School of Athens, Raffaello Sanzio
The Renaissance From the 11 th century on, Italian cities began to grow rapidly in independence and importance. They became centres of political life, banking, and foreign trade. Some became wealthy, and many, including Florence, Rome, Genoa, Milan, Pisa, Siena and Venice, grew into nearly independent city states. Each had its own foreign policy and political life. During the 14 th and 15 th centuries, some Italian city -states ranked among the most important powers of Europe. They helped the development of Renaissance which began in Florence in the 14 th century and led to a flourishing of the arts, literature, music, and science. The School of Athens, Raffaello Sanzio
 The kingdom of Italy After the Congress of Vienna, which allowed the restoration of many of the old rulers and systems under Austrian domination, the concept of nationalism became stronger, especially in Italy. The Risorgimento movement brought to a successful conclusion under the able guidance of Camillo Benso, conte di Cavour, prime minister of Piedmont. Cavour managed to unite most of Italy under the headship of Victor Emmanuel II of the House of Savoy, and on 17 March 1861, the Kingdom of Italy was proclaimed with Victor Emmanuel II as king. Giuseppe Garibaldi, the popular republican hero of Italy, contributed much to this achievement and to the subsequent incorporation of the Papal States under the Italian monarch. Italian troops occupied Rome in 1870, and in July 1871, this formally became the capital of the kingdom. Camillo Benso
The kingdom of Italy After the Congress of Vienna, which allowed the restoration of many of the old rulers and systems under Austrian domination, the concept of nationalism became stronger, especially in Italy. The Risorgimento movement brought to a successful conclusion under the able guidance of Camillo Benso, conte di Cavour, prime minister of Piedmont. Cavour managed to unite most of Italy under the headship of Victor Emmanuel II of the House of Savoy, and on 17 March 1861, the Kingdom of Italy was proclaimed with Victor Emmanuel II as king. Giuseppe Garibaldi, the popular republican hero of Italy, contributed much to this achievement and to the subsequent incorporation of the Papal States under the Italian monarch. Italian troops occupied Rome in 1870, and in July 1871, this formally became the capital of the kingdom. Camillo Benso
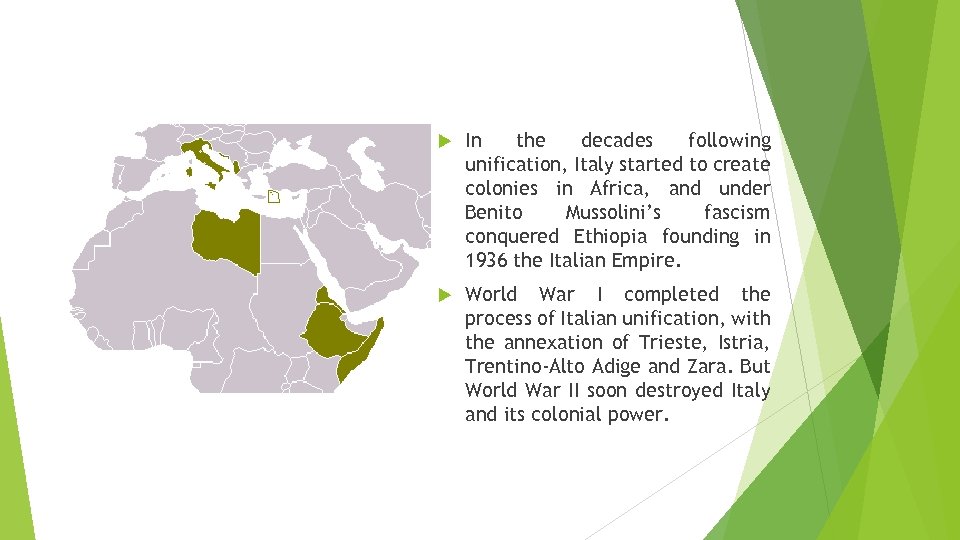 In the decades following unification, Italy started to create colonies in Africa, and under Benito Mussolini’s fascism conquered Ethiopia founding in 1936 the Italian Empire. World War I completed the process of Italian unification, with the annexation of Trieste, Istria, Trentino-Alto Adige and Zara. But World War II soon destroyed Italy and its colonial power.
In the decades following unification, Italy started to create colonies in Africa, and under Benito Mussolini’s fascism conquered Ethiopia founding in 1936 the Italian Empire. World War I completed the process of Italian unification, with the annexation of Trieste, Istria, Trentino-Alto Adige and Zara. But World War II soon destroyed Italy and its colonial power.
 The Italian Republic Between 1945 and 1948, the outlines of a new Italy began to appear. Victor Emmanuel III gave up the throne on 9 May 1946, and his son, Umberto II, became king. On 2 June Italy held its first free election after 20 years of Fascist rule (the so-called Ventennio). Italians chose a republic to replace the monarchy, which had been closely associated with Fascism. They elected a Constituent Assembly to prepare a new democratic constitution. The Assembly approved the constitution in 1947, which came into force since 1 January 1948.
The Italian Republic Between 1945 and 1948, the outlines of a new Italy began to appear. Victor Emmanuel III gave up the throne on 9 May 1946, and his son, Umberto II, became king. On 2 June Italy held its first free election after 20 years of Fascist rule (the so-called Ventennio). Italians chose a republic to replace the monarchy, which had been closely associated with Fascism. They elected a Constituent Assembly to prepare a new democratic constitution. The Assembly approved the constitution in 1947, which came into force since 1 January 1948.
 Classi 3 C e 3 D IPSSEOA
Classi 3 C e 3 D IPSSEOA


