fe0111c13f976850c56fa8ec74195f3a.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 49
 Program Slicing for Refactoring Advanced SW Tools Seminar Jan 2005 Yossi Peery
Program Slicing for Refactoring Advanced SW Tools Seminar Jan 2005 Yossi Peery
 Agenda l l l l Slicing Overview Slicing Algorithms Slicing with Inference Rules Refactoring Overview Slice Extraction Refactoring Example NATE – Slicing Based Refactoring Tool Yossi Peery Advanced SW Tools Seminar Jan-05
Agenda l l l l Slicing Overview Slicing Algorithms Slicing with Inference Rules Refactoring Overview Slice Extraction Refactoring Example NATE – Slicing Based Refactoring Tool Yossi Peery Advanced SW Tools Seminar Jan-05
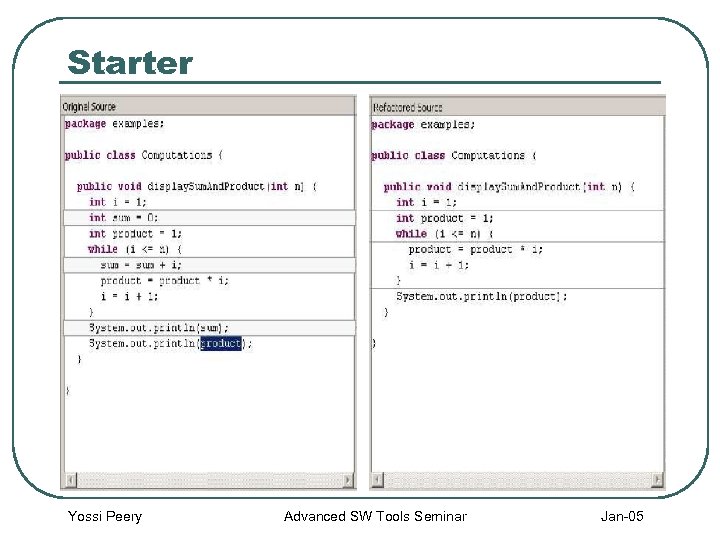 Starter Yossi Peery Advanced SW Tools Seminar Jan-05
Starter Yossi Peery Advanced SW Tools Seminar Jan-05
 Program Slicing History l Mark Weiser, 1981 • Experimented with programmers to show that slices are: “The mental abstraction people make when they are debugging a program” [Weiser] • Used Data Flow Equations l l Ottenstein & Ottenstein – PDG, 1984 Horowitz, Reps & Binkly – SDG, 1990 Yossi Peery Advanced SW Tools Seminar Jan-05
Program Slicing History l Mark Weiser, 1981 • Experimented with programmers to show that slices are: “The mental abstraction people make when they are debugging a program” [Weiser] • Used Data Flow Equations l l Ottenstein & Ottenstein – PDG, 1984 Horowitz, Reps & Binkly – SDG, 1990 Yossi Peery Advanced SW Tools Seminar Jan-05
 What is a Slice? l All the statements of a program that may affect the values of some variables in a set V at some point of interest p. l Slicing Criterion: C = (p , V) Yossi Peery Advanced SW Tools Seminar Jan-05
What is a Slice? l All the statements of a program that may affect the values of some variables in a set V at some point of interest p. l Slicing Criterion: C = (p , V) Yossi Peery Advanced SW Tools Seminar Jan-05
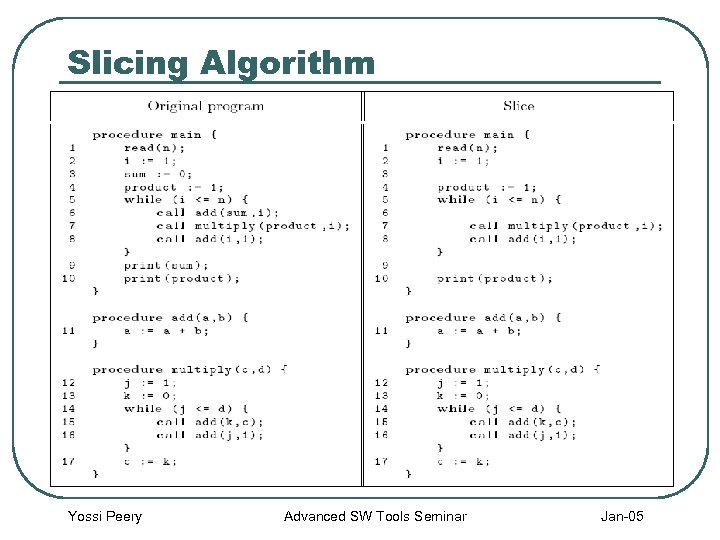
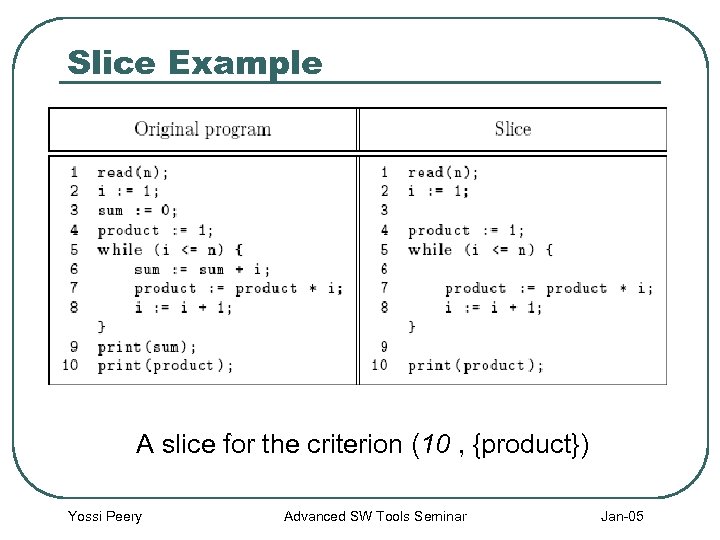 Slice Example A slice for the criterion (10 , {product}) Yossi Peery Advanced SW Tools Seminar Jan-05
Slice Example A slice for the criterion (10 , {product}) Yossi Peery Advanced SW Tools Seminar Jan-05
 What is it good for? l l l Debugging Program Comprehension Reverse Engineering Program Testing Measuring Program Metrics Coverage, Overlap, Clustering l Refactoring Yossi Peery Advanced SW Tools Seminar Jan-05
What is it good for? l l l Debugging Program Comprehension Reverse Engineering Program Testing Measuring Program Metrics Coverage, Overlap, Clustering l Refactoring Yossi Peery Advanced SW Tools Seminar Jan-05
 Slicing Properties l Static Slicing • Statically available information only • No assumptions made on input • Computed slice can never be accurate • • • (minimal slice) Problem is undecidable – reduction to the halting problem Current static methods can only compute approximations Result may not be usefull Yossi Peery Advanced SW Tools Seminar Jan-05
Slicing Properties l Static Slicing • Statically available information only • No assumptions made on input • Computed slice can never be accurate • • • (minimal slice) Problem is undecidable – reduction to the halting problem Current static methods can only compute approximations Result may not be usefull Yossi Peery Advanced SW Tools Seminar Jan-05
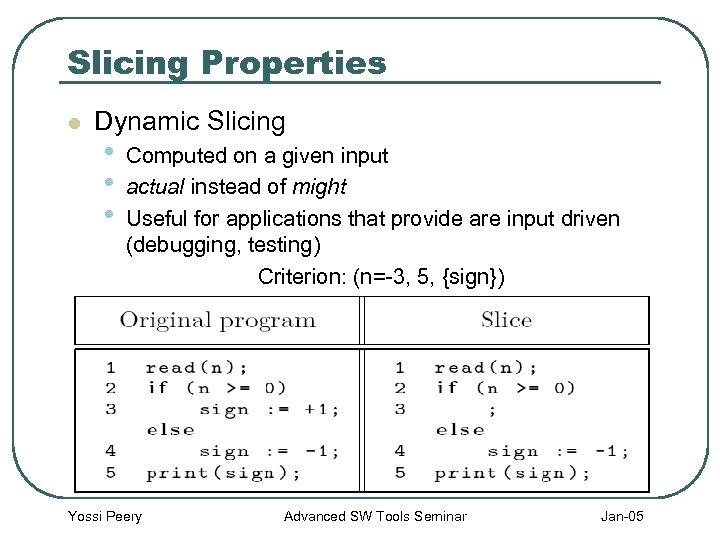 Slicing Properties l Dynamic Slicing • • • Computed on a given input actual instead of might Useful for applications that provide are input driven (debugging, testing) Criterion: (n=-3, 5, {sign}) Yossi Peery Advanced SW Tools Seminar Jan-05
Slicing Properties l Dynamic Slicing • • • Computed on a given input actual instead of might Useful for applications that provide are input driven (debugging, testing) Criterion: (n=-3, 5, {sign}) Yossi Peery Advanced SW Tools Seminar Jan-05
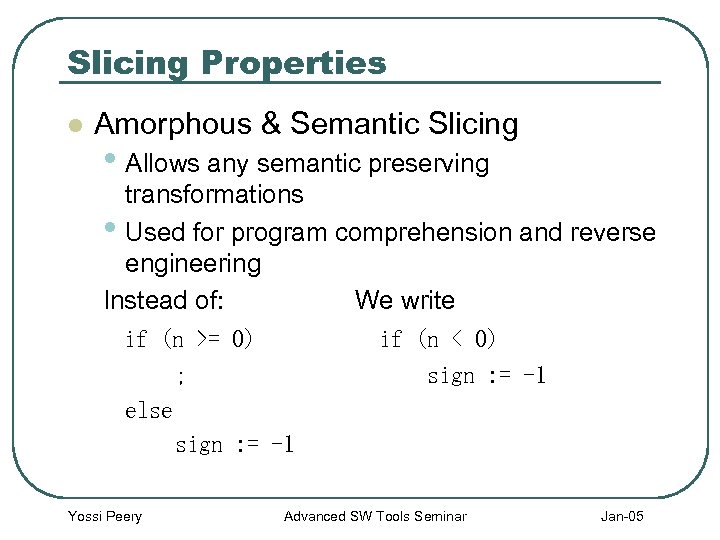 Slicing Properties l Amorphous & Semantic Slicing • Allows any semantic preserving transformations • Used for program comprehension and reverse engineering Instead of: We write if (n >= 0) if (n < 0) ; sign : = -1 else sign : = -1 Yossi Peery Advanced SW Tools Seminar Jan-05
Slicing Properties l Amorphous & Semantic Slicing • Allows any semantic preserving transformations • Used for program comprehension and reverse engineering Instead of: We write if (n >= 0) if (n < 0) ; sign : = -1 else sign : = -1 Yossi Peery Advanced SW Tools Seminar Jan-05
 Slicing Properties l Backward Slicing • • Original Slicing Method Backward Traversal of Program Flow Slicing starts from point p (C = (p , V)) Examines statements that are executed before p • • Keep statements that affect value of V at p, or execution of p. (in run-time) Not only statements that appear before p Yossi Peery Advanced SW Tools Seminar Jan-05
Slicing Properties l Backward Slicing • • Original Slicing Method Backward Traversal of Program Flow Slicing starts from point p (C = (p , V)) Examines statements that are executed before p • • Keep statements that affect value of V at p, or execution of p. (in run-time) Not only statements that appear before p Yossi Peery Advanced SW Tools Seminar Jan-05
 Slicing Properties l Forward Slicing • Forward Traversal of Program Flow • Slicing starts from p (C = (p , V)) • Examine all statements that are executed after p • Keep statements that are affected by the values of V at p or by the execution of p • Shows downstream code that depend on a • specific variable or statement Can show the code affected by a modification to a single statement Yossi Peery Advanced SW Tools Seminar Jan-05
Slicing Properties l Forward Slicing • Forward Traversal of Program Flow • Slicing starts from p (C = (p , V)) • Examine all statements that are executed after p • Keep statements that are affected by the values of V at p or by the execution of p • Shows downstream code that depend on a • specific variable or statement Can show the code affected by a modification to a single statement Yossi Peery Advanced SW Tools Seminar Jan-05
 Slicing Properties l Intraprocedural Slicing l Interprocedural Slicing • Computes slice within one procedure • Assumes worse case for function calls • Compute slice over an entire program • Two ways for crossing procedure boundary • Up – going from sliced procedure into calling procedure • Down – going from sliced procedure into called procedure • Must Be Context Sensitive Yossi Peery Advanced SW Tools Seminar Jan-05
Slicing Properties l Intraprocedural Slicing l Interprocedural Slicing • Computes slice within one procedure • Assumes worse case for function calls • Compute slice over an entire program • Two ways for crossing procedure boundary • Up – going from sliced procedure into calling procedure • Down – going from sliced procedure into called procedure • Must Be Context Sensitive Yossi Peery Advanced SW Tools Seminar Jan-05
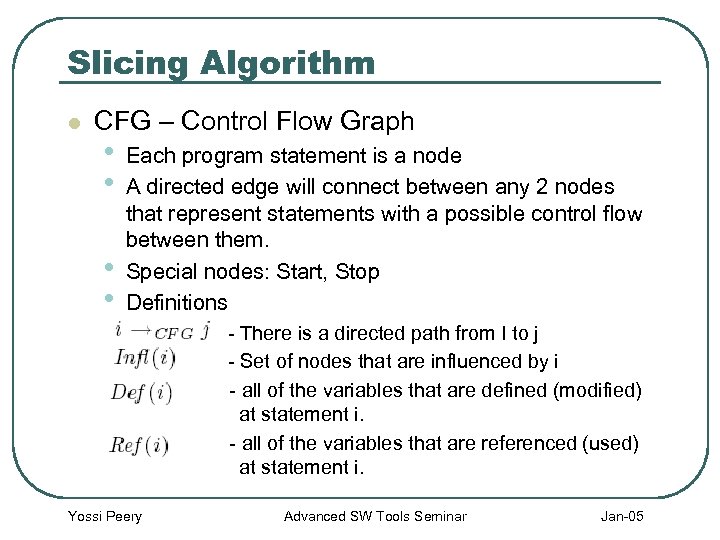 Slicing Algorithm l CFG – Control Flow Graph • • Each program statement is a node A directed edge will connect between any 2 nodes that represent statements with a possible control flow between them. Special nodes: Start, Stop Definitions - There is a directed path from I to j - Set of nodes that are influenced by i - all of the variables that are defined (modified) at statement i. - all of the variables that are referenced (used) at statement i. Yossi Peery Advanced SW Tools Seminar Jan-05
Slicing Algorithm l CFG – Control Flow Graph • • Each program statement is a node A directed edge will connect between any 2 nodes that represent statements with a possible control flow between them. Special nodes: Start, Stop Definitions - There is a directed path from I to j - Set of nodes that are influenced by i - all of the variables that are defined (modified) at statement i. - all of the variables that are referenced (used) at statement i. Yossi Peery Advanced SW Tools Seminar Jan-05
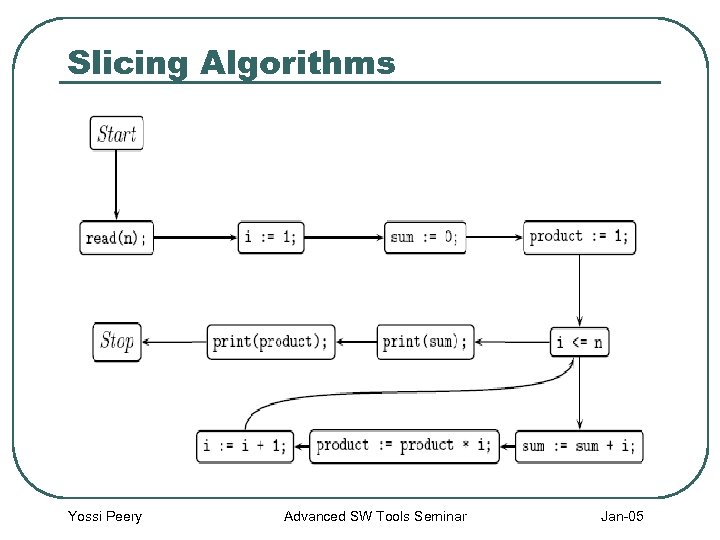 Slicing Algorithms Yossi Peery Advanced SW Tools Seminar Jan-05
Slicing Algorithms Yossi Peery Advanced SW Tools Seminar Jan-05
 Slicing Algorithms l Data Flow Equations (Weiser) • Iterative Process (Over CFG) • Compute consecutive sets of “relevant” variables for each node in the CFG using data dependencies • Control dependences are not computed explicitly • Variables of control predicates (if, while) are “indirectly relevant” if any one of the statements in their body is relevant • Start with slicing criterion: C = (p, V) • Continue until a fixed point is reached – last iteration didn’t find new relevant statements Yossi Peery Advanced SW Tools Seminar Jan-05
Slicing Algorithms l Data Flow Equations (Weiser) • Iterative Process (Over CFG) • Compute consecutive sets of “relevant” variables for each node in the CFG using data dependencies • Control dependences are not computed explicitly • Variables of control predicates (if, while) are “indirectly relevant” if any one of the statements in their body is relevant • Start with slicing criterion: C = (p, V) • Continue until a fixed point is reached – last iteration didn’t find new relevant statements Yossi Peery Advanced SW Tools Seminar Jan-05
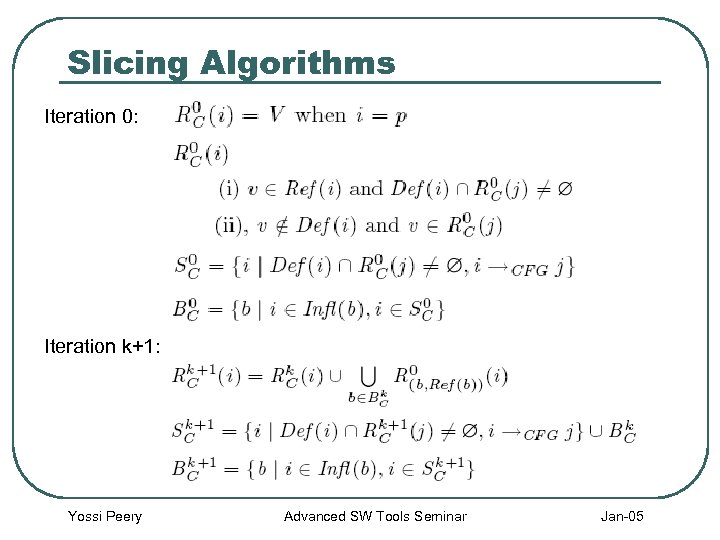 Slicing Algorithms Iteration 0: Iteration k+1: Yossi Peery Advanced SW Tools Seminar Jan-05
Slicing Algorithms Iteration 0: Iteration k+1: Yossi Peery Advanced SW Tools Seminar Jan-05
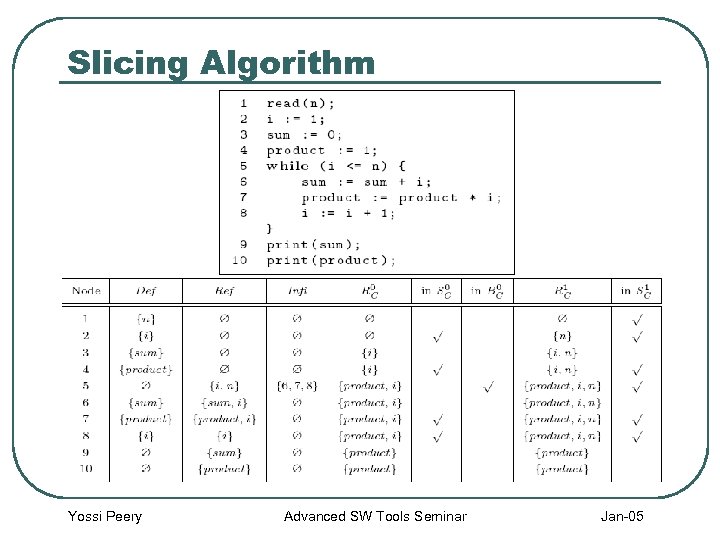 Slicing Algorithm Yossi Peery Advanced SW Tools Seminar Jan-05
Slicing Algorithm Yossi Peery Advanced SW Tools Seminar Jan-05
 Slicing Algorithms l Issues with algorithm • Output statements are not included in slice Solution: print(x) ≡ out = out + x , • Interprocedural Slicing out V • Solution proposed by Weiser • Can go up or down procedure calls • Actual parameters of function call are changed to call parameters (or the opposite) • Variables not in scope are removed • Is not “context sensitive” – too inaccurate Yossi Peery Advanced SW Tools Seminar Jan-05
Slicing Algorithms l Issues with algorithm • Output statements are not included in slice Solution: print(x) ≡ out = out + x , • Interprocedural Slicing out V • Solution proposed by Weiser • Can go up or down procedure calls • Actual parameters of function call are changed to call parameters (or the opposite) • Variables not in scope are removed • Is not “context sensitive” – too inaccurate Yossi Peery Advanced SW Tools Seminar Jan-05
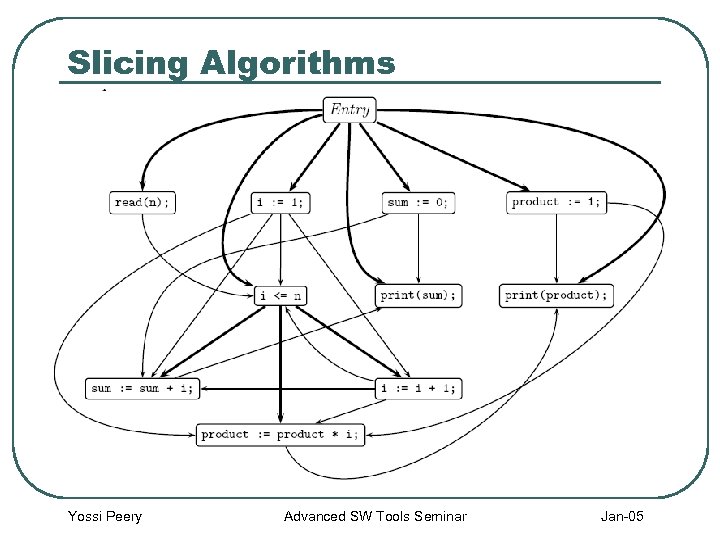
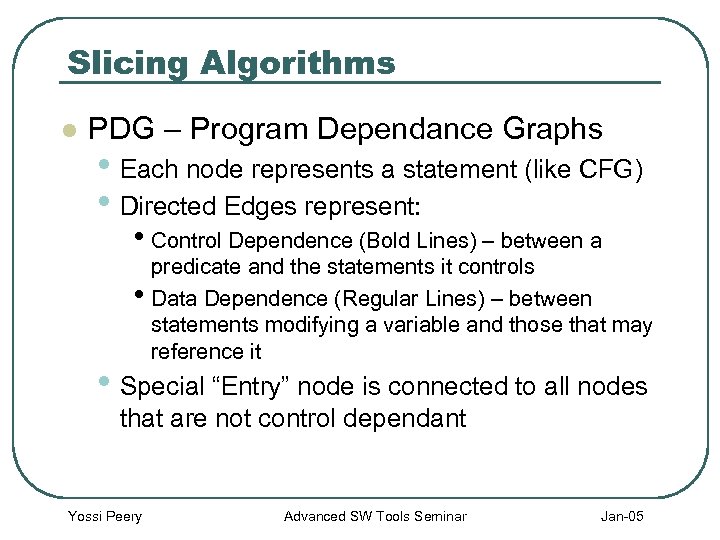 Slicing Algorithms l PDG – Program Dependance Graphs • Each node represents a statement (like CFG) • Directed Edges represent: • Control Dependence (Bold Lines) – between a predicate and the statements it controls • Data Dependence (Regular Lines) – between statements modifying a variable and those that may reference it • Special “Entry” node is connected to all nodes that are not control dependant Yossi Peery Advanced SW Tools Seminar Jan-05
Slicing Algorithms l PDG – Program Dependance Graphs • Each node represents a statement (like CFG) • Directed Edges represent: • Control Dependence (Bold Lines) – between a predicate and the statements it controls • Data Dependence (Regular Lines) – between statements modifying a variable and those that may reference it • Special “Entry” node is connected to all nodes that are not control dependant Yossi Peery Advanced SW Tools Seminar Jan-05
 Slicing Algorithms Yossi Peery Advanced SW Tools Seminar Jan-05
Slicing Algorithms Yossi Peery Advanced SW Tools Seminar Jan-05
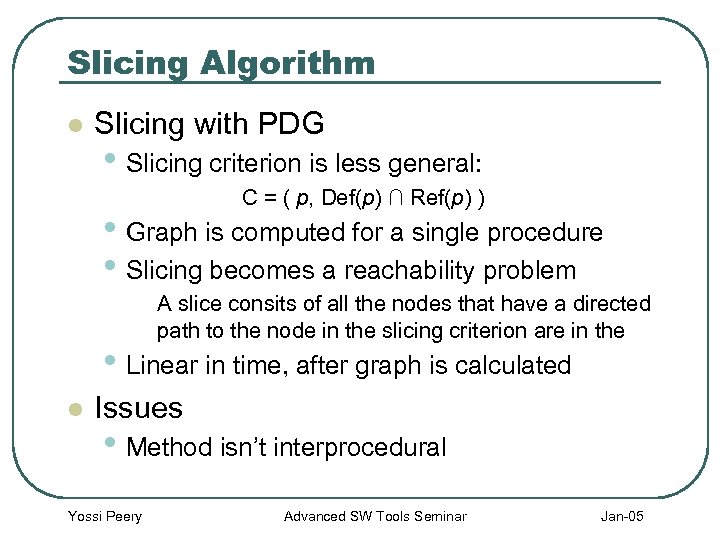 Slicing Algorithm l Slicing with PDG • Slicing criterion is less general: C = ( p, Def(p) ∩ Ref(p) ) • Graph is computed for a single procedure • Slicing becomes a reachability problem A slice consits of all the nodes that have a directed path to the node in the slicing criterion are in the • Linear in time, after graph is calculated l Issues • Method isn’t interprocedural Yossi Peery Advanced SW Tools Seminar Jan-05
Slicing Algorithm l Slicing with PDG • Slicing criterion is less general: C = ( p, Def(p) ∩ Ref(p) ) • Graph is computed for a single procedure • Slicing becomes a reachability problem A slice consits of all the nodes that have a directed path to the node in the slicing criterion are in the • Linear in time, after graph is calculated l Issues • Method isn’t interprocedural Yossi Peery Advanced SW Tools Seminar Jan-05
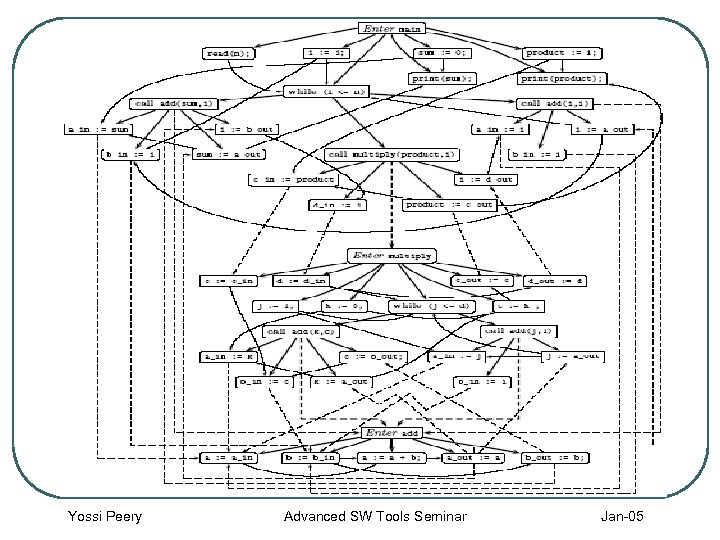
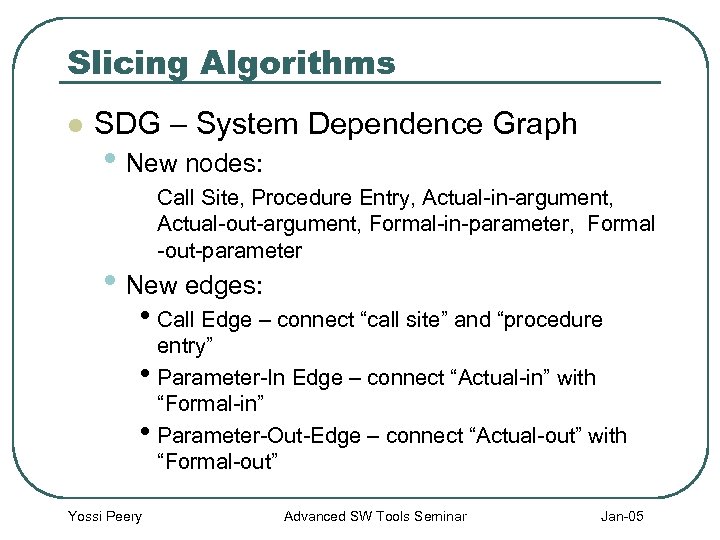 Slicing Algorithms l SDG – System Dependence Graph • New nodes: Call Site, Procedure Entry, Actual-in-argument, Actual-out-argument, Formal-in-parameter, Formal -out-parameter • New edges: • Call Edge – connect “call site” and “procedure entry” • Parameter-In Edge – connect “Actual-in” with “Formal-in” • Parameter-Out-Edge – connect “Actual-out” with “Formal-out” Yossi Peery Advanced SW Tools Seminar Jan-05
Slicing Algorithms l SDG – System Dependence Graph • New nodes: Call Site, Procedure Entry, Actual-in-argument, Actual-out-argument, Formal-in-parameter, Formal -out-parameter • New edges: • Call Edge – connect “call site” and “procedure entry” • Parameter-In Edge – connect “Actual-in” with “Formal-in” • Parameter-Out-Edge – connect “Actual-out” with “Formal-out” Yossi Peery Advanced SW Tools Seminar Jan-05
 Slicing Algorithm Yossi Peery Advanced SW Tools Seminar Jan-05
Slicing Algorithm Yossi Peery Advanced SW Tools Seminar Jan-05
 Yossi Peery Advanced SW Tools Seminar Jan-05
Yossi Peery Advanced SW Tools Seminar Jan-05
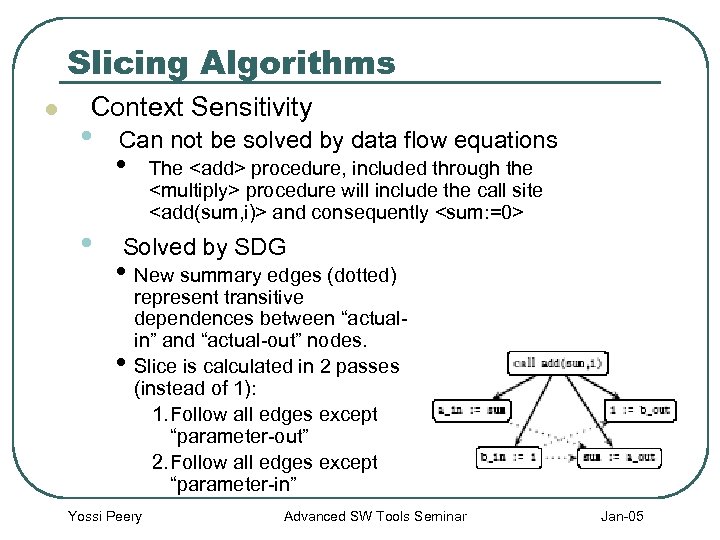 Slicing Algorithms l Context Sensitivity • • Can not be solved by data flow equations • The
Slicing Algorithms l Context Sensitivity • • Can not be solved by data flow equations • The
 Yossi Peery Advanced SW Tools Seminar Jan-05
Yossi Peery Advanced SW Tools Seminar Jan-05
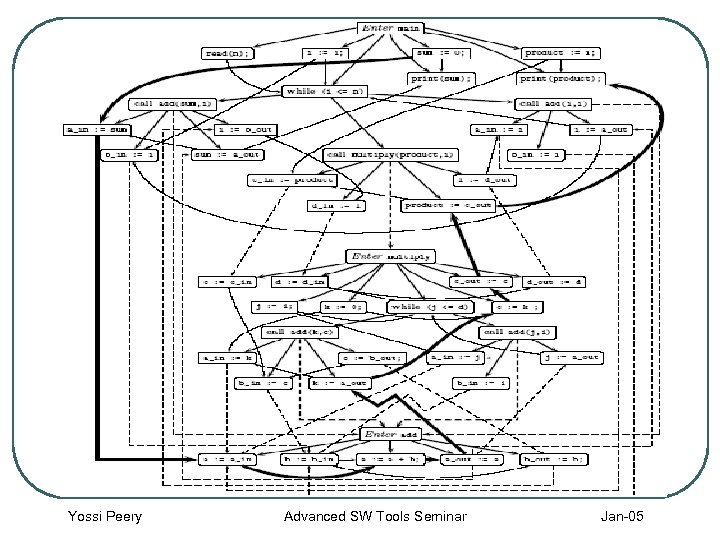
 Slicing Algorithm l SDG - Issues • Slicing remains a reachability problem • SDG of a program is complex and costly to • • • build (time, space) After computation, many different slices can be found using the same graph Is not efficient for developing code OO concepts and unstructured control flow (jump statements, exceptions) further complicate the graph Yossi Peery Advanced SW Tools Seminar Jan-05
Slicing Algorithm l SDG - Issues • Slicing remains a reachability problem • SDG of a program is complex and costly to • • • build (time, space) After computation, many different slices can be found using the same graph Is not efficient for developing code OO concepts and unstructured control flow (jump statements, exceptions) further complicate the graph Yossi Peery Advanced SW Tools Seminar Jan-05
 Slicing with Inference Rules l Concept • Use inference rules when traversing • backwards the flow of the program to determine relevant statements Rules are applied on a specific configuration of
Slicing with Inference Rules l Concept • Use inference rules when traversing • backwards the flow of the program to determine relevant statements Rules are applied on a specific configuration of
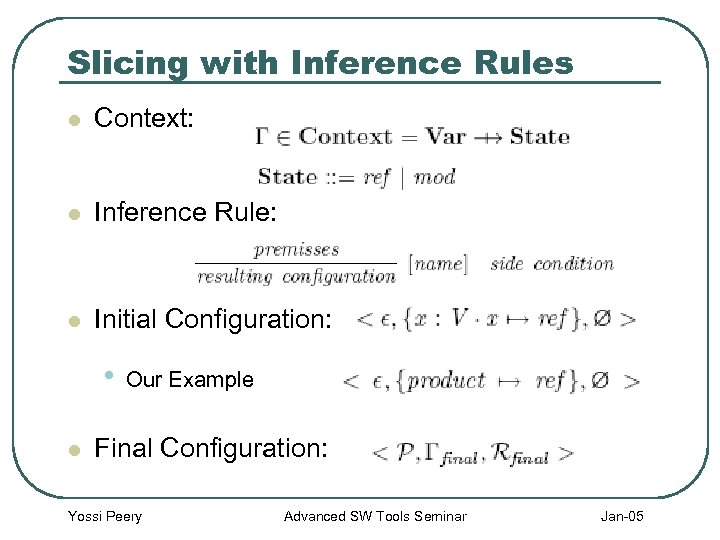 Slicing with Inference Rules l Context: l Inference Rule: l Initial Configuration: • l Our Example Final Configuration: Yossi Peery Advanced SW Tools Seminar Jan-05
Slicing with Inference Rules l Context: l Inference Rule: l Initial Configuration: • l Our Example Final Configuration: Yossi Peery Advanced SW Tools Seminar Jan-05
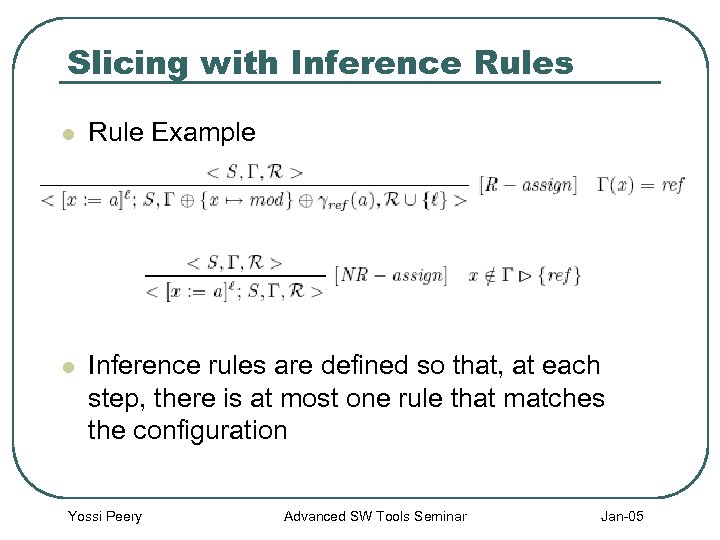 Slicing with Inference Rules l Rule Example l Inference rules are defined so that, at each step, there is at most one rule that matches the configuration Yossi Peery Advanced SW Tools Seminar Jan-05
Slicing with Inference Rules l Rule Example l Inference rules are defined so that, at each step, there is at most one rule that matches the configuration Yossi Peery Advanced SW Tools Seminar Jan-05
 Slicing with Inference Rules l Features • Supports interprocedural slicing • Context Sensitive • Can be extended to support other language features such as: • Complex expressions • Array access • Variable declarations • Structured Jumps (break, continue) • Object-oriented slicing (scoping, polymorphism) • Aliasing Yossi Peery Advanced SW Tools Seminar Jan-05
Slicing with Inference Rules l Features • Supports interprocedural slicing • Context Sensitive • Can be extended to support other language features such as: • Complex expressions • Array access • Variable declarations • Structured Jumps (break, continue) • Object-oriented slicing (scoping, polymorphism) • Aliasing Yossi Peery Advanced SW Tools Seminar Jan-05
 Refactoring Overview l l l Gradually improving design of existing code • • • Source code transformations that, Preserve behavior of original system Manually or Automated Introduced by William Opdyke, 1992 • Formally defined the reasonable behavior preservation degree expected from a refactoring tool Formally Disciplined by Martin Fowler 2000 • • Formal description of a refactoring Catalog of refactoring techniques Yossi Peery Advanced SW Tools Seminar Jan-05
Refactoring Overview l l l Gradually improving design of existing code • • • Source code transformations that, Preserve behavior of original system Manually or Automated Introduced by William Opdyke, 1992 • Formally defined the reasonable behavior preservation degree expected from a refactoring tool Formally Disciplined by Martin Fowler 2000 • • Formal description of a refactoring Catalog of refactoring techniques Yossi Peery Advanced SW Tools Seminar Jan-05
 Refactoring Overview l l Over 70 refactoring techniques can be found at: www. refactoring. com/catalog/index. html Refactoring categories: Composing Methods, Moving features between Objects, Organizing Data, Making Method Calls Simpler l Some refactorings: Rename Method, Extract Method, Move Method, Replace Conditional with Polymorphism Yossi Peery Advanced SW Tools Seminar Jan-05
Refactoring Overview l l Over 70 refactoring techniques can be found at: www. refactoring. com/catalog/index. html Refactoring categories: Composing Methods, Moving features between Objects, Organizing Data, Making Method Calls Simpler l Some refactorings: Rename Method, Extract Method, Move Method, Replace Conditional with Polymorphism Yossi Peery Advanced SW Tools Seminar Jan-05
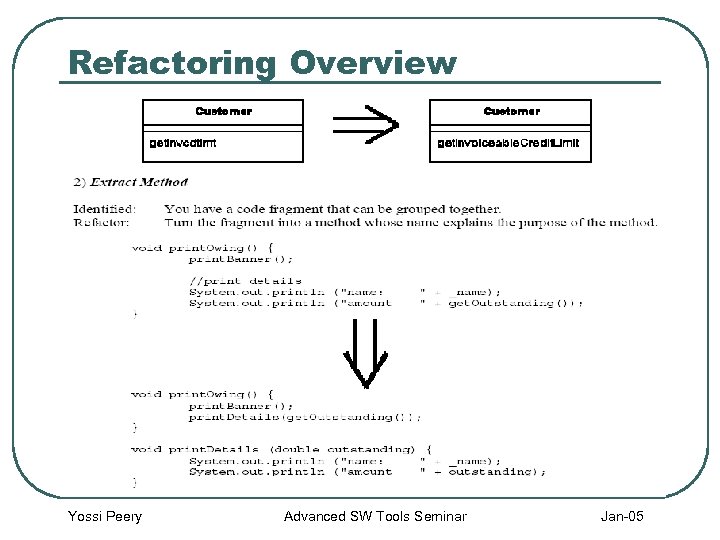 Refactoring Overview Yossi Peery Advanced SW Tools Seminar Jan-05
Refactoring Overview Yossi Peery Advanced SW Tools Seminar Jan-05
 Slice Extraction Refactoring Yossi Peery Advanced SW Tools Seminar Jan-05
Slice Extraction Refactoring Yossi Peery Advanced SW Tools Seminar Jan-05
 Slice Extraction Refactoring Yossi Peery Advanced SW Tools Seminar Jan-05
Slice Extraction Refactoring Yossi Peery Advanced SW Tools Seminar Jan-05
 Slice Extraction Refactoring l l Idea introduced by K. Maruyama, 2001 Is not limited to consecutive statements (like extract method) Allows the untangling of a single concern from a complex method Extracted slice can be refactored to • New Method • New Object • New Aspect Yossi Peery Advanced SW Tools Seminar Jan-05
Slice Extraction Refactoring l l Idea introduced by K. Maruyama, 2001 Is not limited to consecutive statements (like extract method) Allows the untangling of a single concern from a complex method Extracted slice can be refactored to • New Method • New Object • New Aspect Yossi Peery Advanced SW Tools Seminar Jan-05
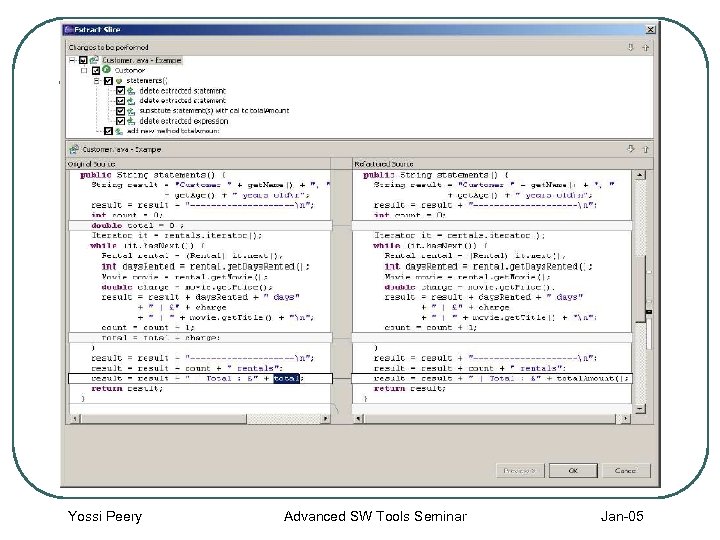
 Slice Extraction Refactoring l l Slice Extraction Refactoring Concerns • • Not all of the statements in the slice can be deleted Deleted statements are determined by re-slicing for variables in statements that were not sliced: Preconditions & Limitations • • Clean compilation Return statement Global-scoped variables Input/Output statements Yossi Peery Advanced SW Tools Seminar Jan-05
Slice Extraction Refactoring l l Slice Extraction Refactoring Concerns • • Not all of the statements in the slice can be deleted Deleted statements are determined by re-slicing for variables in statements that were not sliced: Preconditions & Limitations • • Clean compilation Return statement Global-scoped variables Input/Output statements Yossi Peery Advanced SW Tools Seminar Jan-05
 Example – original code Yossi Peery Advanced SW Tools Seminar Jan-05
Example – original code Yossi Peery Advanced SW Tools Seminar Jan-05
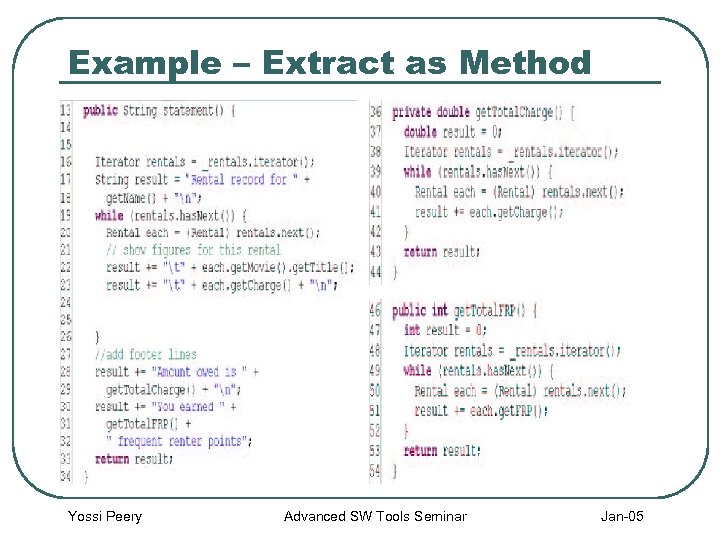 Example – Extract as Method Yossi Peery Advanced SW Tools Seminar Jan-05
Example – Extract as Method Yossi Peery Advanced SW Tools Seminar Jan-05
 Example – Extract as Object Yossi Peery Advanced SW Tools Seminar Jan-05
Example – Extract as Object Yossi Peery Advanced SW Tools Seminar Jan-05
 Example – Extract as Aspect Yossi Peery Advanced SW Tools Seminar Jan-05
Example – Extract as Aspect Yossi Peery Advanced SW Tools Seminar Jan-05
 Example – Extract as Aspect Yossi Peery Advanced SW Tools Seminar Jan-05
Example – Extract as Aspect Yossi Peery Advanced SW Tools Seminar Jan-05
 NATE – Slicing based Refactoring Tool l Oxford University – Programming Tools Group http: //web. comlab. ox. ac. uk/oucl/research/areas/progtools/proje cts/nate. html l Slicing based refactoring techniques for the Java programming language • Currently supports a small subset of Java • l (March 2004) Extract Slice as Method Refactoring An Eclipse Plug-in Yossi Peery Advanced SW Tools Seminar Jan-05
NATE – Slicing based Refactoring Tool l Oxford University – Programming Tools Group http: //web. comlab. ox. ac. uk/oucl/research/areas/progtools/proje cts/nate. html l Slicing based refactoring techniques for the Java programming language • Currently supports a small subset of Java • l (March 2004) Extract Slice as Method Refactoring An Eclipse Plug-in Yossi Peery Advanced SW Tools Seminar Jan-05
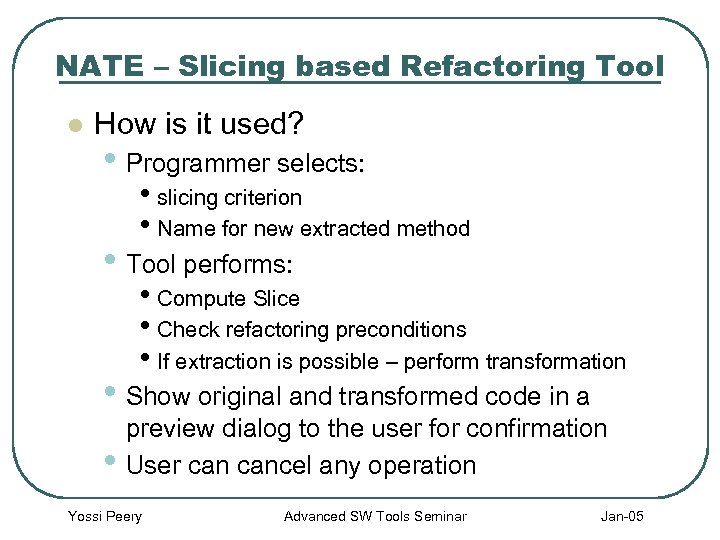 NATE – Slicing based Refactoring Tool l How is it used? • Programmer selects: • slicing criterion • Name for new extracted method • Tool performs: • Compute Slice • Check refactoring preconditions • If extraction is possible – perform transformation • Show original and transformed code in a • preview dialog to the user for confirmation User cancel any operation Yossi Peery Advanced SW Tools Seminar Jan-05
NATE – Slicing based Refactoring Tool l How is it used? • Programmer selects: • slicing criterion • Name for new extracted method • Tool performs: • Compute Slice • Check refactoring preconditions • If extraction is possible – perform transformation • Show original and transformed code in a • preview dialog to the user for confirmation User cancel any operation Yossi Peery Advanced SW Tools Seminar Jan-05
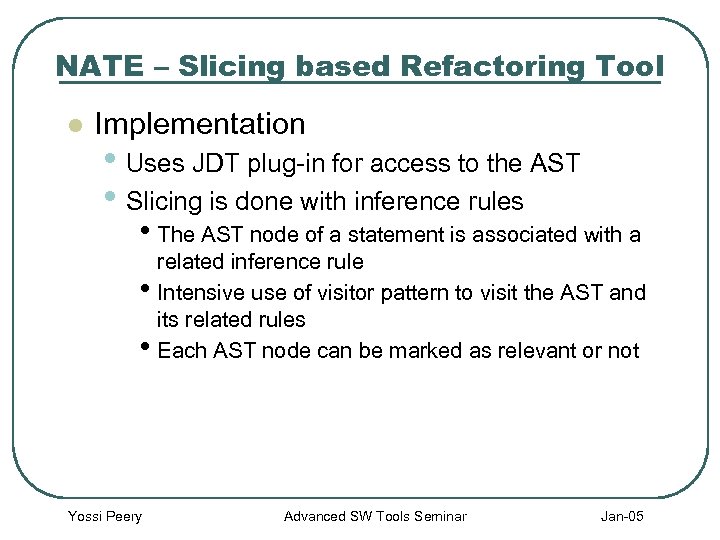 NATE – Slicing based Refactoring Tool l Implementation • Uses JDT plug-in for access to the AST • Slicing is done with inference rules • The AST node of a statement is associated with a related inference rule • Intensive use of visitor pattern to visit the AST and its related rules • Each AST node can be marked as relevant or not Yossi Peery Advanced SW Tools Seminar Jan-05
NATE – Slicing based Refactoring Tool l Implementation • Uses JDT plug-in for access to the AST • Slicing is done with inference rules • The AST node of a statement is associated with a related inference rule • Intensive use of visitor pattern to visit the AST and its related rules • Each AST node can be marked as relevant or not Yossi Peery Advanced SW Tools Seminar Jan-05
 Yossi Peery Advanced SW Tools Seminar Jan-05
Yossi Peery Advanced SW Tools Seminar Jan-05
 Refernces l “Untangling: A Slice Extraction Refactoring Ran Ettinger and Mathieu Verbaere (March 2004) l “Program Slicing for Refactoring” Mathieu Verbaere (September 2003) l “Automated Tools for Refactoring” Ran Ettinger (June 2003) l “Program Slicing” Mark Weiser (1981) Yossi Peery Advanced SW Tools Seminar Jan-05
Refernces l “Untangling: A Slice Extraction Refactoring Ran Ettinger and Mathieu Verbaere (March 2004) l “Program Slicing for Refactoring” Mathieu Verbaere (September 2003) l “Automated Tools for Refactoring” Ran Ettinger (June 2003) l “Program Slicing” Mark Weiser (1981) Yossi Peery Advanced SW Tools Seminar Jan-05


