Program Introduction Lecture Created by:






















- Размер: 10.4 Mегабайта
- Количество слайдов: 32
Описание презентации Program Introduction Lecture Created by: по слайдам
 Program Introduction Lecture Created by: Christopher Jackson, Howard Johnson, Gary Hampson © Imperial College London AAPGImperial. Barrel. Award. Program
Program Introduction Lecture Created by: Christopher Jackson, Howard Johnson, Gary Hampson © Imperial College London AAPGImperial. Barrel. Award. Program
 Rationale of Scenario • New Business Opportunities (NBO) provide the growth engines for oil companies in the search for increasing their reserves base. • NBO often arise as the current operator is prepared to offer an equity stake in the acreage to your company – known as a “farm-out” opportunity. • The operator may “farm-out” for numerous reasons, e. g. (1) to dilute equity or relinquish acreage in an area considered to have low potential, (2) to acquire new, more prospective acreage, (3) to finance a drilling campaign elsewhere, etc. • To encourage companies to buy-in to the opportunity the operator opens up a “data room” where prospective farm-inees can view the data for a few days and assess its hydrocarbon potential. • This exercise mimicks this process but over a timeframe significantly longer than typically encountered in the real world…
Rationale of Scenario • New Business Opportunities (NBO) provide the growth engines for oil companies in the search for increasing their reserves base. • NBO often arise as the current operator is prepared to offer an equity stake in the acreage to your company – known as a “farm-out” opportunity. • The operator may “farm-out” for numerous reasons, e. g. (1) to dilute equity or relinquish acreage in an area considered to have low potential, (2) to acquire new, more prospective acreage, (3) to finance a drilling campaign elsewhere, etc. • To encourage companies to buy-in to the opportunity the operator opens up a “data room” where prospective farm-inees can view the data for a few days and assess its hydrocarbon potential. • This exercise mimicks this process but over a timeframe significantly longer than typically encountered in the real world…
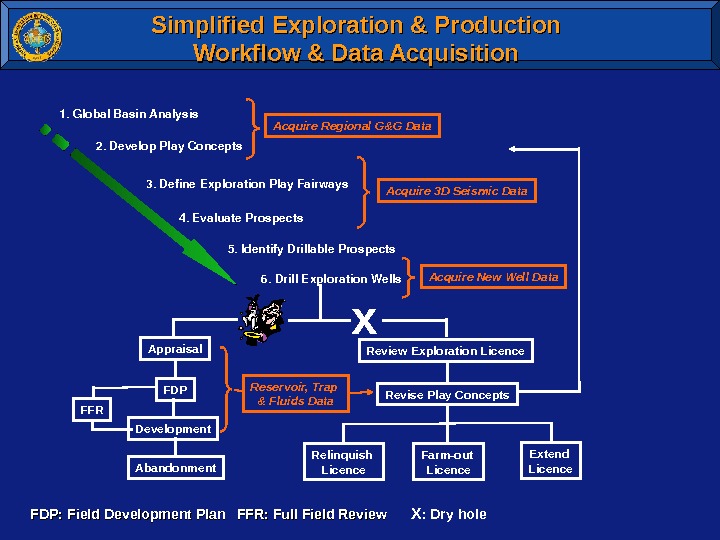
 Simplified Exploration & Production Workflow & Data Acquisition 1. Global. Basin. Analysis 2. Develop. Play. Concepts 3. Define. Exploration. Play. Fairways 4. Evaluate. Prospects 5. Identify. Drillable. Prospects 6. Drill. Exploration. Wells x Appraisal FDP Development. FFR Abandonment Reservoir, Trap & Fluids Data Acquire New Well Data. Acquire 3 D Seismic Data. Acquire Regional G&G Data FDP: Field Development Plan FFR: Full Field Review X : Dry hole. Review Exploration Licence Revise Play Concepts Relinquish Licence Extend Licence. Farm-out Licence
Simplified Exploration & Production Workflow & Data Acquisition 1. Global. Basin. Analysis 2. Develop. Play. Concepts 3. Define. Exploration. Play. Fairways 4. Evaluate. Prospects 5. Identify. Drillable. Prospects 6. Drill. Exploration. Wells x Appraisal FDP Development. FFR Abandonment Reservoir, Trap & Fluids Data Acquire New Well Data. Acquire 3 D Seismic Data. Acquire Regional G&G Data FDP: Field Development Plan FFR: Full Field Review X : Dry hole. Review Exploration Licence Revise Play Concepts Relinquish Licence Extend Licence. Farm-out Licence
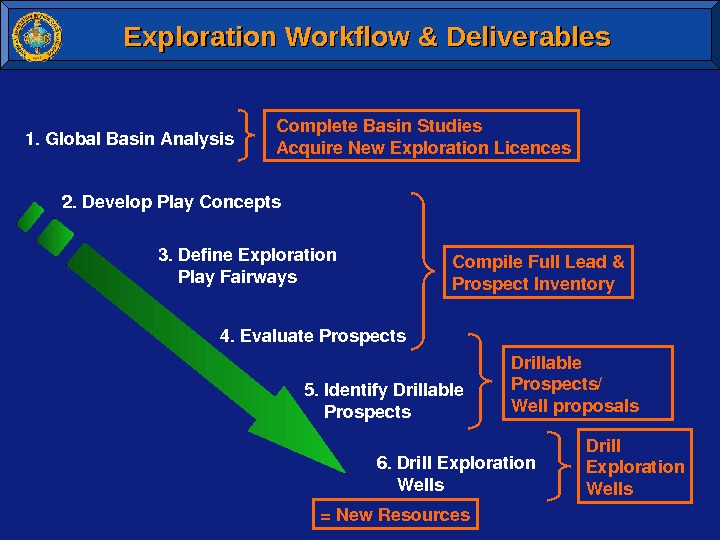
 Exploration Workflow & Deliverables 1. Global. Basin. Analysis 2. Develop. Play. Concepts 3. Define. Exploration Play. Fairways 4. Evaluate. Prospects 5. Identify. Drillable Prospects 6. Drill. Exploration Wells Complete. Basin. Studies Acquire. New. Exploration. Licences Compile. Full. Lead& Prospect. Inventory Drillable Prospects/ Wellproposals Drill Exploration Wells =New. Resources
Exploration Workflow & Deliverables 1. Global. Basin. Analysis 2. Develop. Play. Concepts 3. Define. Exploration Play. Fairways 4. Evaluate. Prospects 5. Identify. Drillable Prospects 6. Drill. Exploration Wells Complete. Basin. Studies Acquire. New. Exploration. Licences Compile. Full. Lead& Prospect. Inventory Drillable Prospects/ Wellproposals Drill Exploration Wells =New. Resources
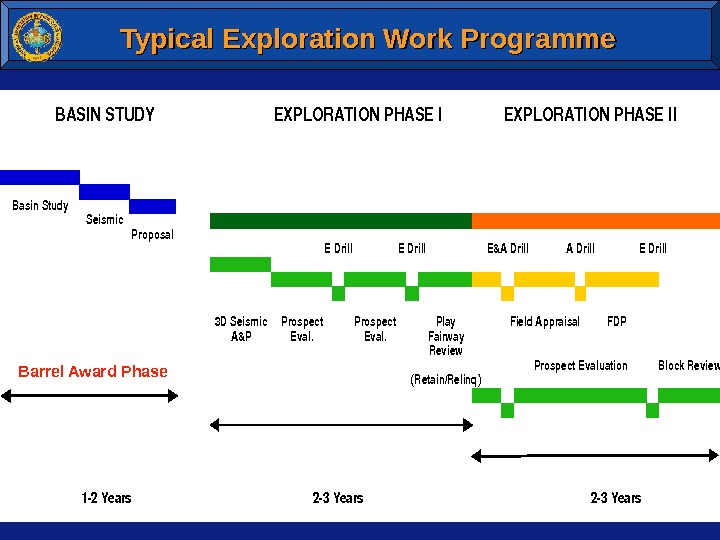
 Typical Exploration Work Programme. BASINSTUDYEXPLORATIONPHASEII Basin. Study Seismic Proposal EDrill. E&ADrill. EDrill 3 DSeismic. Prospect. Play. Field. Appraisal. FDP A&PEval. Fairway Review Prospect. Evaluation. Block. Review (Retain/Relinq) 12 Years 23 Years Barrel Award Phase
Typical Exploration Work Programme. BASINSTUDYEXPLORATIONPHASEII Basin. Study Seismic Proposal EDrill. E&ADrill. EDrill 3 DSeismic. Prospect. Play. Field. Appraisal. FDP A&PEval. Fairway Review Prospect. Evaluation. Block. Review (Retain/Relinq) 12 Years 23 Years Barrel Award Phase
 Regionalgeologicalstudiesarefocusedonidentifying potentiallyeffectivepetroleumsystems Regional Geology/Basin Analysis Geographic Opportunity. Palaeogeography Petroleum Systems Exploration Plays
Regionalgeologicalstudiesarefocusedonidentifying potentiallyeffectivepetroleumsystems Regional Geology/Basin Analysis Geographic Opportunity. Palaeogeography Petroleum Systems Exploration Plays
 55 R. Hall, 2000 Plate Tectonic Setting & Tectonic Evolution-1 Note how petroleum systems develop Example: SE Asia
55 R. Hall, 2000 Plate Tectonic Setting & Tectonic Evolution-1 Note how petroleum systems develop Example: SE Asia
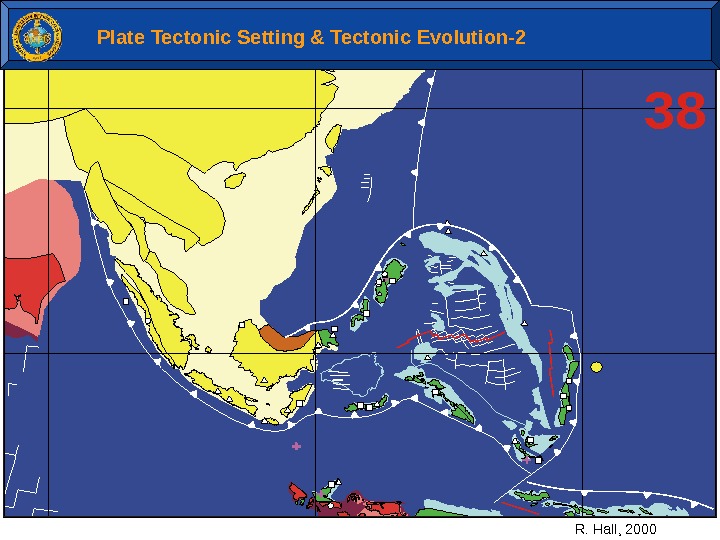
 38 R. Hall, 2000 Plate Tectonic Setting & Tectonic Evolution-
38 R. Hall, 2000 Plate Tectonic Setting & Tectonic Evolution-
 18 R. Hall, 2000 Plate Tectonic Setting & Tectonic Evolution-
18 R. Hall, 2000 Plate Tectonic Setting & Tectonic Evolution-
 0 R. Hall, 2000 Plate Tectonic Setting & Tectonic Evolution-
0 R. Hall, 2000 Plate Tectonic Setting & Tectonic Evolution-
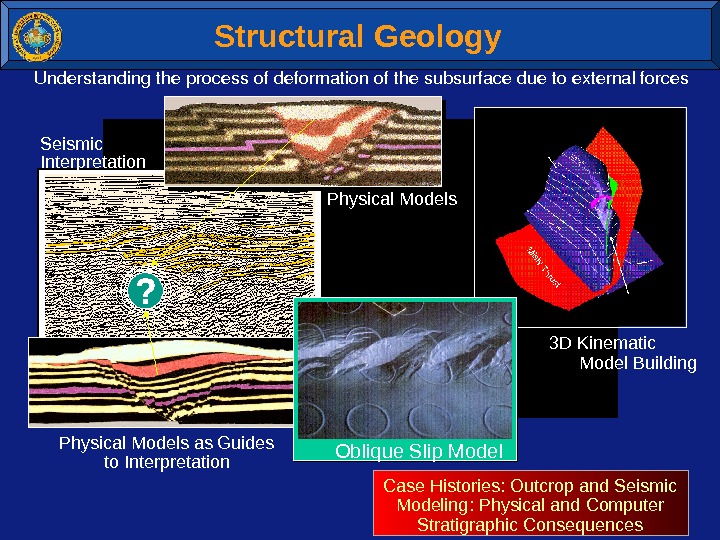
 Structural Geology Understandingtheprocessofdeformationofthesubsurfaceduetoexternalforces 3 D Kinematic Model Building Physical Models as Guides to Interpretation Oblique Slip Model Case Histories: Outcrop and Seismic Modeling: Physical and Computer Stratigraphic Consequences. Physical Models. Seismic Interpretation
Structural Geology Understandingtheprocessofdeformationofthesubsurfaceduetoexternalforces 3 D Kinematic Model Building Physical Models as Guides to Interpretation Oblique Slip Model Case Histories: Outcrop and Seismic Modeling: Physical and Computer Stratigraphic Consequences. Physical Models. Seismic Interpretation
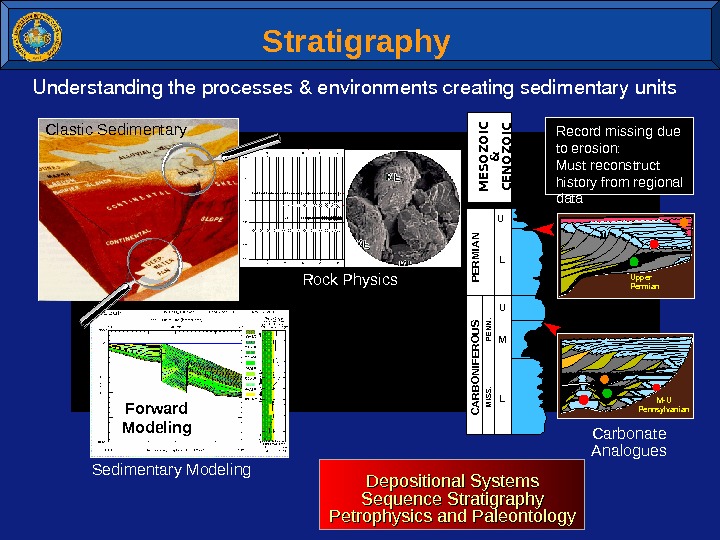
 Shale/Wet Sand Top of Gas Sand Base of Gas Sand. Forward Modeling Stratigraphy Understandingtheprocesses&environmentscreatingsedimentaryunits PERMIAN CARBONIFEROUS U LMU L MISS. PENN. MU Pennsylvanian. Upper Permian. Record missing due to erosion: Must reconstruct history from regional data M ESO ZO IC & CENO ZO IC Rock Physics Sedimentary Modeling Carbonate Analogues Depositional Systems Sequence Stratigraphy Petrophysics and Paleontology Clastic Sedimentary
Shale/Wet Sand Top of Gas Sand Base of Gas Sand. Forward Modeling Stratigraphy Understandingtheprocesses&environmentscreatingsedimentaryunits PERMIAN CARBONIFEROUS U LMU L MISS. PENN. MU Pennsylvanian. Upper Permian. Record missing due to erosion: Must reconstruct history from regional data M ESO ZO IC & CENO ZO IC Rock Physics Sedimentary Modeling Carbonate Analogues Depositional Systems Sequence Stratigraphy Petrophysics and Paleontology Clastic Sedimentary
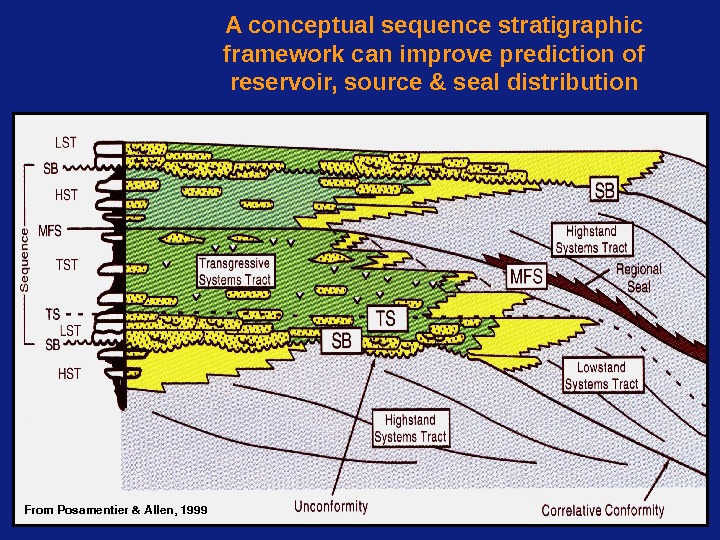
 A conceptual sequence stratigraphic framework can improve prediction of reservoir, source & seal distribution From. Posamentier&Allen,
A conceptual sequence stratigraphic framework can improve prediction of reservoir, source & seal distribution From. Posamentier&Allen,
 Creaming. Curves&Sequence. Stratigraphy Timeor. Numberof. Wells. Drilled. C u m u la tiv e D is c o ve re d H yd ro c a rb o n V o lu m e Modifiedfrom Sneddenetal. ,
Creaming. Curves&Sequence. Stratigraphy Timeor. Numberof. Wells. Drilled. C u m u la tiv e D is c o ve re d H yd ro c a rb o n V o lu m e Modifiedfrom Sneddenetal. ,
 Accumulation Petroleum. Migration Seal Reservoir Leakage Petroleum. Charge Source Rock Migration Pathways Determine Age of Oils Coaly Source Model. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Gamma. Density. Resistivity. Heavy Oil Lite Oil Gas 0 my G eneration Rate Predict Oil Quality 100 my Source Rock Prediction Sequence Stratigraphy. Characterizing the type, history and origin of petroleum Exploration Geochemistry Inorganic and Organic Sedimentology
Accumulation Petroleum. Migration Seal Reservoir Leakage Petroleum. Charge Source Rock Migration Pathways Determine Age of Oils Coaly Source Model. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Gamma. Density. Resistivity. Heavy Oil Lite Oil Gas 0 my G eneration Rate Predict Oil Quality 100 my Source Rock Prediction Sequence Stratigraphy. Characterizing the type, history and origin of petroleum Exploration Geochemistry Inorganic and Organic Sedimentology
 Petroleum Systems Analysis • Source Rock • Reservoir Rock • Seal Rock • Migration Route • Trap • Generation • Migration • Accumulation • Preservation • Timing = critical 1. Petroleum Systems Elements 2. Petroleum Systems Processes Note: if just oneone element is missing = failure!Key Play Elements
Petroleum Systems Analysis • Source Rock • Reservoir Rock • Seal Rock • Migration Route • Trap • Generation • Migration • Accumulation • Preservation • Timing = critical 1. Petroleum Systems Elements 2. Petroleum Systems Processes Note: if just oneone element is missing = failure!Key Play Elements
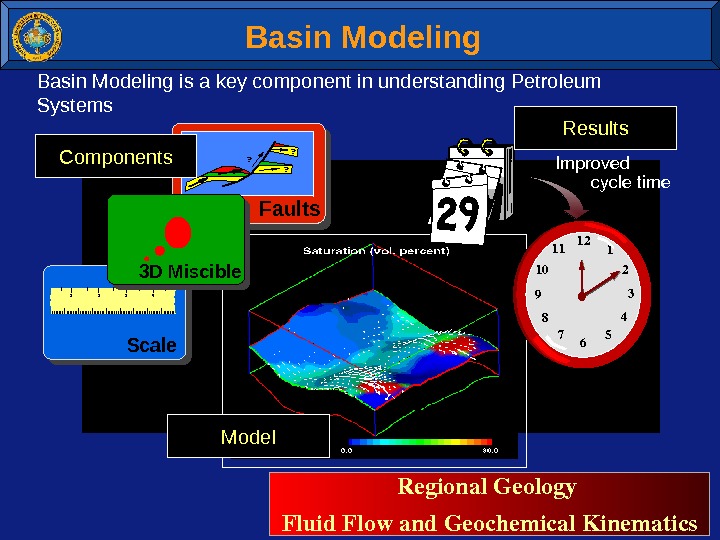
 Basin Modeling is a key component in understanding Petroleum Systems. Faults ? ? ? 1234 Scale 3 D Miscible 112 2 3 4 567 8 9 10 11 Improved cycletime Regional. Geology Fluid. Flowand. Geochemical. Kinematics Basin Modeling Model. Components Results
Basin Modeling is a key component in understanding Petroleum Systems. Faults ? ? ? 1234 Scale 3 D Miscible 112 2 3 4 567 8 9 10 11 Improved cycletime Regional. Geology Fluid. Flowand. Geochemical. Kinematics Basin Modeling Model. Components Results
 Generation and Migration Reservoir Extent. Source Extent. Seal Extent Critical Reconstruction Present Past Components HC Charge Preservation. Time Present. Timing Sheets. Play Maps Petroleum System, Play Definition and Risk Analysis Jeff Brown, Mobil, 1999 Trap
Generation and Migration Reservoir Extent. Source Extent. Seal Extent Critical Reconstruction Present Past Components HC Charge Preservation. Time Present. Timing Sheets. Play Maps Petroleum System, Play Definition and Risk Analysis Jeff Brown, Mobil, 1999 Trap
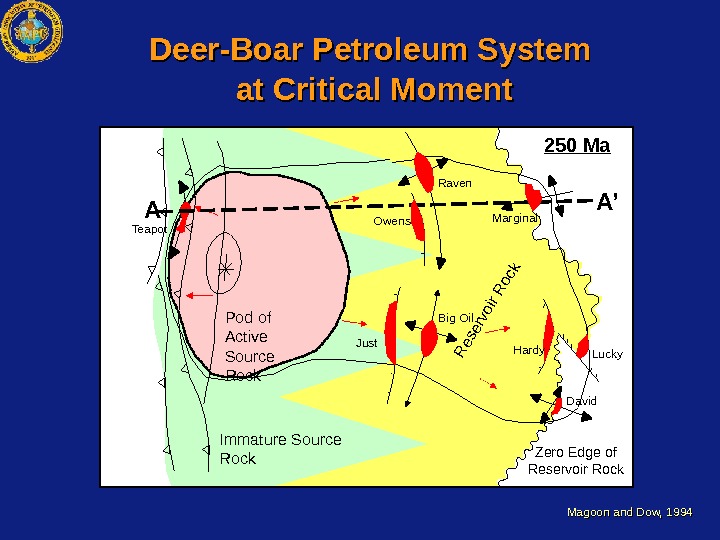
 Teapot Owens Pod of Active Source Rock Just Big Oil Hardy Lucky Zero Edge of Reservoir Rock. Immature Source Rock Raven Marginal 250 Ma A A’Deer-Boar Petroleum System at Critical Moment Magoon and Dow, 1994 Reservoir Rock. David
Teapot Owens Pod of Active Source Rock Just Big Oil Hardy Lucky Zero Edge of Reservoir Rock. Immature Source Rock Raven Marginal 250 Ma A A’Deer-Boar Petroleum System at Critical Moment Magoon and Dow, 1994 Reservoir Rock. David
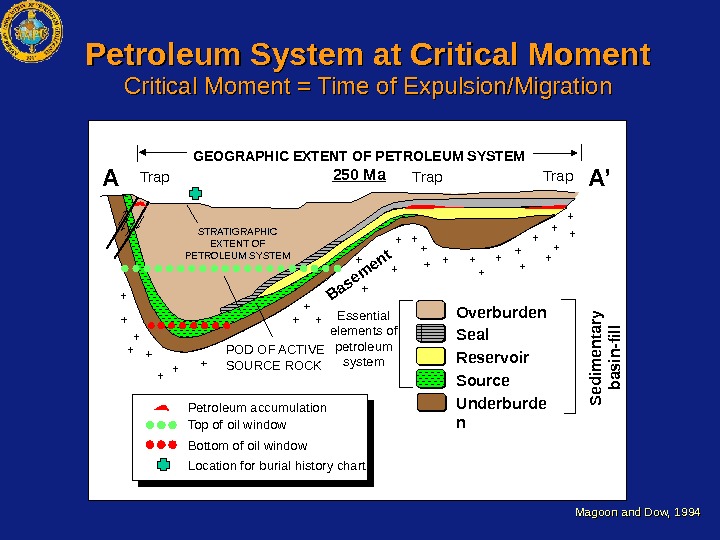
 Overburden Seal Reservoir Source. STRATIGRAPHIC EXTENT OF PETROLEUM SYSTEM Trap Essential elements of petroleum system. POD OF ACTIVE SOURCE ROCKBasement Underburde n S edim entary basin-fill. GEOGRAPHIC EXTENT OF PETROLEUM SYSTEM 250 Ma Trap Petroleum accumulation Top of oil window Bottom of oil window Location for burial history chart. A A’Petroleum System at Critical Moment = Time of Expulsion/Migration Magoon and Dow,
Overburden Seal Reservoir Source. STRATIGRAPHIC EXTENT OF PETROLEUM SYSTEM Trap Essential elements of petroleum system. POD OF ACTIVE SOURCE ROCKBasement Underburde n S edim entary basin-fill. GEOGRAPHIC EXTENT OF PETROLEUM SYSTEM 250 Ma Trap Petroleum accumulation Top of oil window Bottom of oil window Location for burial history chart. A A’Petroleum System at Critical Moment = Time of Expulsion/Migration Magoon and Dow,
 Basement. GEOGRAPHIC EXTENT OF PETROLEUM SYSTEM Present-Day STRATIGRAPHIC EXTENT OF PETROLEUM SYSTEM Petroleum accumulation Top of oil window Bottom of oil window Trap Seal Reservoir Source Underburden. Overburden. A A’ Magoon and Dow, 1994 Present-Day Petroleum System
Basement. GEOGRAPHIC EXTENT OF PETROLEUM SYSTEM Present-Day STRATIGRAPHIC EXTENT OF PETROLEUM SYSTEM Petroleum accumulation Top of oil window Bottom of oil window Trap Seal Reservoir Source Underburden. Overburden. A A’ Magoon and Dow, 1994 Present-Day Petroleum System
 400400 300300 200200 100100 Paleozoic Mesozoic Cen. PP NN KK JJT PP MM DD PPLithology Rock Unit Depth (Km ) Source Reservoir Seal O verburden 11 22 33 Placer Fm George Sh Boar Ss Deer Sh Elk Fm. Top gas window Critical Moment Thick Fm. RR Burial History Chart Magoon and Dow, 1994 Generation Time of Expulsion and Migration. (Trap must already exist)Top oil window
400400 300300 200200 100100 Paleozoic Mesozoic Cen. PP NN KK JJT PP MM DD PPLithology Rock Unit Depth (Km ) Source Reservoir Seal O verburden 11 22 33 Placer Fm George Sh Boar Ss Deer Sh Elk Fm. Top gas window Critical Moment Thick Fm. RR Burial History Chart Magoon and Dow, 1994 Generation Time of Expulsion and Migration. (Trap must already exist)Top oil window
 400400 300300 200200 100100 Geologic Time Scale Petroleum System Events Rock Units Source Rock Reservoir Rock Seal Rock Trap Formation Overburden Rock Gen/Migration/Accum Preservation Critical Moment. Paleozoic Mesozoic Cenozoic DD MM PP PP TT RR JJ KK PP NNE le m e n ts P ro c e s s e s Magoon and Dow, 1994 Petroleum System Events Chart Timing of Elements and Processes Critical Moment Time of Expulsion and Migration (Trap must already exist)
400400 300300 200200 100100 Geologic Time Scale Petroleum System Events Rock Units Source Rock Reservoir Rock Seal Rock Trap Formation Overburden Rock Gen/Migration/Accum Preservation Critical Moment. Paleozoic Mesozoic Cenozoic DD MM PP PP TT RR JJ KK PP NNE le m e n ts P ro c e s s e s Magoon and Dow, 1994 Petroleum System Events Chart Timing of Elements and Processes Critical Moment Time of Expulsion and Migration (Trap must already exist)
 Modified from Dolivo, 1991 Anticlinal Traps. Fault Traps Channel Pinch-Out Traps Concepts of HC migration & entrapment (Balingian Province, offshore Sarawak) Top of Oil Window Gas Generated Deeper Sub-unconformity truncation traps
Modified from Dolivo, 1991 Anticlinal Traps. Fault Traps Channel Pinch-Out Traps Concepts of HC migration & entrapment (Balingian Province, offshore Sarawak) Top of Oil Window Gas Generated Deeper Sub-unconformity truncation traps
 1. 0 00 5000 MMBOEP ro b a b ility o f F in d in g. Most Probable Field Size. Quantitative Play Analysis Risked Potential Speculative Potential Statistical Estimate of Chance for Success
1. 0 00 5000 MMBOEP ro b a b ility o f F in d in g. Most Probable Field Size. Quantitative Play Analysis Risked Potential Speculative Potential Statistical Estimate of Chance for Success
 Barrel Award: aim, objectives & deliverables General aim : to document the tectono-stratigraphy of a sedimentary basin in order to assess its petroleum potential Specific objectives : • Literature review to establish regional geodynamics/plate tectonics • Regional stratigraphic framework, depositional environments & palaeogeography • Basin type: classification and tectonic setting • Seismic interpretation (key horizons and associated maps) • Well log interpretation and correlation • Formation evaluation • Sequence stratigraphic analysis • Reservoir/source/seal evaluation (incl. reservoir thickness and quality maps) • Subsurface fluids and pressure regimes • Subsidence history and source rock maturation and migration (inc. 1 D basin modelling) • Play fairway maps • Analysis of structural and stratigraphic traps • Prospect evaluation • Hydrocarbon volumetric and rick assessment.
Barrel Award: aim, objectives & deliverables General aim : to document the tectono-stratigraphy of a sedimentary basin in order to assess its petroleum potential Specific objectives : • Literature review to establish regional geodynamics/plate tectonics • Regional stratigraphic framework, depositional environments & palaeogeography • Basin type: classification and tectonic setting • Seismic interpretation (key horizons and associated maps) • Well log interpretation and correlation • Formation evaluation • Sequence stratigraphic analysis • Reservoir/source/seal evaluation (incl. reservoir thickness and quality maps) • Subsurface fluids and pressure regimes • Subsidence history and source rock maturation and migration (inc. 1 D basin modelling) • Play fairway maps • Analysis of structural and stratigraphic traps • Prospect evaluation • Hydrocarbon volumetric and rick assessment.
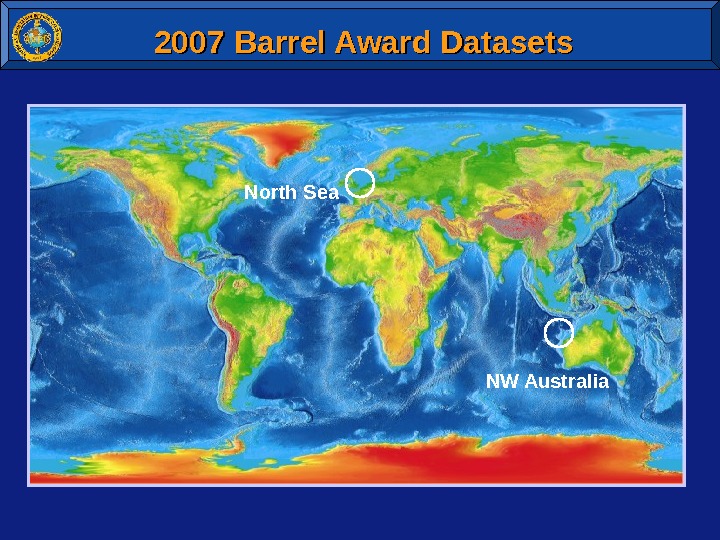
 2007 Barrel Award Datasets North Sea NW Australia
2007 Barrel Award Datasets North Sea NW Australia
 Datasets: General Geological Setting Lower Indus Basin, Pakistan (Passive Margin)Cooper-Eromanga Basin, Australia (Compressional) Lower Congo Basin, West Africa (Salt-influenced basin) Bellatrix Basin, Bay of Biscay (Inverted Rift)
Datasets: General Geological Setting Lower Indus Basin, Pakistan (Passive Margin)Cooper-Eromanga Basin, Australia (Compressional) Lower Congo Basin, West Africa (Salt-influenced basin) Bellatrix Basin, Bay of Biscay (Inverted Rift)
 Assessment • Final 30 minute talk (Friday 31 st March) to a panel of senior oil industry geoscientists: preceded by talk “dry-runs” on Monday 20 th March • Talk will be assessed on technical quality, thoroughness, imagination, convincing arguments and enthusiasm. • Talk should be supported by a short (1 page) handout summarising key findings of the study – similar in format to Wytch Farm handouts. • Each team will be given a mark which will form part of each individual team member’s assessed coursework. • Executive report which summarises key structural stratigraphic and petroleum potential observations • 20 page limit (12 pt – 1. 5 spaced text) not including figures • Maximum of 10 pages additional material as appendices • Report should be clearly sectioned, bound, numbered and ready-to-read
Assessment • Final 30 minute talk (Friday 31 st March) to a panel of senior oil industry geoscientists: preceded by talk “dry-runs” on Monday 20 th March • Talk will be assessed on technical quality, thoroughness, imagination, convincing arguments and enthusiasm. • Talk should be supported by a short (1 page) handout summarising key findings of the study – similar in format to Wytch Farm handouts. • Each team will be given a mark which will form part of each individual team member’s assessed coursework. • Executive report which summarises key structural stratigraphic and petroleum potential observations • 20 page limit (12 pt – 1. 5 spaced text) not including figures • Maximum of 10 pages additional material as appendices • Report should be clearly sectioned, bound, numbered and ready-to-read
 What do we do now? • Get to know the Data Package: Seismic data, well data and other available material • It is suggested that the team organize a data system to store additional collated material alogn with those in the data package. • It is important to delegate work tasks to each group member early in the project: • Data QC and preliminary seismic interpretation • Regional literature review • Preliminary well data analysis • … after looking over the data, “brainstormed” ideas
What do we do now? • Get to know the Data Package: Seismic data, well data and other available material • It is suggested that the team organize a data system to store additional collated material alogn with those in the data package. • It is important to delegate work tasks to each group member early in the project: • Data QC and preliminary seismic interpretation • Regional literature review • Preliminary well data analysis • … after looking over the data, “brainstormed” ideas
 DATA ROOM VISIT CHECK LIST This list attempts to assign certain tasks to the respective disciplines when attending data rooms, but it should be recognized that some of the ŌtasksÕ may require cross- discipline investigation. Some general questions that the Team should address while considering or attending any data rooms are as follows: 1. What has worked well, and not, in this basin/region? 2. What has been the exploration strategy in the area? 3. Is there any new technology that can be applied to this area to enhance chance of geologic and commercial success? 4. What could be done differently that would improve success in this venture/proposal? 5. What are the key petroleum system elements of this opportunity and what data are required to accurately represent this opportunity to management? Is there a source rock and a vbiab; e reservoir? 6. What data havenÕt they shown you that may be available? 7. Why is this opportunity available now? 8. Do we have the right people on this data room visit to accurately obtain/evaluate subject data? 9. Has a confidentiality agreement been signed and does it conflict with other potential Kufpec operations/projects? 10. What hard data are currently in-house and what is needed to improve our understanding of the opportunity? 11. What has changed to improve the economics (better infrastructure, new laws and fiscal terms, new discoveries, etc? ) 12. Is a translator necessary for presentations and/or data review? Who will provide any translations, if necessary? 13. Are we looking for oil or gas? Is this the appropriate basin to explore for oil or gas? 14. Which are the possible scenerios? Are there existing pipelines? What is their ullage? Is there any spare capacity and what is it? 15. Are there any possible drilling problems in this area (e. g. shallow gas, overpressures, ice, jungle, mountains, hurricanes, etc. )?
DATA ROOM VISIT CHECK LIST This list attempts to assign certain tasks to the respective disciplines when attending data rooms, but it should be recognized that some of the ŌtasksÕ may require cross- discipline investigation. Some general questions that the Team should address while considering or attending any data rooms are as follows: 1. What has worked well, and not, in this basin/region? 2. What has been the exploration strategy in the area? 3. Is there any new technology that can be applied to this area to enhance chance of geologic and commercial success? 4. What could be done differently that would improve success in this venture/proposal? 5. What are the key petroleum system elements of this opportunity and what data are required to accurately represent this opportunity to management? Is there a source rock and a vbiab; e reservoir? 6. What data havenÕt they shown you that may be available? 7. Why is this opportunity available now? 8. Do we have the right people on this data room visit to accurately obtain/evaluate subject data? 9. Has a confidentiality agreement been signed and does it conflict with other potential Kufpec operations/projects? 10. What hard data are currently in-house and what is needed to improve our understanding of the opportunity? 11. What has changed to improve the economics (better infrastructure, new laws and fiscal terms, new discoveries, etc? ) 12. Is a translator necessary for presentations and/or data review? Who will provide any translations, if necessary? 13. Are we looking for oil or gas? Is this the appropriate basin to explore for oil or gas? 14. Which are the possible scenerios? Are there existing pipelines? What is their ullage? Is there any spare capacity and what is it? 15. Are there any possible drilling problems in this area (e. g. shallow gas, overpressures, ice, jungle, mountains, hurricanes, etc. )?
 AAPGImperial. Barrel. Award. Program Acknowledgments: This presentation is authored by Dr. Chris Jackson, Dr. Howard Johnson, and Dr. Gary Hampson The AAPG is grateful for their contribution to this program and thanks them and Imperial College, London for supply this presentation to universities participating in the Imperial Barrel Award Program.
AAPGImperial. Barrel. Award. Program Acknowledgments: This presentation is authored by Dr. Chris Jackson, Dr. Howard Johnson, and Dr. Gary Hampson The AAPG is grateful for their contribution to this program and thanks them and Imperial College, London for supply this presentation to universities participating in the Imperial Barrel Award Program.

