c1208756b1068ae2f5d84bfb849d3f21.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 64

Profitability, Longevity and Growth The Next Level Ó 2005 Grant W. Howard Company Grant W. Howard 13214 Wallace Road Manchester, MI 48158 (734) 428 -0529 ghoward 685@aol. com 1

Our Discussion Today n n n The Big Picture The Replenishment Process Getting Results: – Customer Service: » Path to Success » Getting Results – Profitability: » Path to Success » Getting Results n n “Discussion” Today is different from the last two days… Day 1 - How it Works, Day 2 - How to Use it Today - Less whiteboard and system, and more how to make it all come together to GET RESULTS! The Power of Your System Summary - Some Final Thoughts Through Slide 33 - “Lite” System and Summary Ó 2005 Grant W. Howard Company 2
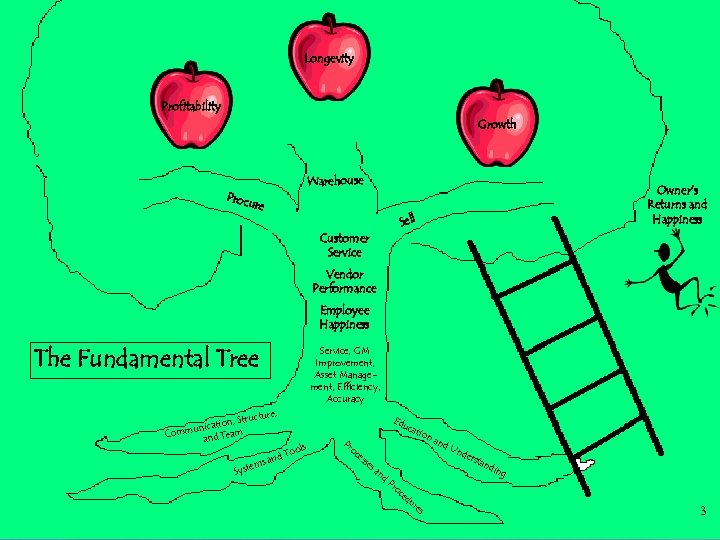
Longevity Profitability Growth Warehouse Proc ure Owner’s Returns and Happiness Sell Customer Service Vendor Performance Employee Happiness The Fundamental Tree Service, GM Improvement, Asset Management, Efficiency, Accuracy cture, n, Stru unicatio m Comm and Tea ls Too and s em Syst Edu Pr oc cat ion es se sa nd Pr oc ed Ó 2005 Grant W. Howard Company ur es and Un der stan din g 3
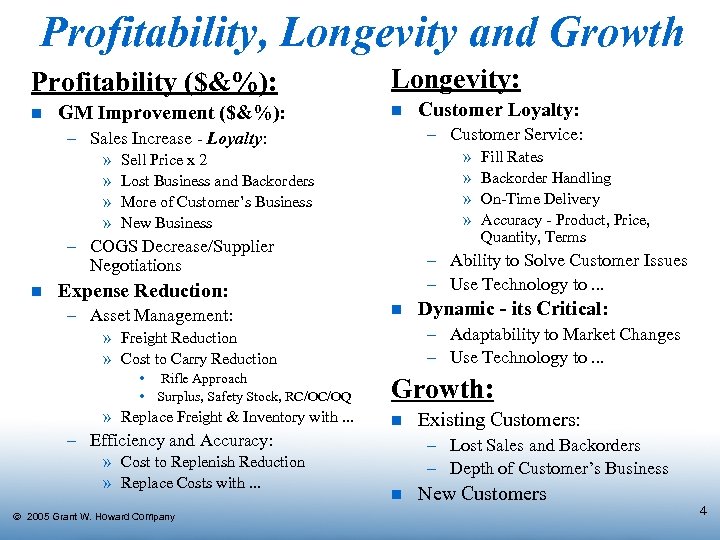
Profitability, Longevity and Growth Profitability ($&%): n GM Improvement ($&%): Longevity: n – Customer Service: – Sales Increase - Loyalty: » » » » Sell Price x 2 Lost Business and Backorders More of Customer’s Business New Business – COGS Decrease/Supplier Negotiations n n » Replace Freight & Inventory with. . . – Efficiency and Accuracy: » Cost to Replenish Reduction » Replace Costs with. . . Ó 2005 Grant W. Howard Company Dynamic - its Critical: – Adaptability to Market Changes – Use Technology to. . . » Freight Reduction » Cost to Carry Reduction • Rifle Approach • Surplus, Safety Stock, RC/OC/OQ Fill Rates Backorder Handling On-Time Delivery Accuracy - Product, Price, Quantity, Terms – Ability to Solve Customer Issues – Use Technology to. . . Expense Reduction: – Asset Management: Customer Loyalty: Growth: n Existing Customers: – Lost Sales and Backorders – Depth of Customer’s Business n New Customers 4

Profitability, Longevity and Growth Procure: n n n Inventory Management/Control Operations Sales Marketing Systems and Technology Warehouse: n n n Sell: n Seems to be a Pattern? n Where does Management fit into all of this? n n n Ó 2005 Grant W. Howard Company Operations Inventory Management/Control Systems and Technology Sales Marketing Inventory Management/Control Operations Systems and Technology 5

Profitability, Longevity and Growth Customers: n n Availability Backorder Handling On-Time Delivery Accuracy – – n n Product Quantity Price Terms Win-Win MEASURE Vendors: n n n Employees: n n n Ó 2005 Grant W. Howard Company Win-Win Not Just Price MEASURE Want to do a Good Job Balanced Objectives/Team Tools, Processes, EDUCATE! Remove Stress, Give Method Win-Win MEASURE 6

Profitability, Longevity and Growth n Communication, Structure and Team: Companies need to have a team concept, KNOWN balanced objectives, with a way to get there Management! n Systems and Tools: Companies need to understand use more than 20, 30, 50% of their systems! Ó 2005 Grant W. Howard Company n Processes and Procedures: Companies need to have closed-loop, actual working processes and procedures! n Education and Understanding: Companies need to education their people and help them be part of the solution! 7

Inventory Management Getting Results When, What, How Much Ó 2005 Grant W. Howard Company 8
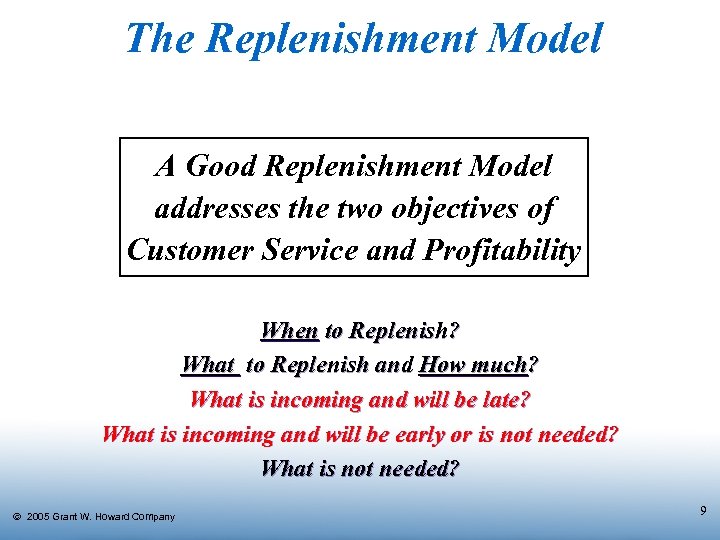
The Replenishment Model A Good Replenishment Model addresses the two objectives of Customer Service and Profitability When to Replenish? What to Replenish and How much? What is incoming and will be late? What is incoming and will be early or is not needed? What is not needed? Ó 2005 Grant W. Howard Company 9
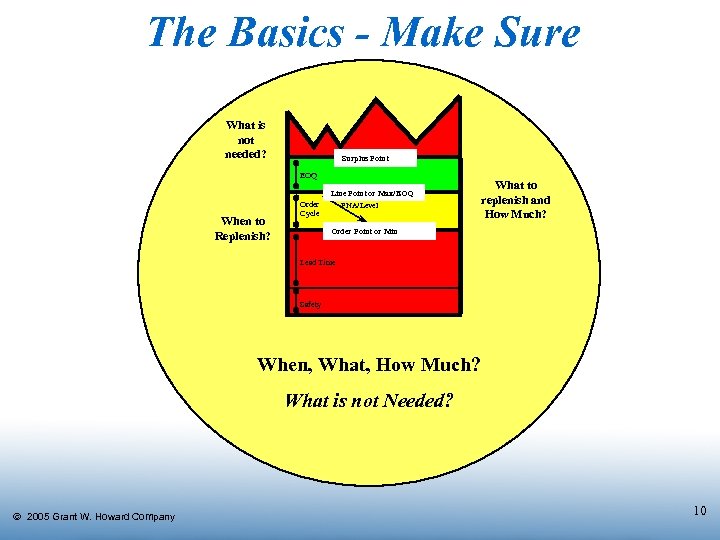
The Basics - Make Sure What is not needed? Surplus Point EOQ Line Point or Max/EOQ When to Replenish? Order Cycle PNA/Level What to replenish and How Much? Order Point or Min Lead Time Safety When, What, How Much? What is not Needed? Ó 2005 Grant W. Howard Company 10

“When and What” n “When to Replenish” – Target/Incentive and RC - Profits – BOP with Target/Incentive and RC considerations - Profits and Service n “What to Replenishment” – Line Buy (Make Target) – Fill In/Emergency Buy – Transfers – Do Nothing Cost to Carry versus Freight, Price and Service Ó 2005 Grant W. Howard Company 11

“What and How Much” Line Buy/Transfer Fill-in Buy/Transfer Items Below LP Items Below OP/“Cycle*” Order Quantity: 1. Up to LP 2. Compare to SOQ 3. Minimum Run 4. Vendor/Transfer Package Order Quantity: 1. Up to OP/”Cycle*” 2. Compare to SOQ? 3. Vendor/Transfer Package * It is important to replenish items not only below OP, but also the items below the “Cycle”. These items should be replenished at least back up to the “Cycle”. Cycle is the days left in the cycle (OC - (Today - LLB)) Ó 2005 Grant W. Howard Company 12
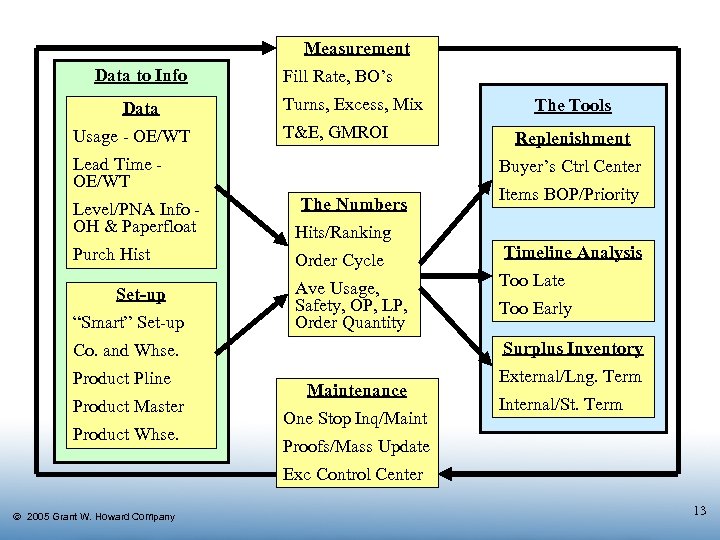
Measurement Data to Info Data Usage - OE/WT Fill Rate, BO’s Turns, Excess, Mix T&E, GMROI Lead Time OE/WT The Numbers Hits/Ranking Purch Hist Order Cycle “Smart” Set-up Ave Usage, Safety, OP, LP, Order Quantity Product Master Product Whse. Items BOP/Priority Timeline Analysis Too Late Too Early Surplus Inventory Co. and Whse. Product Pline Replenishment Buyer’s Ctrl Center Level/PNA Info OH & Paperfloat Set-up The Tools Maintenance One Stop Inq/Maint External/Lng. Term Internal/St. Term Proofs/Mass Update Exc Control Center Ó 2005 Grant W. Howard Company 13
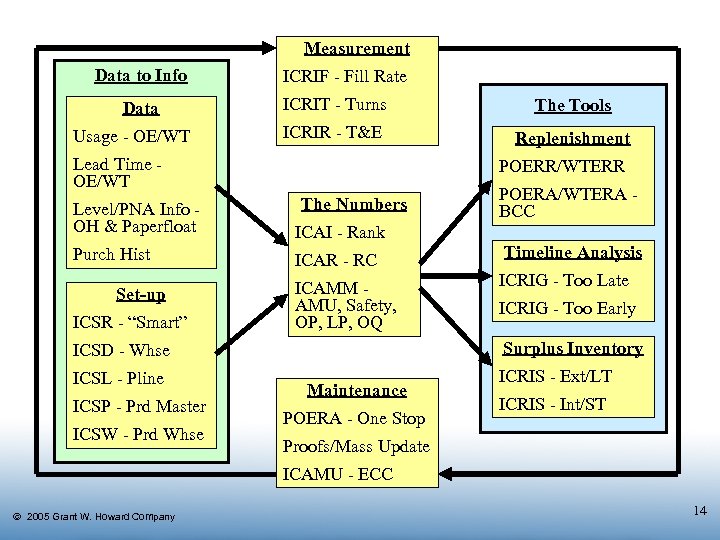
Measurement Data to Info Data Usage - OE/WT ICRIF - Fill Rate ICRIT - Turns The Tools ICRIR - T&E Replenishment Lead Time OE/WT POERR/WTERR The Numbers Level/PNA Info OH & Paperfloat ICAI - Rank Purch Hist ICAR - RC Set-up ICSR - “Smart” ICAMM AMU, Safety, OP, LP, OQ ICSP - Prd Master ICSW - Prd Whse Timeline Analysis ICRIG - Too Late ICRIG - Too Early Surplus Inventory ICSD - Whse ICSL - Pline POERA/WTERA BCC Maintenance POERA - One Stop ICRIS - Ext/LT ICRIS - Int/ST Proofs/Mass Update ICAMU - ECC Ó 2005 Grant W. Howard Company 14

Getting Results! Ó 2005 Grant W. Howard Company 15
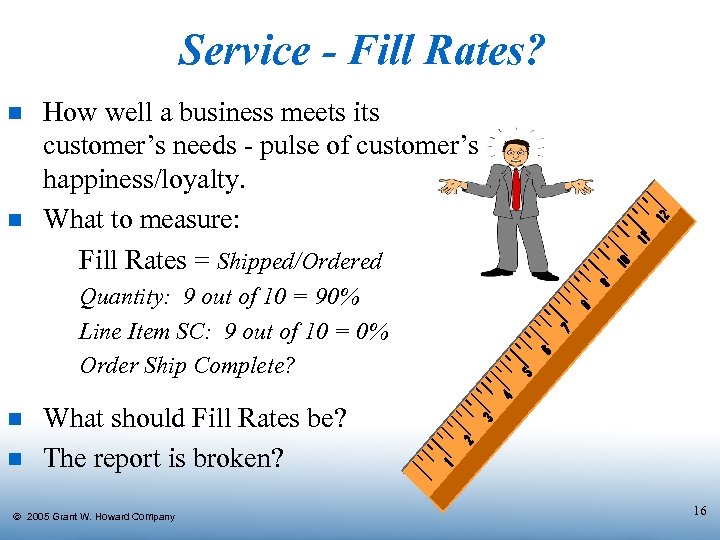
Service - Fill Rates? n n How well a business meets its customer’s needs - pulse of customer’s happiness/loyalty. What to measure: Fill Rates = Shipped/Ordered Quantity: 9 out of 10 = 90% Line Item SC: 9 out of 10 = 0% Order Ship Complete? n n What should Fill Rates be? The report is broken? Ó 2005 Grant W. Howard Company 16
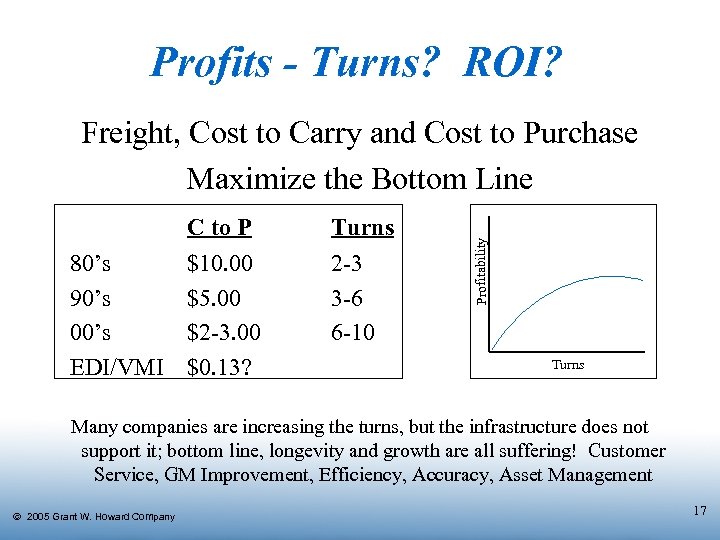
Profits - Turns? ROI? C to P 80’s 90’s 00’s EDI/VMI Turns $10. 00 $5. 00 $2 -3. 00 $0. 13? 2 -3 3 -6 6 -10 Profitability Freight, Cost to Carry and Cost to Purchase Maximize the Bottom Line Turns Many companies are increasing the turns, but the infrastructure does not support it; bottom line, longevity and growth are all suffering! Customer Service, GM Improvement, Efficiency, Accuracy, Asset Management Ó 2005 Grant W. Howard Company 17

Know the Right Things to Do Do these Things Right Inventory Management is at the Time of Replenishment, the “When, What, and How Much”. Everything else is Reacting. Ó 2005 Grant W. Howard Company 18
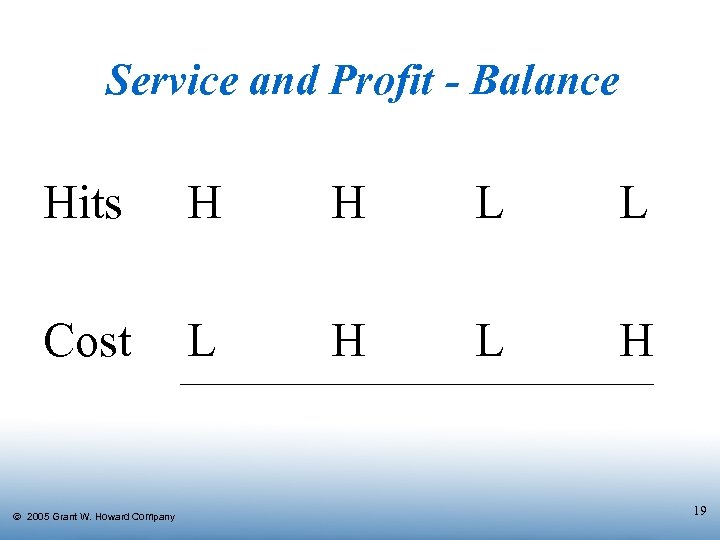
Service and Profit - Balance Hits H H L L Cost L H Ó 2005 Grant W. Howard Company 19

Inventory Management Objectives Customer Service Availability (Fill Rates) Proper Backorder Handling On Time Delivery Accuracy: Item, Quantity, Price Profitability (ROI) GM Improvement (Sales and Cost) Freight Considerations - OC Analysis Efficiency & Asset Mgt: Cto. C and Cto. P Surplus Inventory & Safety Inventory Turns/Days supply, ROI/T&E/GMROI Watch the C to C Watch the C to P (Warehousing, Handling, Obsol. & (Purchasing/Replenishment, Receiving & Shrink, Taxes, Interest) Put-away, A/P) Ó 2005 Grant W. Howard Company 20

The Path to Success - Service 1. Accurate Order Point: – Usage: » Data Collection, Lost Business, Inputs » Method and Window » Seasonal Trending, Advance by Lead Time, and Shift » Roll Up » Correct Paths » Usage Forecast Accuracy Analysis – Lead Time – Safety: 2. Accurate Level: – On-hand Integrity – Paperfloat Control – BIIS 3. Replenish at Order Point: – BOP and Prio – POERA 4. Monitor Changes/Timeline: – Timeline “Gap”/”Too Late” – ICRIG » Safety by Rank/Hits/Velocity » Safety Method by Lead Time » Safety Analysis – Customer Buying Habits – Data, Parameters, Forecasting Ó 2005 Grant W. Howard Company 21

The Path to Success - Service 5. Closed-loop Backorder Process - Service 6. Keep it Working - Maintenance: – Get out of the “Yellow Sticky World” – Watch for Suppressed with Activity – POERA, WTERA, ICAMU 7. Measure and Monitor: – Drill in, Rifle Approach - Don’t Shotgun Approach it, just $$$ and disappointing results. – ICAMU, ICRIF 8. Receiving, Put-away and Backorder Handling - Service 9. Picking, Shipping and On-Time Delivery - Service 10. Billing - Product, Quantity, Price, Terms - Service Ó 2005 Grant W. Howard Company 22

Customer Service Availability, Backorders, OTD, Accuracy Back to Basics 1. Right Inventory not Suffering 5. Operations: because of Wrong – Backorder Policy and Handling – On-Time Delivery 2. Controlled Replenishment – Accuracy of Shipments and Billing 3. Stocking Policy 6. Fill Rates - Monitor, Drill Down, 4. Good Numbers and Proper Find Areas of Improvement Use of Them (OP, Level, LP, and OQ) - Path to Service: – – – Replenish at Order Point - Prio Usage: Lost Sales, DP Freight/C to C vs Service Line Buy vs Emergency Buy Understand LP and OQ Effect Ó 2005 Grant W. Howard Company 23

Customer Service Availability, Backorders, OTD, Accuracy Keys to Good Fill Rates 7. Understand Use: – – Customer Buying Habits Timeline Analysis NOOS Policy and Procedure Smart Selling/Transferring 8. Follow LP and EOQ Suggestions: – Too many Fires – BOP but not at Target Problems 9. “Never-Arrive” Incoming 10. Safety Stock Increase: – Safety Analysis (Over Utilizing) – Safety Increase: » Use a Rifle Approach » Watch the Profits Stellar Customer Service does have to drive your inventory through the roof, it just has to be done smart. Ó 2005 Grant W. Howard Company 24

Customer Service Availability, Backorders, OTD, Accuracy Customer Service Improvement: n Availability n Backorder Handling n On-Time Delivery n Accuracy - Product, Quantity, Price, Terms GM Improvement, Service, Efficiency, Accuracy, Asset Management Ó 2005 Grant W. Howard Company 25

Inventory Management Objectives Customer Service Availability (Fill Rates) Proper Backorder Handling On Time Delivery Accuracy: Item, Quantity, Price Profitability (ROI) GM Improvement (Sales and Cost) Freight Considerations - OC Analysis Efficiency & Asset Mgt: Cto. C and Cto. P Surplus Inventory & Safety Inventory Turns/Days supply, ROI/T&E/GMROI Watch the C to C Watch the C to P (Warehousing, Handling, Obsol. & (Purchasing/Replenishment, Receiving & Shrink, Taxes, Interest) Put-away, A/P) Ó 2005 Grant W. Howard Company 26

The Path to Success - Profits 1. Accurate Line Point and Order Qty: – Accurate Order Point – Usage: » Data Collection, Exceptional Business, Inputs » Method and Window » Seasonal Trending, Advance by Lead Time, and Shift » Roll Up » Correct Paths » Usage Forecast Accuracy Analysis – Accurate Review/Order/Transfer Cycle – Proper OQ Parameters and Controls – Proper Understanding and Use of LP and EOQ – Data, Parameters, Forecasting Ó 2005 Grant W. Howard Company 2. Accurate Level: – On-hand Integrity – Paperfloat Control – BIIS 3. Replenish the Correct Qty: – Line Point, OQ, Pkg – Making Targets Properly – POERA 4. Monitor Changes/Timeline: – Timeline “Too Early” – ICRIG 27

The Path to Success - Profits 5. Surplus Identification and Disposition Process 6. Keep it Working - Maintenance: – Get out of the “Yellow Sticky World” – Watch for slow/inactive stock items – POERA, WTERA, ICAMU 7. Measure and Monitor: – Drill in, Rifle Approach - Don’t Shotgun Approach it, just $$$ and disappointing results. – ICAMU, ICRIT, ICRIR 8. Receiving, Put-away and Backorder Handling - Efficiency 9. Picking, Shipping and On-Time Delivery - Efficiency 10. Billing - Product, Quantity, Price, Terms - Efficiency Ó 2005 Grant W. Howard Company 28

Profitability GM & Expenses (Freight, Cto. C, Cto. P) Back to Basics 1. Stellar Customer Service 2. Controlled Replenishment 3. Stocking Policy 4. Good Numbers and Proper Use of Them (OP, LP, OQ, Level) - Path to Profitability: – – – 5. Vendor Performance and Negotiations 6. T&E and/or GMROI Monitor, Drill Down, Find Areas of Improvement Up to LP, OQ, Min, Package Usage: Exceptional, DP Targets/Incentives Properly Line Buy vs Emergency Buy Availability (Sales, GM, Fires) Ó 2005 Grant W. Howard Company 29
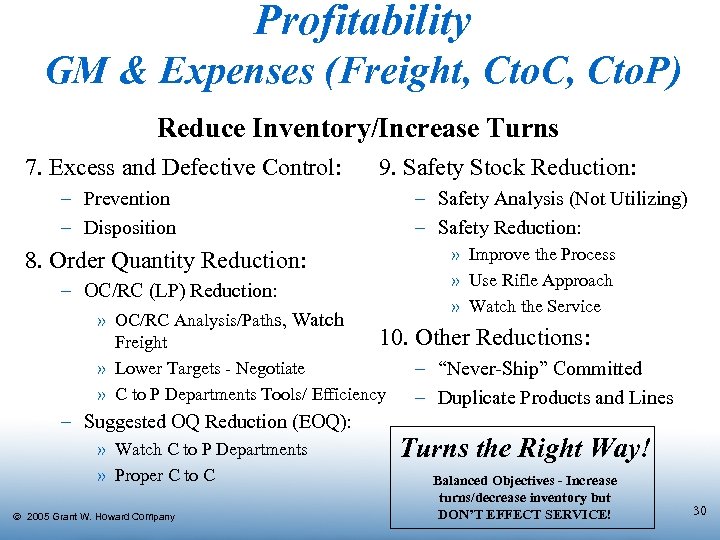
Profitability GM & Expenses (Freight, Cto. C, Cto. P) Reduce Inventory/Increase Turns 7. Excess and Defective Control: – Prevention – Disposition 8. Order Quantity Reduction: – OC/RC (LP) Reduction: » OC/RC Analysis/Paths, Watch 9. Safety Stock Reduction: – Safety Analysis (Not Utilizing) – Safety Reduction: » Improve the Process » Use Rifle Approach » Watch the Service 10. Other Reductions: Freight » Lower Targets - Negotiate – “Never-Ship” Committed » C to P Departments Tools/ Efficiency – Duplicate Products and Lines – Suggested OQ Reduction (EOQ): » Watch C to P Departments » Proper C to C Ó 2005 Grant W. Howard Company Turns the Right Way! Balanced Objectives - Increase turns/decrease inventory but DON’T EFFECT SERVICE! 30
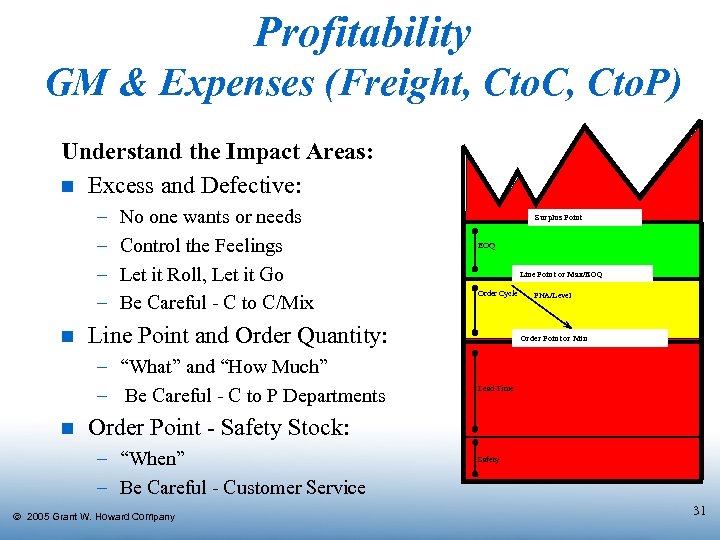
Profitability GM & Expenses (Freight, Cto. C, Cto. P) Understand the Impact Areas: n Excess and Defective: – – n No one wants or needs Control the Feelings Let it Roll, Let it Go Be Careful - C to C/Mix EOQ Line Point or Max/EOQ Order Cycle Line Point and Order Quantity: – “What” and “How Much” – Be Careful - C to P Departments n Surplus Point PNA/Level Order Point or Min Lead Time Order Point - Safety Stock: – “When” – Be Careful - Customer Service Ó 2005 Grant W. Howard Company Safety 31

Vendor Performance and Negotiations - It’s not just Price n n n Lower COGS Lower Freight Minimums Multiple Drops for Freight Combined P/O’s for Minimum Freight Paid Fill-ins n n n RGA’s on New Items Excess Inventory Returns n Win/Win - Partnership n n n Fill Rates Consistent Lead Times and OTD Accurate Shipping (Blanket Receiving) - Product, Quantity, Price Good Backorder Handling Ó 2005 Grant W. Howard Company EDI/VMI/2 -Way Information Flow - B 2 B Automated Product and Pricing Updates 32

Profitability GM & Expenses (Freight, Cto. C, Cto. P) Profitability Improvement: n GM Improvement n Expense Reduction: – Freight – Cost to Carry – Cost to Purchase GM Improvement, Service, Efficiency, Accuracy, Asset Management Ó 2005 Grant W. Howard Company 33

How Much of the System Are You Using? Good System - Over 80% of Items Listed Ó 2005 Grant W. Howard Company 34

“Best Practices” Inventory Management Improve Customer Service, GM, Asset Management, Efficiency, and Accuracy n Better SKU Coverage - System and Buyers – 60 - 80% SKU Coverage to 85 -96% – 5 -25, 000 SKU/Buyer to 40, 000 -100, 000+ n n n n n Improved Time Management Improved Priority Setting Improved Efficiency Improved Accuracy Technology and Core Replace Inventory with Information Rifle Approach Better Numbers and Better Tools Ability to Balance Profits and Service Ó 2005 Grant W. Howard Company 35
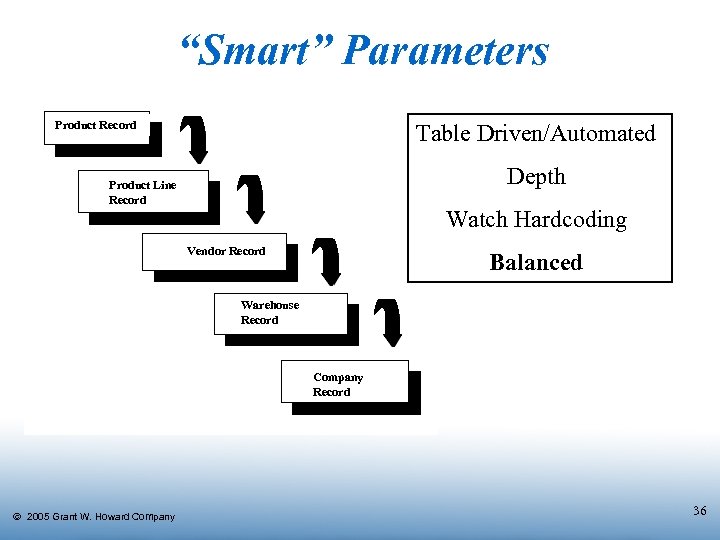
“Smart” Parameters Product Record Table Driven/Automated Depth Product Line Record Watch Hardcoding Vendor Record Balanced Warehouse Record Company Record Ó 2005 Grant W. Howard Company 36
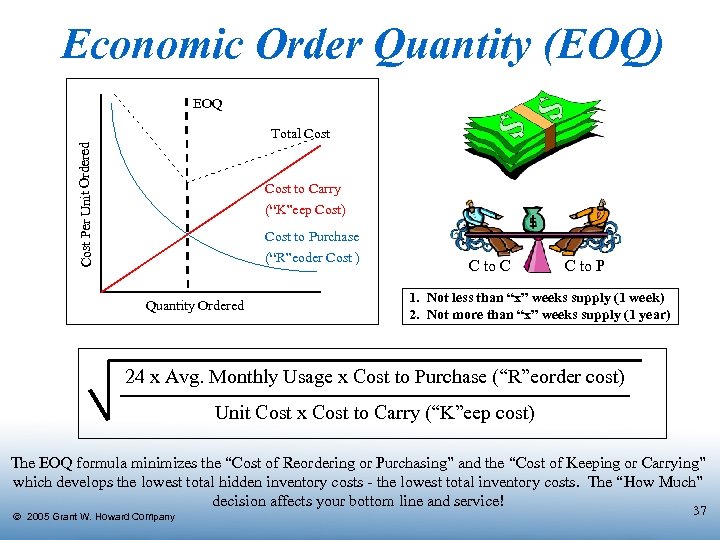
Economic Order Quantity (EOQ) EOQ Cost Per Unit Ordered Total Cost to Carry (“K”eep Cost) Cost to Purchase (“R”eoder Cost ) Quantity Ordered C to C C to P 1. Not less than “x” weeks supply (1 week) 2. Not more than “x” weeks supply (1 year) 24 x Avg. Monthly Usage x Cost to Purchase (“R”eorder cost) Unit Cost x Cost to Carry (“K”eep cost) The EOQ formula minimizes the “Cost of Reordering or Purchasing” and the “Cost of Keeping or Carrying” which develops the lowest total hidden inventory costs - the lowest total inventory costs. The “How Much” decision affects your bottom line and service! Ó 2005 Grant W. Howard Company 37
Paperfloat Control Ó 2005 Grant W. Howard Company 38
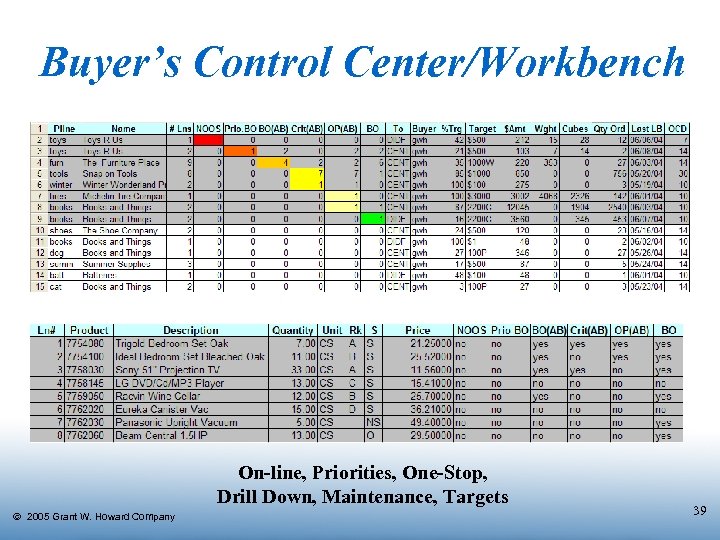
Buyer’s Control Center/Workbench On-line, Priorities, One-Stop, Drill Down, Maintenance, Targets Ó 2005 Grant W. Howard Company 39
Making Targets Properly Cost to Carry vs Freight, Price, and Service: n n n Key is equal days supply Increase or Decrease Use for Proper Emergency Buys/Fill-ins Ó 2005 Grant W. Howard Company General rules of thumb: n n n Days Dollars 1/2 way through OC/RC 40
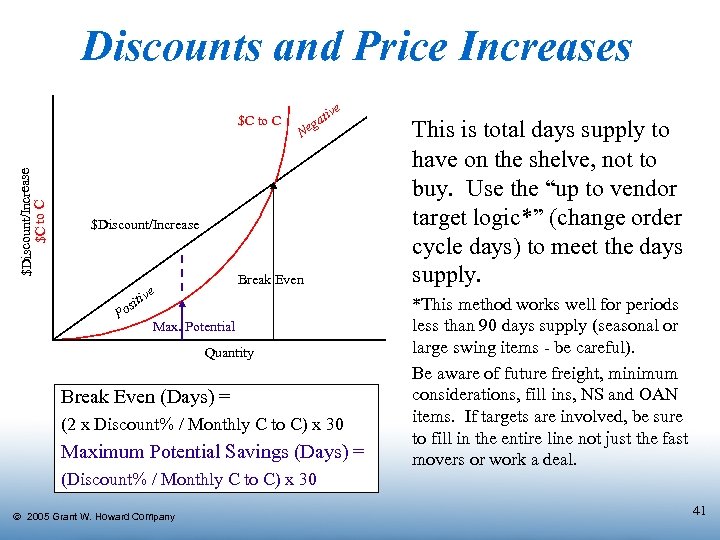
Discounts and Price Increases $Discount/Increase $C to C ve ati g Ne $Discount/Increase Break Even e itiv os P Max. Potential Quantity Break Even (Days) = (2 x Discount% / Monthly C to C) x 30 Maximum Potential Savings (Days) = (Discount% / Monthly C to C) x 30 Ó 2005 Grant W. Howard Company This is total days supply to have on the shelve, not to buy. Use the “up to vendor target logic*” (change order cycle days) to meet the days supply. *This method works well for periods less than 90 days supply (seasonal or large swing items - be careful). Be aware of future freight, minimum considerations, fill ins, NS and OAN items. If targets are involved, be sure to fill in the entire line not just the fast movers or work a deal. 41
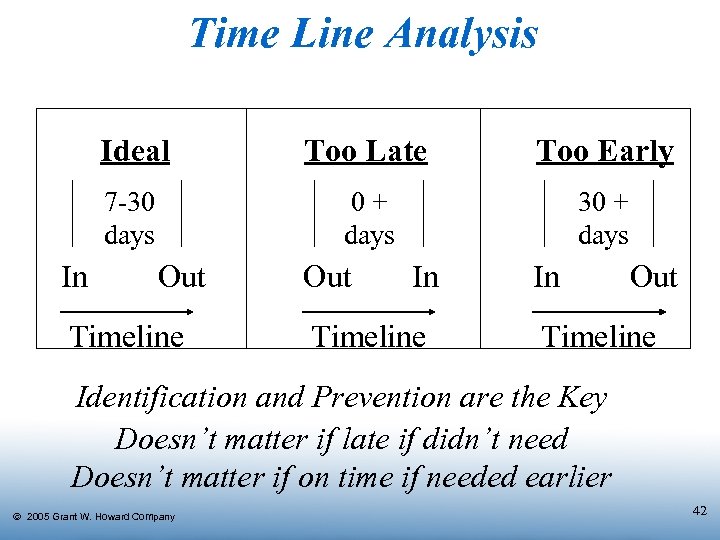
Time Line Analysis Ideal Too Early 7 -30 days In Too Late 0+ days 30 + days Out Timeline Out In Timeline In Out Timeline Identification and Prevention are the Key Doesn’t matter if late if didn’t need Doesn’t matter if on time if needed earlier Ó 2005 Grant W. Howard Company 42
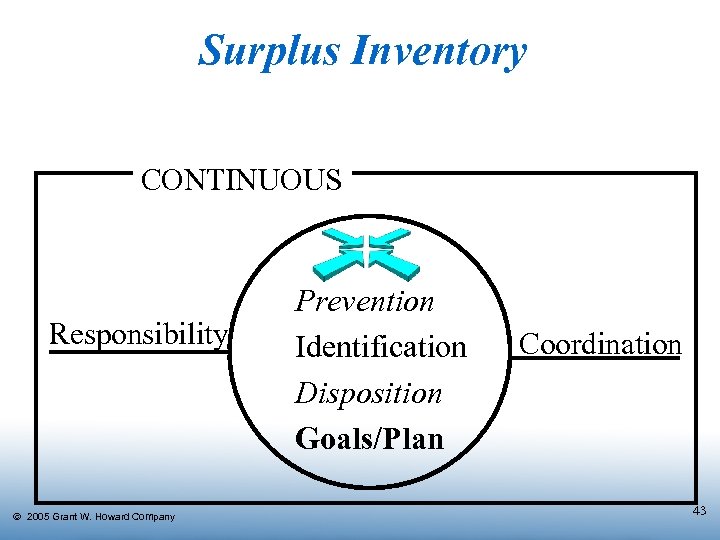
Surplus Inventory CONTINUOUS Responsibility Ó 2005 Grant W. Howard Company Prevention Identification Disposition Goals/Plan Coordination 43
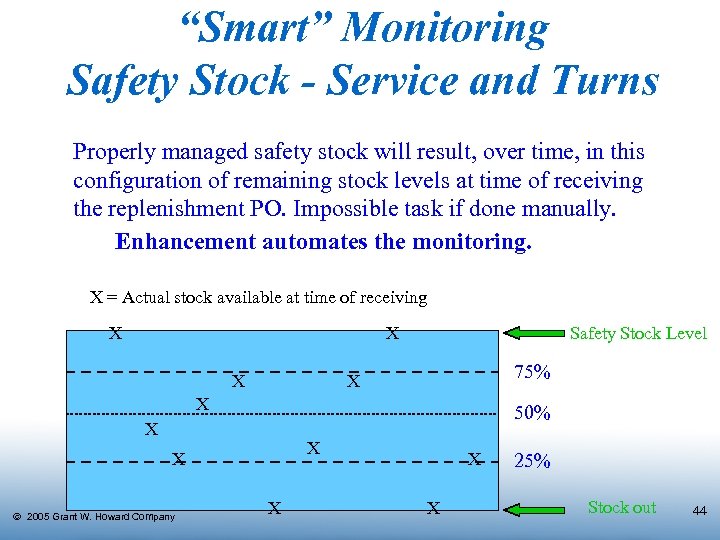
“Smart” Monitoring Safety Stock - Service and Turns Properly managed safety stock will result, over time, in this configuration of remaining stock levels at time of receiving the replenishment PO. Impossible task if done manually. Enhancement automates the monitoring. X = Actual stock available at time of receiving X X X Safety Stock Level 75% X X 50% X X X Ó 2005 Grant W. Howard Company X X X 25% Stock out 44

“Best Practices” Better Numbers - Order Point n Usage Data and Calculation: n – – Lost Sales/Exceptional Sales Capability “Smart” Exception and “Auto” Correction “Path” Exception Reporting Flexibility to Where Usage Placed for Shipments, Backorders, and Credits – DP/MRP Capability – Flexibility with Method and Window by Rank – Seasonal Capabilities: » Individual “Parameter Driven” Seasonal Trending » Lead Time Advance for Seasonal Items » Season Shift Capability » Dual Usage for Seasonal with Long Lead Times – Threshold Minimums – Rollup Capability – Usage Forecasting Accuracy Analysis and Correction Ó 2005 Grant W. Howard Company n Safety Stock Improvements: – Safety Days or Percentage – Safety Control by Rank – Method Control by Lead time – Safety Stock Analysis Lead Time Improvements: – – – Minimum and Maximum History File with Maintenance History/Parameters by Path (Int/Ext) Exceptions w/ Automated Ignore Manual Exceptional Lead Times n Customer Buying Habits, Threshold Minimums and “Automated” Overrides n Use of Hits and “Smart” Item Ranking “Smart” Parameters and Controls n 45
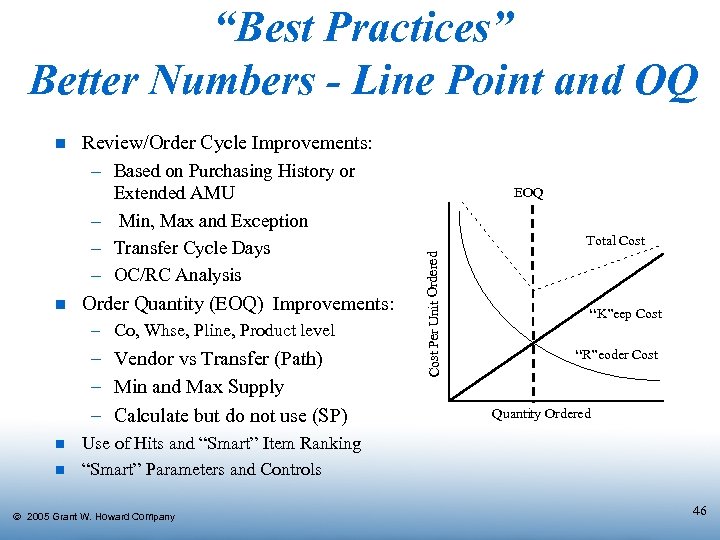
“Best Practices” Better Numbers - Line Point and OQ Review/Order Cycle Improvements: – Based on Purchasing History or Extended AMU – Min, Max and Exception – Transfer Cycle Days – OC/RC Analysis n Order Quantity (EOQ) Improvements: – Co, Whse, Pline, Product level – Vendor vs Transfer (Path) – Min and Max Supply – Calculate but do not use (SP) n n EOQ Total Cost Per Unit Ordered n “K”eep Cost “R”eoder Cost Quantity Ordered Use of Hits and “Smart” Item Ranking “Smart” Parameters and Controls Ó 2005 Grant W. Howard Company 46

“Best Practices” - Better Tools n Buyer’s Control Center - BCC – Priority – Targets – “Smart” Rounding – Drill Down/Maintenance – Proper combination of the three models and use of EOQ – “One-stop” Thinking n n n Time Line Analysis – “Too Late” – “Too Early” “Smart” Surplus - “True” Surplus Exception Control Center - ECC – “Smart” exception reporting – Mass Update – “One-stop” thinking n n quantities n n Safety Stock at Receipt Analysis n n Measurement and Monitoring n Ó 2005 Grant W. Howard Company Rounding Control and Smart WT Three buying methods and WT’s: – LP with or without OQ – WT Cycle and Set weeks supply – Full control and Works together – Proper products, Proper Improved Stock Levels: – Orders, PO’s and WT’s Control – Future Sales Orders – Future P/O’s – Strong Suggested Count Program – WMS Flexible Product Merge Utility Stock Balancing Tools Use of Hits and “Smart” Item Ranking “Smart” Parameters and Controls 47

Some Final Thoughts Ó 2005 Grant W. Howard Company 48

It’s not just good Software and Systems It’s not just good Processes and Procedures It’s not just good People and Education It’s not just good Management IT’S ALL OF THEM! It’s not just good Usage It’s not just good Order Points It’s not just replenishing at Order Point It’s not just the Timeline It’s not just working the Surplus IT’S THE ENTIRE PROCESS Same Company Different Software Ó 2005 Grant W. Howard Company 49

Use measurement and monitoring reports to confirm results and to drill down and find areas of improvement. Be sure to use a rifle approach rather than a shotgun approach, or it will be lots of $$$ and probably disappointing! Ó 2005 Grant W. Howard Company 50
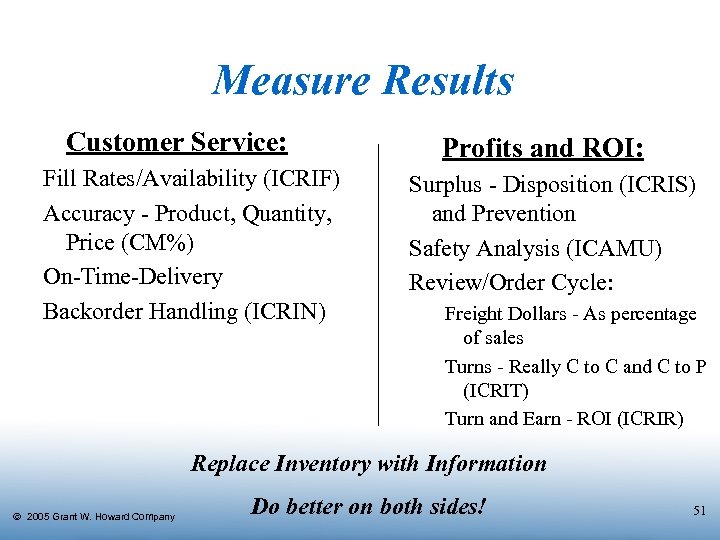
Measure Results Customer Service: Fill Rates/Availability (ICRIF) Accuracy - Product, Quantity, Price (CM%) On-Time-Delivery Backorder Handling (ICRIN) Profits and ROI: Surplus - Disposition (ICRIS) and Prevention Safety Analysis (ICAMU) Review/Order Cycle: Freight Dollars - As percentage of sales Turns - Really C to C and C to P (ICRIT) Turn and Earn - ROI (ICRIR) Replace Inventory with Information Ó 2005 Grant W. Howard Company Do better on both sides! 51

Replace Inventory and Costs and Improve Service with Technology. Improve the Bottom Line with Technology Information, Efficiency, Accuracy (If it is not helping Service, if it is not helping Profits…) Ó 2005 Grant W. Howard Company 52

Keys to “Getting Results” - Top 10 1. Hits/Ranking and “Smart” Parameters 2. Order Point, Line Point and Order Quantity Accuracy: – Usage: » » » – – – Lost/Exceptional Utilization Usage Exceptions and Maint Proper Method and Window Seasonal Trending & Adv LT Roll Up Usage Accuracy Analysis 3. On-hand Paperfloat Accuracy: – SC/CC Program and Address the Issues, Good Processes – Paperfloat Control – WMS, BC, RF Lead Time Exceptions and Maint Safety Set-up and Safety Analysis Order Point Adjusters OC/RC Analysis Proper EOQ Parameters WT “Smart” Rounding Ó 2005 Grant W. Howard Company 53

Keys to “Getting Results” - Top 10 4. Buyer’s Control Center: – Priority - Replenish at OP – On-Stop, On-line, Paperless – Making Targets Properly Keep Equal Days Supply 5. Timeline Analysis: – “GAP”/“Too Late” – “Too Early” 6. Surplus/Excess/Defective: – “Smart” (Long and Short Term) – Visibility, Utilization and Disposition – Incoming with LT Surplus 7. Backorder Policy and Procedure Closed-loop 8. Exception Control Center: – “Smart”/”True” Exceptions – On-Stop Corrections – Mass Update 9. Measurement and Monitoring: – – – Service (Fill, BO, OTD, Accuracy) ROI Mix Excess Freight Vendor Performance 10. Controlled Replenishment and Stocking Policy Ó 2005 Grant W. Howard Company 54

Spend your days reacting to the fires. . . you may be efficient, but will you be effective? Where are Your Systems, Procedures, and Objectives S(p)ending Your People? Ó 2005 Grant W. Howard Company 55
Back to Basics Most distributors DON’T: n Set the system up properly n Feed the system good data n Understand or Use the system properly n Clean up bad processes and procedures n Educate their people on the system or processes n Help departments work together n Help work towards common goals Yet they think it will all just magically work Ó 2005 Grant W. Howard Company 56

n n n n “Branch Participation” It’s Essential! Sell Service the Customer Controlled Replenishment (PO’s and Transfers) Good Data and Information (Rifle vs Shotgun) – Lost and Exceptional Sales – On-hand Integrity and Paperfloat Control Proper Backorder Handling Train the Masses Surplus Prevention & Disposition Teach Them Benefits – Controlled Replenishment – Help utilize the Surplus “Smart” Selling and Transferring Give Them the Tools Eyes and Ears Ó 2005 Grant W. Howard Company 57
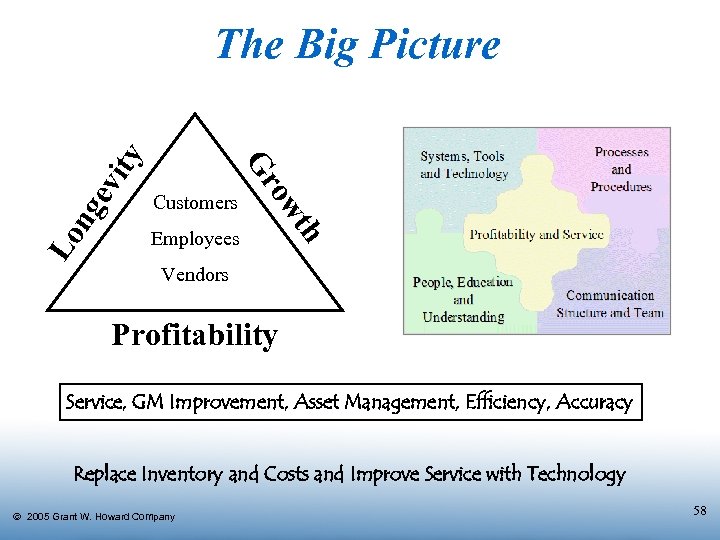
ng ev Employees h Lo Customers t ow Gr ity The Big Picture Vendors Profitability Service, GM Improvement, Asset Management, Efficiency, Accuracy Replace Inventory and Costs and Improve Service with Technology Ó 2005 Grant W. Howard Company 58
REMEMBER! When to Replenish Order Point Service Ó 2005 Grant W. Howard Company What and How Much to Replenish Line Point and OQ Profitability There is Always a Left and Right Side Balance 59

Things to Think About Service: n Fill Rates - Having the RIGHT Inventory: Profits: n – Shotgun - $$$, Poor Results and not Balanced – Rifle - Smart $$$, Great Results and Balance – Replace Inventory with Information n n Understanding “When” Controls Service - NO GAMES, REPLENISH at Order Point The Importance of Order Point Adjusters The Importance of Controlled Replenishment Buying a 90 day supply and it lasts 60 days Ó 2005 Grant W. Howard Company Turns Maximization is not Profits Maximization - The Right Way to Turns: – Excess/Defective: 5% – Safety Stock: 15 -20% – Review/Order Cycle and Order Quantity Reduction - Caution (BCC, EDI/VMI, WMS, BC, RF, Blanket Receiving- Internal and External, EDI Invoice/Trans$, Automated Pricing, Maintenance and Updating) n n Understanding “What and How Much” Controls Profits - NO GAMES - Order what the system recommends. Watch topping the truck, pre-buys, discounts/price increases The Importance of “Equal Days Supply” The Importance of Controlled Replenishment Buying a 90 day supply and it lasts 120 days 60

The Things I Hear. . . n n n n n We know it’s at OP, but. . . LP and EOQ are just suggestions, they don’t really mean any thing. . . It doesn’t matter how you get to the minimum, the important thing is getting the P/O placed and not paying freight. . . It doesn’t matter if anything is BOP, we can place a P/O every day. . . We keep upping the RC, but it hardly changes the P/O. . . Items keep going BOP or GAP sooner than they should, stupid computer. . . The quantities are always wrong on the RARRs, really stupid computer. . . Stocking policy, backorder policy, what policy… Increasing turns is easy, we just buy less or don’t buy at all… Ó 2005 Grant W. Howard Company 61

The Things I Hear. . . n n n n We understand service - everyone can buy and transfer inventory and they do. . . We measure things, our turns are 4. 2394702. . . We’re wondering how the computer invested so much in inventory and we got so little. . . We don’t have time to prevent fires, we are running around all day putting them out. . . Usage is correct by special magic; lost sales and exceptional sales logging are just a waste of time, talk to customers. . . We have to have more people, look at all these THICK reports we look through. We even find something sometimes… We review our lines at least monthly, many weekly. . . We understand the process and maintenance; as long as we push the right buttons… (10 steps) Ó 2005 Grant W. Howard Company 62

The World is Changing! Yesterday Tomorrow Buyers/Inv. Control Turns Dominated Inaccurate Data Four Glass Walls Learned from “Bill” Pencil and Paper Inventory/Asset Managers Customer Service Oriented Data/Information Managers Communications & Team Education & Understanding Technology and Efficiency ? ? ? If you can’t handle today, how will you handle tomorrow? If your company is stuck in Yesterday or having troubles with Today, how will it survive Tomorrow? Ó 2005 Grant W. Howard Company 63

GWHCO www. gwhco. org Grant Howard: ghoward@gwhco. org 734 -428 -0529 Phone 734 -428 -0593 Fax John Cason: jcason@gwhco. org 256 -830 -0676 Phone 256 -830 -0481 Fax Ó 2005 Grant W. Howard Company Our approach involves tailoring the best practices in distribution to the specific needs of our clients. Our working philosophy revolves around building a strong and selfmaintaining infrastructure by developing a working plan based on processes and procedures, education and understanding, implementation of tools and technology; and through communication, organizational structure and team environments. 64
c1208756b1068ae2f5d84bfb849d3f21.ppt