Hormones (continuation).ppt
- Количество слайдов: 30

Professor of Novosibirsk State Agrarian University Korotkevich O. S.

Contents: • • Thyroid hormones Parathyroid hormone The pancreatic hormones The adrenal hormones (medullary and adrenal cortex hormones) • Sex hormones (androgens , estrogens)
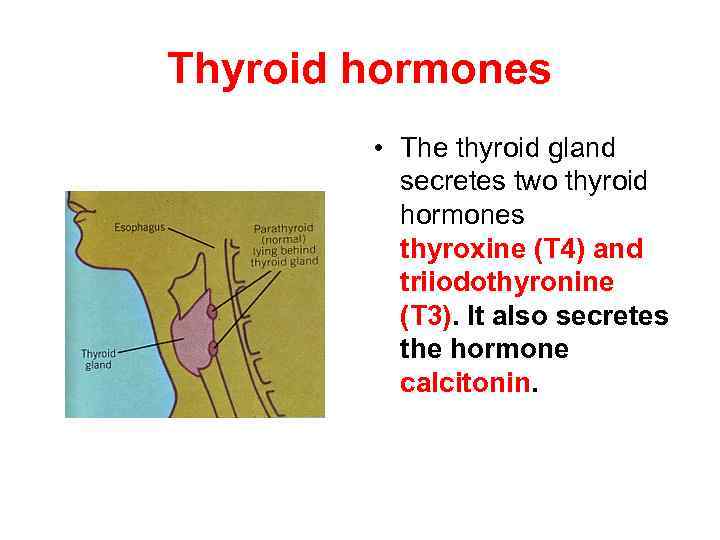
Thyroid hormones • The thyroid gland secretes two thyroid hormones thyroxine (T 4) and triiodothyronine (T 3). It also secretes the hormone calcitonin.
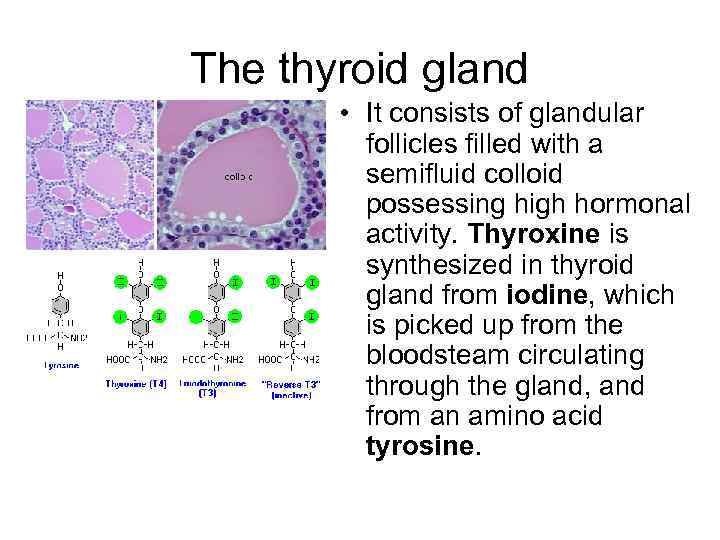
The thyroid gland • It consists of glandular follicles filled with a semifluid colloid possessing high hormonal activity. Thyroxine is synthesized in thyroid gland from iodine, which is picked up from the bloodsteam circulating through the gland, and from an amino acid tyrosine.
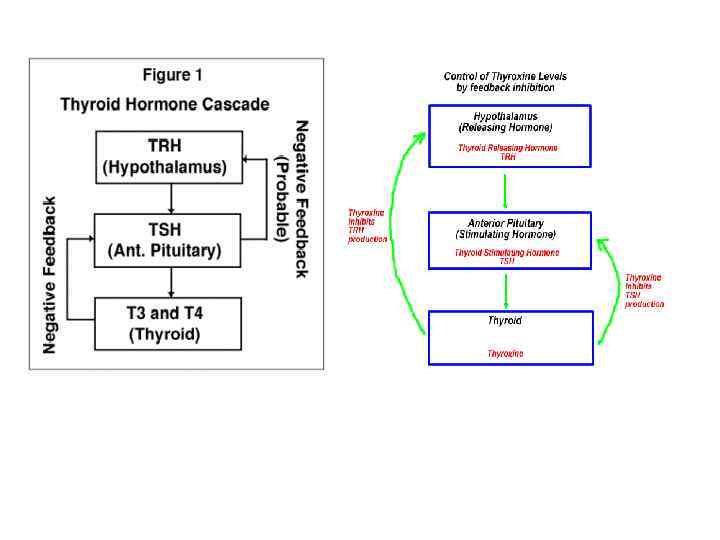
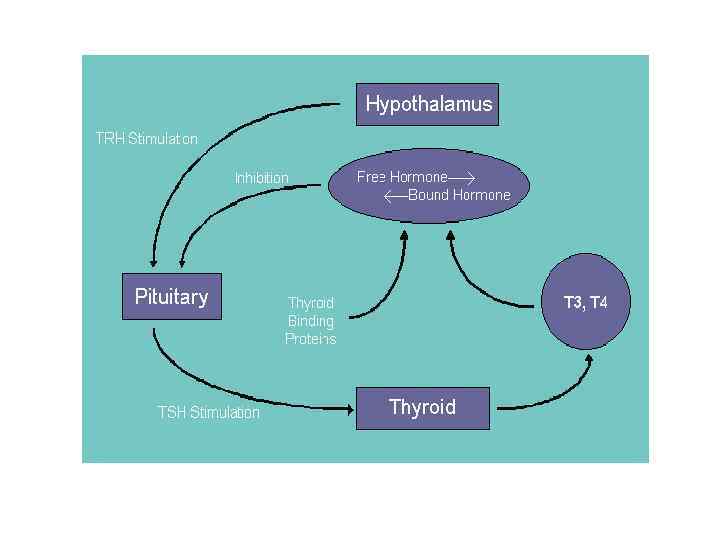

Thyroid hormones have two important functions: • Regulation of growth and development of body • Stimulating effect on total metabolism and sexual maturation

Removal of the thyroid from tadpoles delays their development; • They continue to grow but do not turn into frogs. Conversely the introduction of thyroid extracts facilitates their transition into frogs (metamorphosis), but the latter are small in size.
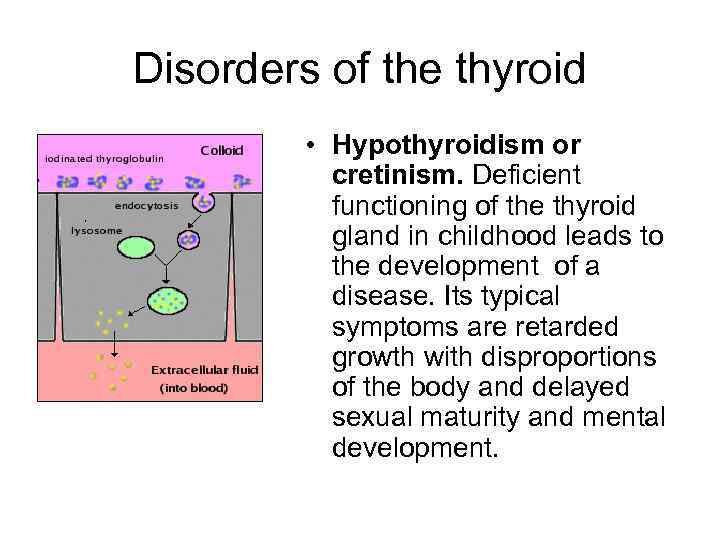
Disorders of the thyroid • Hypothyroidism or cretinism. Deficient functioning of the thyroid gland in childhood leads to the development of a disease. Its typical symptoms are retarded growth with disproportions of the body and delayed sexual maturity and mental development.
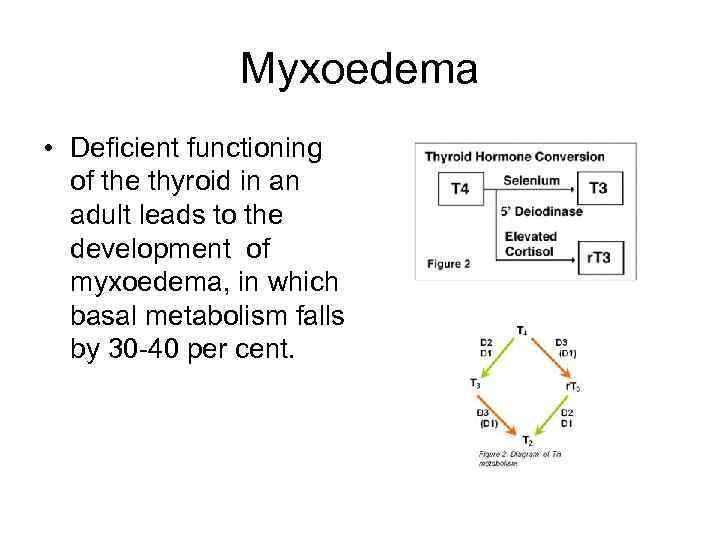
Myxoedema • Deficient functioning of the thyroid in an adult leads to the development of myxoedema, in which basal metabolism falls by 30 -40 per cent.

Thyrotoxicosis • It can be the result of excessive thyroid hormone ingestion, leakage of stored thyroid hormone from storage in the thyroid follicles, or excessive thyroid gland production of thyroid hormone. Graves disease.
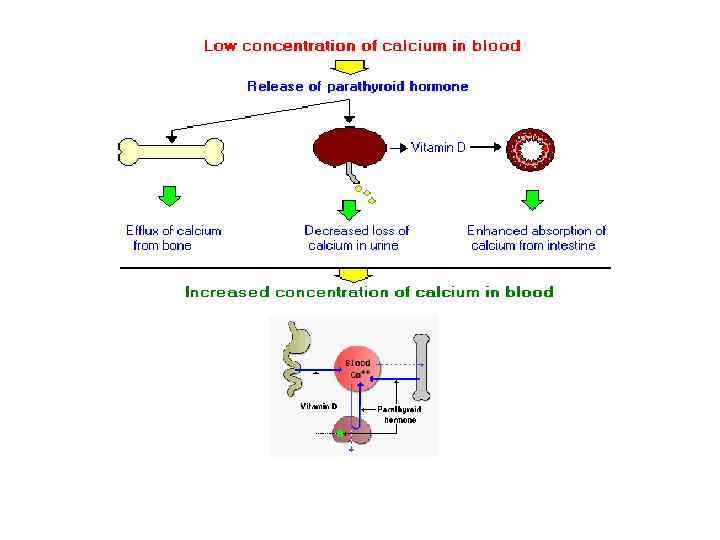
Parathyroid hormone • Parathyroid hormone is secreted by the parathyroid glands. This hormone together with calcitonin regulates the amount of calcium in the blood in a homeostatic manner.
The pancreatic hormones • The pancreas is an endocrine gland located behind the stomach in the region of the 1 st and 2 nd lumber vertebrae. The specialized cells in the pancreas which produce hormones are called the islets of Langerhans.
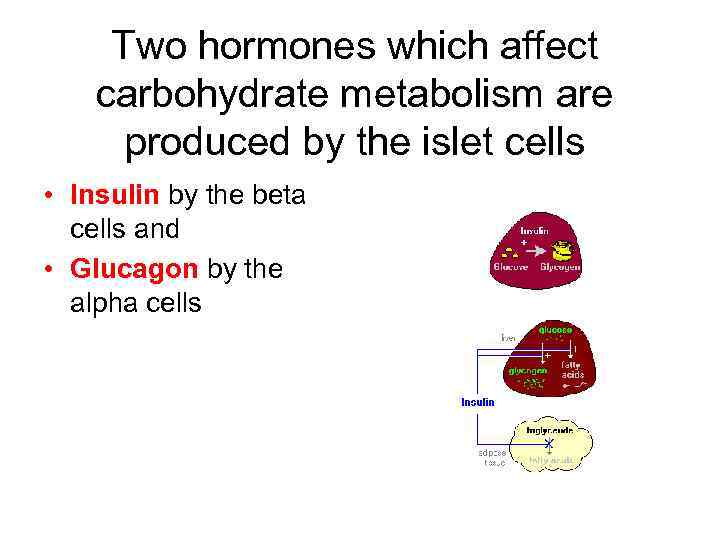
Two hormones which affect carbohydrate metabolism are produced by the islet cells • Insulin by the beta cells and • Glucagon by the alpha cells

Insulin • Insulin and glucagon are antagonists. In other words, insulin decreases blood glucose concentration; glucagon increases it. Insulin is the only one hormone that can decrease blood glucose concentration

• If the pancreatic islets secrete a normal amount of insulin, a normal amount of glucose enters the cells, and a normal amount of glucose stays behind in the blood. If the pancreatic glands secrete too much insulin, as they sometimes do when a person has a tumor of the pancreas.
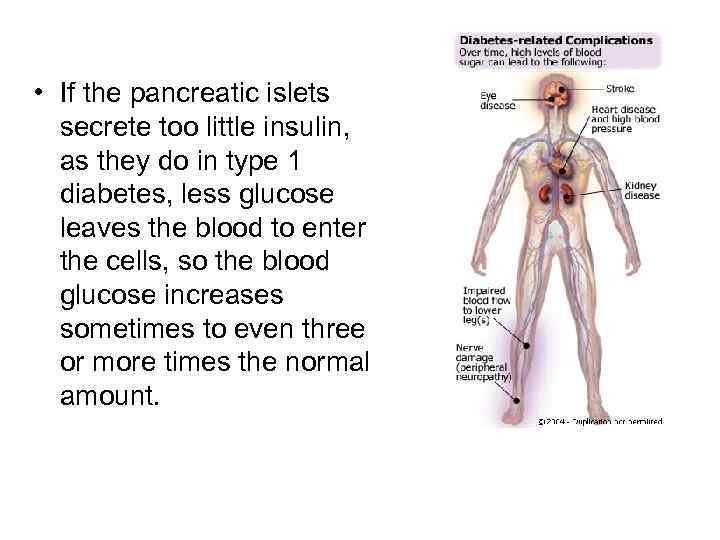
• If the pancreatic islets secrete too little insulin, as they do in type 1 diabetes, less glucose leaves the blood to enter the cells, so the blood glucose increases sometimes to even three or more times the normal amount.
The adrenal hormones • The adrenal gland is multifunctional organ that produces the hormones and neuropeptides essential for life.

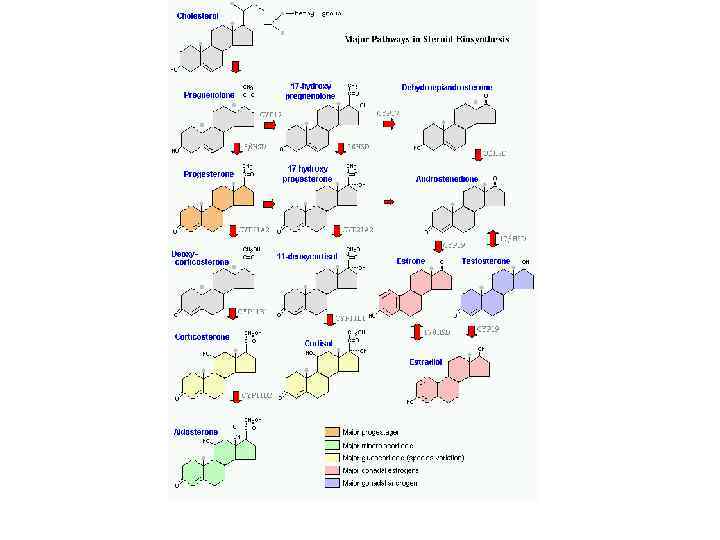
The adrenal cortex by zone • The major cortex hormones, aldosterone, cortisol and dehydroepiandrosterone sulfate are uniquely synthesized from a common precursor by cells located in one of three functionally distinct zonal layers of the adrenal cortex: zona glomerulosa, zona fasciculata and zona reticularis
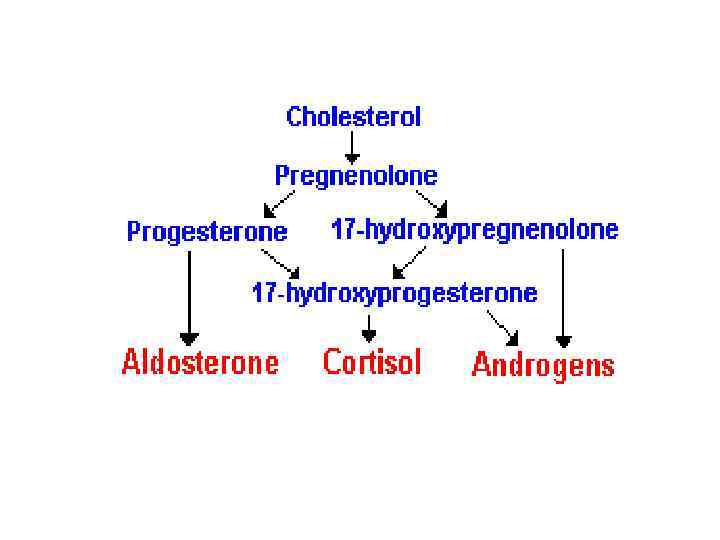

Mineralocorticoids • These hormones are essential to life because they regulate the amount of mineral salts (also called electrolytes) which are retained in the body. A proper balance of water and salts in the blood and tissues is essential to the normal functioning of the body.

Glucocorticoids • These hormones have an important influence on the metabolism of sugar, fats and proteins within all body cells.

Androgens, estrogens and progestins • These are male and female hormones which maintain the secondary sex characteristics such as beard and breast development and are necessary for reproduction.
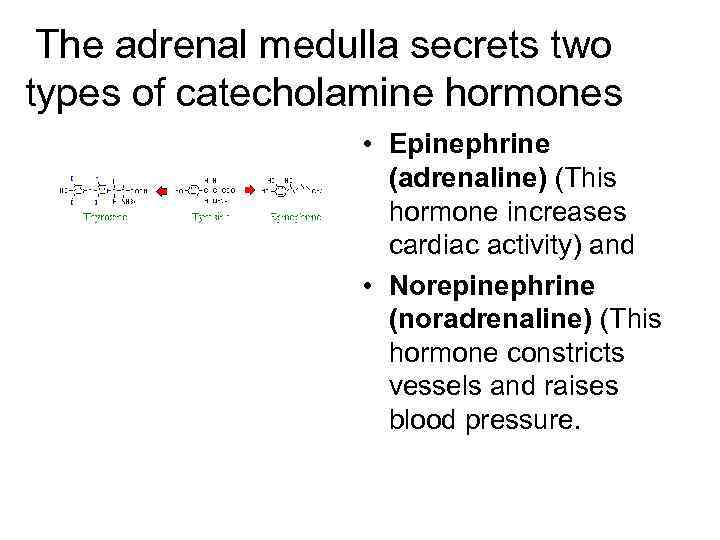
The adrenal medulla secrets two types of catecholamine hormones • Epinephrine (adrenaline) (This hormone increases cardiac activity) and • Norepinephrine (noradrenaline) (This hormone constricts vessels and raises blood pressure.

Sex hormones • The ovarian hormones are estrogen and progesterone. Estrogen is responsible for the development and maintenance of secondary sex characteristics such as hair and breast development. Progesterone is responsible for the preparation and maintenance of the uterus in pregnancy.

Testes • Testosterone is an androgen (male steroid hormone) which stimulates and promotes the growth of secondary sex characteristics in the male.

Hormones (continuation).ppt