fcddf6d9367611d3248aeda2cb679923.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 36
 Products & Services
Products & Services
 Presentation Outline a. The Problem b. HBGary Approach c. Products d. Services
Presentation Outline a. The Problem b. HBGary Approach c. Products d. Services
 Presentation Outline The Problem a. HBGary Approach • Products • Services
Presentation Outline The Problem a. HBGary Approach • Products • Services
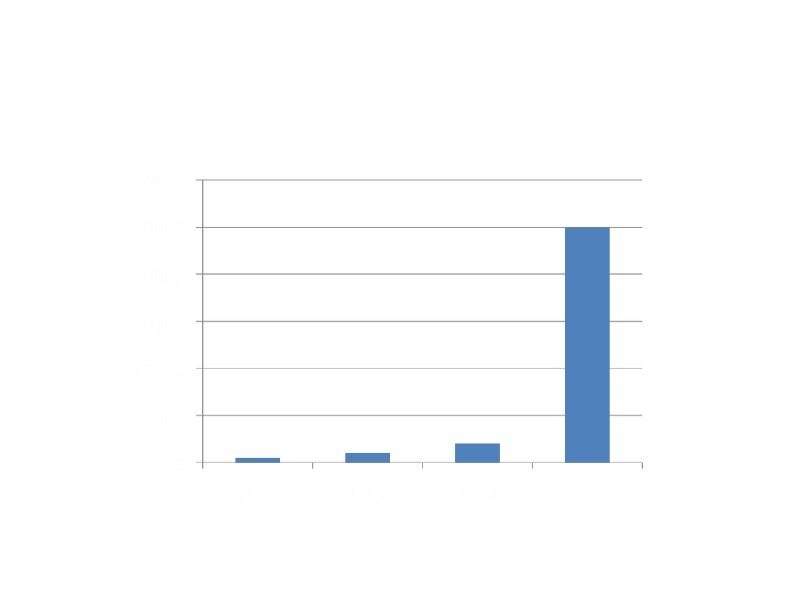 50, 000+ New Malware Every Day!
50, 000+ New Malware Every Day!
 Evolving Risk Environment a. Valuable cyber targets b. Attackers are motivated and well-funded c. Malware is sophisticated and targeted d. Existing security isn’t stopping the attacks
Evolving Risk Environment a. Valuable cyber targets b. Attackers are motivated and well-funded c. Malware is sophisticated and targeted d. Existing security isn’t stopping the attacks
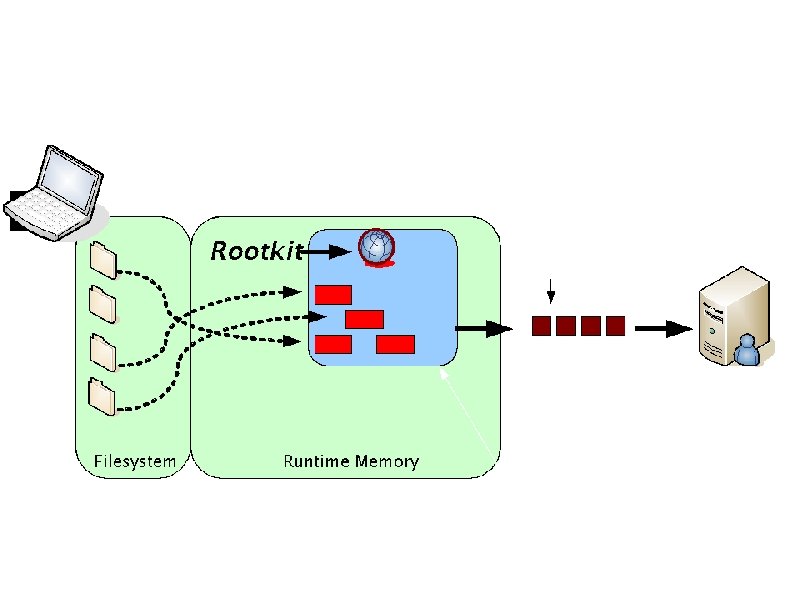 Drive-by Download – Legitimate Websites
Drive-by Download – Legitimate Websites
 Anti-Virus Shortcomings Top 3 AV companies don’t detect 80% of new malware Source: “Eighty percent of new malware defeats antivirus”, ZDNet Australia, July 19, 2006
Anti-Virus Shortcomings Top 3 AV companies don’t detect 80% of new malware Source: “Eighty percent of new malware defeats antivirus”, ZDNet Australia, July 19, 2006
 Traditional Host Security Products Fail to Detect…… a. New malware b. Malware variants c. Polymorphic code d. Injected code e. Memory resident malware f. Rootkits Ultimately, every network can and will be compromised
Traditional Host Security Products Fail to Detect…… a. New malware b. Malware variants c. Polymorphic code d. Injected code e. Memory resident malware f. Rootkits Ultimately, every network can and will be compromised
 Traditional Memory and Malware Analysis is Difficult a. Requires lots of technical expertise b. Time consuming c. Expensive d. Doesn’t scale
Traditional Memory and Malware Analysis is Difficult a. Requires lots of technical expertise b. Time consuming c. Expensive d. Doesn’t scale
 Presentation Outline a. The Problem HBGary Approach • Products • Services
Presentation Outline a. The Problem HBGary Approach • Products • Services
 HBGary Components a. Physical Memory Forensics b. Malware Detection c. Malware Analysis d. Standalone and Enterprise
HBGary Components a. Physical Memory Forensics b. Malware Detection c. Malware Analysis d. Standalone and Enterprise
 Under the Hood
Under the Hood
 Why Physical Memory? a. Malware must be in memory to execute b. Software code in memory is usually unpacked c. Malware can fool the OS, but it cannot hide in physical memory
Why Physical Memory? a. Malware must be in memory to execute b. Software code in memory is usually unpacked c. Malware can fool the OS, but it cannot hide in physical memory
 Useful Information in RAM Processes and Drivers Loaded Modules Network Socket Info Passwords Encryption Keys Decrypted files Order of execution Runtime State Information Rootkits Configuration Information Logged in Users NDIS buffers Open Files Unsaved Documents Live Registry Video Buffers – screen shots BIOS Memory VOIP Phone calls Advanced Malware Instant Messenger chat
Useful Information in RAM Processes and Drivers Loaded Modules Network Socket Info Passwords Encryption Keys Decrypted files Order of execution Runtime State Information Rootkits Configuration Information Logged in Users NDIS buffers Open Files Unsaved Documents Live Registry Video Buffers – screen shots BIOS Memory VOIP Phone calls Advanced Malware Instant Messenger chat
 Digital DNA a. Automated malware detection b. Software classification system c. 3500 software and malware behavioral traits d. Example a. Huge number of key logger variants in the wild b. About 10 logical ways to build a key logger
Digital DNA a. Automated malware detection b. Software classification system c. 3500 software and malware behavioral traits d. Example a. Huge number of key logger variants in the wild b. About 10 logical ways to build a key logger
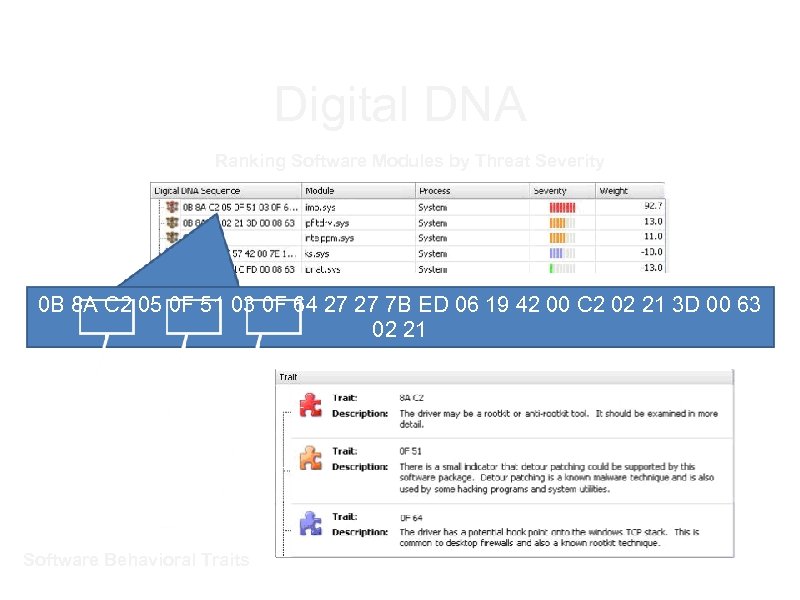 Digital DNA Ranking Software Modules by Threat Severity 0 B 8 A C 2 05 0 F 51 03 0 F 64 27 27 7 B ED 06 19 42 00 C 2 02 21 3 D 00 63 02 21 8 A C 2 0 F 51 0 F 64 Software Behavioral Traits
Digital DNA Ranking Software Modules by Threat Severity 0 B 8 A C 2 05 0 F 51 03 0 F 64 27 27 7 B ED 06 19 42 00 C 2 02 21 3 D 00 63 02 21 8 A C 2 0 F 51 0 F 64 Software Behavioral Traits
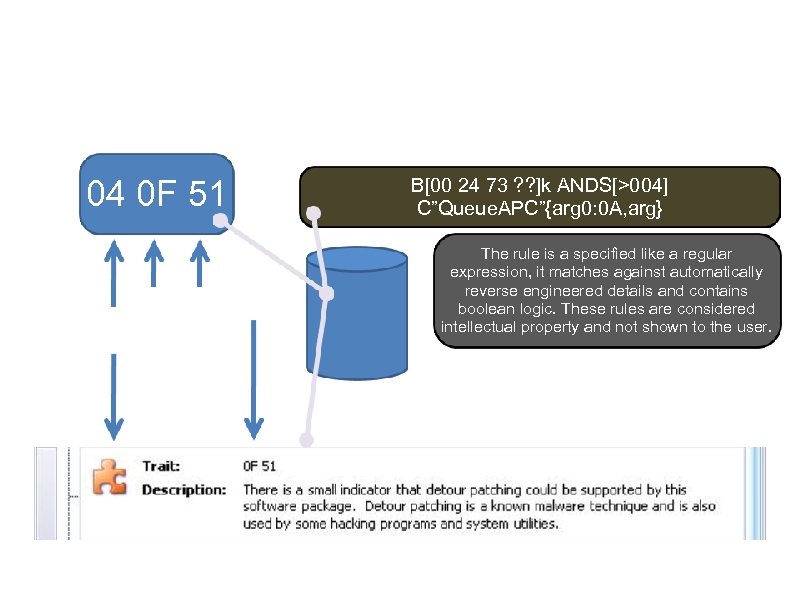 What’s in a Trait? 04 0 F 51 Unique hash code Weight / Control flags B[00 24 73 ? ? ]k ANDS[>004] C”Queue. APC”{arg 0: 0 A, arg} The rule is a specified like a regular expression, it matches against automatically reverse engineered details and contains boolean logic. These rules are considered intellectual property and not shown to the user. The trait, description, and underlying rule are held in a database
What’s in a Trait? 04 0 F 51 Unique hash code Weight / Control flags B[00 24 73 ? ? ]k ANDS[>004] C”Queue. APC”{arg 0: 0 A, arg} The rule is a specified like a regular expression, it matches against automatically reverse engineered details and contains boolean logic. These rules are considered intellectual property and not shown to the user. The trait, description, and underlying rule are held in a database
 Digital DNA in Memory vs. Disk Based Hashing and Signatures
Digital DNA in Memory vs. Disk Based Hashing and Signatures
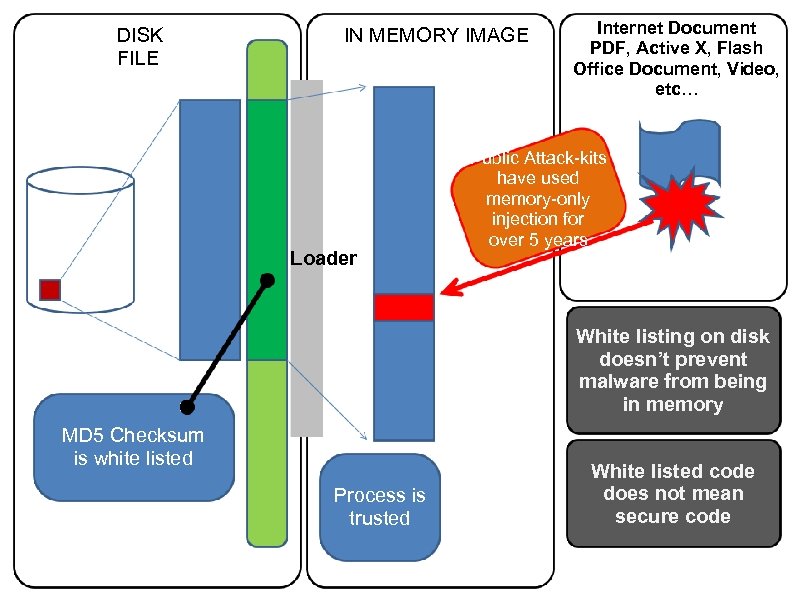 DISK FILE IN MEMORY IMAGE OS Loader Internet Document PDF, Active X, Flash Office Document, Video, etc… Public Attack-kits have used memory-only injection for over 5 years White listing on disk doesn’t prevent malware from being in memory MD 5 Checksum is white listed Process is trusted White listed code does not mean secure code
DISK FILE IN MEMORY IMAGE OS Loader Internet Document PDF, Active X, Flash Office Document, Video, etc… Public Attack-kits have used memory-only injection for over 5 years White listing on disk doesn’t prevent malware from being in memory MD 5 Checksum is white listed Process is trusted White listed code does not mean secure code
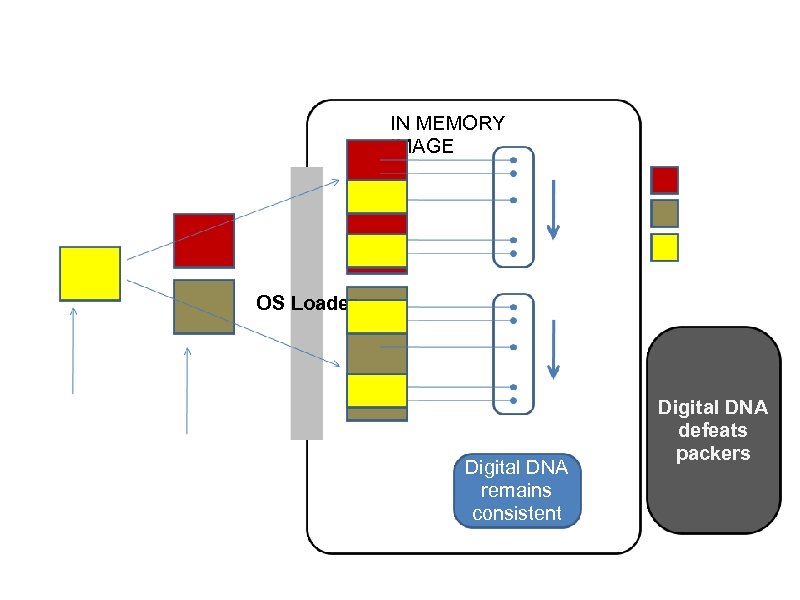 IN MEMORY IMAGE Packer #1 Packer #2 Decrypted Original OS Loader Starting Malware Packed Malware Digital DNA remains consistent Digital DNA defeats packers
IN MEMORY IMAGE Packer #1 Packer #2 Decrypted Original OS Loader Starting Malware Packed Malware Digital DNA remains consistent Digital DNA defeats packers
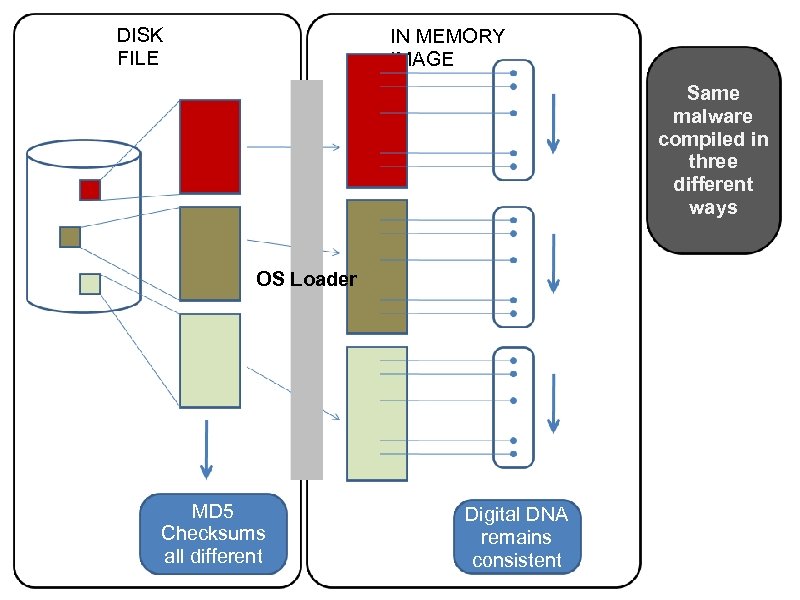 DISK FILE IN MEMORY IMAGE Same malware compiled in three different ways OS Loader MD 5 Checksums all different Digital DNA remains consistent
DISK FILE IN MEMORY IMAGE Same malware compiled in three different ways OS Loader MD 5 Checksums all different Digital DNA remains consistent
 A suspicious file… Now what?
A suspicious file… Now what?
 Why Perform Malware Analysis? a. What happened? b. What is being stolen? c. How did it happen? d. Who is behind it? e. How do I bolster network defenses?
Why Perform Malware Analysis? a. What happened? b. What is being stolen? c. How did it happen? d. Who is behind it? e. How do I bolster network defenses?
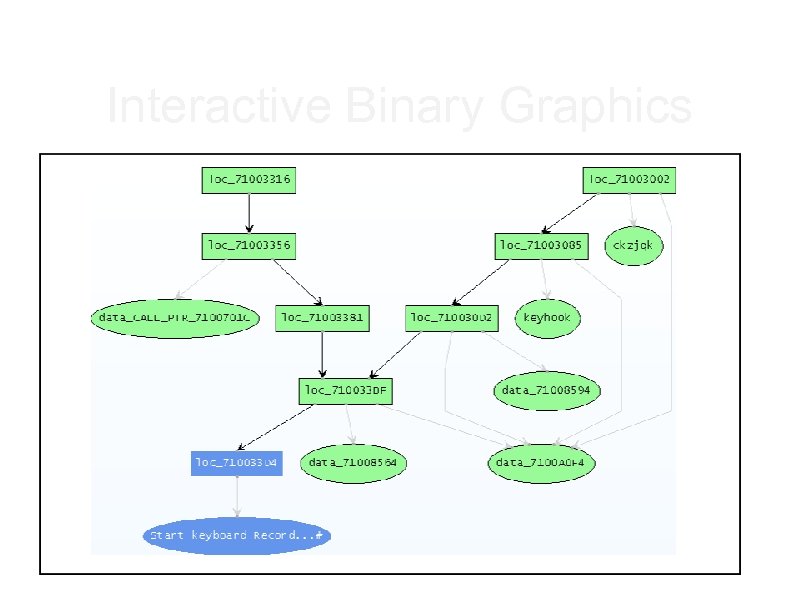 Interactive Binary Graphics
Interactive Binary Graphics
 Presentation Outline a. The Problem b. HBGary Approach Products • Services
Presentation Outline a. The Problem b. HBGary Approach Products • Services
 a. Responder Professional a. Standalone analysis system for incident responders b. Digital DNA a. Malware detection in memory b. Standalone and enterprise
a. Responder Professional a. Standalone analysis system for incident responders b. Digital DNA a. Malware detection in memory b. Standalone and enterprise
 HBGary Responder Professional a. Standalone system for incident response b. Deep dive analysis of memory and malware c. Digital DNA module d. REcon module
HBGary Responder Professional a. Standalone system for incident response b. Deep dive analysis of memory and malware c. Digital DNA module d. REcon module
 Enterprise Systems a. Shipping a. Digital b. Digital DNA for Mc. Afee e. PO (HBSS contract) DNA for Verdaysys Digital Guardian b. 4 th Quarter 2009 a. Digital b. Digital DNA for Guidance En. Case Enterprise DNA Enterprise – all HBGary
Enterprise Systems a. Shipping a. Digital b. Digital DNA for Mc. Afee e. PO (HBSS contract) DNA for Verdaysys Digital Guardian b. 4 th Quarter 2009 a. Digital b. Digital DNA for Guidance En. Case Enterprise DNA Enterprise – all HBGary
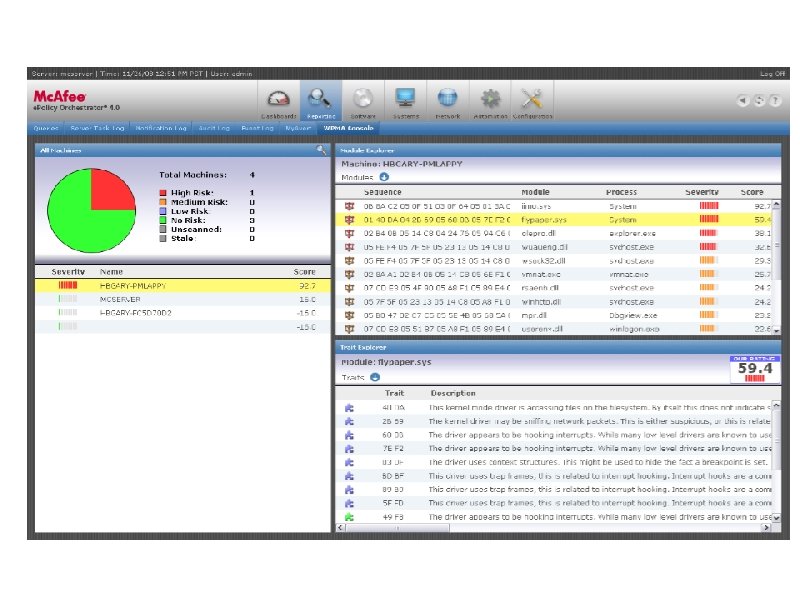
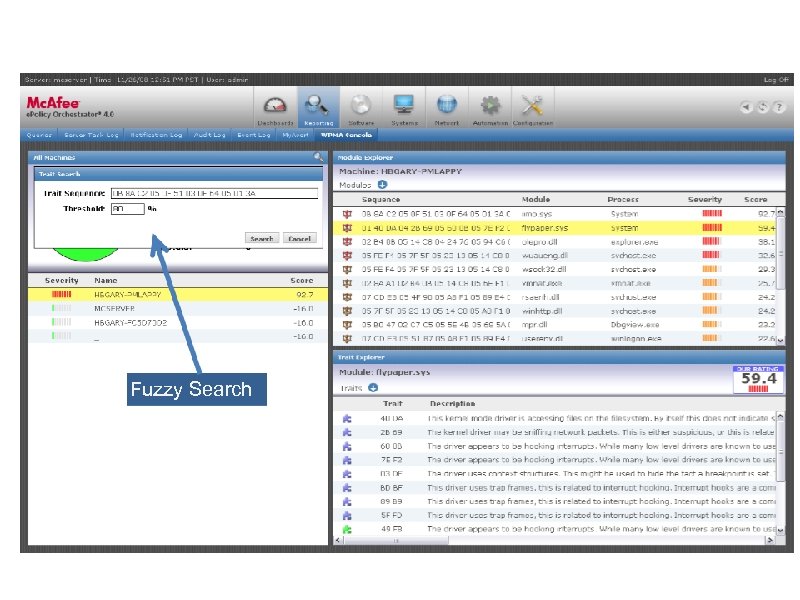 Fuzzy Search
Fuzzy Search
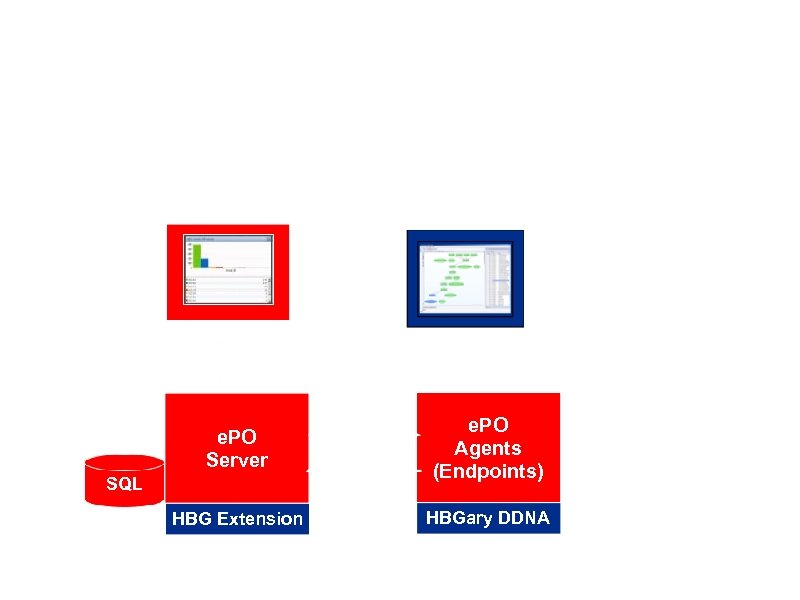 Integration with Mc. Afee e. PO Responder Professional e. PO Console e. PO Server SQL HBG Extension Schedul e Event s e. PO Agents (Endpoints) HBGary DDNA
Integration with Mc. Afee e. PO Responder Professional e. PO Console e. PO Server SQL HBG Extension Schedul e Event s e. PO Agents (Endpoints) HBGary DDNA
 Presentation Outline a. The Problem b. HBGary Approach c. Products Services
Presentation Outline a. The Problem b. HBGary Approach c. Products Services
 Use HBGary Service When… a. Suspicious traffic & AV says machines are clean b. Find malware on your computers c. Need to verify computers are trusted d. Determine root cause of compromise e. Malware damage assessment
Use HBGary Service When… a. Suspicious traffic & AV says machines are clean b. Find malware on your computers c. Need to verify computers are trusted d. Determine root cause of compromise e. Malware damage assessment
 Services Overview a. Incident Response b. Intrusion Forensics c. Malware Analysis
Services Overview a. Incident Response b. Intrusion Forensics c. Malware Analysis
 HBGary Services a. Advance malware detection b. Live first response triage of servers and workstations c. Enterprise scope of breach analysis d. Root cause analysis e. Malware analysis f. Enterprise containment, mitigation and remediation
HBGary Services a. Advance malware detection b. Live first response triage of servers and workstations c. Enterprise scope of breach analysis d. Root cause analysis e. Malware analysis f. Enterprise containment, mitigation and remediation
 Questions?
Questions?


