Topic 11.pptx
- Количество слайдов: 39
 Production Costs of Enterprise 1. Production costs: definition& meaning, kinds and indicators. Classification of expenses that are charged to production costs. 2. Content of the Production Costs Plan. Factors, reserves and ways to reduce the production costs. 3. Calculation of unit costs. 4. Expenditure Budget.
Production Costs of Enterprise 1. Production costs: definition& meaning, kinds and indicators. Classification of expenses that are charged to production costs. 2. Content of the Production Costs Plan. Factors, reserves and ways to reduce the production costs. 3. Calculation of unit costs. 4. Expenditure Budget.
 1. Methodical recommendation for setting costs of goods (works, services) in industries. (2007) 2. Accounting Standard П(С)БО 16 «Costs»
1. Methodical recommendation for setting costs of goods (works, services) in industries. (2007) 2. Accounting Standard П(С)БО 16 «Costs»
 1. Production costs: definition& meaning, kinds and indicators. Classification of expenses that are charged to production costs.
1. Production costs: definition& meaning, kinds and indicators. Classification of expenses that are charged to production costs.
 Costs - one of the most important qualitative indicators of production. Because cost is usually a monetary valuation of (1) effort, (2) material, (3) resources, (4) time and utilities consumed, (5) risks incurred, and (6) opportunity forgone in production and delivery of a good or service. - it is a part of value. - it is an amount that has to be paid or given up in order to get something.
Costs - one of the most important qualitative indicators of production. Because cost is usually a monetary valuation of (1) effort, (2) material, (3) resources, (4) time and utilities consumed, (5) risks incurred, and (6) opportunity forgone in production and delivery of a good or service. - it is a part of value. - it is an amount that has to be paid or given up in order to get something.
 Operating Costs - Cost per unit of a product or service, or the annual cost incurre on a continuous process. Operating costs do not include capital outlays or the costs incurred in design and implementation phases of a new process
Operating Costs - Cost per unit of a product or service, or the annual cost incurre on a continuous process. Operating costs do not include capital outlays or the costs incurred in design and implementation phases of a new process
 Kinds of Costs According to coverage of costs for production and delivery : Manufacturing costs Production & delivery costs Finished costs Marginal costs According to the object: unit of product (SF, FG, Gi. P) costs of production / sale (CO, GOP, GS, Gi. P) According to period of time : in accounting period (actual) in planning period (plan)
Kinds of Costs According to coverage of costs for production and delivery : Manufacturing costs Production & delivery costs Finished costs Marginal costs According to the object: unit of product (SF, FG, Gi. P) costs of production / sale (CO, GOP, GS, Gi. P) According to period of time : in accounting period (actual) in planning period (plan)
 Costs Figures Absolute Comparative
Costs Figures Absolute Comparative
 Classification of Expenses Features Cost centers (places of their origin) Costs of production, shop, section, service, working place, department Kinds of goods (work, service) Costs of component parts, assemblies, products, order, processes etc Types of costs • In economic elements, • In Costing items Homogeneity of costs One-element costs, Complex costs How they are related to the production Direct costs, of the product Indirect costs Dependence on the production volume Variable costs Fixed costs
Classification of Expenses Features Cost centers (places of their origin) Costs of production, shop, section, service, working place, department Kinds of goods (work, service) Costs of component parts, assemblies, products, order, processes etc Types of costs • In economic elements, • In Costing items Homogeneity of costs One-element costs, Complex costs How they are related to the production Direct costs, of the product Indirect costs Dependence on the production volume Variable costs Fixed costs
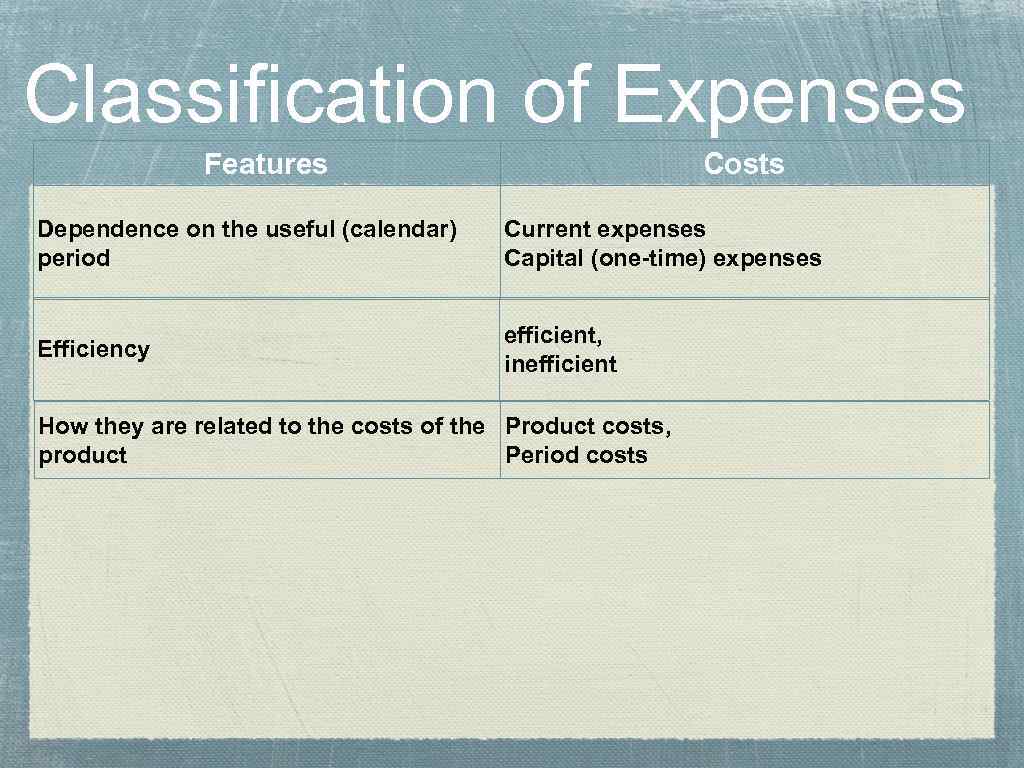 Classification of Expenses Features Costs Dependence on the useful (calendar) period Current expenses Capital (one-time) expenses Efficiency efficient, inefficient How they are related to the costs of the Product costs, product Period costs
Classification of Expenses Features Costs Dependence on the useful (calendar) period Current expenses Capital (one-time) expenses Efficiency efficient, inefficient How they are related to the costs of the Product costs, product Period costs
 2. Content of the Production Costs Plan. Factors, reserves and ways to reduce the production costs.
2. Content of the Production Costs Plan. Factors, reserves and ways to reduce the production costs.
 Production Costs Plan includes: Calculations. Розрахунки зниження собівартості продукції. Plan Calculations of the unit costs of certain goods. Calculations of the Commodity Output (CO) and Goods Sold. Production Budget. Costs Budget.
Production Costs Plan includes: Calculations. Розрахунки зниження собівартості продукції. Plan Calculations of the unit costs of certain goods. Calculations of the Commodity Output (CO) and Goods Sold. Production Budget. Costs Budget.
 COSTS • Factors • Reserves • Ways to reduce 1. Main directions for cost reduction and real approaches to do it 2. Cost estimating relationship in which a cost is directly proportional to one independent variable, such as a certain percentage of the material consumed in producing a good. 3. unutilized opportunities of costs reduction
COSTS • Factors • Reserves • Ways to reduce 1. Main directions for cost reduction and real approaches to do it 2. Cost estimating relationship in which a cost is directly proportional to one independent variable, such as a certain percentage of the material consumed in producing a good. 3. unutilized opportunities of costs reduction
 Factors Changes in production volume Changes in the Manufacturing Program Enhancement of technical production level Improvement of Production and Labor Organization Improvement of natural resources usage
Factors Changes in production volume Changes in the Manufacturing Program Enhancement of technical production level Improvement of Production and Labor Organization Improvement of natural resources usage
 Ways to reduce Reduction of material capacity of the product Enhancement of the labor productivity Reduction of costs for production service and management
Ways to reduce Reduction of material capacity of the product Enhancement of the labor productivity Reduction of costs for production service and management
 3. Calculation of a unit costs
3. Calculation of a unit costs
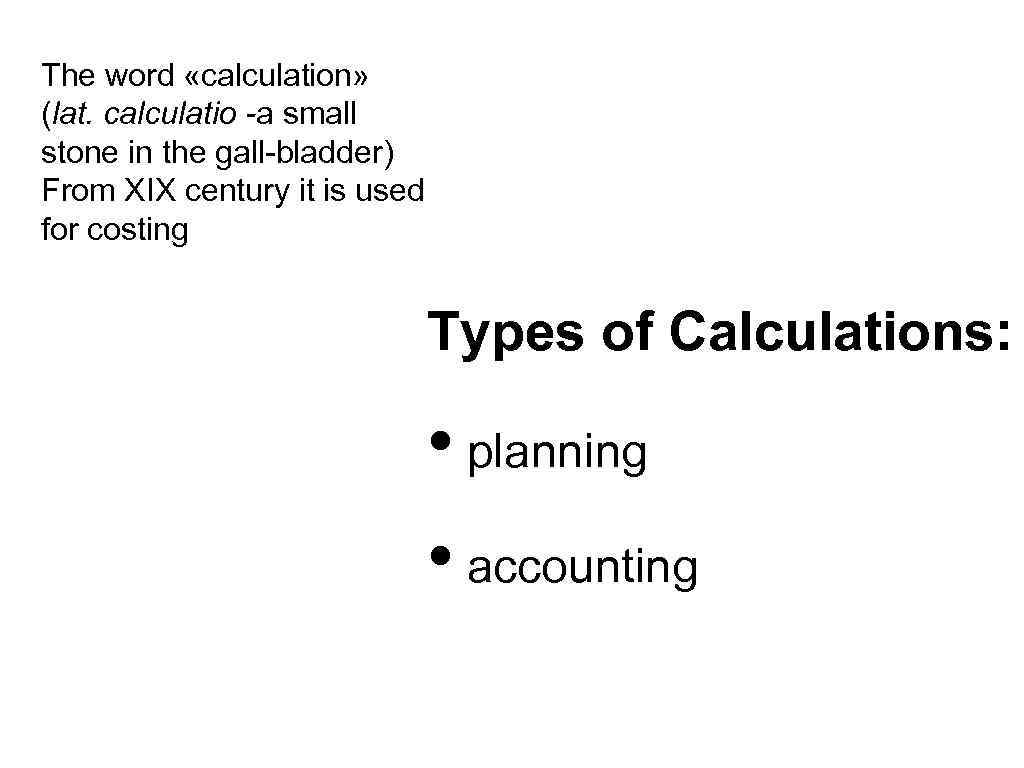 The word «calculation» (lat. calculatio -a small stone in the gall-bladder) From XIX century it is used for costing Types of Calculations: • planning • accounting
The word «calculation» (lat. calculatio -a small stone in the gall-bladder) From XIX century it is used for costing Types of Calculations: • planning • accounting
 How to calculate costs: Justify classification of production costs Define objects of calculation and units of calculation Choose an absorption of overheads method
How to calculate costs: Justify classification of production costs Define objects of calculation and units of calculation Choose an absorption of overheads method
 How to classify costs in calculations In costing items In the way they refer unit costs If the production volume influences particular costs
How to classify costs in calculations In costing items In the way they refer unit costs If the production volume influences particular costs
 Costing items 1. Row materials 2. Bought Semi-finished products, component parts, industrial works and services provided by other enterprises 3. Fuel and Energy 4. transport/logistic costs 5. Recycling waste (deduction) 6. Main/additional wages or workers (in production) 7. Social insurance deduction 8. Overheads (to be continued)
Costing items 1. Row materials 2. Bought Semi-finished products, component parts, industrial works and services provided by other enterprises 3. Fuel and Energy 4. transport/logistic costs 5. Recycling waste (deduction) 6. Main/additional wages or workers (in production) 7. Social insurance deduction 8. Overheads (to be continued)
 Objects of calculation product / work, service Semi-finished product Set of homogeneous products (usually made from homogeneous materials with usage of uniform technological processes) Representative of the group Stage/ phase
Objects of calculation product / work, service Semi-finished product Set of homogeneous products (usually made from homogeneous materials with usage of uniform technological processes) Representative of the group Stage/ phase
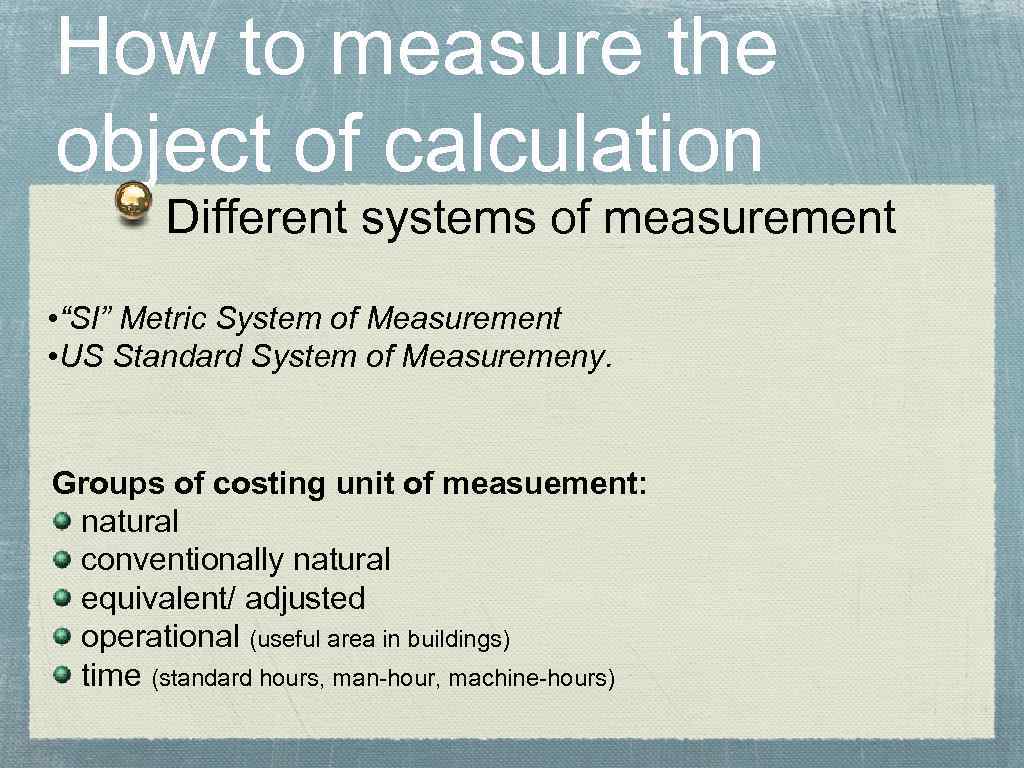 How to measure the object of calculation Different systems of measurement • “SI” Metric System of Measurement • US Standard System of Measuremeny. Groups of costing unit of measuement: natural conventionally natural equivalent/ adjusted operational (useful area in buildings) time (standard hours, man-hour, machine-hours)
How to measure the object of calculation Different systems of measurement • “SI” Metric System of Measurement • US Standard System of Measuremeny. Groups of costing unit of measuement: natural conventionally natural equivalent/ adjusted operational (useful area in buildings) time (standard hours, man-hour, machine-hours)
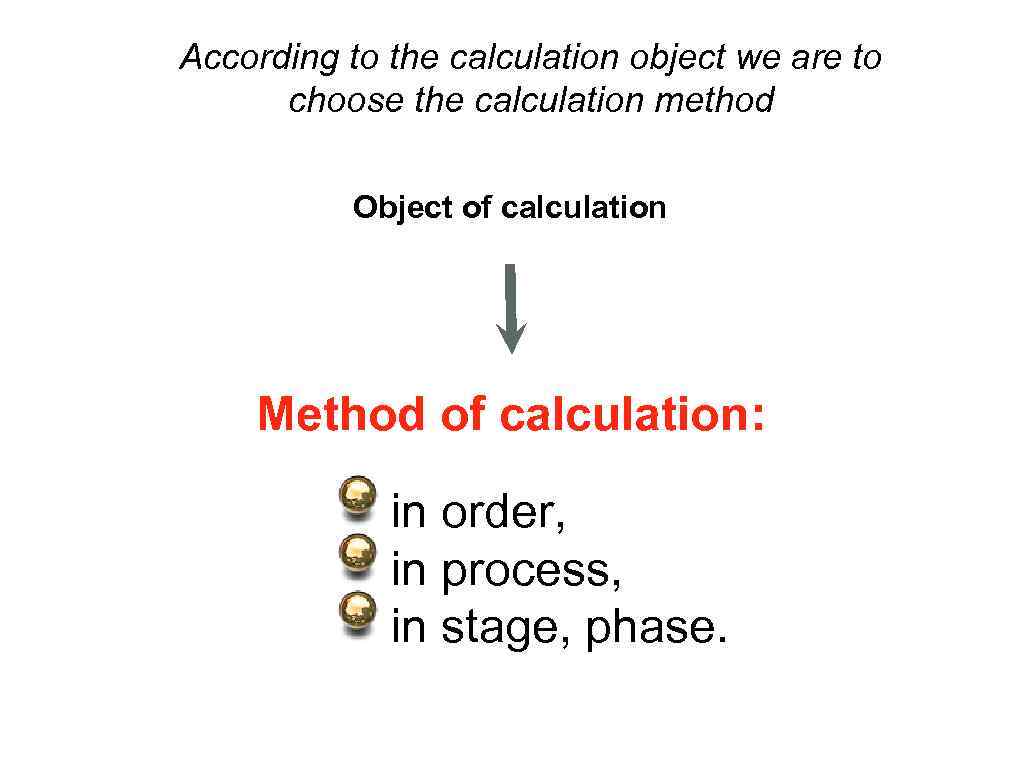 According to the calculation object we are to choose the calculation method Object of calculation Method of calculation: in order, in process, in stage, phase.
According to the calculation object we are to choose the calculation method Object of calculation Method of calculation: in order, in process, in stage, phase.
 Absorption of Overheads • Overhead Absorption Rate • Overhead absorbed in a product = = overhead rate x units of base per product
Absorption of Overheads • Overhead Absorption Rate • Overhead absorbed in a product = = overhead rate x units of base per product
 Methods of Overhead Absorption • Rate per unit of production • Direct Material Cost Method • Direct Labour Cost Method • Prime Cost Method • Direct Labour Hour Rate • Machine Hour Rate Method
Methods of Overhead Absorption • Rate per unit of production • Direct Material Cost Method • Direct Labour Cost Method • Prime Cost Method • Direct Labour Hour Rate • Machine Hour Rate Method
 Calculation Approach
Calculation Approach
 Example of calculation of one product
Example of calculation of one product
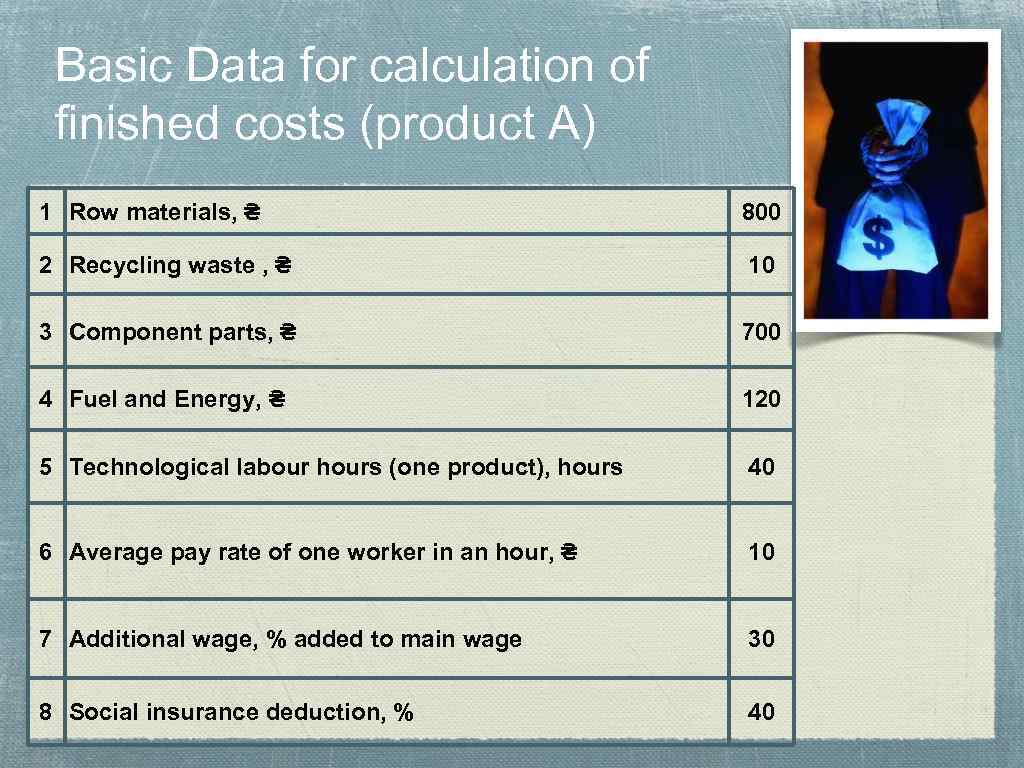 Basic Data for calculation of finished costs (product A) 1 Row materials, ₴ 800 2 Recycling waste , ₴ 10 3 Component parts, ₴ 700 4 Fuel and Energy, ₴ 120 5 Technological labour hours (one product), hours 40 6 Average pay rate of one worker in an hour, ₴ 10 7 Additional wage, % added to main wage 30 8 Social insurance deduction, % 40
Basic Data for calculation of finished costs (product A) 1 Row materials, ₴ 800 2 Recycling waste , ₴ 10 3 Component parts, ₴ 700 4 Fuel and Energy, ₴ 120 5 Technological labour hours (one product), hours 40 6 Average pay rate of one worker in an hour, ₴ 10 7 Additional wage, % added to main wage 30 8 Social insurance deduction, % 40
 Basic Data for calculation of finished costs (product A) 9 Budget of production overheads, thousand ₴ 40000 10 Budget of administrative overheads, thousand ₴ 30000 11 Budget of sales costs, thousand ₴ 10000 12 Payroll of production workers, thousand ₴ 12000 13 Plan production volume, units 500 The enterprise will produce also the Product B, with manufacturing 14 costs of all yearly production volume, thousand ₴ 40000
Basic Data for calculation of finished costs (product A) 9 Budget of production overheads, thousand ₴ 40000 10 Budget of administrative overheads, thousand ₴ 30000 11 Budget of sales costs, thousand ₴ 10000 12 Payroll of production workers, thousand ₴ 12000 13 Plan production volume, units 500 The enterprise will produce also the Product B, with manufacturing 14 costs of all yearly production volume, thousand ₴ 40000
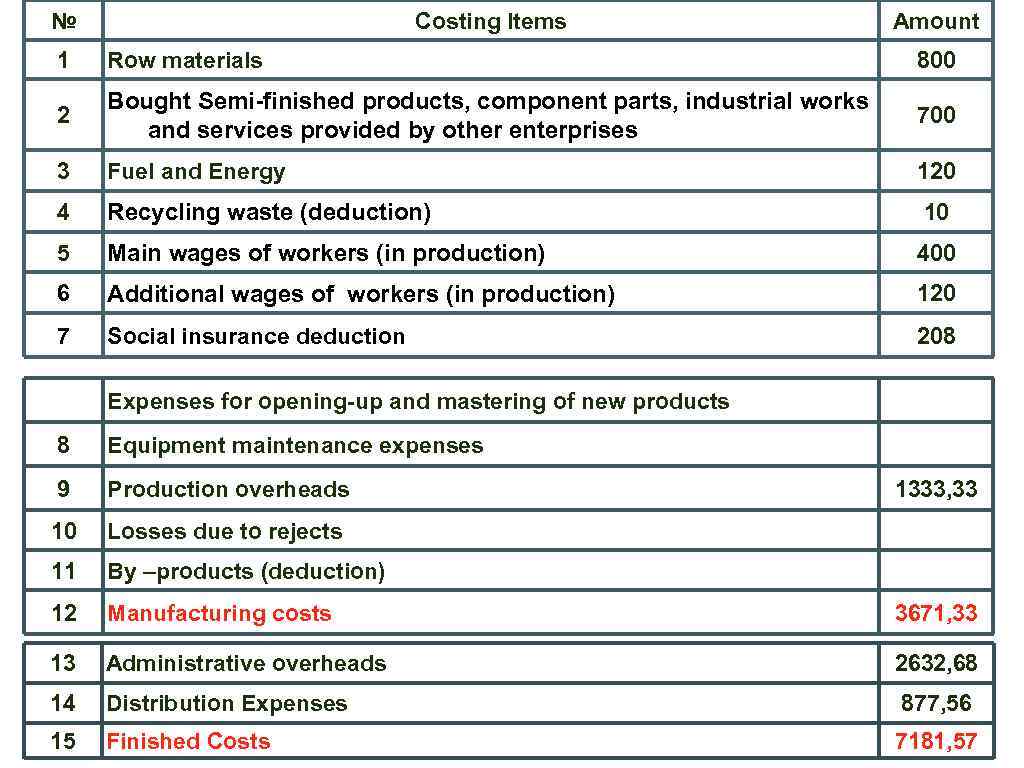 № Costing Items Amount 1 Row materials 800 2 Bought Semi-finished products, component parts, industrial works and services provided by other enterprises 700 3 Fuel and Energy 120 4 Recycling waste (deduction) 10 5 Main wages of workers (in production) 400 6 Additional wages of workers (in production) 120 7 Social insurance deduction 208 Expenses for opening-up and mastering of new products 8 Equipment maintenance expenses 9 Production overheads 10 Losses due to rejects 11 By –products (deduction) 12 Manufacturing costs 3671, 33 13 Administrative overheads 2632, 68 14 Distribution Expenses 877, 56 15 Finished Costs 7181, 57 1333, 33
№ Costing Items Amount 1 Row materials 800 2 Bought Semi-finished products, component parts, industrial works and services provided by other enterprises 700 3 Fuel and Energy 120 4 Recycling waste (deduction) 10 5 Main wages of workers (in production) 400 6 Additional wages of workers (in production) 120 7 Social insurance deduction 208 Expenses for opening-up and mastering of new products 8 Equipment maintenance expenses 9 Production overheads 10 Losses due to rejects 11 By –products (deduction) 12 Manufacturing costs 3671, 33 13 Administrative overheads 2632, 68 14 Distribution Expenses 877, 56 15 Finished Costs 7181, 57 1333, 33
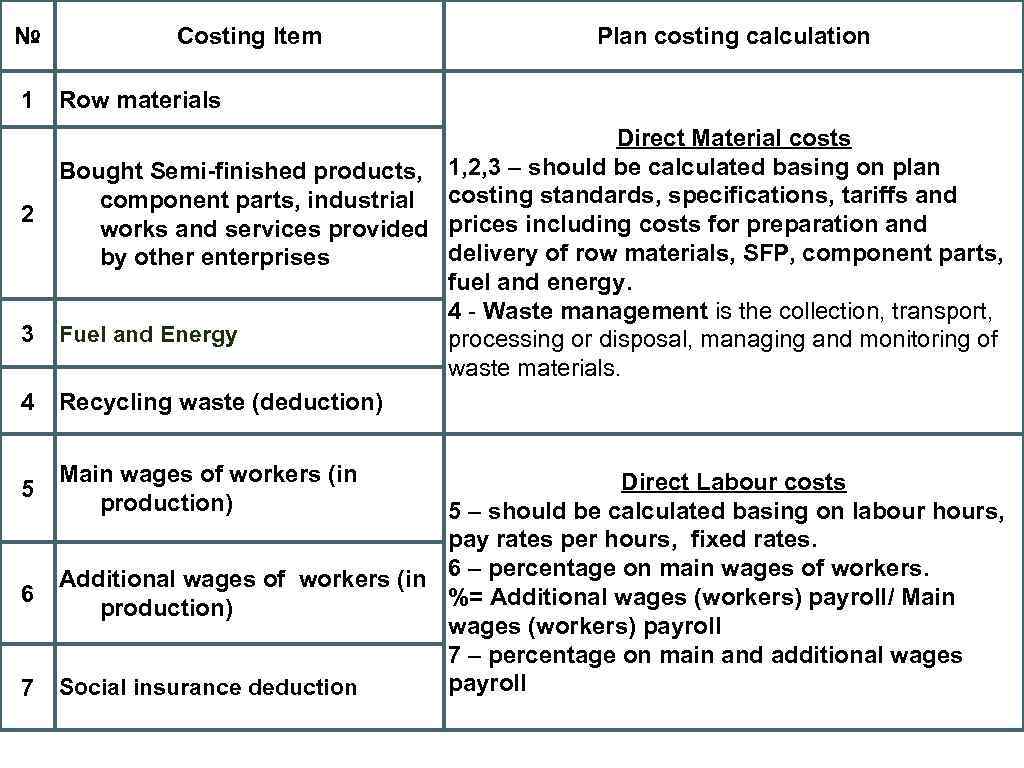 № 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 Costing Item Plan costing calculation Row materials Direct Material costs Bought Semi-finished products, 1, 2, 3 – should be calculated basing on plan component parts, industrial costing standards, specifications, tariffs and works and services provided prices including costs for preparation and delivery of row materials, SFP, component parts, by other enterprises fuel and energy. 4 - Waste management is the collection, transport, Fuel and Energy processing or disposal, managing and monitoring of waste materials. Recycling waste (deduction) Main wages of workers (in production) Direct Labour costs 5 – should be calculated basing on labour hours, pay rates per hours, fixed rates. Additional wages of workers (in 6 – percentage on main wages of workers. %= Additional wages (workers) payroll/ Main production) wages (workers) payroll 7 – percentage on main and additional wages payroll Social insurance deduction
№ 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 Costing Item Plan costing calculation Row materials Direct Material costs Bought Semi-finished products, 1, 2, 3 – should be calculated basing on plan component parts, industrial costing standards, specifications, tariffs and works and services provided prices including costs for preparation and delivery of row materials, SFP, component parts, by other enterprises fuel and energy. 4 - Waste management is the collection, transport, Fuel and Energy processing or disposal, managing and monitoring of waste materials. Recycling waste (deduction) Main wages of workers (in production) Direct Labour costs 5 – should be calculated basing on labour hours, pay rates per hours, fixed rates. Additional wages of workers (in 6 – percentage on main wages of workers. %= Additional wages (workers) payroll/ Main production) wages (workers) payroll 7 – percentage on main and additional wages payroll Social insurance deduction
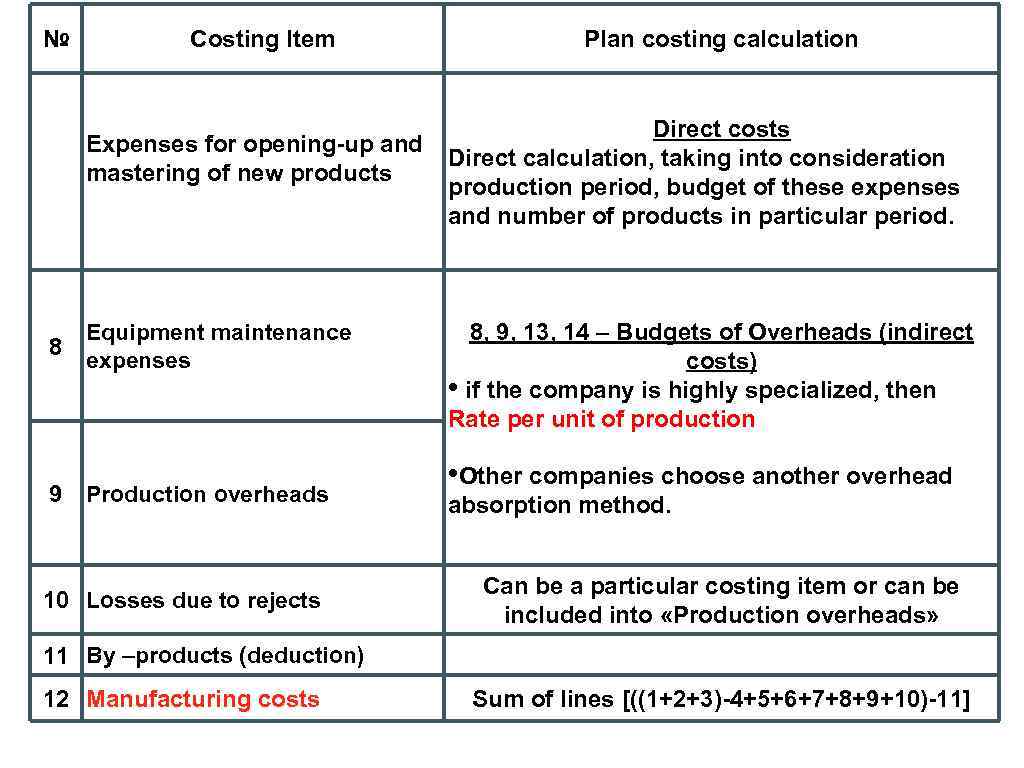 № Costing Item Plan costing calculation Direct costs Expenses for opening-up and Direct calculation, taking into consideration mastering of new products production period, budget of these expenses and number of products in particular period. 8 Equipment maintenance expenses 9 Production overheads 10 Losses due to rejects 8, 9, 13, 14 – Budgets of Overheads (indirect costs) • if the company is highly specialized, then Rate per unit of production • Other companies choose another overhead absorption method. Can be a particular costing item or can be included into «Production overheads» 11 By –products (deduction) 12 Manufacturing costs Sum of lines [((1+2+3)-4+5+6+7+8+9+10)-11]
№ Costing Item Plan costing calculation Direct costs Expenses for opening-up and Direct calculation, taking into consideration mastering of new products production period, budget of these expenses and number of products in particular period. 8 Equipment maintenance expenses 9 Production overheads 10 Losses due to rejects 8, 9, 13, 14 – Budgets of Overheads (indirect costs) • if the company is highly specialized, then Rate per unit of production • Other companies choose another overhead absorption method. Can be a particular costing item or can be included into «Production overheads» 11 By –products (deduction) 12 Manufacturing costs Sum of lines [((1+2+3)-4+5+6+7+8+9+10)-11]
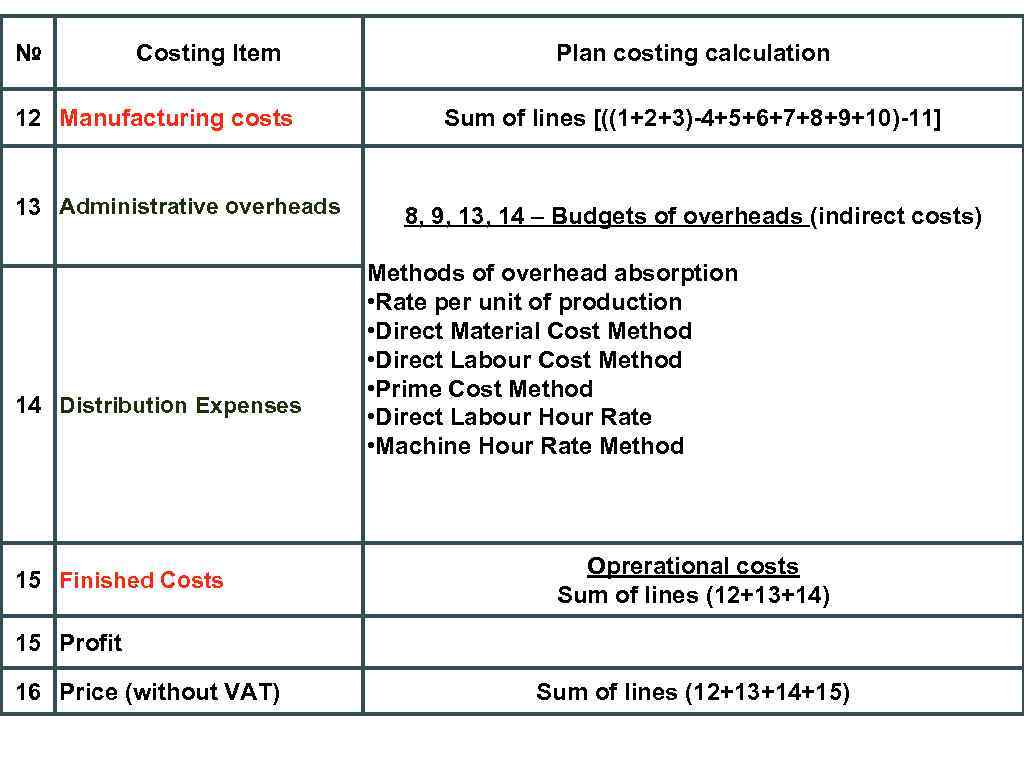 № Costing Item 12 Manufacturing costs 13 Administrative overheads 14 Distribution Expenses 15 Finished Costs Plan costing calculation Sum of lines [((1+2+3)-4+5+6+7+8+9+10)-11] 8, 9, 13, 14 – Budgets of overheads (indirect costs) Methods of overhead absorption • Rate per unit of production • Direct Material Cost Method • Direct Labour Cost Method • Prime Cost Method • Direct Labour Hour Rate • Machine Hour Rate Method Oprerational costs Sum of lines (12+13+14) 15 Profit 16 Price (without VAT) Sum of lines (12+13+14+15)
№ Costing Item 12 Manufacturing costs 13 Administrative overheads 14 Distribution Expenses 15 Finished Costs Plan costing calculation Sum of lines [((1+2+3)-4+5+6+7+8+9+10)-11] 8, 9, 13, 14 – Budgets of overheads (indirect costs) Methods of overhead absorption • Rate per unit of production • Direct Material Cost Method • Direct Labour Cost Method • Prime Cost Method • Direct Labour Hour Rate • Machine Hour Rate Method Oprerational costs Sum of lines (12+13+14) 15 Profit 16 Price (without VAT) Sum of lines (12+13+14+15)
 4. Expenditure Budget of the Enterprise
4. Expenditure Budget of the Enterprise
 Expenditure Budget - The annual (quarter) expense plan of a commercial enterprise. - One of main documents of business plan. There all needs of enterprise in inventory. There all expenses according to economic meaning, i. e. their production applicability and cost centers don’t matter. As an integral part of the Expenditure Budget, the calculation of capital spending is based on the submission of facts for acceptance, from various portfolio departments
Expenditure Budget - The annual (quarter) expense plan of a commercial enterprise. - One of main documents of business plan. There all needs of enterprise in inventory. There all expenses according to economic meaning, i. e. their production applicability and cost centers don’t matter. As an integral part of the Expenditure Budget, the calculation of capital spending is based on the submission of facts for acceptance, from various portfolio departments
 Calculation of the Expenditure Budget (for industrial enterprise)
Calculation of the Expenditure Budget (for industrial enterprise)
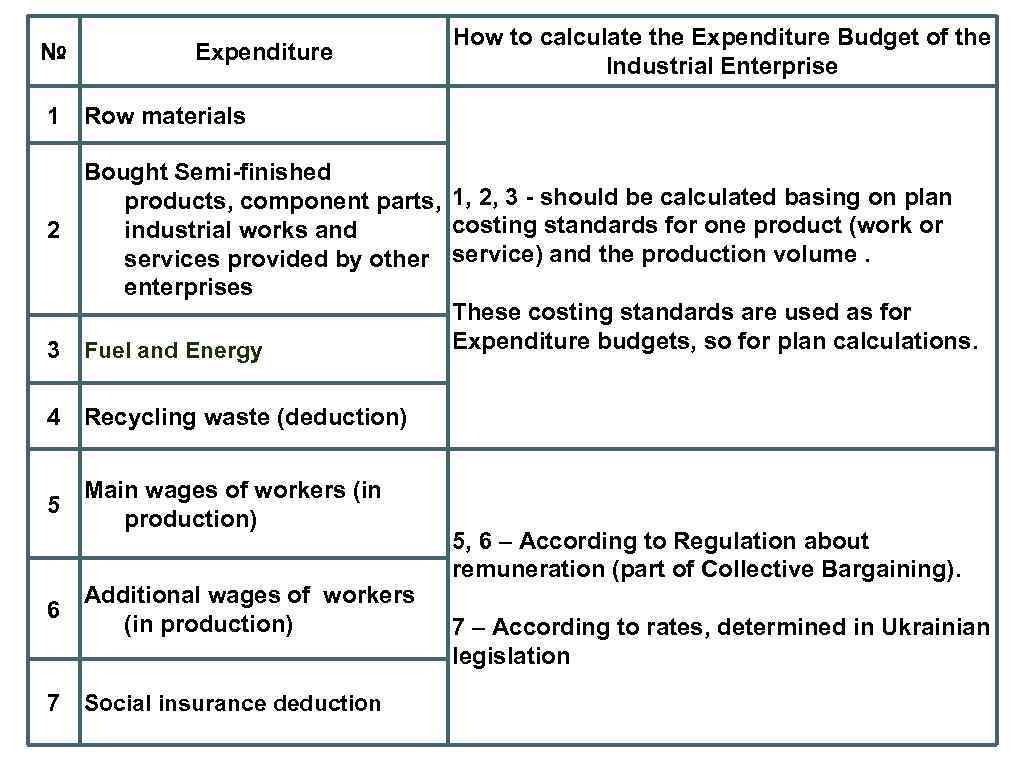 № Expenditure How to calculate the Expenditure Budget of the Industrial Enterprise 1 Row materials Bought Semi-finished products, component parts, 1, 2, 3 - should be calculated basing on plan costing standards for one product (work or industrial works and 2 services provided by other service) and the production volume. enterprises These costing standards are used as for Expenditure budgets, so for plan calculations. 3 Fuel and Energy 4 Recycling waste (deduction) Main wages of workers (in 5 production) Additional wages of workers 6 (in production) 7 Social insurance deduction 5, 6 – According to Regulation about remuneration (part of Collective Bargaining). 7 – According to rates, determined in Ukrainian legislation
№ Expenditure How to calculate the Expenditure Budget of the Industrial Enterprise 1 Row materials Bought Semi-finished products, component parts, 1, 2, 3 - should be calculated basing on plan costing standards for one product (work or industrial works and 2 services provided by other service) and the production volume. enterprises These costing standards are used as for Expenditure budgets, so for plan calculations. 3 Fuel and Energy 4 Recycling waste (deduction) Main wages of workers (in 5 production) Additional wages of workers 6 (in production) 7 Social insurance deduction 5, 6 – According to Regulation about remuneration (part of Collective Bargaining). 7 – According to rates, determined in Ukrainian legislation
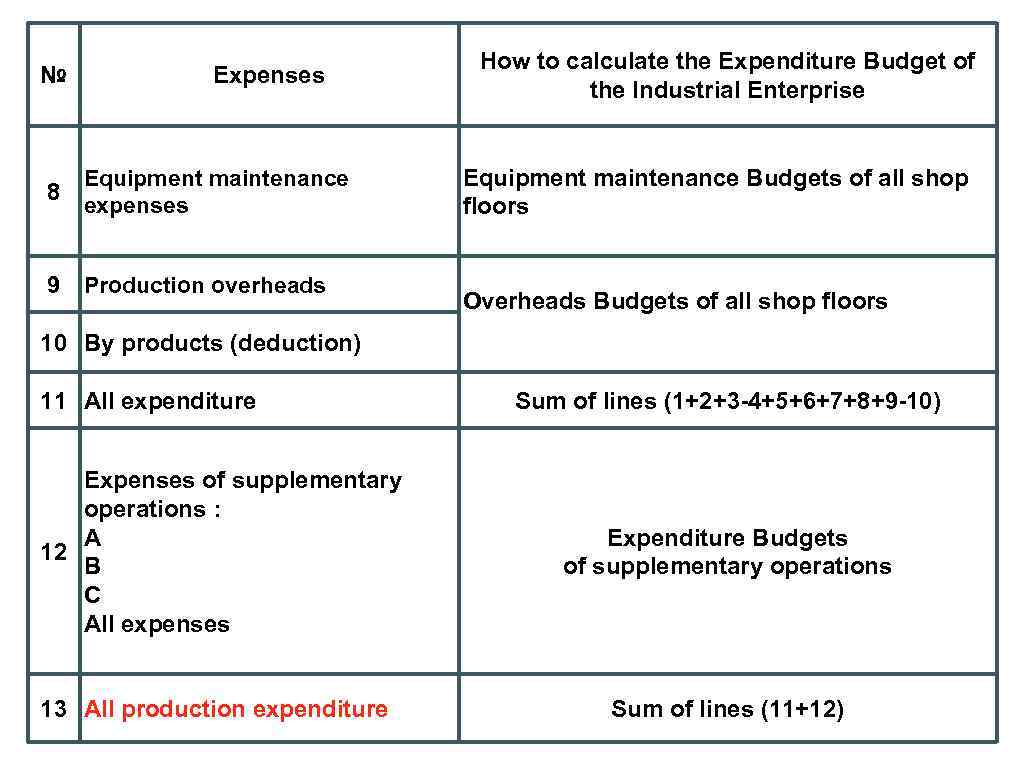 № 8 Expenses Equipment maintenance expenses 9 Production overheads How to calculate the Expenditure Budget of the Industrial Enterprise Equipment maintenance Budgets of all shop floors Overheads Budgets of all shop floors 10 By products (deduction) 11 All expenditure Expenses of supplementary operations : А 12 B C All expenses 13 All production expenditure Sum of lines (1+2+3 -4+5+6+7+8+9 -10) Expenditure Budgets of supplementary operations Sum of lines (11+12)
№ 8 Expenses Equipment maintenance expenses 9 Production overheads How to calculate the Expenditure Budget of the Industrial Enterprise Equipment maintenance Budgets of all shop floors Overheads Budgets of all shop floors 10 By products (deduction) 11 All expenditure Expenses of supplementary operations : А 12 B C All expenses 13 All production expenditure Sum of lines (1+2+3 -4+5+6+7+8+9 -10) Expenditure Budgets of supplementary operations Sum of lines (11+12)
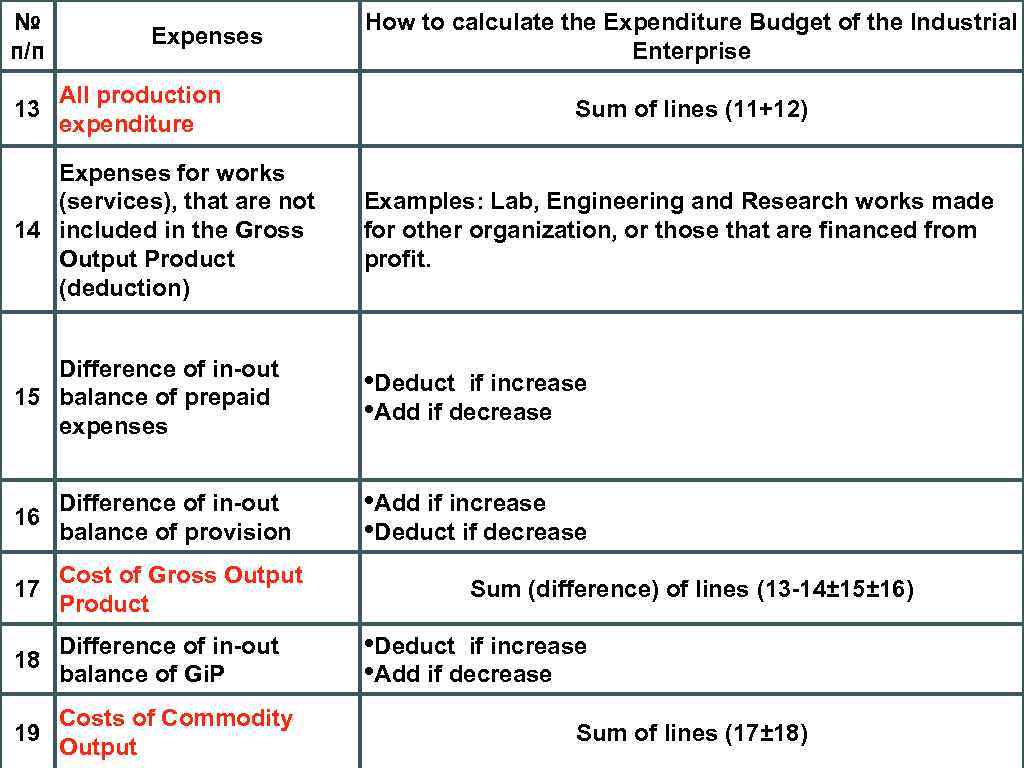 № п/п Expenses All production 13 expenditure How to calculate the Expenditure Budget of the Industrial Enterprise Sum of lines (11+12) Expenses for works (services), that are not 14 included in the Gross Output Product (deduction) Examples: Lab, Engineering and Research works made for other organization, or those that are financed from profit. Difference of in-out 15 balance of prepaid expenses • Deduct if increase • Add if decrease Difference of in-out 16 balance of provision • Add if increase • Deduct if decrease Cost of Gross Output 17 Product 18 Difference of in-out balance of Gi. P Costs of Commodity 19 Output Sum (difference) of lines (13 -14± 15± 16) • Deduct if increase • Add if decrease Sum of lines (17± 18)
№ п/п Expenses All production 13 expenditure How to calculate the Expenditure Budget of the Industrial Enterprise Sum of lines (11+12) Expenses for works (services), that are not 14 included in the Gross Output Product (deduction) Examples: Lab, Engineering and Research works made for other organization, or those that are financed from profit. Difference of in-out 15 balance of prepaid expenses • Deduct if increase • Add if decrease Difference of in-out 16 balance of provision • Add if increase • Deduct if decrease Cost of Gross Output 17 Product 18 Difference of in-out balance of Gi. P Costs of Commodity 19 Output Sum (difference) of lines (13 -14± 15± 16) • Deduct if increase • Add if decrease Sum of lines (17± 18)
 Costs per one ₴ (UAH) COSTS/ Goods Sold
Costs per one ₴ (UAH) COSTS/ Goods Sold


