3750727b1f7461933c25404121362a4b.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 54
 PRODUCTION AND OPERATIONS MANAGEMENT Ch. 7: Process Strategy POM - J. Galván 1
PRODUCTION AND OPERATIONS MANAGEMENT Ch. 7: Process Strategy POM - J. Galván 1
 Process Strategy n n n Process strategy is the pattern of decisions made in managing processes so that they will achieve their competitive priorities. A process involves the use of an organization’s resources to provide something of value. Major process decisions include: • Process Structure • Customer Involvement • Resource Flexibility • Capital Intensity POM - J. Galván 2
Process Strategy n n n Process strategy is the pattern of decisions made in managing processes so that they will achieve their competitive priorities. A process involves the use of an organization’s resources to provide something of value. Major process decisions include: • Process Structure • Customer Involvement • Resource Flexibility • Capital Intensity POM - J. Galván 2
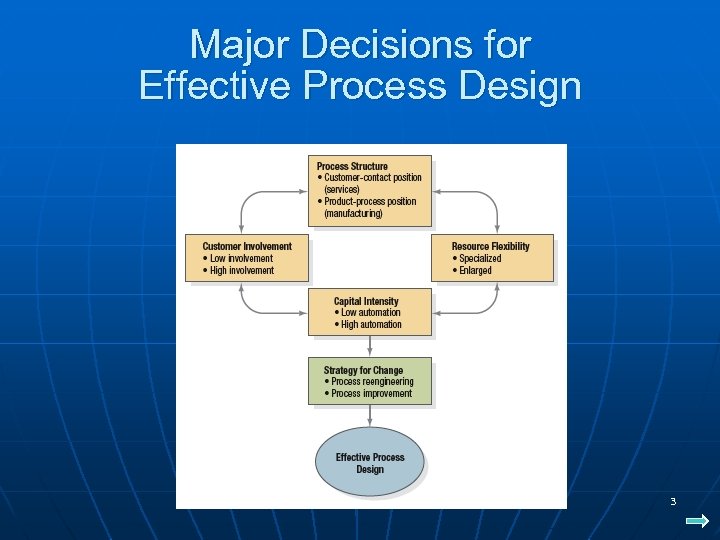 Major Decisions for Effective Process Design POM - J. Galván 3
Major Decisions for Effective Process Design POM - J. Galván 3
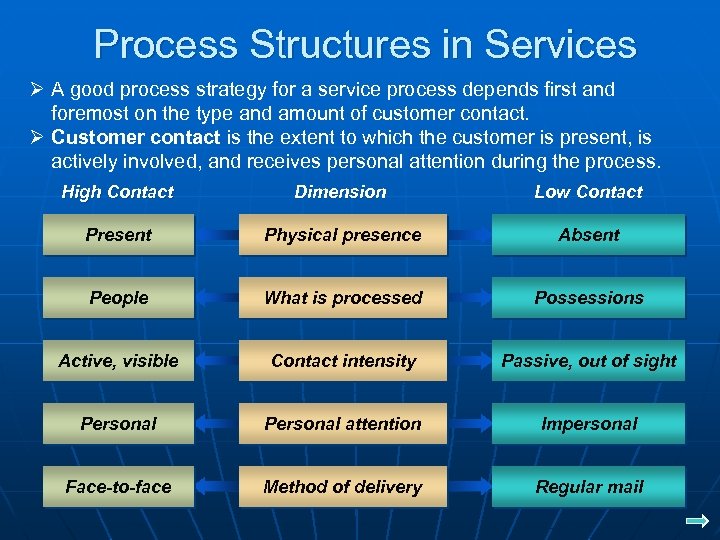 Process Structures in Services Ø A good process strategy for a service process depends first and foremost on the type and amount of customer contact. Ø Customer contact is the extent to which the customer is present, is actively involved, and receives personal attention during the process. High Contact Dimension Low Contact Present Physical presence Absent People What is processed Possessions Active, visible Contact intensity Passive, out of sight Personal attention Impersonal Face-to-face Method of delivery Regular mail POM - J. Galván 4
Process Structures in Services Ø A good process strategy for a service process depends first and foremost on the type and amount of customer contact. Ø Customer contact is the extent to which the customer is present, is actively involved, and receives personal attention during the process. High Contact Dimension Low Contact Present Physical presence Absent People What is processed Possessions Active, visible Contact intensity Passive, out of sight Personal attention Impersonal Face-to-face Method of delivery Regular mail POM - J. Galván 4
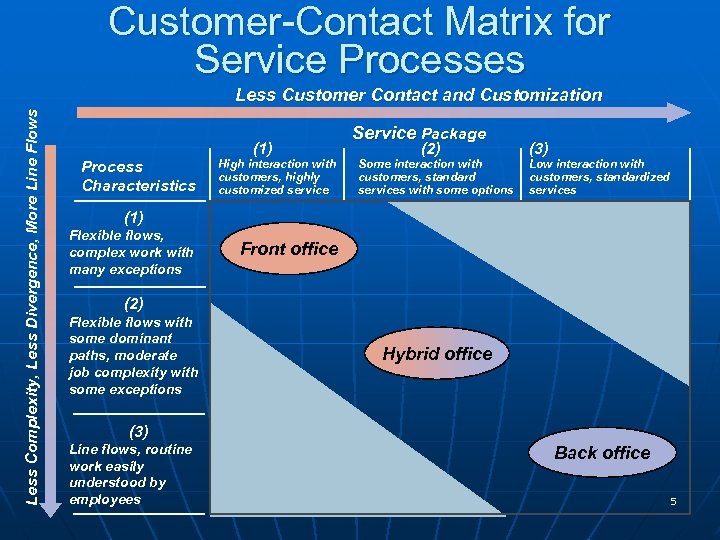 Customer-Contact Matrix for Service Processes Less Complexity, Less Divergence, More Line Flows Less Customer Contact and Customization Process Characteristics Service Package (1) High interaction with customers, highly customized service (2) Some interaction with customers, standard services with some options (3) Low interaction with customers, standardized services (1) Flexible flows, complex work with many exceptions Front office (2) Flexible flows with some dominant paths, moderate job complexity with some exceptions Hybrid office (3) Line flows, routine work easily understood by employees Back office POM - J. Galván 5
Customer-Contact Matrix for Service Processes Less Complexity, Less Divergence, More Line Flows Less Customer Contact and Customization Process Characteristics Service Package (1) High interaction with customers, highly customized service (2) Some interaction with customers, standard services with some options (3) Low interaction with customers, standardized services (1) Flexible flows, complex work with many exceptions Front office (2) Flexible flows with some dominant paths, moderate job complexity with some exceptions Hybrid office (3) Line flows, routine work easily understood by employees Back office POM - J. Galván 5
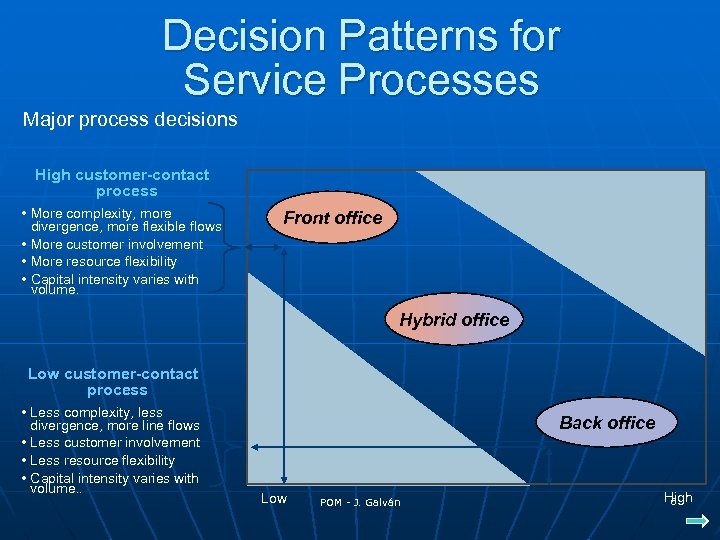 Decision Patterns for Service Processes Major process decisions High customer-contact process • More complexity, more divergence, more flexible flows • More customer involvement • More resource flexibility • Capital intensity varies with volume. Front office Hybrid office Low customer-contact process • Less complexity, less divergence, more line flows • Less customer involvement • Less resource flexibility • Capital intensity varies with volume. . Back office Low POM - J. Galván High 6
Decision Patterns for Service Processes Major process decisions High customer-contact process • More complexity, more divergence, more flexible flows • More customer involvement • More resource flexibility • Capital intensity varies with volume. Front office Hybrid office Low customer-contact process • Less complexity, less divergence, more line flows • Less customer involvement • Less resource flexibility • Capital intensity varies with volume. . Back office Low POM - J. Galván High 6
 Front office in services POM - J. Galván 7
Front office in services POM - J. Galván 7
 Back office POM - J. Galván 8
Back office POM - J. Galván 8
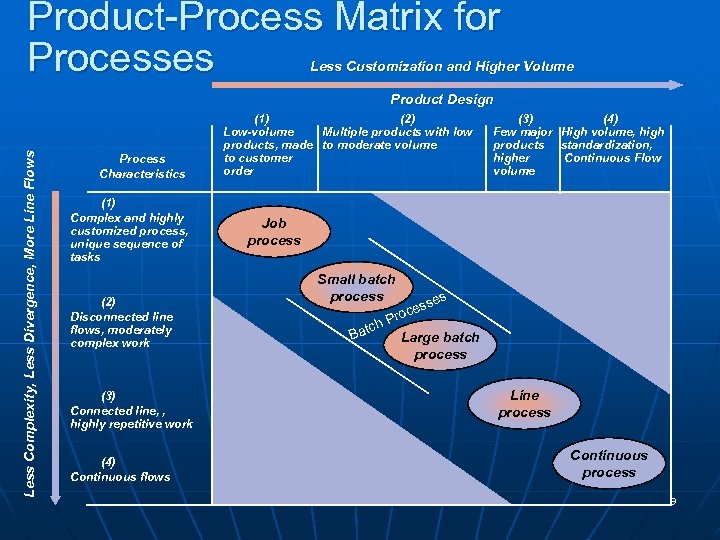 Product-Process Matrix for Processes Less Customization and Higher Volume Less Complexity, Less Divergence, More Line Flows Product Design Process Characteristics (1) Complex and highly customized process, unique sequence of tasks (2) Disconnected line flows, moderately complex work (1) (2) Low-volume Multiple products with low products, made to moderate volume to customer order (3) (4) Few major High volume, high products standardization, higher Continuous Flow volume Job process Small batch process ch Bat es ss oce Pr Large batch process Line process (3) Connected line, , highly repetitive work Continuous process (4) Continuous flows POM - J. Galván 9
Product-Process Matrix for Processes Less Customization and Higher Volume Less Complexity, Less Divergence, More Line Flows Product Design Process Characteristics (1) Complex and highly customized process, unique sequence of tasks (2) Disconnected line flows, moderately complex work (1) (2) Low-volume Multiple products with low products, made to moderate volume to customer order (3) (4) Few major High volume, high products standardization, higher Continuous Flow volume Job process Small batch process ch Bat es ss oce Pr Large batch process Line process (3) Connected line, , highly repetitive work Continuous process (4) Continuous flows POM - J. Galván 9
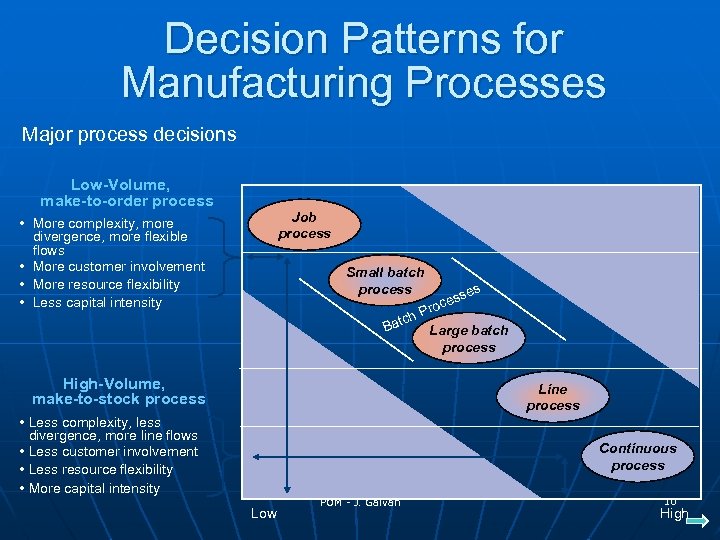 Decision Patterns for Manufacturing Processes Major process decisions Low-Volume, make-to-order process Job process • More complexity, more divergence, more flexible flows • More customer involvement • More resource flexibility • Less capital intensity Small batch process ch Bat High-Volume, make-to-stock process es ss oce Pr Large batch process Line process • Less complexity, less divergence, more line flows • Less customer involvement • Less resource flexibility • More capital intensity Continuous process Low POM - J. Galván 10 High
Decision Patterns for Manufacturing Processes Major process decisions Low-Volume, make-to-order process Job process • More complexity, more divergence, more flexible flows • More customer involvement • More resource flexibility • Less capital intensity Small batch process ch Bat High-Volume, make-to-stock process es ss oce Pr Large batch process Line process • Less complexity, less divergence, more line flows • Less customer involvement • Less resource flexibility • More capital intensity Continuous process Low POM - J. Galván 10 High
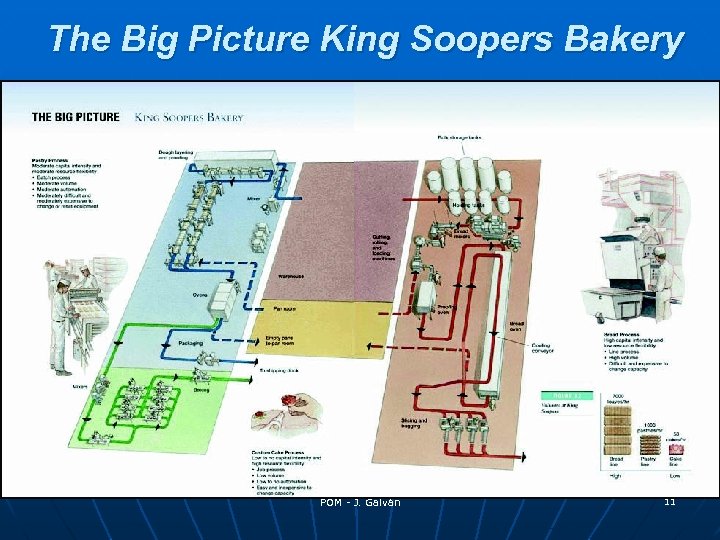 The Big Picture King Soopers Bakery POM - J. Galván 11
The Big Picture King Soopers Bakery POM - J. Galván 11
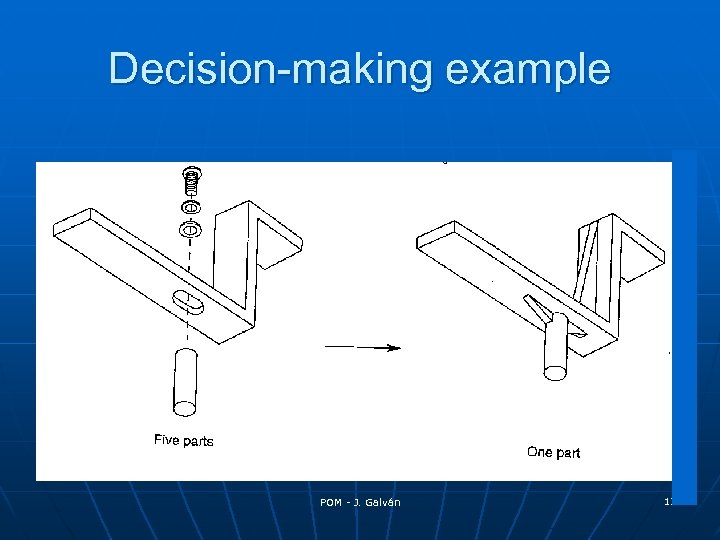 Decision-making example POM - J. Galván 12
Decision-making example POM - J. Galván 12
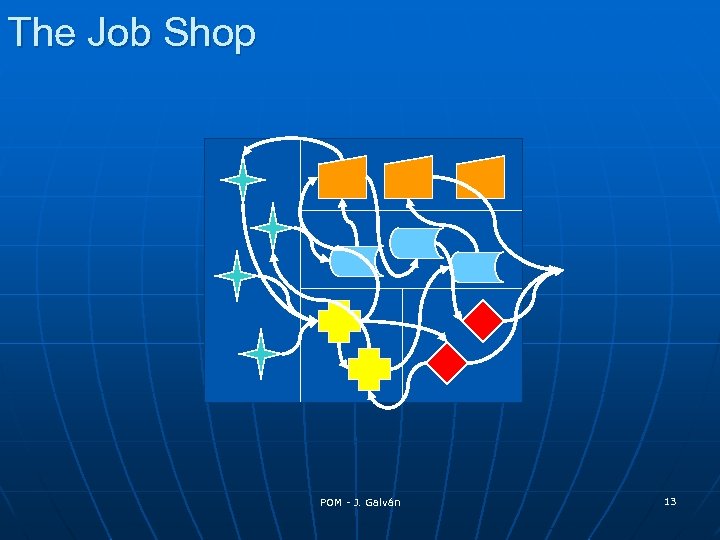 The Job Shop POM - J. Galván 13
The Job Shop POM - J. Galván 13
 AIRPLANE JOB SHOP POM - J. Galván 14
AIRPLANE JOB SHOP POM - J. Galván 14
 SMALL JOB SHOP POM - J. Galván 15
SMALL JOB SHOP POM - J. Galván 15
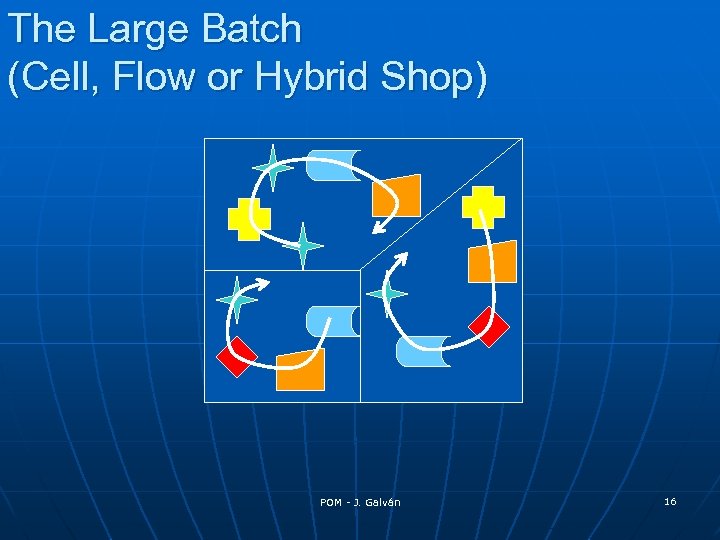 The Large Batch (Cell, Flow or Hybrid Shop) POM - J. Galván 16
The Large Batch (Cell, Flow or Hybrid Shop) POM - J. Galván 16
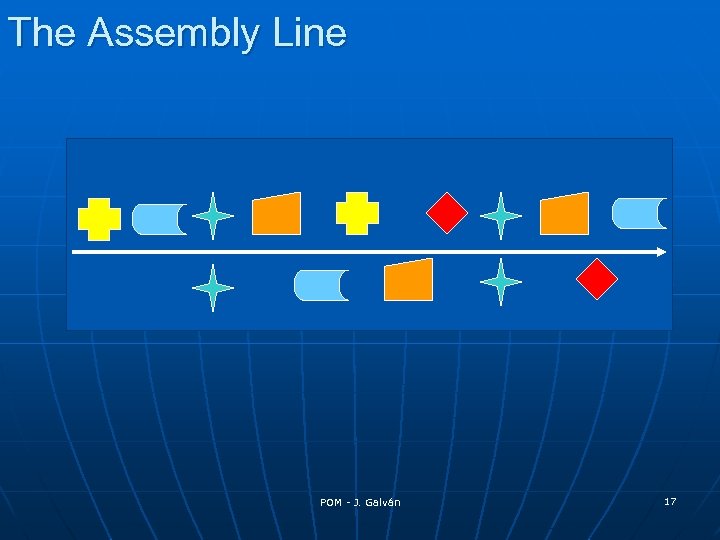 The Assembly Line POM - J. Galván 17
The Assembly Line POM - J. Galván 17
 ASSEMBLY LINE (1930) POM - J. Galván 18
ASSEMBLY LINE (1930) POM - J. Galván 18
 MODERN ASSEMBLY LINE POM - J. Galván 19
MODERN ASSEMBLY LINE POM - J. Galván 19
 CHINESE ASSEMBLY LINE POM - J. Galván 20
CHINESE ASSEMBLY LINE POM - J. Galván 20
 CONTINUOUS PRODUCTION PROCESS (OLD) POM - J. Galván 21
CONTINUOUS PRODUCTION PROCESS (OLD) POM - J. Galván 21
 MODERN CONTINUOUS PRODUCTION PROCESS POM - J. Galván 22
MODERN CONTINUOUS PRODUCTION PROCESS POM - J. Galván 22
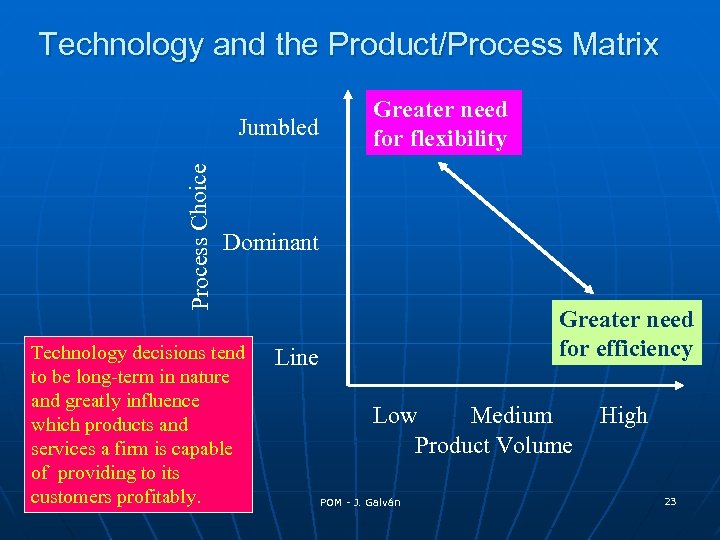 Technology and the Product/Process Matrix Process Choice Jumbled Greater need for flexibility Dominant Technology decisions tend to be long-term in nature and greatly influence which products and services a firm is capable of providing to its customers profitably. Greater need for efficiency Line Low Medium Product Volume POM - J. Galván High 23
Technology and the Product/Process Matrix Process Choice Jumbled Greater need for flexibility Dominant Technology decisions tend to be long-term in nature and greatly influence which products and services a firm is capable of providing to its customers profitably. Greater need for efficiency Line Low Medium Product Volume POM - J. Galván High 23
 Tools for Process Design Flow Diagrams n Process Charts n Time-Function/Process Mapping n Work Flow Analysis n POM - J. Galván 24
Tools for Process Design Flow Diagrams n Process Charts n Time-Function/Process Mapping n Work Flow Analysis n POM - J. Galván 24
 Flow Diagrams POM - J. Galván 25
Flow Diagrams POM - J. Galván 25
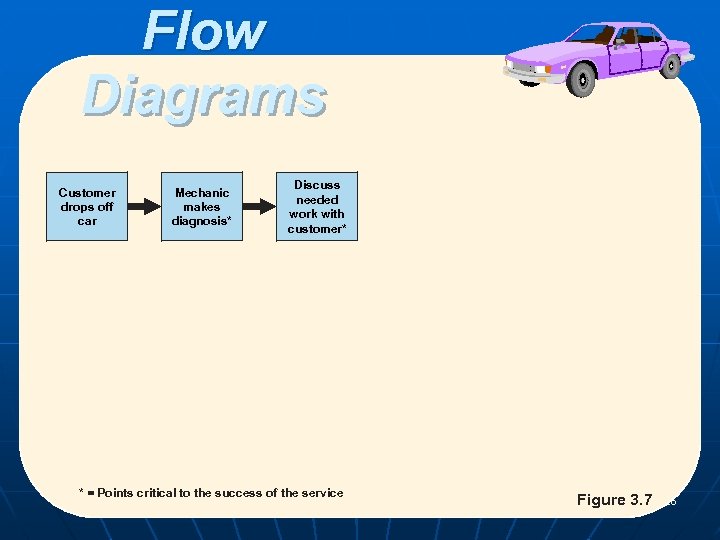 Flow Diagrams Customer drops off car Mechanic makes diagnosis* Discuss needed work with customer* * = Points critical to the success of the service POM - J. Galván Figure 3. 7 26
Flow Diagrams Customer drops off car Mechanic makes diagnosis* Discuss needed work with customer* * = Points critical to the success of the service POM - J. Galván Figure 3. 7 26
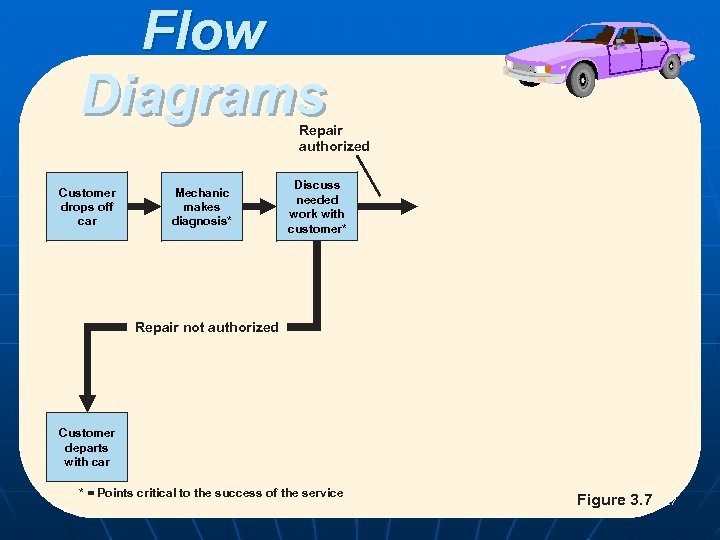 Flow Diagrams Repair authorized Customer drops off car Mechanic makes diagnosis* Discuss needed work with customer* Repair not authorized Customer departs with car * = Points critical to the success of the service POM - J. Galván Figure 3. 7 27
Flow Diagrams Repair authorized Customer drops off car Mechanic makes diagnosis* Discuss needed work with customer* Repair not authorized Customer departs with car * = Points critical to the success of the service POM - J. Galván Figure 3. 7 27
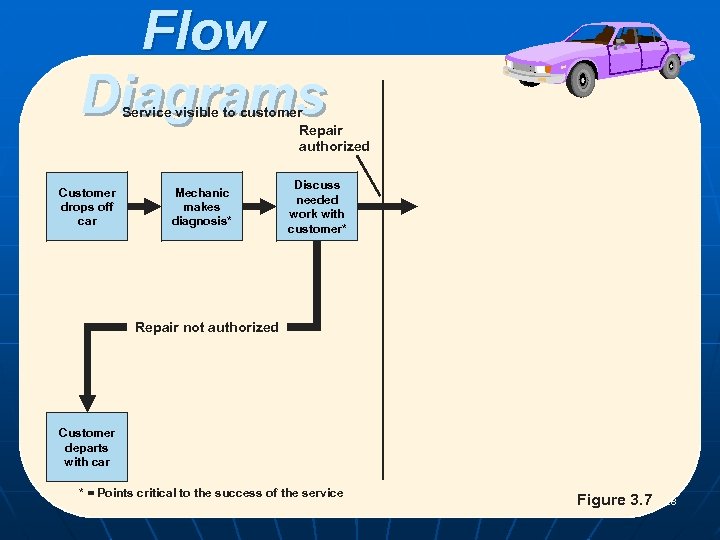 Flow Diagrams Service visible to customer Repair authorized Customer drops off car Mechanic makes diagnosis* Discuss needed work with customer* Repair not authorized Customer departs with car * = Points critical to the success of the service POM - J. Galván Figure 3. 7 28
Flow Diagrams Service visible to customer Repair authorized Customer drops off car Mechanic makes diagnosis* Discuss needed work with customer* Repair not authorized Customer departs with car * = Points critical to the success of the service POM - J. Galván Figure 3. 7 28
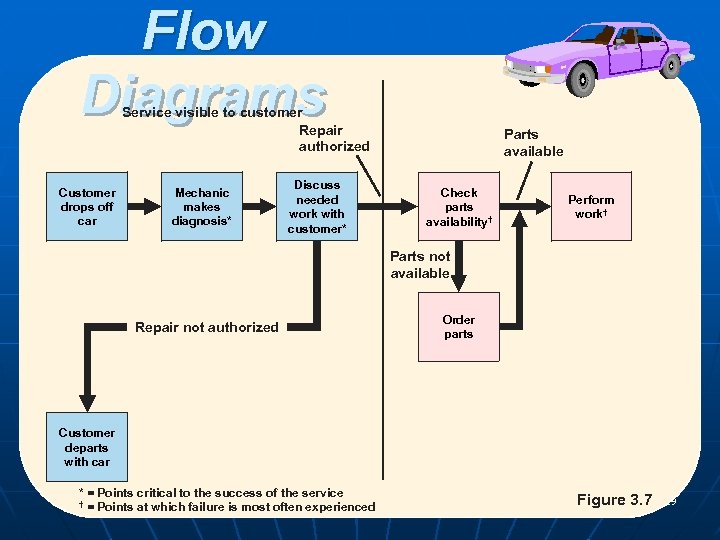 Flow Diagrams Service visible to customer Repair authorized Customer drops off car Mechanic makes diagnosis* Parts available Discuss needed work with customer* Check parts availability† Perform work† Parts not available Repair not authorized Order parts Customer departs with car * = Points critical to the success of the service POM - J. Galván † = Points at which failure is most often experienced Figure 3. 7 29
Flow Diagrams Service visible to customer Repair authorized Customer drops off car Mechanic makes diagnosis* Parts available Discuss needed work with customer* Check parts availability† Perform work† Parts not available Repair not authorized Order parts Customer departs with car * = Points critical to the success of the service POM - J. Galván † = Points at which failure is most often experienced Figure 3. 7 29
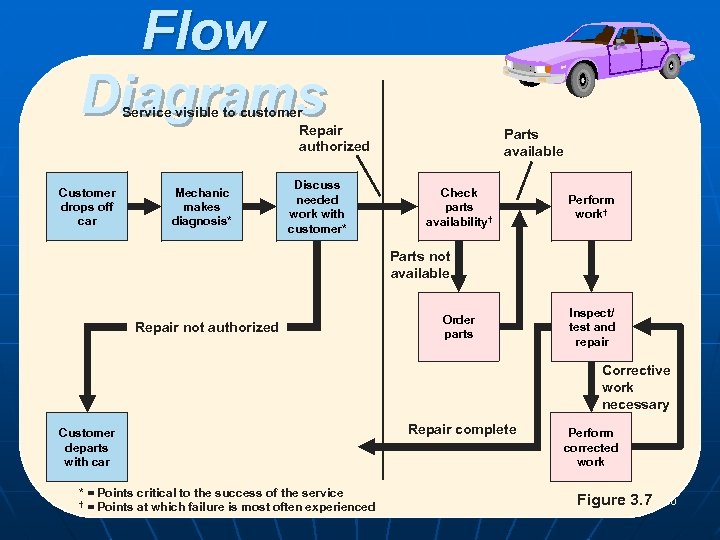 Flow Diagrams Service visible to customer Repair authorized Customer drops off car Mechanic makes diagnosis* Parts available Discuss needed work with customer* Check parts availability† Perform work† Parts not available Repair not authorized Order parts Inspect/ test and repair Corrective work necessary Customer departs with car * = Points critical to the success of the service POM - J. Galván † = Points at which failure is most often experienced Repair complete Perform corrected work Figure 3. 7 30
Flow Diagrams Service visible to customer Repair authorized Customer drops off car Mechanic makes diagnosis* Parts available Discuss needed work with customer* Check parts availability† Perform work† Parts not available Repair not authorized Order parts Inspect/ test and repair Corrective work necessary Customer departs with car * = Points critical to the success of the service POM - J. Galván † = Points at which failure is most often experienced Repair complete Perform corrected work Figure 3. 7 30
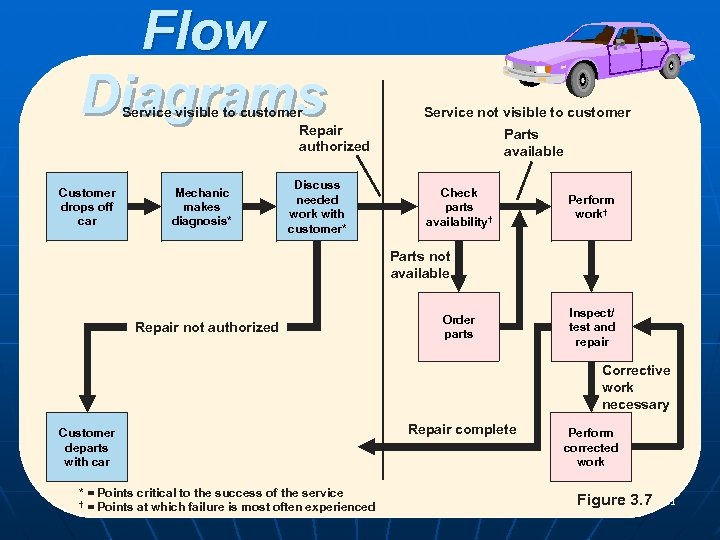 Flow Diagrams Service visible to customer Repair authorized Customer drops off car Mechanic makes diagnosis* Service not visible to customer Parts available Discuss needed work with customer* Check parts availability† Perform work† Parts not available Repair not authorized Order parts Inspect/ test and repair Corrective work necessary Customer departs with car * = Points critical to the success of the service POM - J. Galván † = Points at which failure is most often experienced Repair complete Perform corrected work Figure 3. 7 31
Flow Diagrams Service visible to customer Repair authorized Customer drops off car Mechanic makes diagnosis* Service not visible to customer Parts available Discuss needed work with customer* Check parts availability† Perform work† Parts not available Repair not authorized Order parts Inspect/ test and repair Corrective work necessary Customer departs with car * = Points critical to the success of the service POM - J. Galván † = Points at which failure is most often experienced Repair complete Perform corrected work Figure 3. 7 31
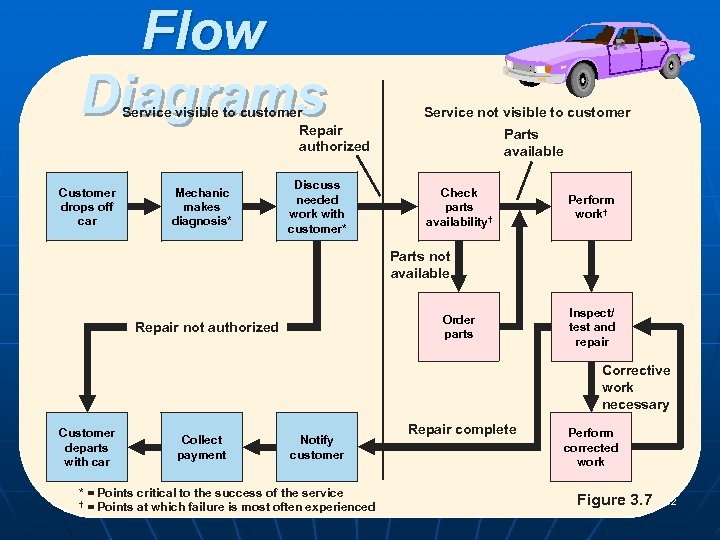 Flow Diagrams Service visible to customer Repair authorized Customer drops off car Mechanic makes diagnosis* Service not visible to customer Parts available Discuss needed work with customer* Check parts availability† Perform work† Parts not available Order parts Repair not authorized Inspect/ test and repair Corrective work necessary Customer departs with car Collect payment Notify customer * = Points critical to the success of the service POM - J. Galván † = Points at which failure is most often experienced Repair complete Perform corrected work Figure 3. 7 32
Flow Diagrams Service visible to customer Repair authorized Customer drops off car Mechanic makes diagnosis* Service not visible to customer Parts available Discuss needed work with customer* Check parts availability† Perform work† Parts not available Order parts Repair not authorized Inspect/ test and repair Corrective work necessary Customer departs with car Collect payment Notify customer * = Points critical to the success of the service POM - J. Galván † = Points at which failure is most often experienced Repair complete Perform corrected work Figure 3. 7 32
 Process Charts POM - J. Galván 33
Process Charts POM - J. Galván 33
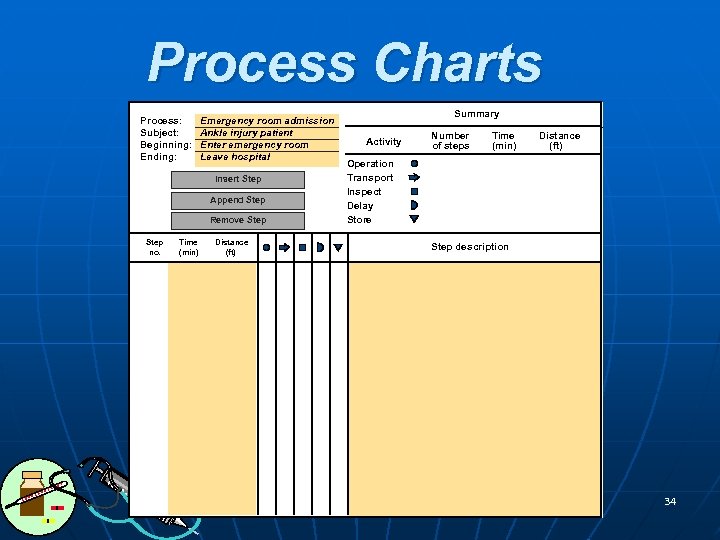 Process Charts Process: Subject: Beginning: Ending: Emergency room admission Ankle injury patient Enter emergency room Leave hospital Insert Step Append Step Remove Step no. Time (min) Summary Activity Number of steps Time (min) Distance (ft) Operation Transport Inspect Delay Store Distance (ft) Step description POM - J. Galván 34
Process Charts Process: Subject: Beginning: Ending: Emergency room admission Ankle injury patient Enter emergency room Leave hospital Insert Step Append Step Remove Step no. Time (min) Summary Activity Number of steps Time (min) Distance (ft) Operation Transport Inspect Delay Store Distance (ft) Step description POM - J. Galván 34
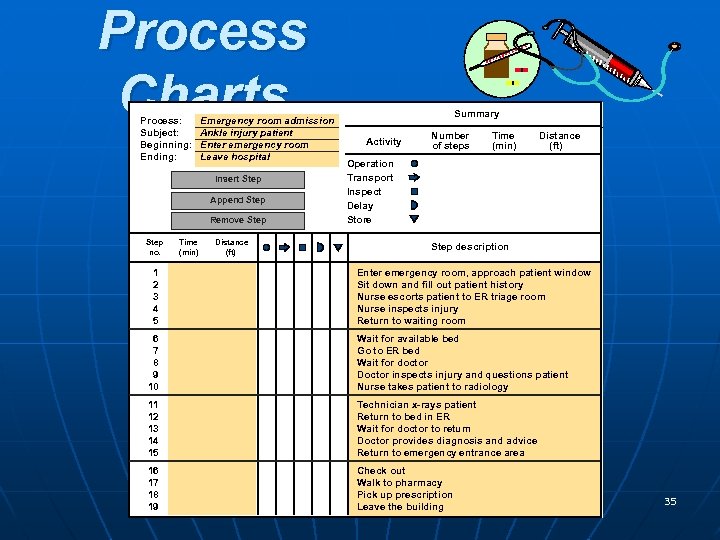 Process Charts Process: Subject: Beginning: Ending: Emergency room admission Ankle injury patient Enter emergency room Leave hospital Insert Step Append Step Remove Step no. 1 2 3 4 5 Time (min) Distance (ft) Summary Activity Number of steps Time (min) Distance (ft) Operation Transport Inspect Delay Store Step description Enter emergency room, approach patient window Sit down and fill out patient history Nurse escorts patient to ER triage room Nurse inspects injury Return to waiting room 6 7 8 9 10 Wait for available bed Go to ER bed Wait for doctor Doctor inspects injury and questions patient Nurse takes patient to radiology 11 12 13 14 15 Technician x-rays patient Return to bed in ER Wait for doctor to return Doctor provides diagnosis and advice Return to emergency entrance area 16 17 18 19 Check out Walk to pharmacy Pick up prescription POM - J. Galván building Leave the 35
Process Charts Process: Subject: Beginning: Ending: Emergency room admission Ankle injury patient Enter emergency room Leave hospital Insert Step Append Step Remove Step no. 1 2 3 4 5 Time (min) Distance (ft) Summary Activity Number of steps Time (min) Distance (ft) Operation Transport Inspect Delay Store Step description Enter emergency room, approach patient window Sit down and fill out patient history Nurse escorts patient to ER triage room Nurse inspects injury Return to waiting room 6 7 8 9 10 Wait for available bed Go to ER bed Wait for doctor Doctor inspects injury and questions patient Nurse takes patient to radiology 11 12 13 14 15 Technician x-rays patient Return to bed in ER Wait for doctor to return Doctor provides diagnosis and advice Return to emergency entrance area 16 17 18 19 Check out Walk to pharmacy Pick up prescription POM - J. Galván building Leave the 35
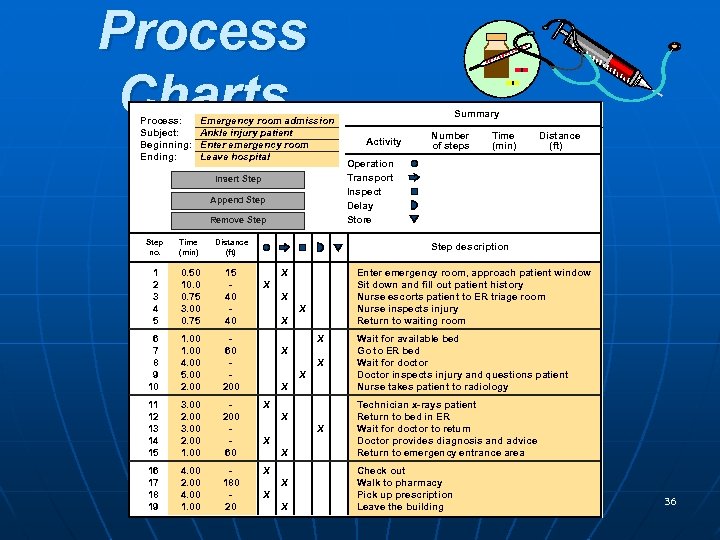 Process Charts Process: Subject: Beginning: Ending: Emergency room admission Ankle injury patient Enter emergency room Leave hospital Insert Step Append Step Remove Step no. Time (min) Distance (ft) 1 2 3 4 5 0. 50 10. 0 0. 75 3. 00 0. 75 15 40 40 6 7 8 9 10 1. 00 4. 00 5. 00 2. 00 60 200 11 12 13 14 15 3. 00 2. 00 1. 00 200 60 X 16 17 18 19 4. 00 2. 00 4. 00 180 20 X Summary Activity Number of steps Time (min) Distance (ft) Operation Transport Inspect Delay Store Step description X Enter emergency room, approach patient window Sit down and fill out patient history Nurse escorts patient to ER triage room Nurse inspects injury Return to waiting room X X X Wait for available bed Go to ER bed Wait for doctor Doctor inspects injury and questions patient Nurse takes patient to radiology X Technician x-rays patient Return to bed in ER Wait for doctor to return Doctor provides diagnosis and advice Return to emergency entrance area X X X X X Check out Walk to pharmacy Pick up prescription POM - J. Galván building Leave the 36
Process Charts Process: Subject: Beginning: Ending: Emergency room admission Ankle injury patient Enter emergency room Leave hospital Insert Step Append Step Remove Step no. Time (min) Distance (ft) 1 2 3 4 5 0. 50 10. 0 0. 75 3. 00 0. 75 15 40 40 6 7 8 9 10 1. 00 4. 00 5. 00 2. 00 60 200 11 12 13 14 15 3. 00 2. 00 1. 00 200 60 X 16 17 18 19 4. 00 2. 00 4. 00 180 20 X Summary Activity Number of steps Time (min) Distance (ft) Operation Transport Inspect Delay Store Step description X Enter emergency room, approach patient window Sit down and fill out patient history Nurse escorts patient to ER triage room Nurse inspects injury Return to waiting room X X X Wait for available bed Go to ER bed Wait for doctor Doctor inspects injury and questions patient Nurse takes patient to radiology X Technician x-rays patient Return to bed in ER Wait for doctor to return Doctor provides diagnosis and advice Return to emergency entrance area X X X X X Check out Walk to pharmacy Pick up prescription POM - J. Galván building Leave the 36
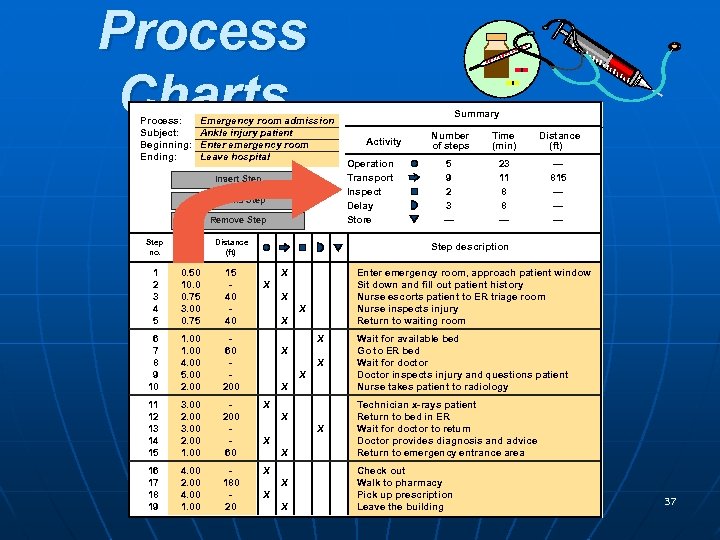 Process Charts Process: Subject: Beginning: Ending: Emergency room admission Ankle injury patient Enter emergency room Leave hospital Insert Step Append Step Remove Step no. Time (min) Distance (ft) 1 2 3 4 5 0. 50 10. 0 0. 75 3. 00 0. 75 15 40 40 6 7 8 9 10 1. 00 4. 00 5. 00 2. 00 60 200 11 12 13 14 15 3. 00 2. 00 1. 00 200 60 X 16 17 18 19 4. 00 2. 00 4. 00 180 20 X Summary Activity Operation Transport Inspect Delay Store Number of steps Time (min) Distance (ft) 5 9 2 3 — 23 11 8 8 — — 815 — — — Step description X Enter emergency room, approach patient window Sit down and fill out patient history Nurse escorts patient to ER triage room Nurse inspects injury Return to waiting room X X X Wait for available bed Go to ER bed Wait for doctor Doctor inspects injury and questions patient Nurse takes patient to radiology X Technician x-rays patient Return to bed in ER Wait for doctor to return Doctor provides diagnosis and advice Return to emergency entrance area X X X X X Check out Walk to pharmacy Pick up prescription POM - J. Galván building Leave the 37
Process Charts Process: Subject: Beginning: Ending: Emergency room admission Ankle injury patient Enter emergency room Leave hospital Insert Step Append Step Remove Step no. Time (min) Distance (ft) 1 2 3 4 5 0. 50 10. 0 0. 75 3. 00 0. 75 15 40 40 6 7 8 9 10 1. 00 4. 00 5. 00 2. 00 60 200 11 12 13 14 15 3. 00 2. 00 1. 00 200 60 X 16 17 18 19 4. 00 2. 00 4. 00 180 20 X Summary Activity Operation Transport Inspect Delay Store Number of steps Time (min) Distance (ft) 5 9 2 3 — 23 11 8 8 — — 815 — — — Step description X Enter emergency room, approach patient window Sit down and fill out patient history Nurse escorts patient to ER triage room Nurse inspects injury Return to waiting room X X X Wait for available bed Go to ER bed Wait for doctor Doctor inspects injury and questions patient Nurse takes patient to radiology X Technician x-rays patient Return to bed in ER Wait for doctor to return Doctor provides diagnosis and advice Return to emergency entrance area X X X X X Check out Walk to pharmacy Pick up prescription POM - J. Galván building Leave the 37
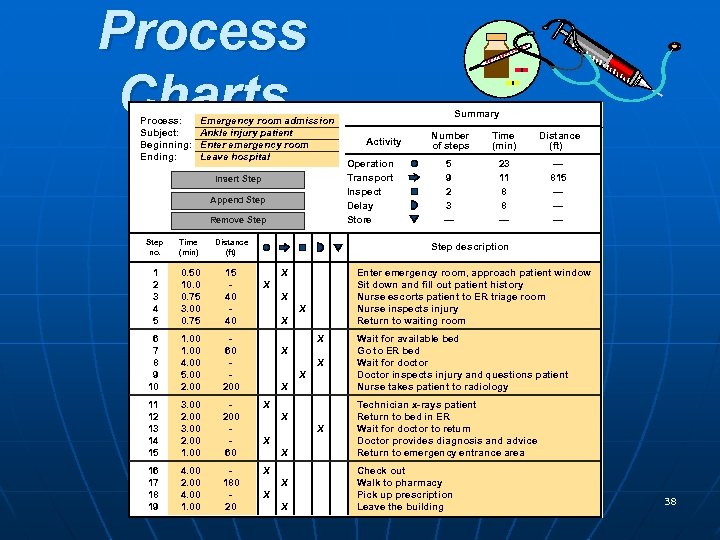 Process Charts Process: Subject: Beginning: Ending: Emergency room admission Ankle injury patient Enter emergency room Leave hospital Insert Step Append Step Remove Step no. Time (min) Distance (ft) 1 2 3 4 5 0. 50 10. 0 0. 75 3. 00 0. 75 15 40 40 6 7 8 9 10 1. 00 4. 00 5. 00 2. 00 60 200 11 12 13 14 15 3. 00 2. 00 1. 00 200 60 X 16 17 18 19 4. 00 2. 00 4. 00 180 20 X Summary Activity Operation Transport Inspect Delay Store Number of steps Time (min) Distance (ft) 5 9 2 3 — 23 11 8 8 — — 815 — — — Step description X Enter emergency room, approach patient window Sit down and fill out patient history Nurse escorts patient to ER triage room Nurse inspects injury Return to waiting room X X X Wait for available bed Go to ER bed Wait for doctor Doctor inspects injury and questions patient Nurse takes patient to radiology X Technician x-rays patient Return to bed in ER Wait for doctor to return Doctor provides diagnosis and advice Return to emergency entrance area X X X X X Check out Walk to pharmacy Pick up prescription POM - J. Galván building Leave the 38
Process Charts Process: Subject: Beginning: Ending: Emergency room admission Ankle injury patient Enter emergency room Leave hospital Insert Step Append Step Remove Step no. Time (min) Distance (ft) 1 2 3 4 5 0. 50 10. 0 0. 75 3. 00 0. 75 15 40 40 6 7 8 9 10 1. 00 4. 00 5. 00 2. 00 60 200 11 12 13 14 15 3. 00 2. 00 1. 00 200 60 X 16 17 18 19 4. 00 2. 00 4. 00 180 20 X Summary Activity Operation Transport Inspect Delay Store Number of steps Time (min) Distance (ft) 5 9 2 3 — 23 11 8 8 — — 815 — — — Step description X Enter emergency room, approach patient window Sit down and fill out patient history Nurse escorts patient to ER triage room Nurse inspects injury Return to waiting room X X X Wait for available bed Go to ER bed Wait for doctor Doctor inspects injury and questions patient Nurse takes patient to radiology X Technician x-rays patient Return to bed in ER Wait for doctor to return Doctor provides diagnosis and advice Return to emergency entrance area X X X X X Check out Walk to pharmacy Pick up prescription POM - J. Galván building Leave the 38
 Simulation POM - J. Galván 39
Simulation POM - J. Galván 39
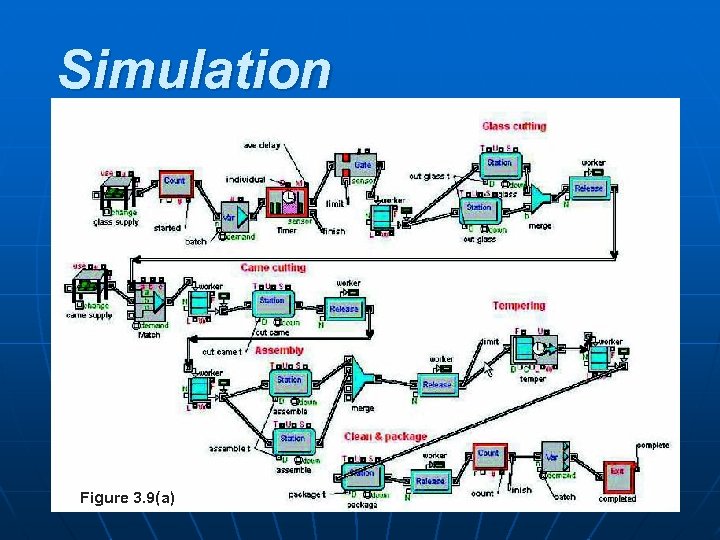 Simulation Figure 3. 9(a) POM - J. Galván 40
Simulation Figure 3. 9(a) POM - J. Galván 40
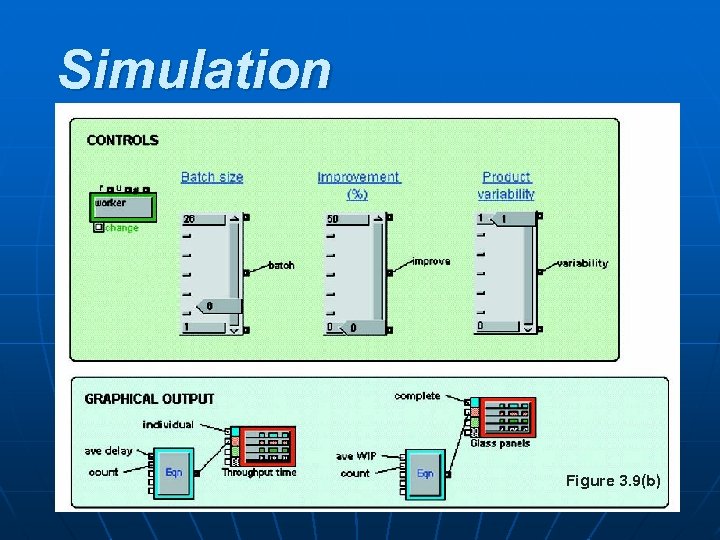 Simulation Figure 3. 9(b) POM - J. Galván 41
Simulation Figure 3. 9(b) POM - J. Galván 41
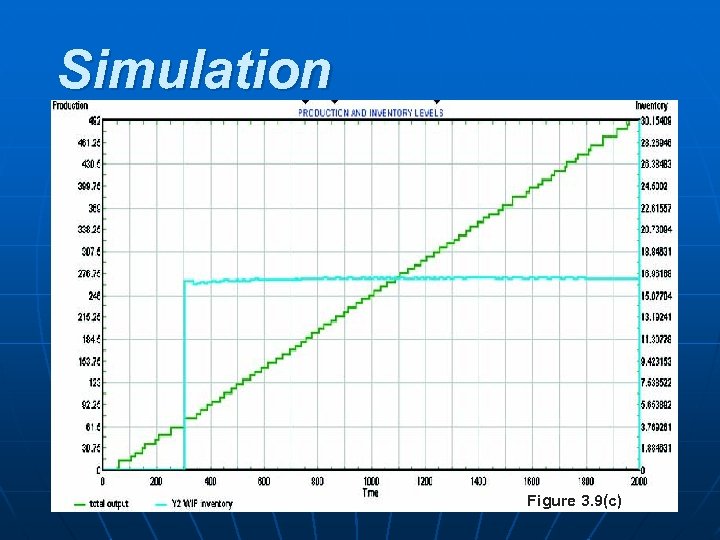 Simulation POM - J. Galván Figure 3. 9(c) 42
Simulation POM - J. Galván Figure 3. 9(c) 42
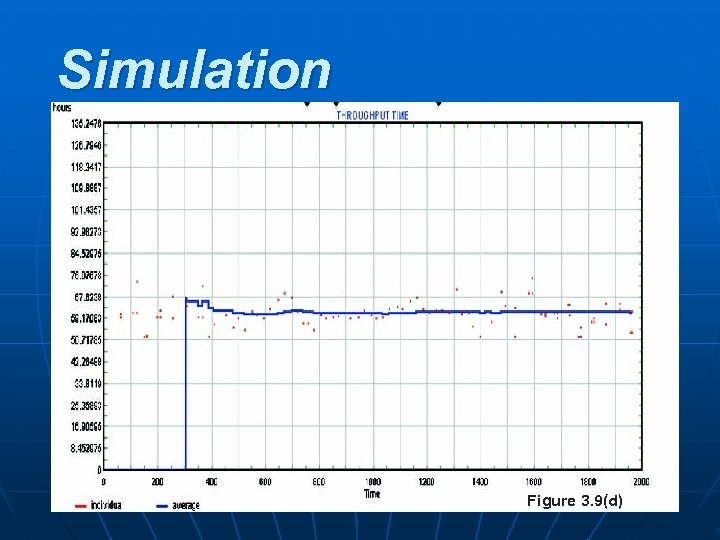 Simulation POM - J. Galván Figure 3. 9(d) 43
Simulation POM - J. Galván Figure 3. 9(d) 43
 TOOLS FOR AUTOMATION n How has been automation implemented through time? POM - J. Galván 44
TOOLS FOR AUTOMATION n How has been automation implemented through time? POM - J. Galván 44
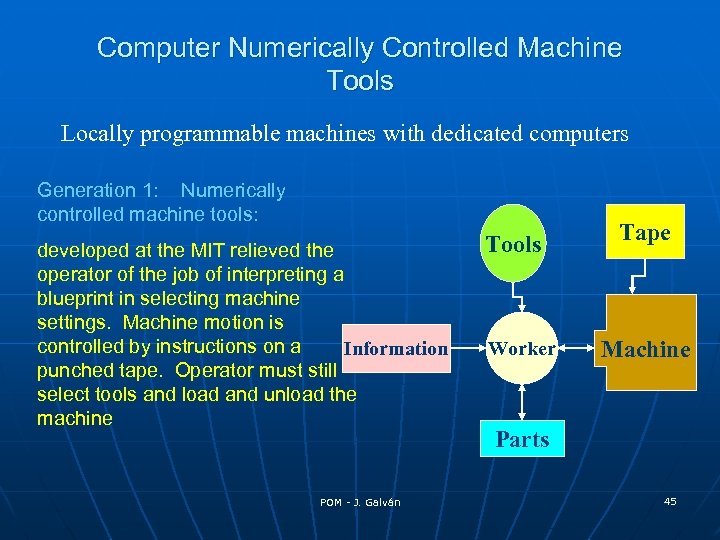 Computer Numerically Controlled Machine Tools Locally programmable machines with dedicated computers Generation 1: Numerically controlled machine tools: developed at the MIT relieved the operator of the job of interpreting a blueprint in selecting machine settings. Machine motion is controlled by instructions on a Information punched tape. Operator must still select tools and load and unload the machine POM - J. Galván Tools Worker Tape Machine Parts 45
Computer Numerically Controlled Machine Tools Locally programmable machines with dedicated computers Generation 1: Numerically controlled machine tools: developed at the MIT relieved the operator of the job of interpreting a blueprint in selecting machine settings. Machine motion is controlled by instructions on a Information punched tape. Operator must still select tools and load and unload the machine POM - J. Galván Tools Worker Tape Machine Parts 45
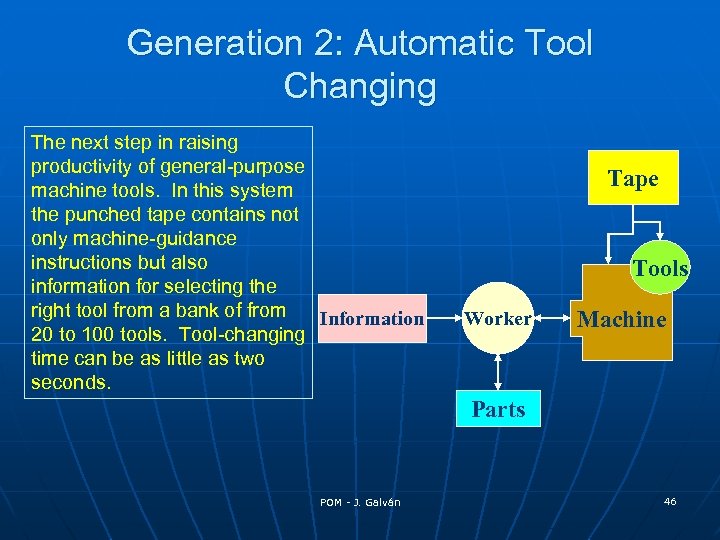 Generation 2: Automatic Tool Changing The next step in raising productivity of general-purpose machine tools. In this system the punched tape contains not only machine-guidance instructions but also information for selecting the right tool from a bank of from Information 20 to 100 tools. Tool-changing time can be as little as two seconds. Tape Tools Worker Machine Parts POM - J. Galván 46
Generation 2: Automatic Tool Changing The next step in raising productivity of general-purpose machine tools. In this system the punched tape contains not only machine-guidance instructions but also information for selecting the right tool from a bank of from Information 20 to 100 tools. Tool-changing time can be as little as two seconds. Tape Tools Worker Machine Parts POM - J. Galván 46
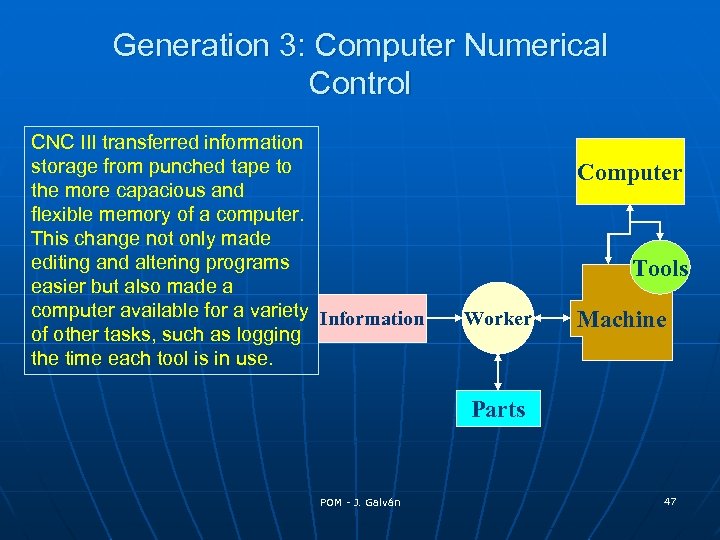 Generation 3: Computer Numerical Control CNC III transferred information storage from punched tape to the more capacious and flexible memory of a computer. This change not only made editing and altering programs easier but also made a computer available for a variety Information of other tasks, such as logging the time each tool is in use. Computer Tools Worker Machine Parts POM - J. Galván 47
Generation 3: Computer Numerical Control CNC III transferred information storage from punched tape to the more capacious and flexible memory of a computer. This change not only made editing and altering programs easier but also made a computer available for a variety Information of other tasks, such as logging the time each tool is in use. Computer Tools Worker Machine Parts POM - J. Galván 47
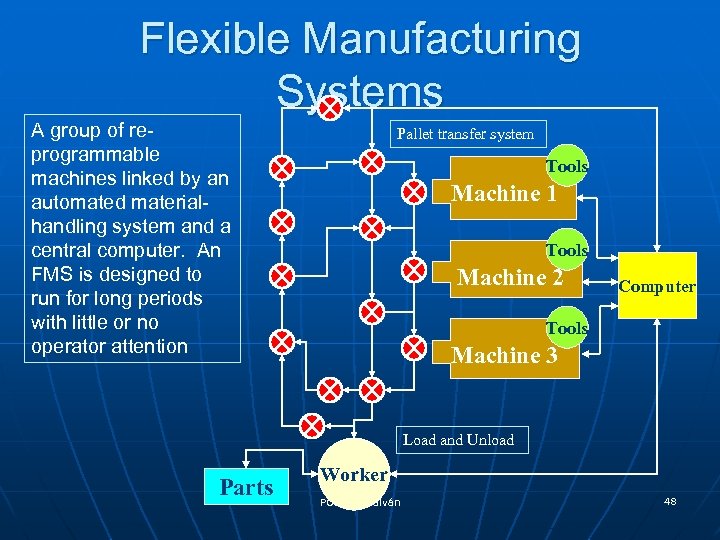 Flexible Manufacturing Systems A group of reprogrammable machines linked by an automated materialhandling system and a central computer. An FMS is designed to run for long periods with little or no operator attention Pallet transfer system Tools Machine 1 Tools Machine 2 Computer Tools Machine 3 Load and Unload Parts Worker POM - J. Galván 48
Flexible Manufacturing Systems A group of reprogrammable machines linked by an automated materialhandling system and a central computer. An FMS is designed to run for long periods with little or no operator attention Pallet transfer system Tools Machine 1 Tools Machine 2 Computer Tools Machine 3 Load and Unload Parts Worker POM - J. Galván 48
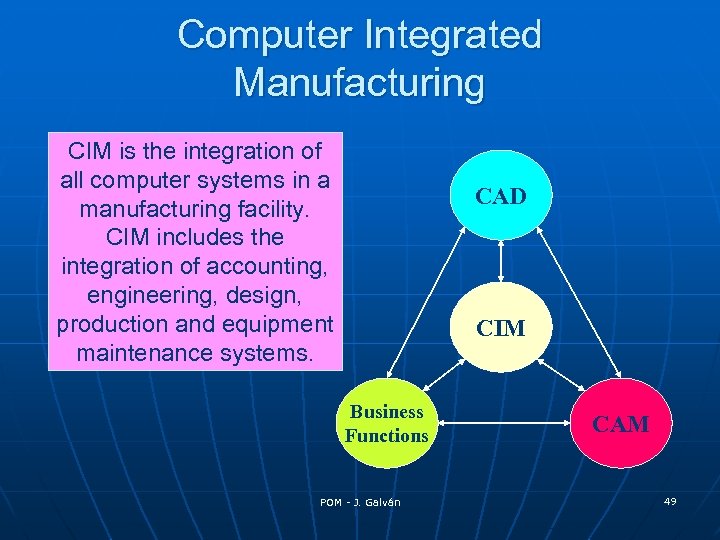 Computer Integrated Manufacturing CIM is the integration of all computer systems in a manufacturing facility. CIM includes the integration of accounting, engineering, design, production and equipment maintenance systems. CAD CIM Business Functions POM - J. Galván CAM 49
Computer Integrated Manufacturing CIM is the integration of all computer systems in a manufacturing facility. CIM includes the integration of accounting, engineering, design, production and equipment maintenance systems. CAD CIM Business Functions POM - J. Galván CAM 49
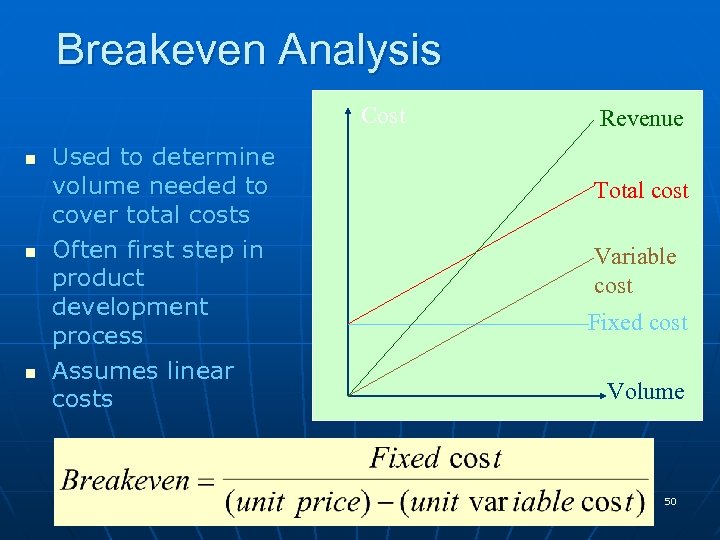 Breakeven Analysis Cost n n n Used to determine volume needed to cover total costs Often first step in product development process Assumes linear costs Revenue Total cost Variable cost Fixed cost Volume POM - J. Galván 50
Breakeven Analysis Cost n n n Used to determine volume needed to cover total costs Often first step in product development process Assumes linear costs Revenue Total cost Variable cost Fixed cost Volume POM - J. Galván 50
 Breakeven Example A firm is considering marketing a new toothbrush. The firm expects to sell each toothbrush for $2. 10. The per brush cost of material, labor and overhead equals $1. 45. The required investment in plant and equipment is $50, 000. How many brushes must be sold for the firm to breakeven? POM - J. Galván If only 65, 000 brushes are expected to sell, what must the variable costs be in order to allow the firm to breakeven? 51
Breakeven Example A firm is considering marketing a new toothbrush. The firm expects to sell each toothbrush for $2. 10. The per brush cost of material, labor and overhead equals $1. 45. The required investment in plant and equipment is $50, 000. How many brushes must be sold for the firm to breakeven? POM - J. Galván If only 65, 000 brushes are expected to sell, what must the variable costs be in order to allow the firm to breakeven? 51
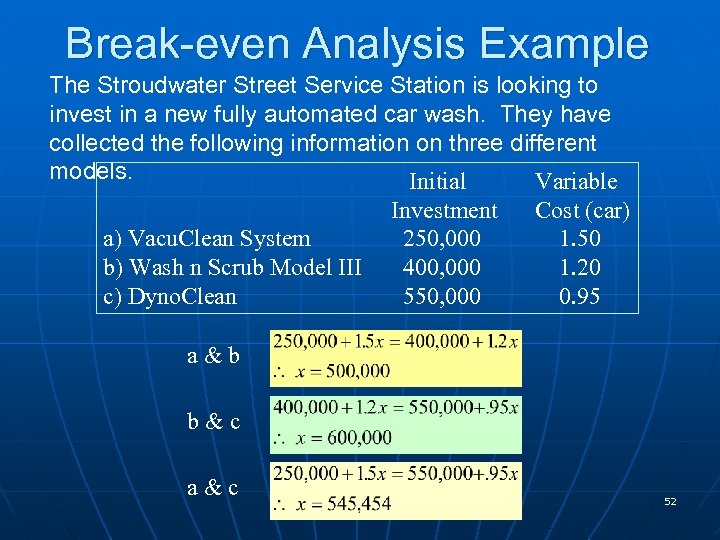 Break-even Analysis Example The Stroudwater Street Service Station is looking to invest in a new fully automated car wash. They have collected the following information on three different models. Initial Variable a) Vacu. Clean System b) Wash n Scrub Model III c) Dyno. Clean Investment 250, 000 400, 000 550, 000 Cost (car) 1. 50 1. 20 0. 95 a&b b&c a&c POM - J. Galván 52
Break-even Analysis Example The Stroudwater Street Service Station is looking to invest in a new fully automated car wash. They have collected the following information on three different models. Initial Variable a) Vacu. Clean System b) Wash n Scrub Model III c) Dyno. Clean Investment 250, 000 400, 000 550, 000 Cost (car) 1. 50 1. 20 0. 95 a&b b&c a&c POM - J. Galván 52
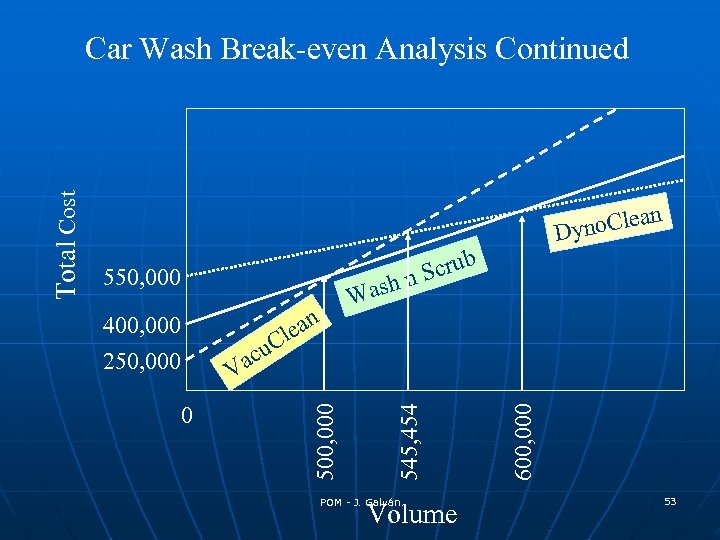 n 550, 000 400, 000 250, 000 h Was ean l a yno. Cle D crub n. S POM - J. Galván Volume 600, 000 0 545, 454 C acu V 500, 000 Total Cost Car Wash Break-even Analysis Continued 53
n 550, 000 400, 000 250, 000 h Was ean l a yno. Cle D crub n. S POM - J. Galván Volume 600, 000 0 545, 454 C acu V 500, 000 Total Cost Car Wash Break-even Analysis Continued 53
 Car Wash Break-even Analysis Continued If we were able to charge $1. 75 for a car wash, at what volumes would we breakeven? a) Vacu. Clean System b) Wash n Scrub Model III c) Dyno. Clean Initial Variable Investment Cost (car) 250, 000 1. 50 400, 000 1. 20 550, 000 0. 95 a) 250, 000/1. 75 -1. 50=1, 000 b) 400, 000/1. 75 -1. 20= 727, 272 c) 550, 000/1. 75 -0. 95= 687, 500 Note that the best profit-making process decision is 54 POM J. Dynoclean and only -if. Galván demand is greater than 687, 500
Car Wash Break-even Analysis Continued If we were able to charge $1. 75 for a car wash, at what volumes would we breakeven? a) Vacu. Clean System b) Wash n Scrub Model III c) Dyno. Clean Initial Variable Investment Cost (car) 250, 000 1. 50 400, 000 1. 20 550, 000 0. 95 a) 250, 000/1. 75 -1. 50=1, 000 b) 400, 000/1. 75 -1. 20= 727, 272 c) 550, 000/1. 75 -0. 95= 687, 500 Note that the best profit-making process decision is 54 POM J. Dynoclean and only -if. Galván demand is greater than 687, 500


