4bf5463bdfb7df06ee9851950c625bf1.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 43
 Product Innovation: Opportunity Identification Idea Generation, and Design Dr. Yushan Zhao College of Business and Economics UW-Whitewater Spring 2006
Product Innovation: Opportunity Identification Idea Generation, and Design Dr. Yushan Zhao College of Business and Economics UW-Whitewater Spring 2006
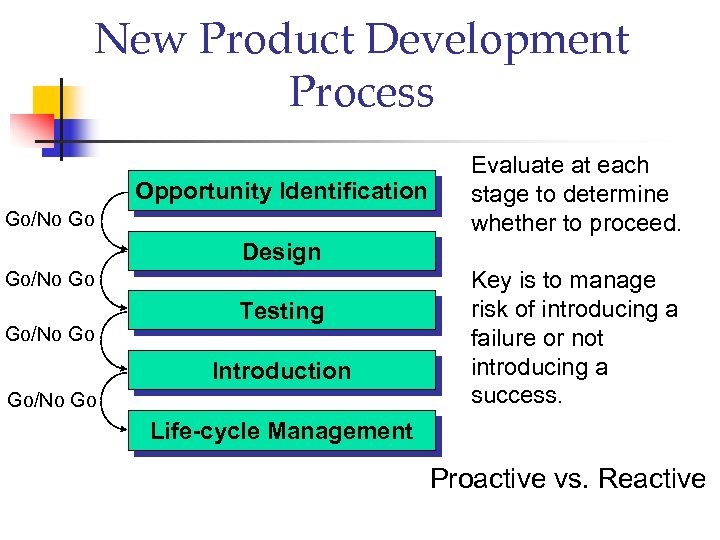 New Product Development Process Opportunity Identification Go/No Go Evaluate at each stage to determine whether to proceed. Design Go/No Go Testing Introduction Go/No Go Key is to manage risk of introducing a failure or not introducing a success. Life-cycle Management Proactive vs. Reactive
New Product Development Process Opportunity Identification Go/No Go Evaluate at each stage to determine whether to proceed. Design Go/No Go Testing Introduction Go/No Go Key is to manage risk of introducing a failure or not introducing a success. Life-cycle Management Proactive vs. Reactive
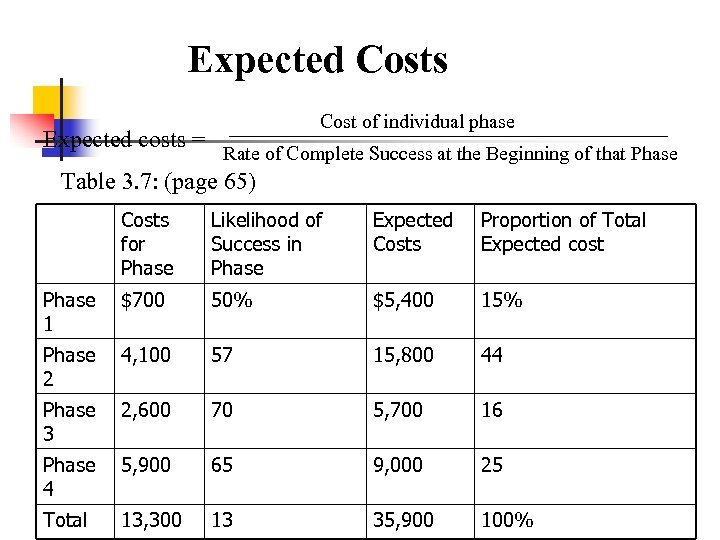 Expected Costs Expected costs = Cost of individual phase Rate of Complete Success at the Beginning of that Phase Table 3. 7: (page 65) Costs for Phase Likelihood of Success in Phase Expected Costs Proportion of Total Expected cost Phase 1 $700 50% $5, 400 15% Phase 2 4, 100 57 15, 800 44 Phase 3 2, 600 70 5, 700 16 Phase 4 5, 900 65 9, 000 25 Total 13, 300 13 35, 900 100%
Expected Costs Expected costs = Cost of individual phase Rate of Complete Success at the Beginning of that Phase Table 3. 7: (page 65) Costs for Phase Likelihood of Success in Phase Expected Costs Proportion of Total Expected cost Phase 1 $700 50% $5, 400 15% Phase 2 4, 100 57 15, 800 44 Phase 3 2, 600 70 5, 700 16 Phase 4 5, 900 65 9, 000 25 Total 13, 300 13 35, 900 100%
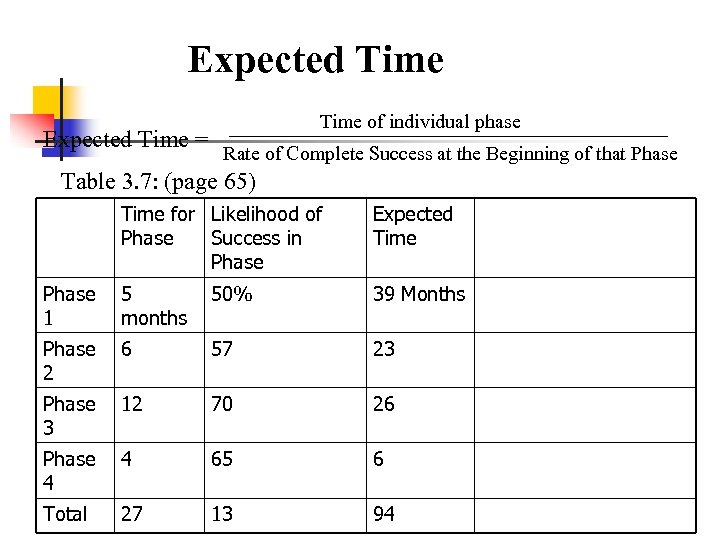 Expected Time = Time of individual phase Rate of Complete Success at the Beginning of that Phase Table 3. 7: (page 65) Time for Likelihood of Phase Success in Phase Expected Time Phase 1 5 months 50% 39 Months Phase 2 6 57 23 Phase 3 12 70 26 Phase 4 4 65 6 Total 27 13 94
Expected Time = Time of individual phase Rate of Complete Success at the Beginning of that Phase Table 3. 7: (page 65) Time for Likelihood of Phase Success in Phase Expected Time Phase 1 5 months 50% 39 Months Phase 2 6 57 23 Phase 3 12 70 26 Phase 4 4 65 6 Total 27 13 94
 High-Tech Market 1. Assessing market opportunity in high-tech markets 2. Selected strategies: Growth, first mover
High-Tech Market 1. Assessing market opportunity in high-tech markets 2. Selected strategies: Growth, first mover
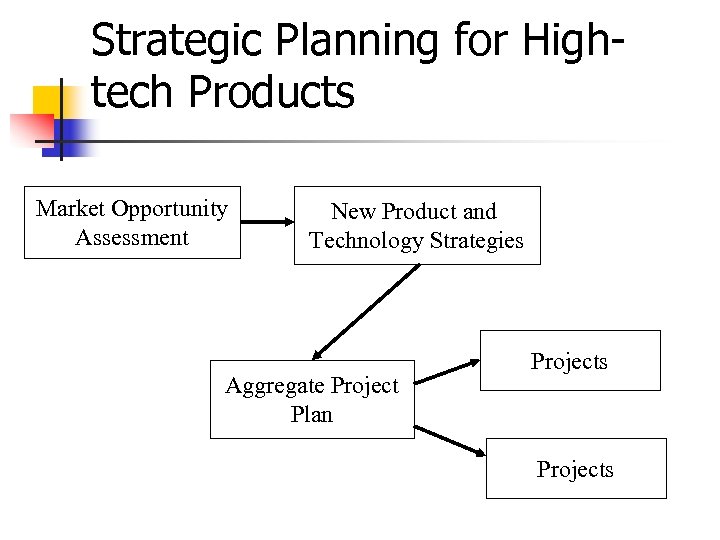 Strategic Planning for Hightech Products Market Opportunity Assessment New Product and Technology Strategies Aggregate Project Plan Projects
Strategic Planning for Hightech Products Market Opportunity Assessment New Product and Technology Strategies Aggregate Project Plan Projects
 Assessing Market Opportunity 1. Product-market characteristics • Market size/growth potential • Unmet customer needs • Entry barriers • Competitive attractiveness • Profit potential • Risk 2. Organization’s capabilities and position
Assessing Market Opportunity 1. Product-market characteristics • Market size/growth potential • Unmet customer needs • Entry barriers • Competitive attractiveness • Profit potential • Risk 2. Organization’s capabilities and position
 Size/Growth Potential in High. Tech Markets Heavy reliance on: • Expert opinion • Analogous product sales history • Diffusion estimates • Customer measurement in NPD process
Size/Growth Potential in High. Tech Markets Heavy reliance on: • Expert opinion • Analogous product sales history • Diffusion estimates • Customer measurement in NPD process
 Speeding Innovation Diffusion q Significant advantage over existing products q Compatible with existing values, and past experiences q Easy to understand q Easy product trial q Benefits from using product highly visible and easily communicated to others
Speeding Innovation Diffusion q Significant advantage over existing products q Compatible with existing values, and past experiences q Easy to understand q Easy product trial q Benefits from using product highly visible and easily communicated to others
 Bass Diffusion Model • Forecasts market size and growth characteristics for first time product purchases in a new product category. • Assumes innovators who adopt new products without influence from others, and imitators who rely on word-of-mouth from earlier adopters of the product.
Bass Diffusion Model • Forecasts market size and growth characteristics for first time product purchases in a new product category. • Assumes innovators who adopt new products without influence from others, and imitators who rely on word-of-mouth from earlier adopters of the product.
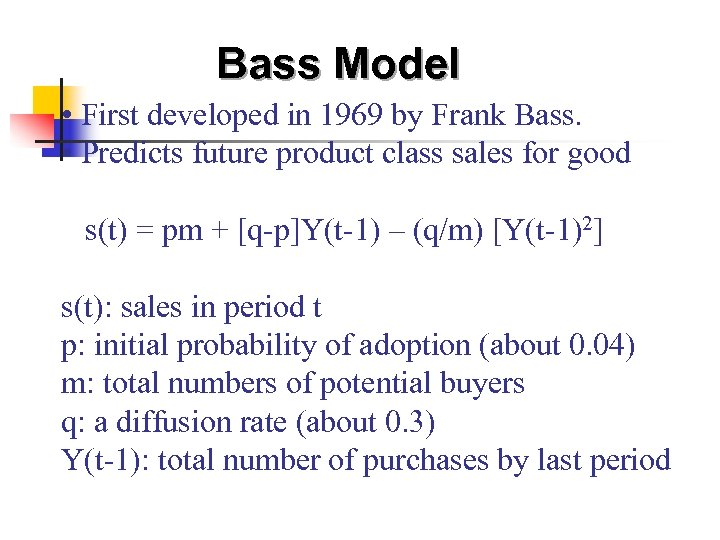 Bass Model • First developed in 1969 by Frank Bass. • Predicts future product class sales for good s(t) = pm + [q-p]Y(t-1) – (q/m) [Y(t-1)2] s(t): sales in period t p: initial probability of adoption (about 0. 04) m: total numbers of potential buyers q: a diffusion rate (about 0. 3) Y(t-1): total number of purchases by last period
Bass Model • First developed in 1969 by Frank Bass. • Predicts future product class sales for good s(t) = pm + [q-p]Y(t-1) – (q/m) [Y(t-1)2] s(t): sales in period t p: initial probability of adoption (about 0. 04) m: total numbers of potential buyers q: a diffusion rate (about 0. 3) Y(t-1): total number of purchases by last period
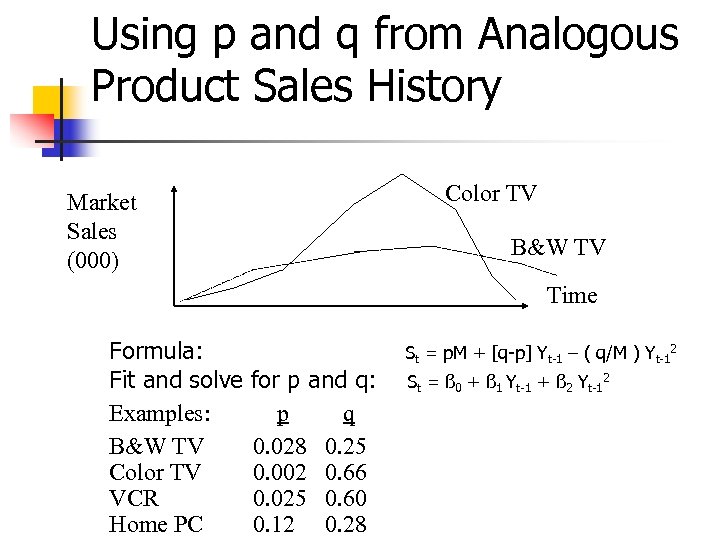 Using p and q from Analogous Product Sales History Color TV Market Sales (000) B&W TV Time Formula: Fit and solve Examples: B&W TV Color TV VCR Home PC for p and q: p q 0. 028 0. 25 0. 002 0. 66 0. 025 0. 60 0. 12 0. 28 St = p. M + [q-p] Yt-1 – ( q/M ) Yt-12 St = ß 0 + ß 1 Yt-1 + ß 2 Yt-12
Using p and q from Analogous Product Sales History Color TV Market Sales (000) B&W TV Time Formula: Fit and solve Examples: B&W TV Color TV VCR Home PC for p and q: p q 0. 028 0. 25 0. 002 0. 66 0. 025 0. 60 0. 12 0. 28 St = p. M + [q-p] Yt-1 – ( q/M ) Yt-12 St = ß 0 + ß 1 Yt-1 + ß 2 Yt-12
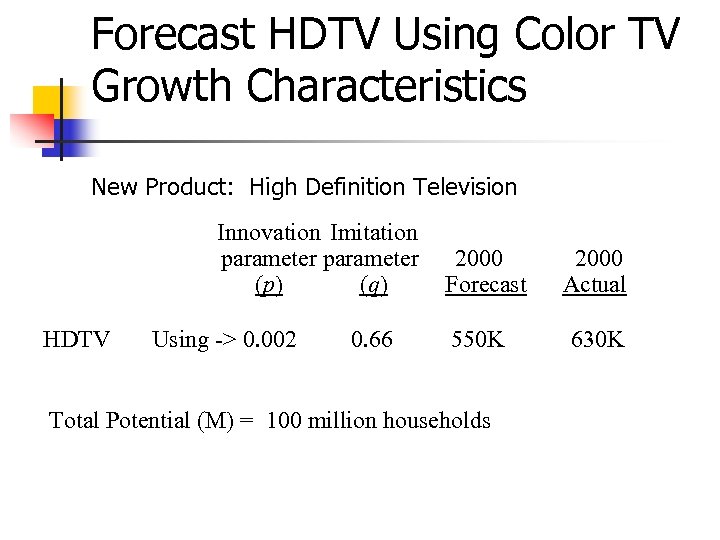 Forecast HDTV Using Color TV Growth Characteristics New Product: High Definition Television Innovation Imitation parameter 2000 (p) (q) Forecast Actual HDTV Using -> 0. 002 0. 66 550 K 630 K Total Potential (M) = 100 million households
Forecast HDTV Using Color TV Growth Characteristics New Product: High Definition Television Innovation Imitation parameter 2000 (p) (q) Forecast Actual HDTV Using -> 0. 002 0. 66 550 K 630 K Total Potential (M) = 100 million households
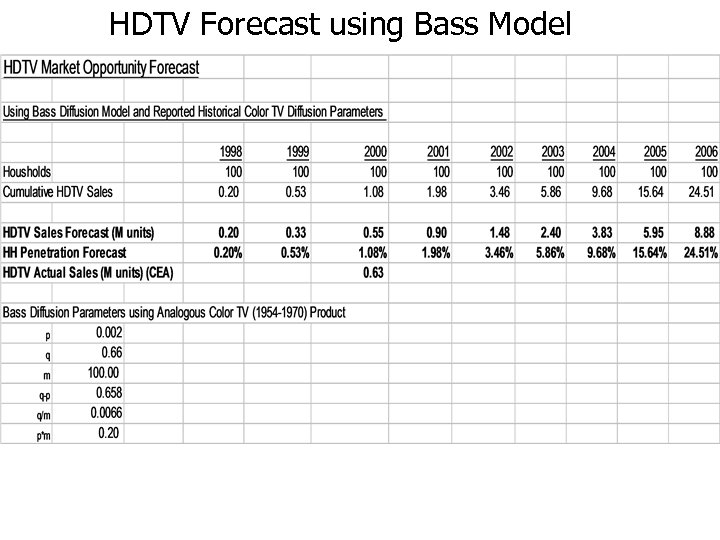 HDTV Forecast using Bass Model
HDTV Forecast using Bass Model
 Customer Measurement in NPD Testing q Test environments: • Concept test descriptions, graphics, prototypes • Simulated shopping • Test markets q Measure preferences for product alternatives, purchase intentions, after-use satisfaction, trial and repeat purchase rates
Customer Measurement in NPD Testing q Test environments: • Concept test descriptions, graphics, prototypes • Simulated shopping • Test markets q Measure preferences for product alternatives, purchase intentions, after-use satisfaction, trial and repeat purchase rates
 Issues in Customer Measurement of Opportunity q Is the target market(s) well represented in the sample? q Can customers give you accurate responses? Do they lack understanding of the new product and its benefit. q Does the test environment/procedure approximate purchases/purchase process well? q How well are competitor’s moves incorporated?
Issues in Customer Measurement of Opportunity q Is the target market(s) well represented in the sample? q Can customers give you accurate responses? Do they lack understanding of the new product and its benefit. q Does the test environment/procedure approximate purchases/purchase process well? q How well are competitor’s moves incorporated?
 Entry Barriers • Experience curve/economies of scale • Brand image • Cognitive advantage • Customer switching costs • Proprietary technology/knowledge • Legal protections • Other (e. g. pricing, shelf space, production capacity, investment requirements)
Entry Barriers • Experience curve/economies of scale • Brand image • Cognitive advantage • Customer switching costs • Proprietary technology/knowledge • Legal protections • Other (e. g. pricing, shelf space, production capacity, investment requirements)
 Competitor Analysis in High Tech Markets q Potential competitors may be as important as existing competitors (technology-enabled) q Capabilities (skills and knowledge) are critical q Strategic “intent” of competitor must be assessed. “What are they likely to do? They could, but would they? ”
Competitor Analysis in High Tech Markets q Potential competitors may be as important as existing competitors (technology-enabled) q Capabilities (skills and knowledge) are critical q Strategic “intent” of competitor must be assessed. “What are they likely to do? They could, but would they? ”
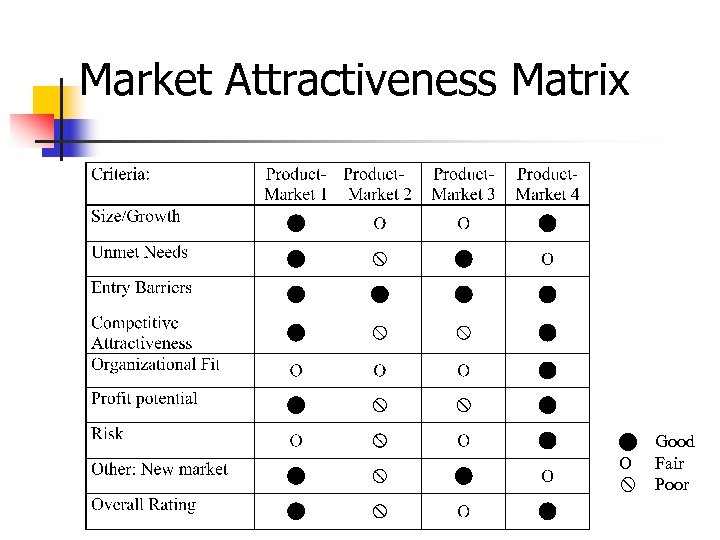 Market Attractiveness Matrix Good O Fair Poor
Market Attractiveness Matrix Good O Fair Poor
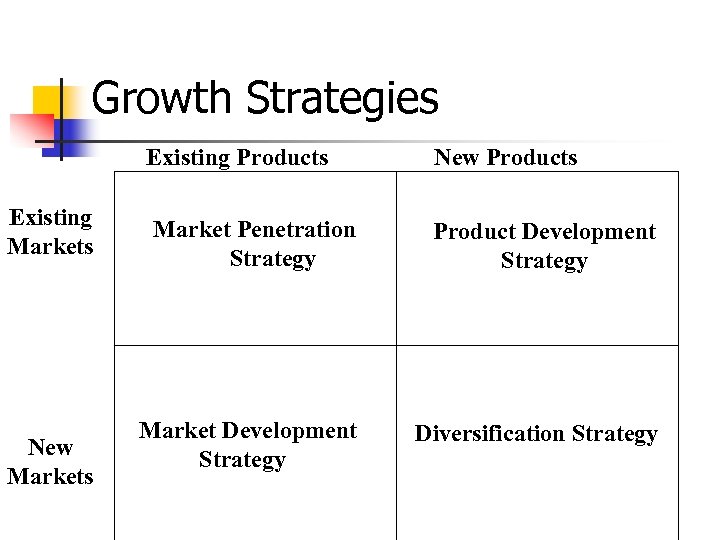 Growth Strategies Existing Products Existing Markets New Products Market Penetration Strategy Product Development Strategy Market Development Strategy Diversification Strategy
Growth Strategies Existing Products Existing Markets New Products Market Penetration Strategy Product Development Strategy Market Development Strategy Diversification Strategy
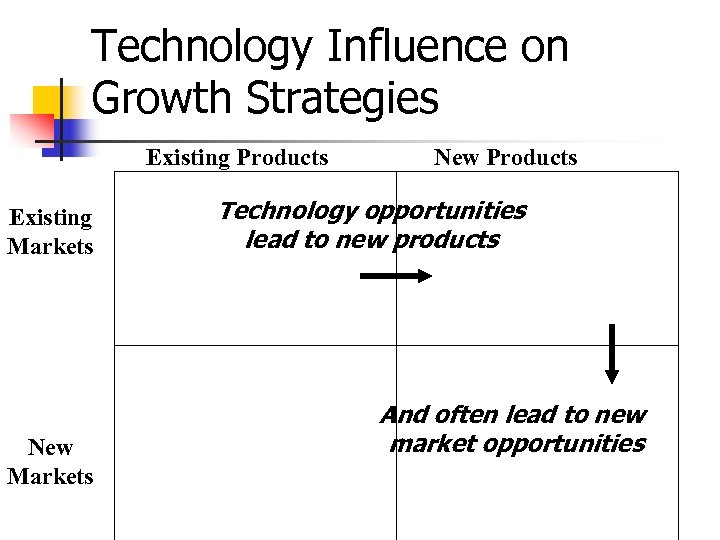 Technology Influence on Growth Strategies Existing Products Existing Markets New Products Technology opportunities lead to new products And often lead to new market opportunities
Technology Influence on Growth Strategies Existing Products Existing Markets New Products Technology opportunities lead to new products And often lead to new market opportunities
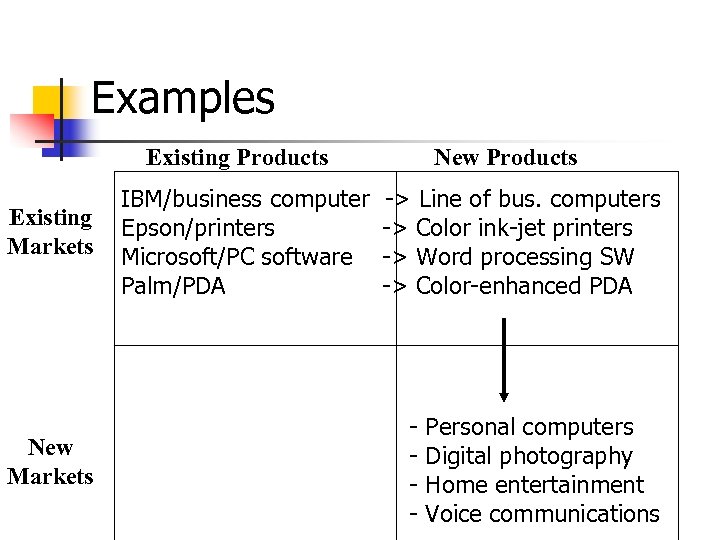 Examples Existing Products Existing Markets New Markets IBM/business computer Epson/printers Microsoft/PC software Palm/PDA New Products -> Line of bus. computers -> Color ink-jet printers -> Word processing SW -> Color-enhanced PDA - Personal computers Digital photography Home entertainment Voice communications
Examples Existing Products Existing Markets New Markets IBM/business computer Epson/printers Microsoft/PC software Palm/PDA New Products -> Line of bus. computers -> Color ink-jet printers -> Word processing SW -> Color-enhanced PDA - Personal computers Digital photography Home entertainment Voice communications
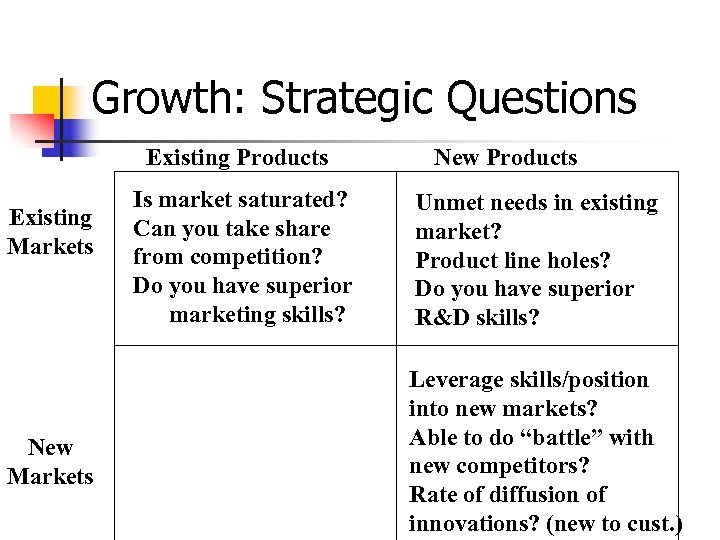 Growth: Strategic Questions Existing Products Existing Markets New Markets Is market saturated? Can you take share from competition? Do you have superior marketing skills? New Products Unmet needs in existing market? Product line holes? Do you have superior R&D skills? Leverage skills/position into new markets? Able to do “battle” with new competitors? Rate of diffusion of innovations? (new to cust. )
Growth: Strategic Questions Existing Products Existing Markets New Markets Is market saturated? Can you take share from competition? Do you have superior marketing skills? New Products Unmet needs in existing market? Product line holes? Do you have superior R&D skills? Leverage skills/position into new markets? Able to do “battle” with new competitors? Rate of diffusion of innovations? (new to cust. )
 Growth Strategy Wisdom • Avoid “incumbent inertia” (complacency, conservatism and conceit) • Beware of “cannibalization phobia” • New markets can be shaped • Early market entrants (first movers or fast followers) can have enduring advantages
Growth Strategy Wisdom • Avoid “incumbent inertia” (complacency, conservatism and conceit) • Beware of “cannibalization phobia” • New markets can be shaped • Early market entrants (first movers or fast followers) can have enduring advantages
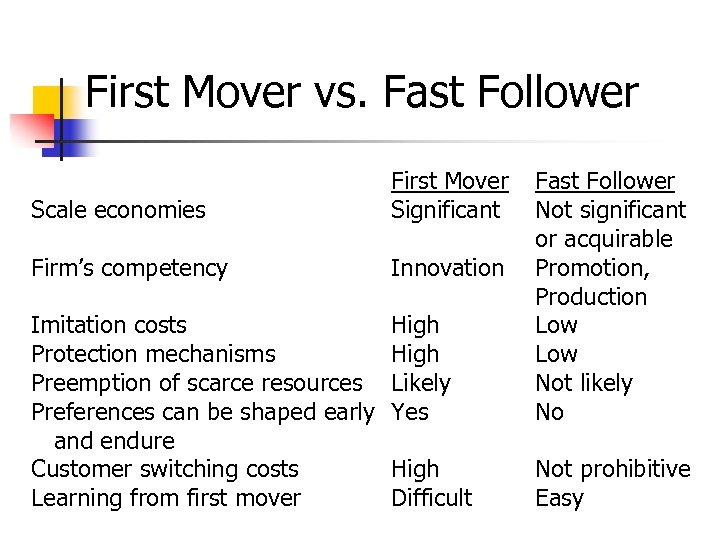 First Mover vs. Fast Follower Scale economies First Mover Significant Firm’s competency Innovation Imitation costs Protection mechanisms Preemption of scarce resources Preferences can be shaped early and endure Customer switching costs Learning from first mover High Likely Yes Fast Follower Not significant or acquirable Promotion, Production Low Not likely No High Difficult Not prohibitive Easy
First Mover vs. Fast Follower Scale economies First Mover Significant Firm’s competency Innovation Imitation costs Protection mechanisms Preemption of scarce resources Preferences can be shaped early and endure Customer switching costs Learning from first mover High Likely Yes Fast Follower Not significant or acquirable Promotion, Production Low Not likely No High Difficult Not prohibitive Easy
 Idea Generation Exercise n n Please take a few minutes to think problems you have in your life or work such as shopping, dining, phone, grooming, pet management, transportation, car maintenance, etc. Then, generate at least three new product ideas to solve the problems. Teams are required to present ideas generated to class.
Idea Generation Exercise n n Please take a few minutes to think problems you have in your life or work such as shopping, dining, phone, grooming, pet management, transportation, car maintenance, etc. Then, generate at least three new product ideas to solve the problems. Teams are required to present ideas generated to class.
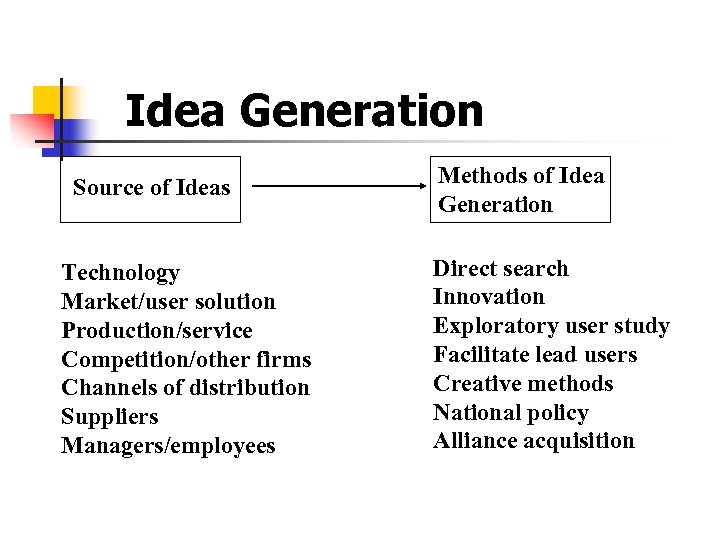 Idea Generation Source of Ideas Technology Market/user solution Production/service Competition/other firms Channels of distribution Suppliers Managers/employees Methods of Idea Generation Direct search Innovation Exploratory user study Facilitate lead users Creative methods National policy Alliance acquisition
Idea Generation Source of Ideas Technology Market/user solution Production/service Competition/other firms Channels of distribution Suppliers Managers/employees Methods of Idea Generation Direct search Innovation Exploratory user study Facilitate lead users Creative methods National policy Alliance acquisition
 Idea Generation: Empathic Methods Empathic methods are methods which provide an understanding user needs through empathy with the user world rather than from user articulation of needs. Methods: - Observation of users’ behaviors - Ethnographic exploration - NPD designers immersed user’s environment
Idea Generation: Empathic Methods Empathic methods are methods which provide an understanding user needs through empathy with the user world rather than from user articulation of needs. Methods: - Observation of users’ behaviors - Ethnographic exploration - NPD designers immersed user’s environment
 Empathic Method 1. Critical observation 2. Capture the data 3. Reflection and analysis 4. Brainstorm solutions 5. Develop prototypes of possible solutions Source: Leonard and Rayport (1997)
Empathic Method 1. Critical observation 2. Capture the data 3. Reflection and analysis 4. Brainstorm solutions 5. Develop prototypes of possible solutions Source: Leonard and Rayport (1997)
 Empathic Information 1. Triggers of use – what prompts usage 2. Unarticulated user needs 3. Interactions with the user’s environment 4. Customization of products 5. Intangible product attributes Source: Leonard and Rayport (1997)
Empathic Information 1. Triggers of use – what prompts usage 2. Unarticulated user needs 3. Interactions with the user’s environment 4. Customization of products 5. Intangible product attributes Source: Leonard and Rayport (1997)
 “Day-in-the-Life” Experiences n n n Learn from doing what they do in everyday and extraordinary situations Use your own and your competitor’s products Acquire training and background similar to your customers
“Day-in-the-Life” Experiences n n n Learn from doing what they do in everyday and extraordinary situations Use your own and your competitor’s products Acquire training and background similar to your customers
 Lead Users 1. Lead users have needs ahead of the general marketplace. They face needs that will be general in a marketplace - but face them months or years ahead of the bulk of the marketplace. (and) 2. Lead users expect to benefit significantly from a solution to those needs.
Lead Users 1. Lead users have needs ahead of the general marketplace. They face needs that will be general in a marketplace - but face them months or years ahead of the bulk of the marketplace. (and) 2. Lead users expect to benefit significantly from a solution to those needs.
 Lead Users Lead users can be any of the following: 1. Lead users in the target application. 2. Lead users in analogous markets. 3. Lead users of important related attributes of products (e. g. technology experts)
Lead Users Lead users can be any of the following: 1. Lead users in the target application. 2. Lead users in analogous markets. 3. Lead users of important related attributes of products (e. g. technology experts)
 Lead-User Process 1. Project Preparation and Planning • achieve top management support and form crossfunctional team • background research on product category 2. Identify Trends and Customer Needs • identify markets and core needs • identify leading-edge expertise 3. Explore Lead User Needs and Solutions • identify lead users; interview and screen • generate concepts in lead user workshops • test concepts with typical users 4. Refine Concept Solution • finalize solution and create strategic plan
Lead-User Process 1. Project Preparation and Planning • achieve top management support and form crossfunctional team • background research on product category 2. Identify Trends and Customer Needs • identify markets and core needs • identify leading-edge expertise 3. Explore Lead User Needs and Solutions • identify lead users; interview and screen • generate concepts in lead user workshops • test concepts with typical users 4. Refine Concept Solution • finalize solution and create strategic plan
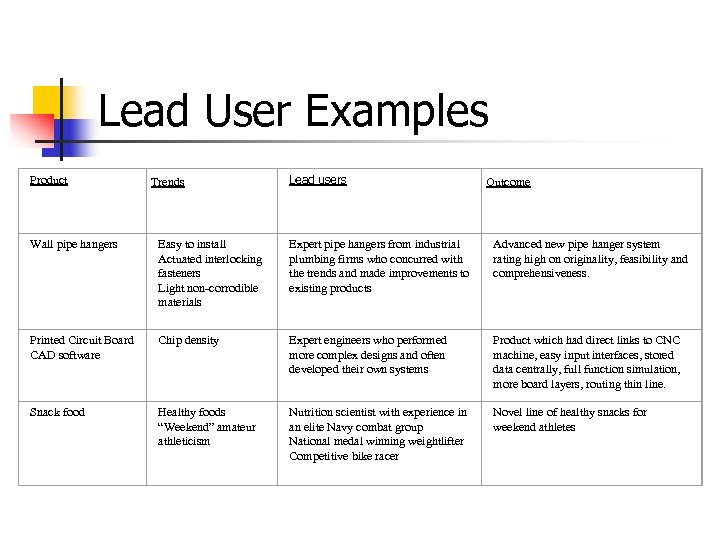 Lead User Examples Product Trends Lead users Outcome Wall pipe hangers Easy to install Actuated interlocking fasteners Light non-corrodible materials Expert pipe hangers from industrial plumbing firms who concurred with the trends and made improvements to existing products Advanced new pipe hanger system rating high on originality, feasibility and comprehensiveness. Printed Circuit Board CAD software Chip density Expert engineers who performed more complex designs and often developed their own systems Product which had direct links to CNC machine, easy input interfaces, stored data centrally, full function simulation, more board layers, routing thin line. Snack food Healthy foods “Weekend” amateur athleticism Nutrition scientist with experience in an elite Navy combat group National medal winning weightlifter Competitive bike racer Novel line of healthy snacks for weekend athletes
Lead User Examples Product Trends Lead users Outcome Wall pipe hangers Easy to install Actuated interlocking fasteners Light non-corrodible materials Expert pipe hangers from industrial plumbing firms who concurred with the trends and made improvements to existing products Advanced new pipe hanger system rating high on originality, feasibility and comprehensiveness. Printed Circuit Board CAD software Chip density Expert engineers who performed more complex designs and often developed their own systems Product which had direct links to CNC machine, easy input interfaces, stored data centrally, full function simulation, more board layers, routing thin line. Snack food Healthy foods “Weekend” amateur athleticism Nutrition scientist with experience in an elite Navy combat group National medal winning weightlifter Competitive bike racer Novel line of healthy snacks for weekend athletes
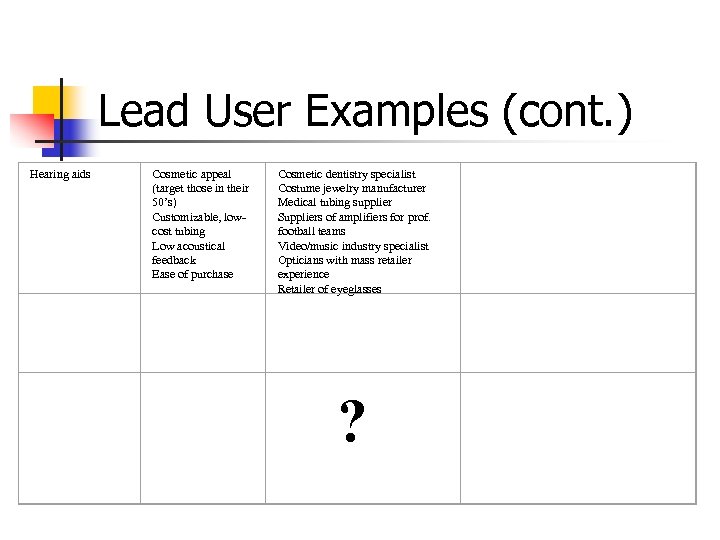 Lead User Examples (cont. ) Hearing aids Cosmetic appeal (target those in their 50’s) Customizable, lowcost tubing Low acoustical feedback Ease of purchase Cosmetic dentistry specialist Costume jewelry manufacturer Medical tubing supplier Suppliers of amplifiers for prof. football teams Video/music industry specialist Opticians with mass retailer experience Retailer of eyeglasses ?
Lead User Examples (cont. ) Hearing aids Cosmetic appeal (target those in their 50’s) Customizable, lowcost tubing Low acoustical feedback Ease of purchase Cosmetic dentistry specialist Costume jewelry manufacturer Medical tubing supplier Suppliers of amplifiers for prof. football teams Video/music industry specialist Opticians with mass retailer experience Retailer of eyeglasses ?
 Identify Lead Users Gatorade White-out fluid Laser Printer Sofa Mountain bikes Surf boards Your Businesses
Identify Lead Users Gatorade White-out fluid Laser Printer Sofa Mountain bikes Surf boards Your Businesses
 Lead User Communities • “if you want something done right, do it yourself” • “Sticky” information is difficult to transfer to manufacturers • Needs are changing, and innovation evolves over time • Lead users willing to reveal innovations freely Source: von Hippel
Lead User Communities • “if you want something done right, do it yourself” • “Sticky” information is difficult to transfer to manufacturers • Needs are changing, and innovation evolves over time • Lead users willing to reveal innovations freely Source: von Hippel
 Lead Users: Advantages and Disadvantages Advantage: Lead users able to articulate future needs and possibly solutions for the general market. Disadvantages: 1) Lead users can be difficult to identify. 2) Lead users may not cooperate.
Lead Users: Advantages and Disadvantages Advantage: Lead users able to articulate future needs and possibly solutions for the general market. Disadvantages: 1) Lead users can be difficult to identify. 2) Lead users may not cooperate.
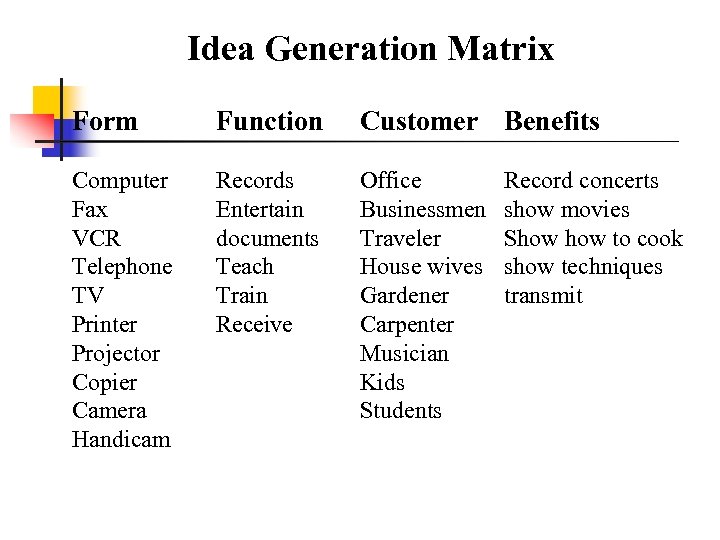 Idea Generation Matrix Form Function Customer Benefits Computer Fax VCR Telephone TV Printer Projector Copier Camera Handicam Records Entertain documents Teach Train Receive Office Businessmen Traveler House wives Gardener Carpenter Musician Kids Students Record concerts show movies Show to cook show techniques transmit
Idea Generation Matrix Form Function Customer Benefits Computer Fax VCR Telephone TV Printer Projector Copier Camera Handicam Records Entertain documents Teach Train Receive Office Businessmen Traveler House wives Gardener Carpenter Musician Kids Students Record concerts show movies Show to cook show techniques transmit
 Idea Evaluation I= Tx. Cx. P D I: index of attractiveness T: probability of successful technological development C: probability of commercial success given that it is technically successful P: profit if successful C: cost of development
Idea Evaluation I= Tx. Cx. P D I: index of attractiveness T: probability of successful technological development C: probability of commercial success given that it is technically successful P: profit if successful C: cost of development
 NEWPROD Scoring Model n n n Developed by Dr. Robert Cooper Database of projects from 100 Canadian industrial firms (2500 new product projects) Found 8 factors which were significantly related to product success Weights for the factors were estimated using regression analysis Managers rate projects on each factor, and the project score is derived from these rating and factor weights.
NEWPROD Scoring Model n n n Developed by Dr. Robert Cooper Database of projects from 100 Canadian industrial firms (2500 new product projects) Found 8 factors which were significantly related to product success Weights for the factors were estimated using regression analysis Managers rate projects on each factor, and the project score is derived from these rating and factor weights.
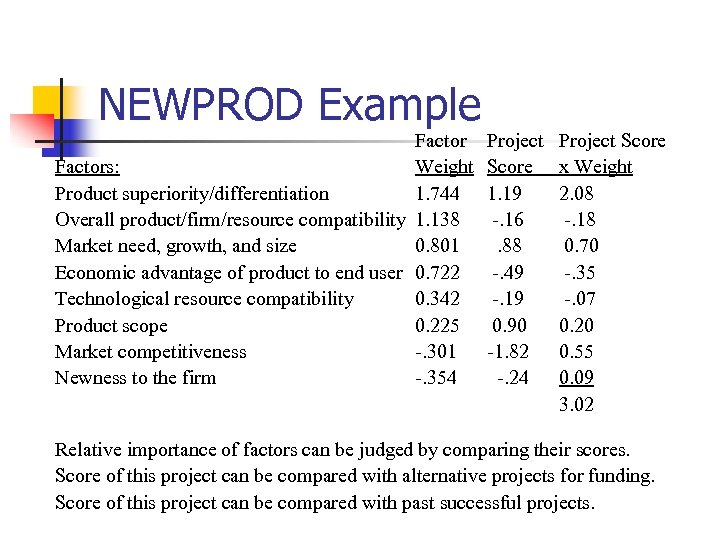 NEWPROD Example Factors: Weight Product superiority/differentiation 1. 744 Overall product/firm/resource compatibility 1. 138 Market need, growth, and size 0. 801 Economic advantage of product to end user 0. 722 Technological resource compatibility 0. 342 Product scope 0. 225 Market competitiveness -. 301 Newness to the firm -. 354 Project Score 1. 19 -. 16 . 88 -. 49 -. 19 0. 90 -1. 82 -. 24 Project Score x Weight 2. 08 -. 18 0. 70 -. 35 -. 07 0. 20 0. 55 0. 09 3. 02 Relative importance of factors can be judged by comparing their scores. Score of this project can be compared with alternative projects for funding. Score of this project can be compared with past successful projects.
NEWPROD Example Factors: Weight Product superiority/differentiation 1. 744 Overall product/firm/resource compatibility 1. 138 Market need, growth, and size 0. 801 Economic advantage of product to end user 0. 722 Technological resource compatibility 0. 342 Product scope 0. 225 Market competitiveness -. 301 Newness to the firm -. 354 Project Score 1. 19 -. 16 . 88 -. 49 -. 19 0. 90 -1. 82 -. 24 Project Score x Weight 2. 08 -. 18 0. 70 -. 35 -. 07 0. 20 0. 55 0. 09 3. 02 Relative importance of factors can be judged by comparing their scores. Score of this project can be compared with alternative projects for funding. Score of this project can be compared with past successful projects.


