Product Development Product Launch Product Upgrade Commercial Innovation

























12442-research_techniques_.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 30
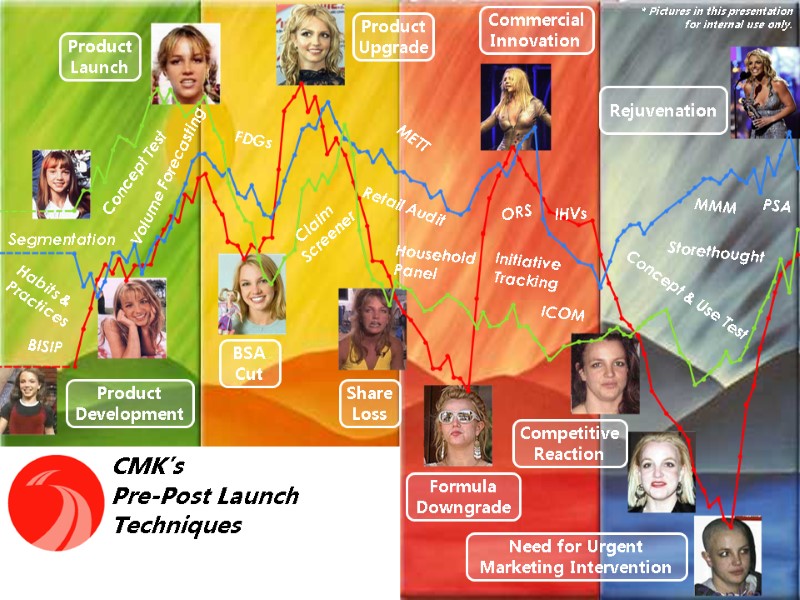
 Product Development Product Launch Product Upgrade Commercial Innovation Rejuvenation BSA Cut Share Loss Formula Downgrade Competitive Reaction Need for Urgent Marketing Intervention CMK’s Pre-Post Launch Techniques * Pictures in this presentation for internal use only.
Product Development Product Launch Product Upgrade Commercial Innovation Rejuvenation BSA Cut Share Loss Formula Downgrade Competitive Reaction Need for Urgent Marketing Intervention CMK’s Pre-Post Launch Techniques * Pictures in this presentation for internal use only.
 Agenda Research Basics CMK’s Roles and Responsibilities Research Process Decision to Conduct a Research Study Qualitative and Quantitative Techniques Sampling Statistical Significance
Agenda Research Basics CMK’s Roles and Responsibilities Research Process Decision to Conduct a Research Study Qualitative and Quantitative Techniques Sampling Statistical Significance
 Agenda Researches in Initiative Life Cycle Idea Generation Concept Development Concept Screening & Evaluating Packaging Development Pricing Communication In-Market Tracking On-line Resources
Agenda Researches in Initiative Life Cycle Idea Generation Concept Development Concept Screening & Evaluating Packaging Development Pricing Communication In-Market Tracking On-line Resources
 RESEARCH BASICS
RESEARCH BASICS
 Roles and Responsibilities
Roles and Responsibilities
 P&G’s Mission & CMK Aspiration Improve the Lives of the World’s Consumers. CMK is the voice of the world’s consumers and shoppers, successfully articulating their needs and dreams to profitably grow the brands they love.
P&G’s Mission & CMK Aspiration Improve the Lives of the World’s Consumers. CMK is the voice of the world’s consumers and shoppers, successfully articulating their needs and dreams to profitably grow the brands they love.
 AWARDED CMK QUESTION Best answer to win P&G formed first market research department in 1924. We talk to about 4 million consumers in a year.
AWARDED CMK QUESTION Best answer to win P&G formed first market research department in 1924. We talk to about 4 million consumers in a year.
 Research Process Business Needs Assessment Learning Plan Development Research Design Research Execution Research Analysis Holistic Understanding & Application
Research Process Business Needs Assessment Learning Plan Development Research Design Research Execution Research Analysis Holistic Understanding & Application
 Decision to Do a Research When it is actionable: Several alternative ways available to pursue. Business question can be answered via research findings. When there is no alternative way of learning: Added value from the research will be higher than alternative learning ways. When the research investment is substantially lower than the $ opportunity at risk.
Decision to Do a Research When it is actionable: Several alternative ways available to pursue. Business question can be answered via research findings. When there is no alternative way of learning: Added value from the research will be higher than alternative learning ways. When the research investment is substantially lower than the $ opportunity at risk.
 Decision to Do a Research Whatever research learning is, course of action won’t change. Unfortunately, research does not replace doing our own homework! We shouldn’t ask consumers for ideas… We don’t really know what we’re looking for… It’s just too late.
Decision to Do a Research Whatever research learning is, course of action won’t change. Unfortunately, research does not replace doing our own homework! We shouldn’t ask consumers for ideas… We don’t really know what we’re looking for… It’s just too late.
 Research Methods Qualitative Why? How? Few people Detailed Free discussion flow Insights, consumer inputs Explanatory – Vague Quantitative How Many? Many People Brief Structured discussion flow Numerical conclusions Conclusive - Precise
Research Methods Qualitative Why? How? Few people Detailed Free discussion flow Insights, consumer inputs Explanatory – Vague Quantitative How Many? Many People Brief Structured discussion flow Numerical conclusions Conclusive - Precise
 Qualitative Research Answers: “Why?” and “How?” Attitudes – Beliefs Motivations – Feelings Behaviors – Life Styles Allows to stay close to consumers & consumer language. Does not answer: How Many? It is explanatory, only helps judgement. never call it a qualification
Qualitative Research Answers: “Why?” and “How?” Attitudes – Beliefs Motivations – Feelings Behaviors – Life Styles Allows to stay close to consumers & consumer language. Does not answer: How Many? It is explanatory, only helps judgement. never call it a qualification
 Qualitative Research Sample size is small. Does not reflect a demographic structure never say x% of respondents... Not representative. Respondents influence each other. Not comparable vs. other studies DON’T MAKE ANY DECISIONS BASED ON A QUALITATIVE RESEARCH OR DRAW CONCLUSIONS ABOUT THE WHOLE POPULATION!
Qualitative Research Sample size is small. Does not reflect a demographic structure never say x% of respondents... Not representative. Respondents influence each other. Not comparable vs. other studies DON’T MAKE ANY DECISIONS BASED ON A QUALITATIVE RESEARCH OR DRAW CONCLUSIONS ABOUT THE WHOLE POPULATION!
 When Qualitative Research? Basic Category Assessment / Idea generation tool: To provide first hand experience about what consumers think/feel and how they behave
When Qualitative Research? Basic Category Assessment / Idea generation tool: To provide first hand experience about what consumers think/feel and how they behave
 When Qualitative Research? Preliminary step for quantitative research: To develop hypothesis on how consumers think/feel/decide To explore consumer issues related to a subject To learn about new target groups To learn consumer language To build and improve concepts To reduce number of concept alternatives before concept test.
When Qualitative Research? Preliminary step for quantitative research: To develop hypothesis on how consumers think/feel/decide To explore consumer issues related to a subject To learn about new target groups To learn consumer language To build and improve concepts To reduce number of concept alternatives before concept test.
 When Qualitative Research? To understand the results of quantitative research: To understand unexpected findings To understand the reasons for certain trends To explore why a product/copy is performing different vs. expectations.
When Qualitative Research? To understand the results of quantitative research: To understand unexpected findings To understand the reasons for certain trends To explore why a product/copy is performing different vs. expectations.
 Qualitative Research Methods Interaction between participants In-depth understanding Focus Groups Mini Group Paired Interview One-on-One In-home Visit
Qualitative Research Methods Interaction between participants In-depth understanding Focus Groups Mini Group Paired Interview One-on-One In-home Visit
 Focus Groups (6-8 interviewees) Used to: Generate ideas/insights for new concepts/products. Check general appeal of concepts/product ideas. (NOT to measure trial generated by concept) Reduce number of concepts/ideas. Learn about: Likes/dislikes – Perceptions Behavior – Motivations Needs – Frustrations
Focus Groups (6-8 interviewees) Used to: Generate ideas/insights for new concepts/products. Check general appeal of concepts/product ideas. (NOT to measure trial generated by concept) Reduce number of concepts/ideas. Learn about: Likes/dislikes – Perceptions Behavior – Motivations Needs – Frustrations
 Focus Groups Group Dynamics (reactions to other consumers’ ideas, discussion support) Relatively cheap Not time consuming Opinions are influenced by each other Consumers help each other to understand things
Focus Groups Group Dynamics (reactions to other consumers’ ideas, discussion support) Relatively cheap Not time consuming Opinions are influenced by each other Consumers help each other to understand things
 Mini Groups (3-5 Interviewees) Used to: Reduce negatives of standard FGDs, Increase possibility of going in-depth behind more time allocated per respondent More readiness to talk Less controlled attitude Less interaction among participants May not be suitable for developing creative ideas due to fewer respondents
Mini Groups (3-5 Interviewees) Used to: Reduce negatives of standard FGDs, Increase possibility of going in-depth behind more time allocated per respondent More readiness to talk Less controlled attitude Less interaction among participants May not be suitable for developing creative ideas due to fewer respondents
 Individual In-Depth Interview Used to: Gain in-depth learning Understand sensitive topics Have specialists’ opinions on certain subjects Check clarity of message More spontaneous information More in-depth information Respondents are not influenced by others Needs more time and effort Not creative
Individual In-Depth Interview Used to: Gain in-depth learning Understand sensitive topics Have specialists’ opinions on certain subjects Check clarity of message More spontaneous information More in-depth information Respondents are not influenced by others Needs more time and effort Not creative
 Paired Interview (2 interviewees) Can be considered instead of individual interviews/one-on-ones It’s a compromise between group and one-on-one It’s not very often used (in comparison with individual interviews) Additional stimulus by a second person Less monotonous than individuals
Paired Interview (2 interviewees) Can be considered instead of individual interviews/one-on-ones It’s a compromise between group and one-on-one It’s not very often used (in comparison with individual interviews) Additional stimulus by a second person Less monotonous than individuals
 In-Home Visits Used to: Be in consumers’ shoes Get information that we can’t get in a studio (HOW do respondents perform their habits, how apply products etc) More relaxed atmosphere First hand information Helps your empathy Needs more time and effort
In-Home Visits Used to: Be in consumers’ shoes Get information that we can’t get in a studio (HOW do respondents perform their habits, how apply products etc) More relaxed atmosphere First hand information Helps your empathy Needs more time and effort
 Quantitative Research Methods Answers: HOW MANY? Large sample Reflects the demographic structure of the society. Representative You can say x% of respondents… Comparable b/t legs, groups, over time and countries, in case key research methodology is not changed. Provides “hard” data to support a decision!
Quantitative Research Methods Answers: HOW MANY? Large sample Reflects the demographic structure of the society. Representative You can say x% of respondents… Comparable b/t legs, groups, over time and countries, in case key research methodology is not changed. Provides “hard” data to support a decision!
 Quantitative Research Methods Do not give deep information on: Why?, How? Questionniare is structured, limited possibility to: Go into details on motivations, attitudes (as in qualitative research) Give answers beyond proposed alternatives (closed questions) Provides numbers, hard to see the real life person behind the data. Followed up with a qualitative research to explain deeper reasons behind findings.
Quantitative Research Methods Do not give deep information on: Why?, How? Questionniare is structured, limited possibility to: Go into details on motivations, attitudes (as in qualitative research) Give answers beyond proposed alternatives (closed questions) Provides numbers, hard to see the real life person behind the data. Followed up with a qualitative research to explain deeper reasons behind findings.
 Sampling
Sampling
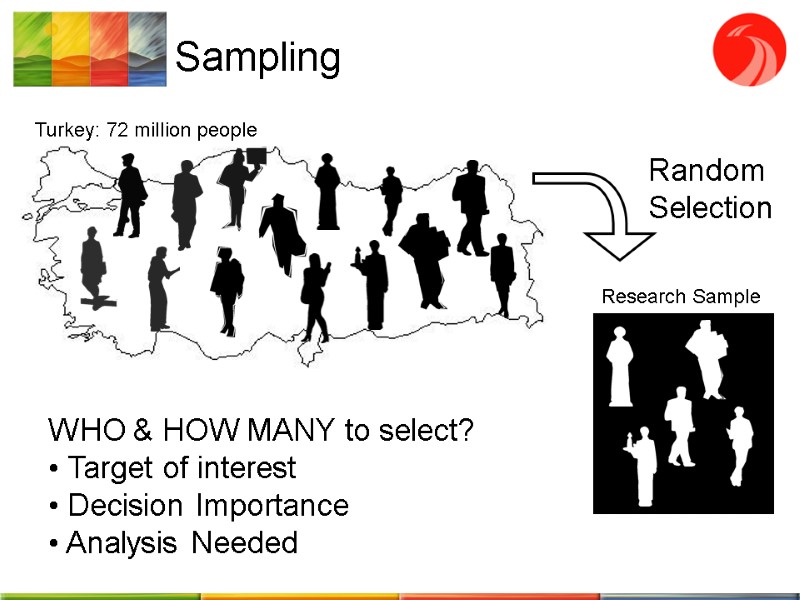
 Sampling Turkey: 72 million people Random Selection Research Sample WHO & HOW MANY to select? Target of interest Decision Importance Analysis Needed
Sampling Turkey: 72 million people Random Selection Research Sample WHO & HOW MANY to select? Target of interest Decision Importance Analysis Needed
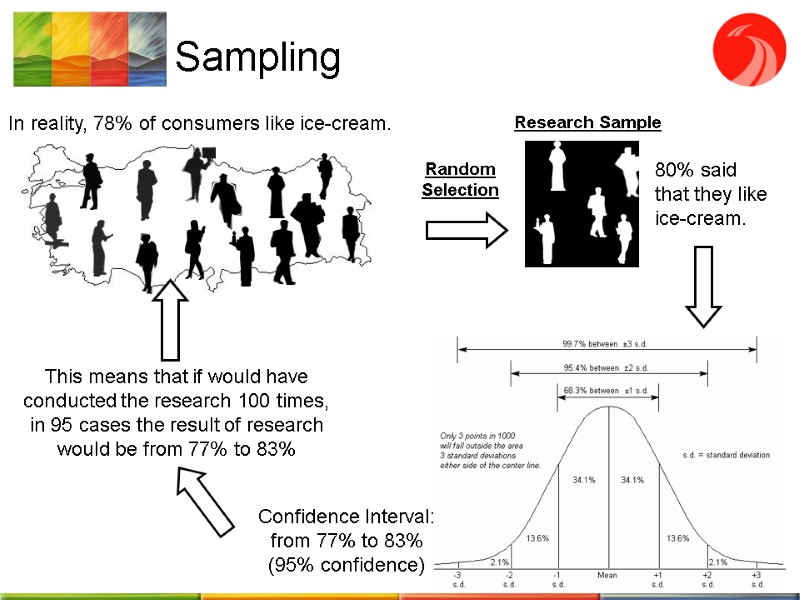
 Sampling In reality, 78% of consumers like ice-cream. Random Selection 80% said that they like ice-cream. Confidence Interval: from 77% to 83% (95% confidence) This means that if would have conducted the research 100 times, in 95 cases the result of research would be from 77% to 83%
Sampling In reality, 78% of consumers like ice-cream. Random Selection 80% said that they like ice-cream. Confidence Interval: from 77% to 83% (95% confidence) This means that if would have conducted the research 100 times, in 95 cases the result of research would be from 77% to 83%
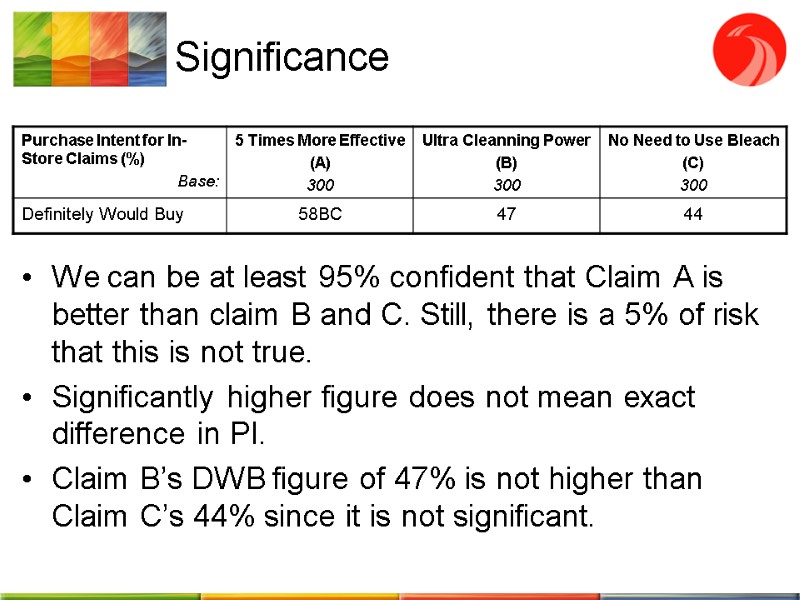
 Significance We can be at least 95% confident that Claim A is better than claim B and C. Still, there is a 5% of risk that this is not true. Significantly higher figure does not mean exact difference in PI. Claim B’s DWB figure of 47% is not higher than Claim C’s 44% since it is not significant.
Significance We can be at least 95% confident that Claim A is better than claim B and C. Still, there is a 5% of risk that this is not true. Significantly higher figure does not mean exact difference in PI. Claim B’s DWB figure of 47% is not higher than Claim C’s 44% since it is not significant.
 Quantitative Design Survey (face-to-face) Panel Diary At home (door-to-door) Central Location In-store Outdoor (streets etc.) Phone, Internet
Quantitative Design Survey (face-to-face) Panel Diary At home (door-to-door) Central Location In-store Outdoor (streets etc.) Phone, Internet

