The Concept of Marketing лекция 10.pptx
- Количество слайдов: 8

Product: basic element of marketing strategy A product is anything that can be offered to a market for attention, acquisition, use, or consumption that might satisfy a want or need. A product has t angible attributes and intangible attributes. Vitaliy Osadchiy, UK Certified Marketer

Branding. Brand is a name, term, sign, symbol or design intended to identify the product of a seller and to differentiate it from those of competitors. It amounts to a promise of consistent quality and value. 1. Brand name 2. Brand image 3. Brand positioning Threats to the brand: 1. Competition 2. Infringement of intellectual property rights 3. Generic names Brand management: co-ordination of all efforts and resources + promotion of customer orientation.
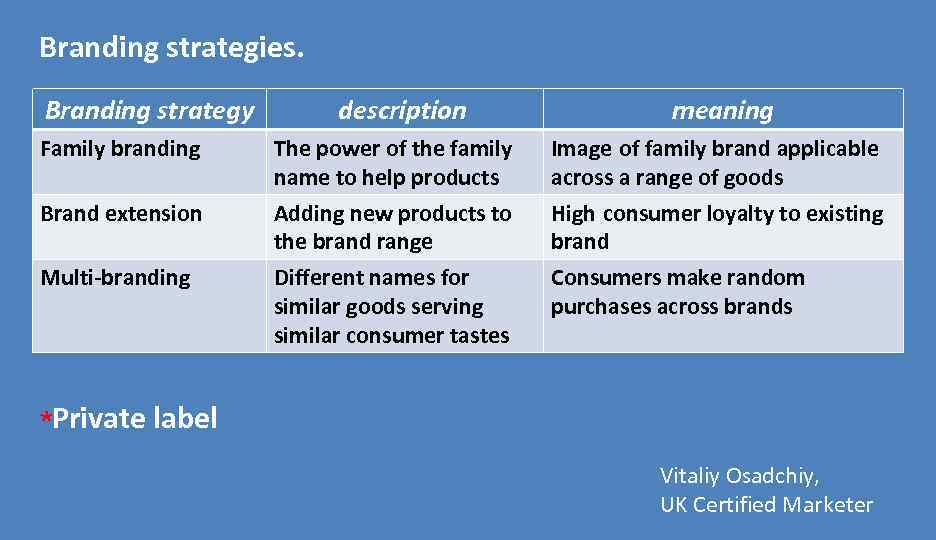
Branding strategies. Branding strategy description meaning Family branding The power of the family name to help products Image of family brand applicable across a range of goods Brand extension Adding new products to the brand range High consumer loyalty to existing brand Multi-branding Different names for similar goods serving similar consumer tastes Consumers make random purchases across brands ٭ Private label Vitaliy Osadchiy, UK Certified Marketer

Price. A measure of the value exchanged by the buyer for the value offered by the seller. The price is expected to reflect the costs to the seller of producing the product and the benefit to the buyer of consuming it. Price is the only element of the marketing mix which generates revenue rather than creating costs.

Price has an important role as a competitive tool to DIFFERENTIATE a product and an organization and thereby exploit market opportunities. Pricing must also be consistent with other elements of the marketing mix since it contributes to the overall image created by the product. No organization can hope to offer an exclusive high quality product to the market with a low price – the price must be consistent with the overall PRODUCT OFFER.

Pricing decisions may be specified by 2 categories of objectives: 1. Maximising profits. 2. Maintaining or increasing market share. There are 3 main types of influence on price setting: 1. Costs 2. Competition 3. Demand.

Price setting strategies: 1. Market penetration objective. 2. Market skimming objective. 3. Early cash recovery objective. 4. Product line promotion objective. 5. Intermediate customers. 6. Cost-plus pricing. 7. Price discrimination (differential pricing). 8. Odd number pricing. 9. One coin purchase. 10. Gift purchases.

More complex models are used to describe markets in which a supplier or group of suppliers has market power: 1. A monopolist is the sole supplier in a market and is able to prevent other suppliers from entering. 2. Oligopolists are members of a small group who between them control supply in a market. Oligopolists typically compete with one another but
The Concept of Marketing лекция 10.pptx