8e6bdb3e51550469ebc63a7b29e8c7cf.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 20
 Produce and Consume Linked Data with Drupal Stephane Corlosquet, Renaud Delbru, Tim Clark, Axel Polleres and Stefan Decker Ioan Toma ©www. sti-innsbruck. at INNSBRUCK www. sti-innsbruck. at Copyright 2008 STI
Produce and Consume Linked Data with Drupal Stephane Corlosquet, Renaud Delbru, Tim Clark, Axel Polleres and Stefan Decker Ioan Toma ©www. sti-innsbruck. at INNSBRUCK www. sti-innsbruck. at Copyright 2008 STI
 Acknowledge • Many of the slides in this presentation are based on: http: //www. slideshare. net/scorlosquet/produce-and-consume-linked-data -with-drupal? src=related_normal&rel=4796732 www. sti-innsbruck. at
Acknowledge • Many of the slides in this presentation are based on: http: //www. slideshare. net/scorlosquet/produce-and-consume-linked-data -with-drupal? src=related_normal&rel=4796732 www. sti-innsbruck. at
 Motivation • There is a lot of data on the web in Content Management Systems (CMS) • Moreover this data is structured data. • However, • It is not possible to reuse this data outside the CMS (except RSS), but RSS limited when it comes to semantic • This data is not available in a unified machine readable format www. sti-innsbruck. at
Motivation • There is a lot of data on the web in Content Management Systems (CMS) • Moreover this data is structured data. • However, • It is not possible to reuse this data outside the CMS (except RSS), but RSS limited when it comes to semantic • This data is not available in a unified machine readable format www. sti-innsbruck. at
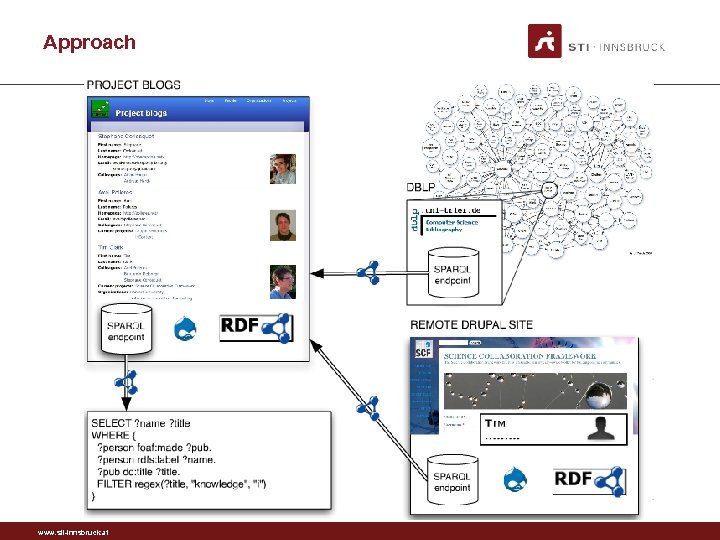
 Approach • Goal: • integrate “any” CMS site to the Web • Implementation in Drupal, why? : • One of the most popular CMS • Lots of extra functionality available as modules • Approach in short: Develop a set of modules that perform: 1. Automatically site vocabulary generation 2. Mapping content models (site vocabulary) to existing vocabularies 3. Data endpoint for SPARQL querying 4. Lazy loading of external data (data import) www. sti-innsbruck. at
Approach • Goal: • integrate “any” CMS site to the Web • Implementation in Drupal, why? : • One of the most popular CMS • Lots of extra functionality available as modules • Approach in short: Develop a set of modules that perform: 1. Automatically site vocabulary generation 2. Mapping content models (site vocabulary) to existing vocabularies 3. Data endpoint for SPARQL querying 4. Lazy loading of external data (data import) www. sti-innsbruck. at
 Approach www. sti-innsbruck. at
Approach www. sti-innsbruck. at
 Related work • • Ontology based CMSs: • Semantic community Web portals (2000) • Model Driven Ontology-Based Web site management Approach in the paper starts from existing CMS infrastructure Mapping RDBMS underlying CMS to RDF/RDFS Approach in the paper starts from site model and constraint and not from underlying data base model • SCF Node proxy architecture - RDF to Drupal mapping, not general, specific to bio domain Approach in the paper has as starting point SCF Node proxy architecture www. sti-innsbruck. at
Related work • • Ontology based CMSs: • Semantic community Web portals (2000) • Model Driven Ontology-Based Web site management Approach in the paper starts from existing CMS infrastructure Mapping RDBMS underlying CMS to RDF/RDFS Approach in the paper starts from site model and constraint and not from underlying data base model • SCF Node proxy architecture - RDF to Drupal mapping, not general, specific to bio domain Approach in the paper has as starting point SCF Node proxy architecture www. sti-innsbruck. at
 Drupal • Drupal: • Easy to use • Large community • Popular on the Web • Modular design • Drupal terminology: • Node – corresponds to Drupal Web page • Module – functionality that alter and extend Drupal core functionality • Site administrators: set up the site and install modules they like/need • Module developers: develop module(s) • Site editors: create the content of the site following the schema defined by the site administrator www. sti-innsbruck. at
Drupal • Drupal: • Easy to use • Large community • Popular on the Web • Modular design • Drupal terminology: • Node – corresponds to Drupal Web page • Module – functionality that alter and extend Drupal core functionality • Site administrators: set up the site and install modules they like/need • Module developers: develop module(s) • Site editors: create the content of the site following the schema defined by the site administrator www. sti-innsbruck. at
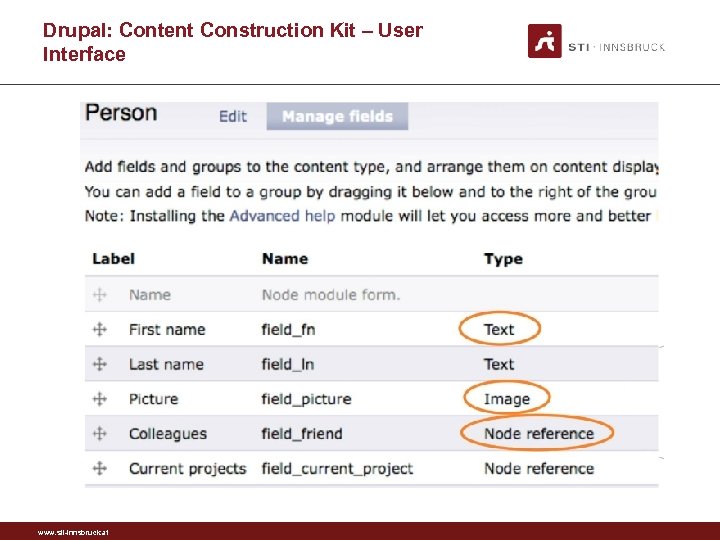
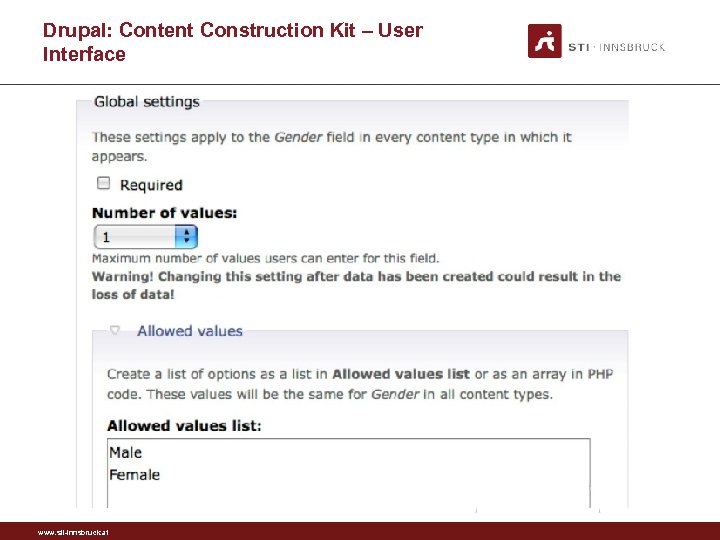
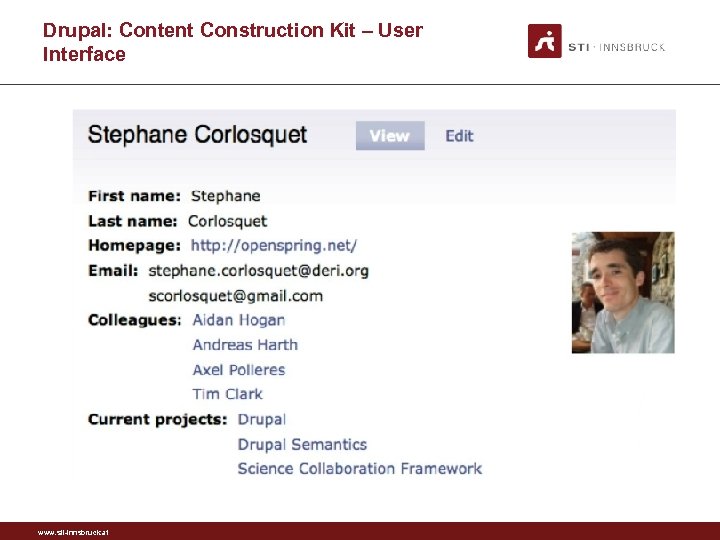
 Drupal: Content Construction Kit • • GUI for extending the internal schema of a Drupal site Used on many Drupal sites Can build new types of pages, known as content types Can create fields for each content types. Fields can be of various types: plain text fields, dates, email addresses, file uploads, references to other pages www. sti-innsbruck. at
Drupal: Content Construction Kit • • GUI for extending the internal schema of a Drupal site Used on many Drupal sites Can build new types of pages, known as content types Can create fields for each content types. Fields can be of various types: plain text fields, dates, email addresses, file uploads, references to other pages www. sti-innsbruck. at
 Drupal: Content Construction Kit – User Interface www. sti-innsbruck. at
Drupal: Content Construction Kit – User Interface www. sti-innsbruck. at
 Drupal: Content Construction Kit – User Interface www. sti-innsbruck. at
Drupal: Content Construction Kit – User Interface www. sti-innsbruck. at
 Drupal: Content Construction Kit – User Interface www. sti-innsbruck. at
Drupal: Content Construction Kit – User Interface www. sti-innsbruck. at
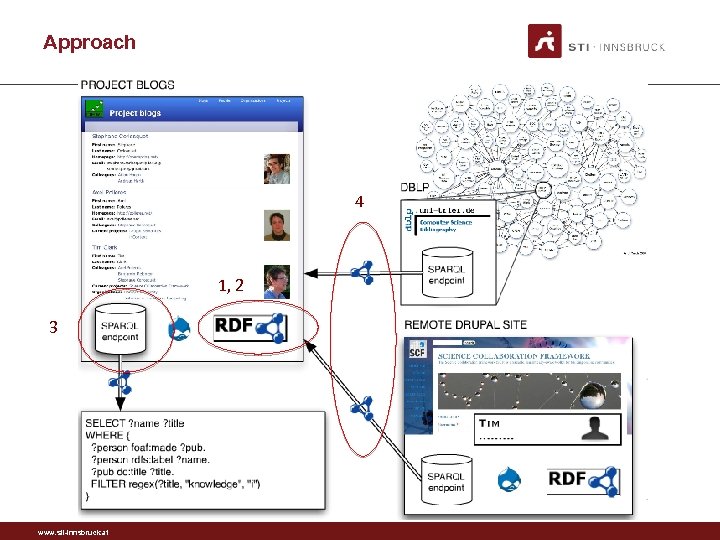 Approach 4 1, 2 3 www. sti-innsbruck. at
Approach 4 1, 2 3 www. sti-innsbruck. at
 1. Site Vocabulary • Automatic site vocabulary in RDFS/OWL: • Content types and fields are mapped to classes (rdfs: Class) and properties (rdf: Property) • Label and descriptions of content types and fields are mapped to rdfs: label and rdf: comment • Cardinality is mapped to cardinality restrictions in OWL • Required – owl: cardinality 1 • Maximum cardinality – owl: max. Cardinality n • Domains and ranges of fields to rdfs: domain and rdfs: range www. sti-innsbruck. at
1. Site Vocabulary • Automatic site vocabulary in RDFS/OWL: • Content types and fields are mapped to classes (rdfs: Class) and properties (rdf: Property) • Label and descriptions of content types and fields are mapped to rdfs: label and rdf: comment • Cardinality is mapped to cardinality restrictions in OWL • Required – owl: cardinality 1 • Maximum cardinality – owl: max. Cardinality n • Domains and ranges of fields to rdfs: domain and rdfs: range www. sti-innsbruck. at
 2. Mapping Content Models to existing ontologies • Import of any vocabulary published online • One needs to specify the URL of the vocabulary • By default FOAF, Dublin. Core, SIOC are imported • External ontology search service • Entity centric search – returns the relevant classes, properties • Based on SWSE and Sindice • Local terms are subclasses/subproperties of public terms • To ensure safe vocabulary reuse – avoid redefinition www. sti-innsbruck. at
2. Mapping Content Models to existing ontologies • Import of any vocabulary published online • One needs to specify the URL of the vocabulary • By default FOAF, Dublin. Core, SIOC are imported • External ontology search service • Entity centric search – returns the relevant classes, properties • Based on SWSE and Sindice • Local terms are subclasses/subproperties of public terms • To ensure safe vocabulary reuse – avoid redefinition www. sti-innsbruck. at
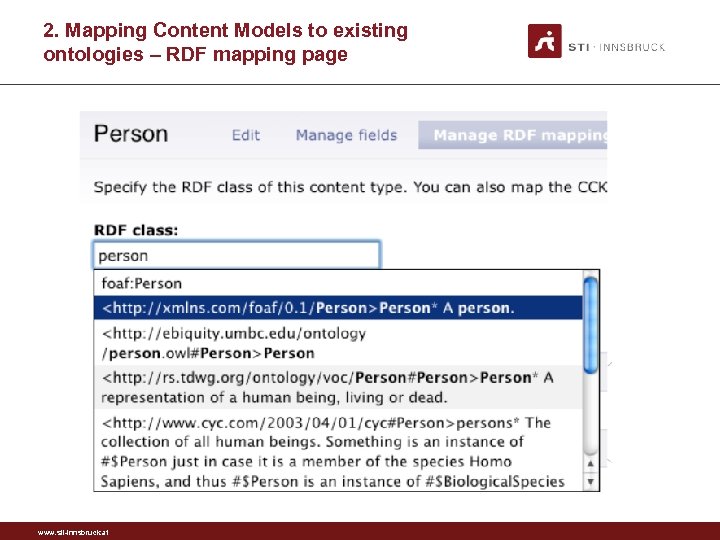 2. Mapping Content Models to existing ontologies – RDF mapping page www. sti-innsbruck. at
2. Mapping Content Models to existing ontologies – RDF mapping page www. sti-innsbruck. at
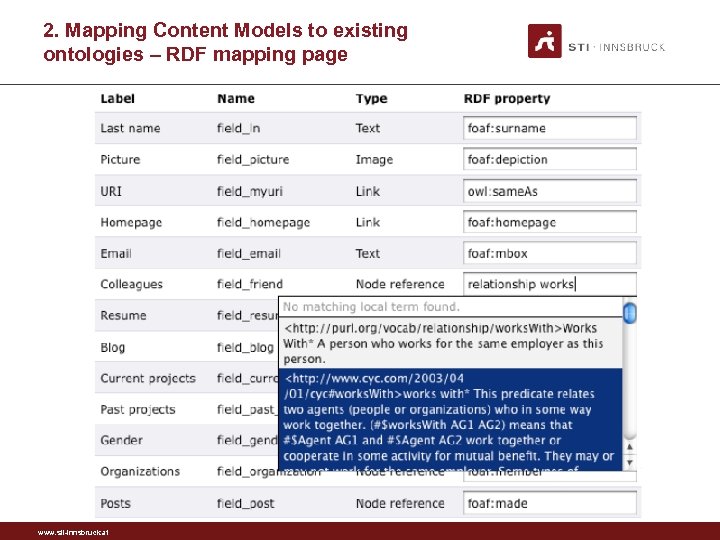 2. Mapping Content Models to existing ontologies – RDF mapping page www. sti-innsbruck. at
2. Mapping Content Models to existing ontologies – RDF mapping page www. sti-innsbruck. at
 3. Data endpoint for complex queries • Local RDF data exposed in a SPARQL endpoint • • Enables interoperability across sites Build on the PHP ARC 2 library All RDF data index in the endpoint Each page stored as a graph an kept up to date www. sti-innsbruck. at
3. Data endpoint for complex queries • Local RDF data exposed in a SPARQL endpoint • • Enables interoperability across sites Build on the PHP ARC 2 library All RDF data index in the endpoint Each page stored as a graph an kept up to date www. sti-innsbruck. at
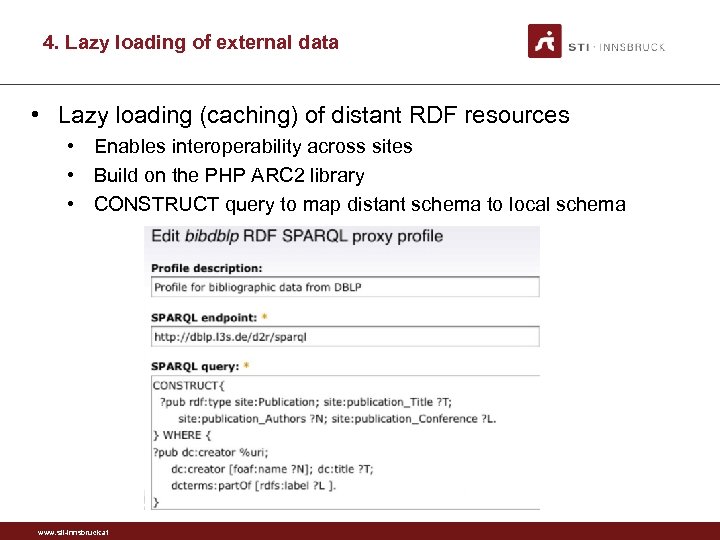 4. Lazy loading of external data • Lazy loading (caching) of distant RDF resources • Enables interoperability across sites • Build on the PHP ARC 2 library • CONSTRUCT query to map distant schema to local schema www. sti-innsbruck. at
4. Lazy loading of external data • Lazy loading (caching) of distant RDF resources • Enables interoperability across sites • Build on the PHP ARC 2 library • CONSTRUCT query to map distant schema to local schema www. sti-innsbruck. at
 Summary • Practical work to add RDF support to Drupal through a set of Drupal modules that do: 1. Automatically site vocabulary generation 2. Mapping content models (site vocabulary) to existing vocabularies 3. Data endpoint for SPARQL querying 4. Lazy loading of external data (data import) www. sti-innsbruck. at
Summary • Practical work to add RDF support to Drupal through a set of Drupal modules that do: 1. Automatically site vocabulary generation 2. Mapping content models (site vocabulary) to existing vocabularies 3. Data endpoint for SPARQL querying 4. Lazy loading of external data (data import) www. sti-innsbruck. at
 Relation to OC work • DERI approach does not use semantic repositories as a backend solution for storing RDF; we use OWLIM • Things that might be relevant for us: • • Mapping approach Lazy loading of data from external sources www. sti-innsbruck. at
Relation to OC work • DERI approach does not use semantic repositories as a backend solution for storing RDF; we use OWLIM • Things that might be relevant for us: • • Mapping approach Lazy loading of data from external sources www. sti-innsbruck. at


