c77e42577db931ab4df7ff1b408cf2dc.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 34
 Processing Nested Complex Sequence Pattern Queries over Event Streams Mo Liu 1, Medhabi Ray 1, Elke A. Rundensteiner 1, Dan Dougherty 1, Chetan Gupta 2, Song Wang 2, Ismail Ari 3, and Abhay Mehta 2 1 Worcester Polytechnic Institute, USA 2 HP Labs, USA 3 Ozyegin University, Turkey DMSN 2010 Singapore Acknowledgements: This work is partly supported by HP Innovations Award, NSF 1018443 and NSF IIS 0917017, Turkish National Science Foundation TUBITAK under career award 109 E 194.
Processing Nested Complex Sequence Pattern Queries over Event Streams Mo Liu 1, Medhabi Ray 1, Elke A. Rundensteiner 1, Dan Dougherty 1, Chetan Gupta 2, Song Wang 2, Ismail Ari 3, and Abhay Mehta 2 1 Worcester Polytechnic Institute, USA 2 HP Labs, USA 3 Ozyegin University, Turkey DMSN 2010 Singapore Acknowledgements: This work is partly supported by HP Innovations Award, NSF 1018443 and NSF IIS 0917017, Turkish National Science Foundation TUBITAK under career award 109 E 194.
 Event Processing—The Big Picture Event Processing Event Producer 2 Event Consumer
Event Processing—The Big Picture Event Processing Event Producer 2 Event Consumer
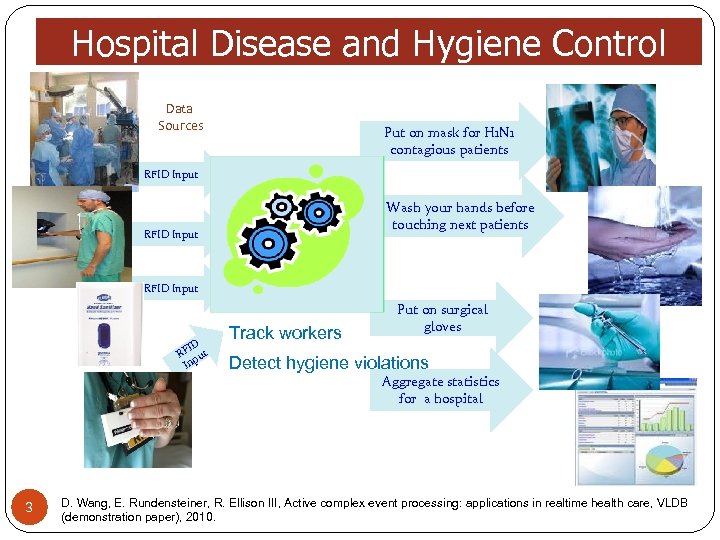 Hospital Disease and Hygiene Control Data Sources Put on mask for H 1 N 1 contagious patients RFID Input Wash your hands before touching next patients RFID Input Query Results RFID Input Data Streams ID RF ut p In Track workers Put on surgical gloves Detect hygiene violations Aggregate statistics for a hospital 3 D. Wang, E. Rundensteiner, R. Ellison III, Active complex event processing: applications in realtime health care, VLDB (demonstration paper), 2010.
Hospital Disease and Hygiene Control Data Sources Put on mask for H 1 N 1 contagious patients RFID Input Wash your hands before touching next patients RFID Input Query Results RFID Input Data Streams ID RF ut p In Track workers Put on surgical gloves Detect hygiene violations Aggregate statistics for a hospital 3 D. Wang, E. Rundensteiner, R. Ellison III, Active complex event processing: applications in realtime health care, VLDB (demonstration paper), 2010.
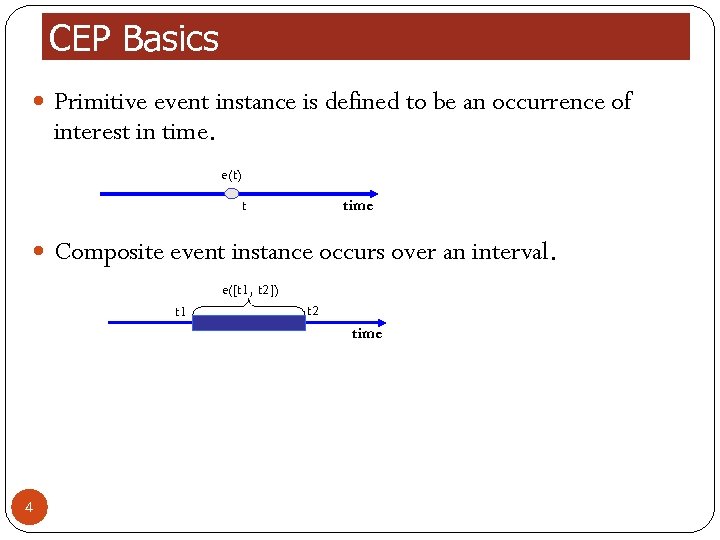 CEP Basics Primitive event instance is defined to be an occurrence of interest in time. e(t) time t Composite event instance occurs over an interval. e([t 1, t 2]) t 1 t 2 time 4
CEP Basics Primitive event instance is defined to be an occurrence of interest in time. e(t) time t Composite event instance occurs over an interval. e([t 1, t 2]) t 1 t 2 time 4
 Outline • • • 5 Motivation NEEL: The Nested Complex Event Language Nested CEP Query Processing Performance Evaluation Nested Query Optimization with Evaluation Conclusion
Outline • • • 5 Motivation NEEL: The Nested Complex Event Language Nested CEP Query Processing Performance Evaluation Nested Query Optimization with Evaluation Conclusion
 Why Nested Queries? Compact Incremental Convenient + + + 6
Why Nested Queries? Compact Incremental Convenient + + + 6
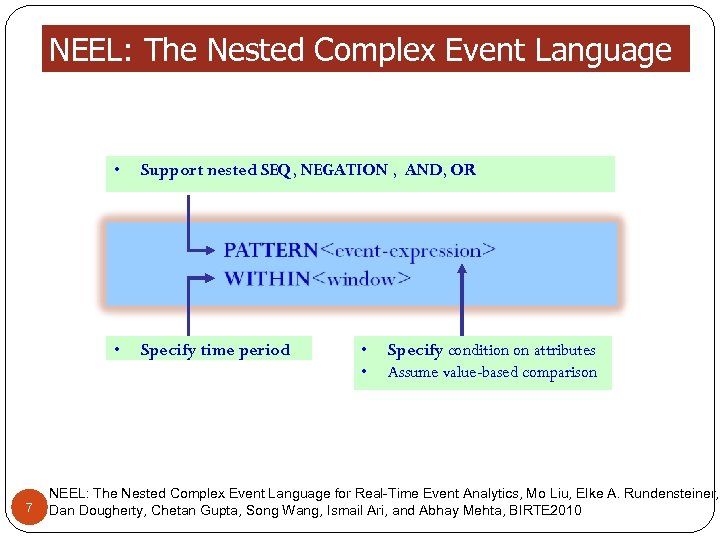 NEEL: The Nested Complex Event Language • • 7 Support nested SEQ, NEGATION , AND, OR Specify time period • • Specify condition on attributes Assume value-based comparison NEEL: The Nested Complex Event Language for Real-Time Event Analytics, Mo Liu, Elke A. Rundensteiner, Dan Dougherty, Chetan Gupta, Song Wang, Ismail Ari, and Abhay Mehta, BIRTE 2010
NEEL: The Nested Complex Event Language • • 7 Support nested SEQ, NEGATION , AND, OR Specify time period • • Specify condition on attributes Assume value-based comparison NEEL: The Nested Complex Event Language for Real-Time Event Analytics, Mo Liu, Elke A. Rundensteiner, Dan Dougherty, Chetan Gupta, Song Wang, Ismail Ari, and Abhay Mehta, BIRTE 2010
 NEEL: The Nested Complex Event Language Time Nested sub-query 8
NEEL: The Nested Complex Event Language Time Nested sub-query 8
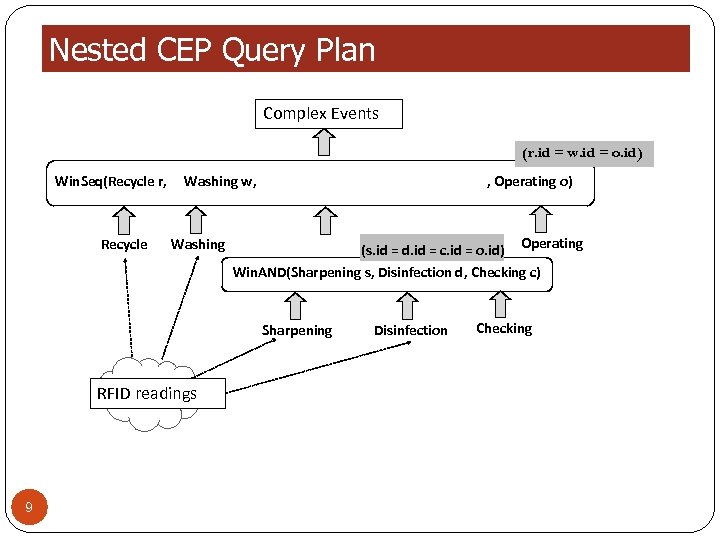 Nested CEP Query Plan Complex Events (r. id = w. id = o. id) Win. Seq(Recycle r, Recycle Washing w, Washing , Operating o) (s. id = d. id = c. id = o. id) Operating Win. AND(Sharpening s, Disinfection d, Checking c) Sharpening RFID readings 9 Disinfection Checking
Nested CEP Query Plan Complex Events (r. id = w. id = o. id) Win. Seq(Recycle r, Recycle Washing w, Washing , Operating o) (s. id = d. id = c. id = o. id) Operating Win. AND(Sharpening s, Disinfection d, Checking c) Sharpening RFID readings 9 Disinfection Checking
 Outline • • • 10 Motivation NEEL: The Nested Complex Event Language Nested CEP Query Processing − Processing Nested Queries with Negation − Processing Nested Queries with Predicate Performance Evaluation Nested Query Optimization with Evaluation Conclusion
Outline • • • 10 Motivation NEEL: The Nested Complex Event Language Nested CEP Query Processing − Processing Nested Queries with Negation − Processing Nested Queries with Predicate Performance Evaluation Nested Query Optimization with Evaluation Conclusion
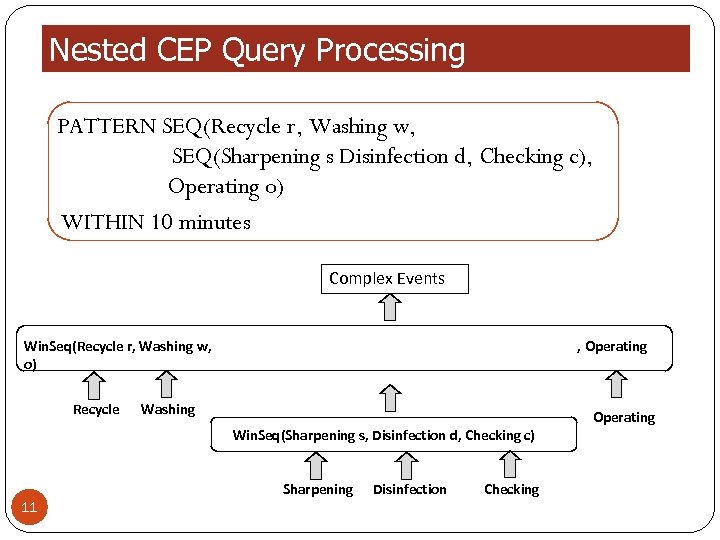 Nested CEP Query Processing PATTERN SEQ(Recycle r, Washing w, SEQ(Sharpening s Disinfection d, Checking c), Operating o) WITHIN 10 minutes Complex Events Win. Seq(Recycle r, Washing w, o) Recycle , Operating Washing Operating Win. Seq(Sharpening s, Disinfection d, Checking c) Sharpening 11 Disinfection Checking
Nested CEP Query Processing PATTERN SEQ(Recycle r, Washing w, SEQ(Sharpening s Disinfection d, Checking c), Operating o) WITHIN 10 minutes Complex Events Win. Seq(Recycle r, Washing w, o) Recycle , Operating Washing Operating Win. Seq(Sharpening s, Disinfection d, Checking c) Sharpening 11 Disinfection Checking
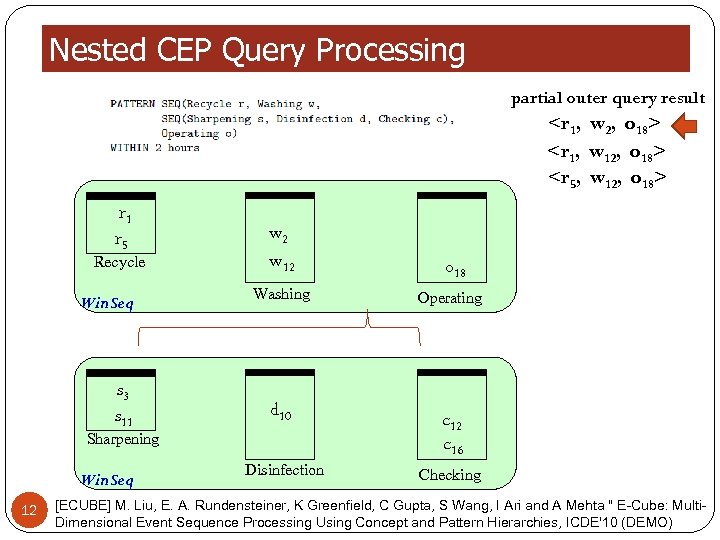 Nested CEP Query Processing partial outer query result
Nested CEP Query Processing partial outer query result
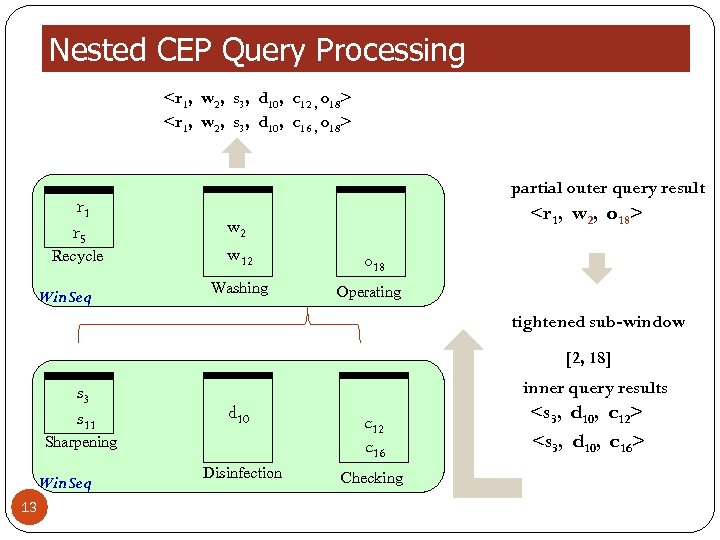 Nested CEP Query Processing
Nested CEP Query Processing
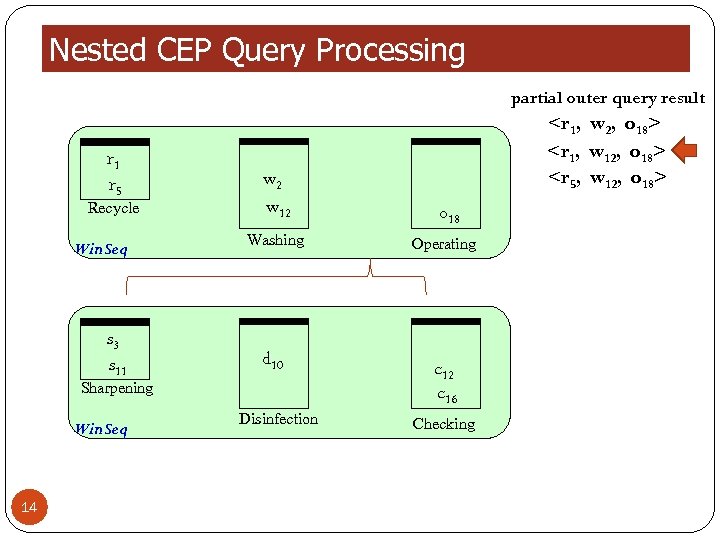 Nested CEP Query Processing partial outer query result r 1 r 5 Recycle Win. Seq s 3 s 11 w 2 w 12 Washing d 10 Sharpening Win. Seq 14 Disinfection
Nested CEP Query Processing partial outer query result r 1 r 5 Recycle Win. Seq s 3 s 11 w 2 w 12 Washing d 10 Sharpening Win. Seq 14 Disinfection
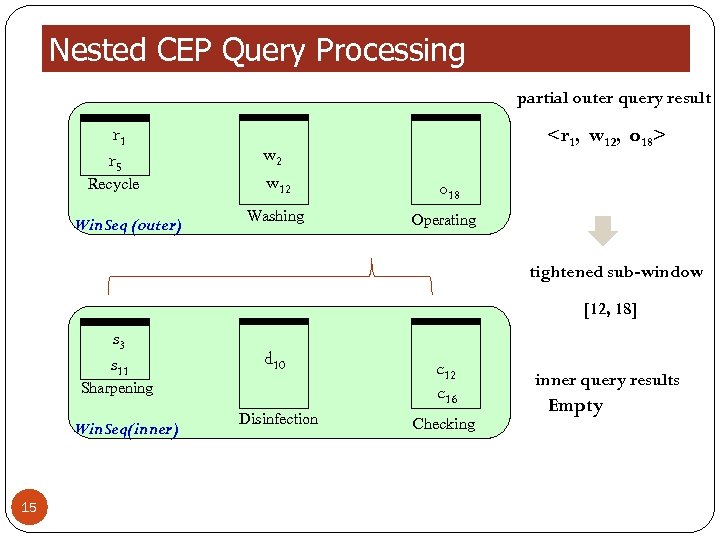 Nested CEP Query Processing partial outer query result r 1 r 5 Recycle Win. Seq (outer) w 2 w 12 Washing
Nested CEP Query Processing partial outer query result r 1 r 5 Recycle Win. Seq (outer) w 2 w 12 Washing
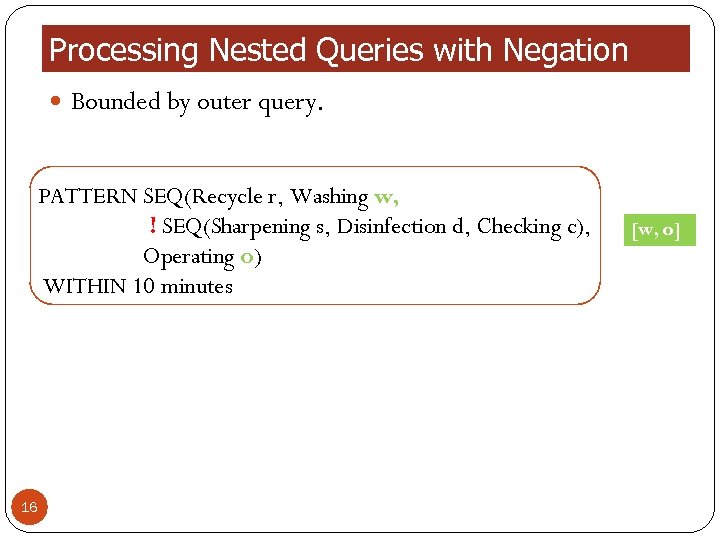 Processing Nested Queries with Negation Bounded by outer query. PATTERN SEQ(Recycle r, Washing w, ! SEQ(Sharpening s, Disinfection d, Checking c), Operating o) WITHIN 10 minutes 16 [w, o]
Processing Nested Queries with Negation Bounded by outer query. PATTERN SEQ(Recycle r, Washing w, ! SEQ(Sharpening s, Disinfection d, Checking c), Operating o) WITHIN 10 minutes 16 [w, o]
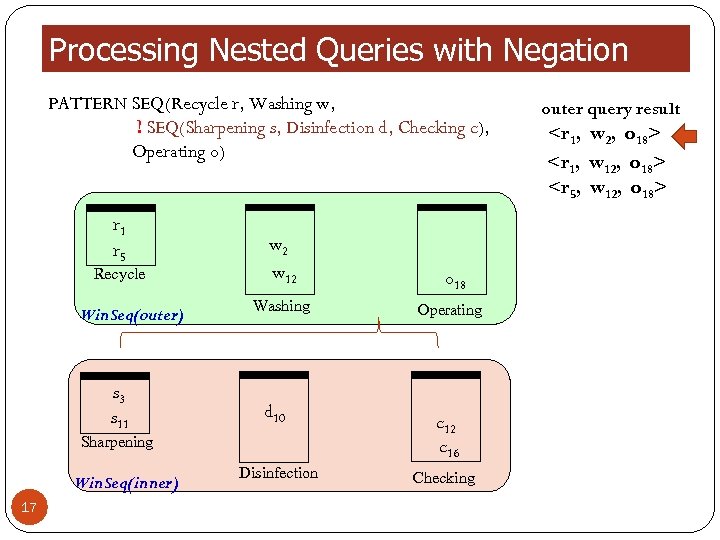 Processing Nested Queries with Negation PATTERN SEQ(Recycle r, Washing w, ! SEQ(Sharpening s, Disinfection d, Checking c), Operating o) r 1 r 5 Recycle Win. Seq(outer) s 3 s 11 w 2 w 12 Washing d 10 Sharpening Win. Seq(inner) 17 Disinfection o 18 Operating c 12 c 16 Checking outer query result
Processing Nested Queries with Negation PATTERN SEQ(Recycle r, Washing w, ! SEQ(Sharpening s, Disinfection d, Checking c), Operating o) r 1 r 5 Recycle Win. Seq(outer) s 3 s 11 w 2 w 12 Washing d 10 Sharpening Win. Seq(inner) 17 Disinfection o 18 Operating c 12 c 16 Checking outer query result
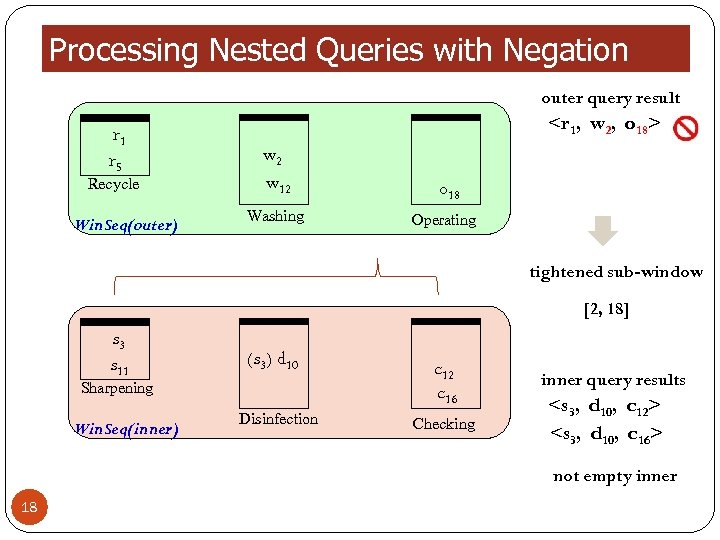 Processing Nested Queries with Negation outer query result r 1 r 5 Recycle Win. Seq(outer)
Processing Nested Queries with Negation outer query result r 1 r 5 Recycle Win. Seq(outer) not empty inner 18
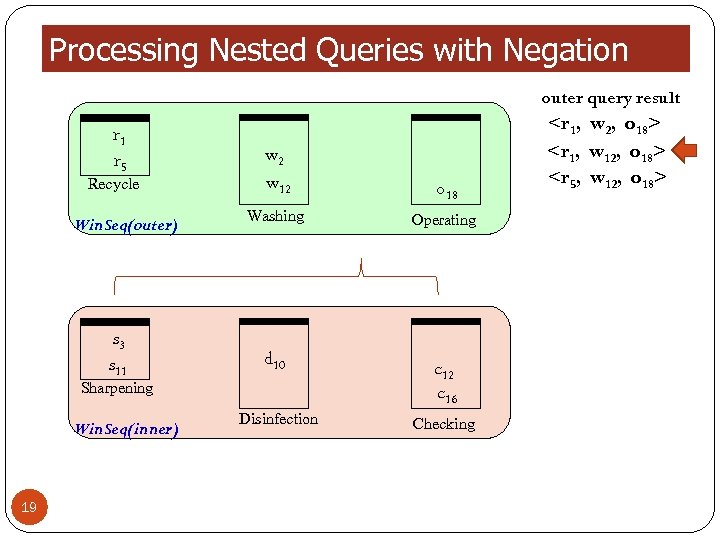 Processing Nested Queries with Negation outer query result r 1 r 5 Recycle Win. Seq(outer) s 3 s 11 w 2 w 12 o 18 Washing Operating d 10 Sharpening Win. Seq(inner) 19 Disinfection c 12 c 16 Checking
Processing Nested Queries with Negation outer query result r 1 r 5 Recycle Win. Seq(outer) s 3 s 11 w 2 w 12 o 18 Washing Operating d 10 Sharpening Win. Seq(inner) 19 Disinfection c 12 c 16 Checking
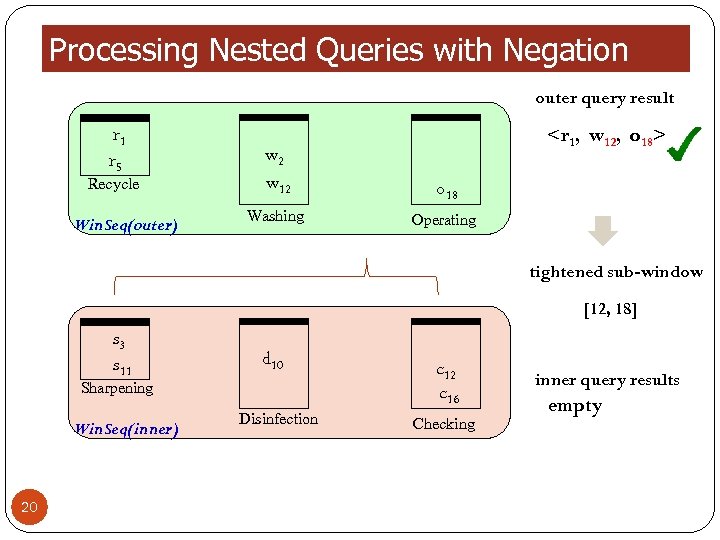 Processing Nested Queries with Negation outer query result r 1 r 5 Recycle Win. Seq(outer)
Processing Nested Queries with Negation outer query result r 1 r 5 Recycle Win. Seq(outer)
 Processing Nested Queries with Negation Bounded by adjacent query. PATTERN SEQ(Recycle b, SEQ(Washing w, ! Sharpening s), SEQ(Disinfection d, Checking c), Operating o) [w, d] WITHIN 10 minutes Challenge: Not yet known bounds at time of subquery processing, as mutually dependent subqueries. 21
Processing Nested Queries with Negation Bounded by adjacent query. PATTERN SEQ(Recycle b, SEQ(Washing w, ! Sharpening s), SEQ(Disinfection d, Checking c), Operating o) [w, d] WITHIN 10 minutes Challenge: Not yet known bounds at time of subquery processing, as mutually dependent subqueries. 21
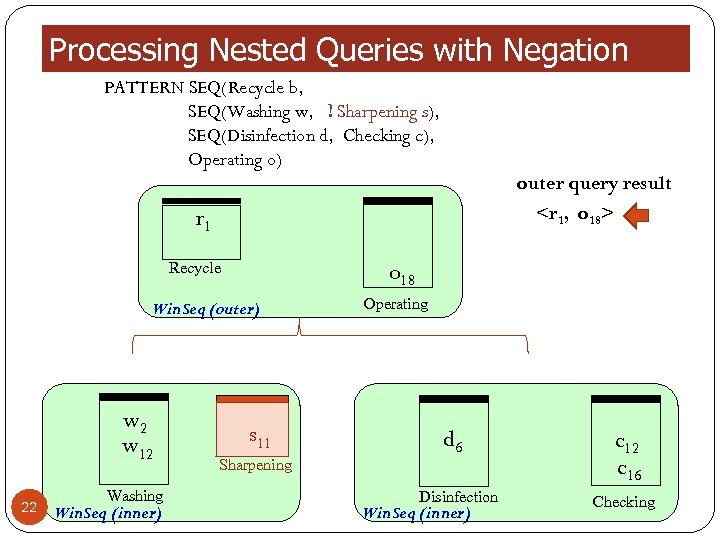 Processing Nested Queries with Negation PATTERN SEQ(Recycle b, SEQ(Washing w, ! Sharpening s), SEQ(Disinfection d, Checking c), Operating o) outer query result
Processing Nested Queries with Negation PATTERN SEQ(Recycle b, SEQ(Washing w, ! Sharpening s), SEQ(Disinfection d, Checking c), Operating o) outer query result
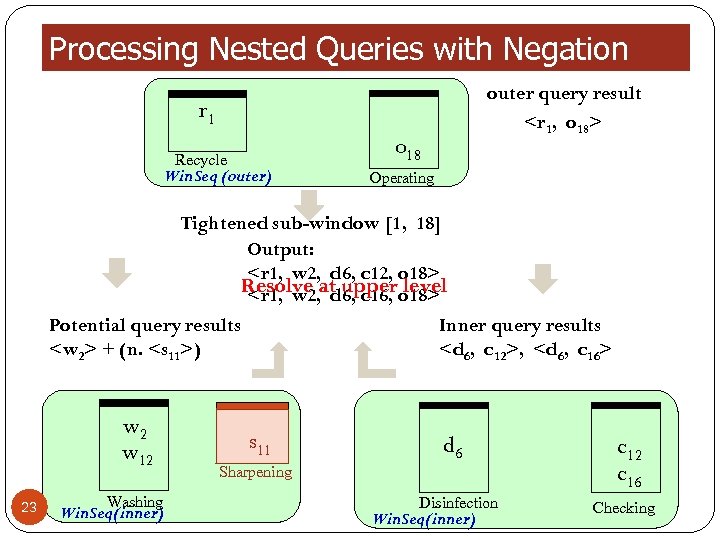 Processing Nested Queries with Negation outer query result
Processing Nested Queries with Negation outer query result )
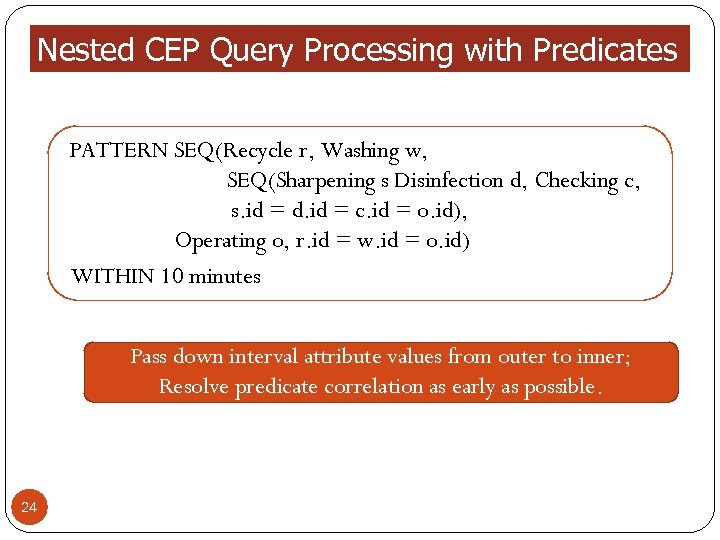 Nested CEP Query Processing with Predicates PATTERN SEQ(Recycle r, Washing w, SEQ(Sharpening s Disinfection d, Checking c, s. id = d. id = c. id = o. id), Operating o, r. id = w. id = o. id) WITHIN 10 minutes Pass down interval attribute values from outer to inner; Resolve predicate correlation as early as possible. 24
Nested CEP Query Processing with Predicates PATTERN SEQ(Recycle r, Washing w, SEQ(Sharpening s Disinfection d, Checking c, s. id = d. id = c. id = o. id), Operating o, r. id = w. id = o. id) WITHIN 10 minutes Pass down interval attribute values from outer to inner; Resolve predicate correlation as early as possible. 24
 Outline • • • 25 Motivation NEEL: The Nested Complex Event Language Nested CEP Query Processing Performance Evaluation Nested Query Optimization with Evaluation Conclusion
Outline • • • 25 Motivation NEEL: The Nested Complex Event Language Nested CEP Query Processing Performance Evaluation Nested Query Optimization with Evaluation Conclusion
 Experimental Setup • Implemented in ECube Event Analytics System • Use real stock trades data • Sample queries [ECube] M. Liu, E. A. Rundensteiner, K. Greenfield, C. Gupta, S. Wang, I. Ari, and A. Mehta, “E-Cube: Multi-dimensional event sequence processing using concept and pattern hierarchies, ” in ICDE, 2010, pp. 1097– 1100. [Stock] “I. inetats. stock trade traces. http: //www. inetats. com/. ” 26
Experimental Setup • Implemented in ECube Event Analytics System • Use real stock trades data • Sample queries [ECube] M. Liu, E. A. Rundensteiner, K. Greenfield, C. Gupta, S. Wang, I. Ari, and A. Mehta, “E-Cube: Multi-dimensional event sequence processing using concept and pattern hierarchies, ” in ICDE, 2010, pp. 1097– 1100. [Stock] “I. inetats. stock trade traces. http: //www. inetats. com/. ” 26
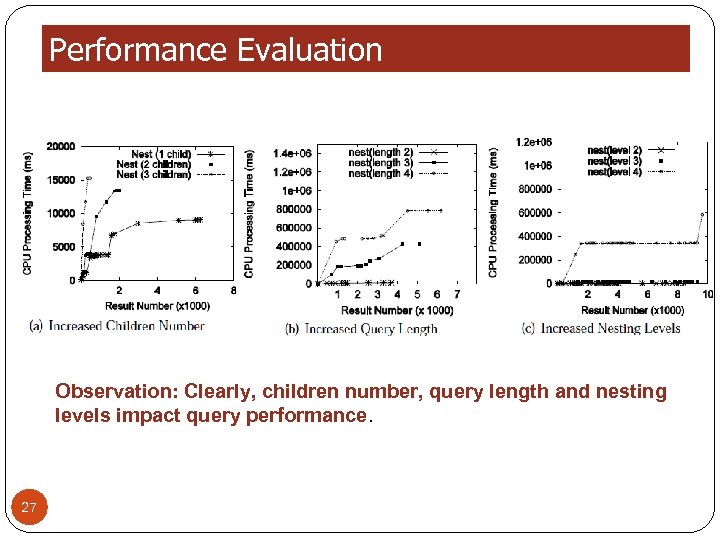 Performance Evaluation Observation: Clearly, children number, query length and nesting levels impact query performance. 27
Performance Evaluation Observation: Clearly, children number, query length and nesting levels impact query performance. 27
 Outline • • • 28 Motivation NEEL: The Nested Complex Event Language Nested CEP Query Processing Performance Evaluation Nested Query Optimization with Evaluation Conclusion
Outline • • • 28 Motivation NEEL: The Nested Complex Event Language Nested CEP Query Processing Performance Evaluation Nested Query Optimization with Evaluation Conclusion
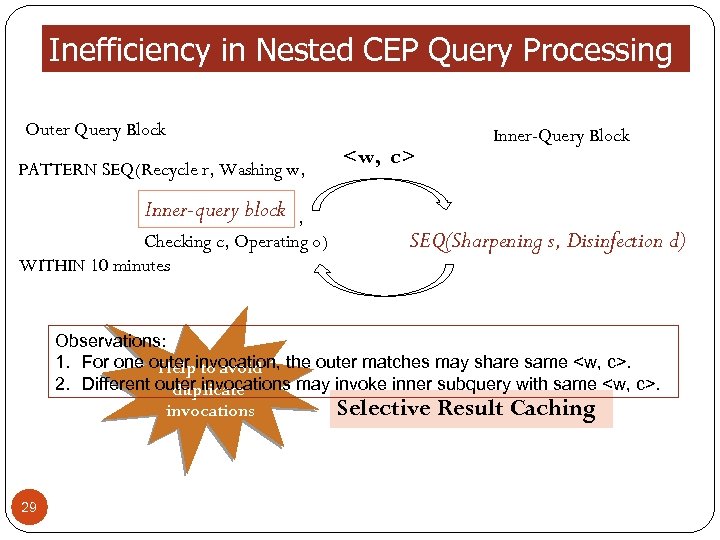 Inefficiency in Nested CEP Query Processing Outer Query Block PATTERN SEQ(Recycle r, Washing w,
Inefficiency in Nested CEP Query Processing Outer Query Block PATTERN SEQ(Recycle r, Washing w,
![Nested Query Optimization • Cache Design. Semantic descriptor interval [leftbound, rightbound] indicates the time Nested Query Optimization • Cache Design. Semantic descriptor interval [leftbound, rightbound] indicates the time](https://present5.com/presentation/c77e42577db931ab4df7ff1b408cf2dc/image-30.jpg) Nested Query Optimization • Cache Design. Semantic descriptor interval [leftbound, rightbound] indicates the time validity of the current cache content. • Cache Usage. Reuse cached results if the query interval matches the cache interval. • Cache Maintenance. −Interval-driven Cache Expansion: Stream insertion − Interval-driven Cache Reduction: Window purge 30
Nested Query Optimization • Cache Design. Semantic descriptor interval [leftbound, rightbound] indicates the time validity of the current cache content. • Cache Usage. Reuse cached results if the query interval matches the cache interval. • Cache Maintenance. −Interval-driven Cache Expansion: Stream insertion − Interval-driven Cache Reduction: Window purge 30
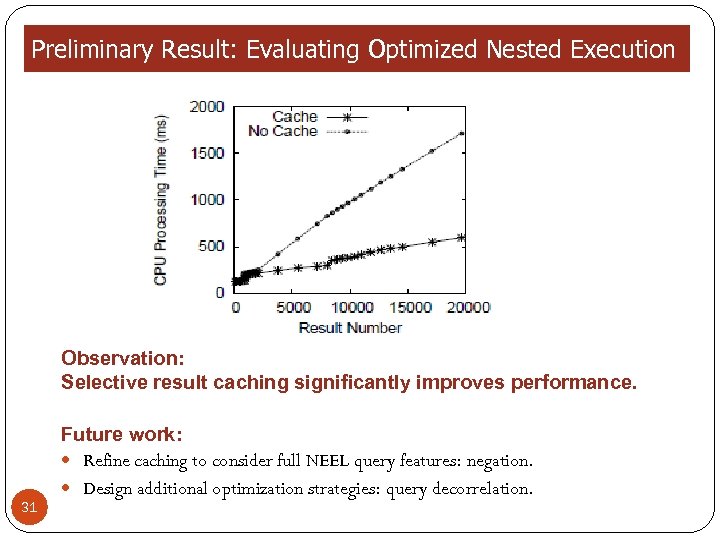 Preliminary Result: Evaluating Optimized Nested Execution Observation: Selective result caching significantly improves performance. 31 Future work: Refine caching to consider full NEEL query features: negation. Design additional optimization strategies: query decorrelation.
Preliminary Result: Evaluating Optimized Nested Execution Observation: Selective result caching significantly improves performance. 31 Future work: Refine caching to consider full NEEL query features: negation. Design additional optimization strategies: query decorrelation.
![Related Work Complex Event Processing Systems [SASE, CEDR…] Query Decorrelation [Decorrelation 96, Dayal 87…] Related Work Complex Event Processing Systems [SASE, CEDR…] Query Decorrelation [Decorrelation 96, Dayal 87…]](https://present5.com/presentation/c77e42577db931ab4df7ff1b408cf2dc/image-32.jpg) Related Work Complex Event Processing Systems [SASE, CEDR…] Query Decorrelation [Decorrelation 96, Dayal 87…] Semantic Caching [Dar 96, Chen 02, …] [SASE] E. Wu, Y. Diao, and S. Rizvi, High-performance complex event processing over streams, SIGMOD, 2006, pp. 407 -418. [CEDR] R. S. Barga, J. Goldstein, M. Ali, and M. Hong, Consistent streaming through time: A vision for event stream processing, CIDR, 2007, pp. 363 -374. [Decorrelation 96] P. Seshadri, H. Pirahesh, and T. Y. C. Leung, “Complex query decorrelation, ” in ICDE ’ 96: Proceedings of the Twelfth International Conference on Data Engineering. IEEE Computer Society, 1996, pp. 450– 458 [Dayal 87] U. Dayal, “Of nests and trees: A unified approach to processing queries that contain nested subqueries, aggregates, and quantifiers, ” in VLDB, 1987, pp. 197– 208. [Dar 96] S. Dar, M. J. Franklin, B. T. J´onsson, and etc, “Semantic data caching and replacement, ” in VLDB, 1996, pp. 330– 341. [Chen 02] L. Chen, E. Rundensteiner, and etc, “Xcache: A semantic caching system for xml queries, ” in ACM SIGMOD, 2002, pp. 618– 618 32
Related Work Complex Event Processing Systems [SASE, CEDR…] Query Decorrelation [Decorrelation 96, Dayal 87…] Semantic Caching [Dar 96, Chen 02, …] [SASE] E. Wu, Y. Diao, and S. Rizvi, High-performance complex event processing over streams, SIGMOD, 2006, pp. 407 -418. [CEDR] R. S. Barga, J. Goldstein, M. Ali, and M. Hong, Consistent streaming through time: A vision for event stream processing, CIDR, 2007, pp. 363 -374. [Decorrelation 96] P. Seshadri, H. Pirahesh, and T. Y. C. Leung, “Complex query decorrelation, ” in ICDE ’ 96: Proceedings of the Twelfth International Conference on Data Engineering. IEEE Computer Society, 1996, pp. 450– 458 [Dayal 87] U. Dayal, “Of nests and trees: A unified approach to processing queries that contain nested subqueries, aggregates, and quantifiers, ” in VLDB, 1987, pp. 197– 208. [Dar 96] S. Dar, M. J. Franklin, B. T. J´onsson, and etc, “Semantic data caching and replacement, ” in VLDB, 1996, pp. 330– 341. [Chen 02] L. Chen, E. Rundensteiner, and etc, “Xcache: A semantic caching system for xml queries, ” in ACM SIGMOD, 2002, pp. 618– 618 32
 Conclusion Introduce an algebraic query plan for queries expressed in NEEL. Design an iterative execution strategy for NEEL. Evaluate our proposed execution strategy on real data streams. Demonstrate promise of selective caching in NEEL execution. 33
Conclusion Introduce an algebraic query plan for queries expressed in NEEL. Design an iterative execution strategy for NEEL. Evaluate our proposed execution strategy on real data streams. Demonstrate promise of selective caching in NEEL execution. 33
 Thank You! 34
Thank You! 34


