e89503f182fed4f6b3379e57a088a9df.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 39
 Process Evaluation Intermediate Injury Prevention Course August 23 -26, 2011 Billings, MT
Process Evaluation Intermediate Injury Prevention Course August 23 -26, 2011 Billings, MT
 Session Goal To provide Participants with the information to design a process evaluation for an injury prevention project.
Session Goal To provide Participants with the information to design a process evaluation for an injury prevention project.
 Session Objectives • Define Process Evaluation • Describe why and when to use process evaluation • Recognize the type of data collected during Process Evaluation • Describe Process Evaluation methods • Design a Process Evaluation for an injury prevention project
Session Objectives • Define Process Evaluation • Describe why and when to use process evaluation • Recognize the type of data collected during Process Evaluation • Describe Process Evaluation methods • Design a Process Evaluation for an injury prevention project
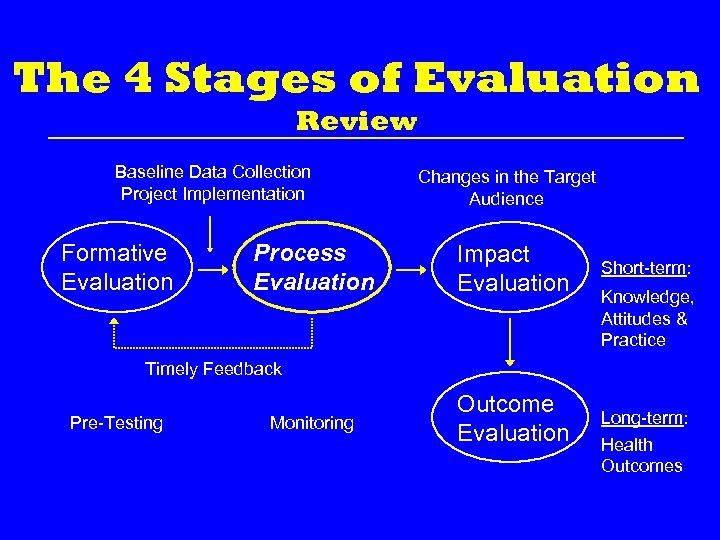 The 4 Stages of Evaluation Review Baseline Data Collection Project Implementation Formative Evaluation Process Evaluation Changes in the Target Audience Impact Evaluation Short-term: Knowledge, Attitudes & Practice Timely Feedback Pre-Testing Monitoring Outcome Evaluation Long-term: Health Outcomes
The 4 Stages of Evaluation Review Baseline Data Collection Project Implementation Formative Evaluation Process Evaluation Changes in the Target Audience Impact Evaluation Short-term: Knowledge, Attitudes & Practice Timely Feedback Pre-Testing Monitoring Outcome Evaluation Long-term: Health Outcomes
 Process Evaluation Defined The type of evaluation used to determine if your project is: • Being implemented as planned, and • Reaching its target audience.
Process Evaluation Defined The type of evaluation used to determine if your project is: • Being implemented as planned, and • Reaching its target audience.
 Process Evaluation Defined “Did I do what I set out to do, Process Evaluation and did it make a difference? ” Impact/ Outcome Evaluation
Process Evaluation Defined “Did I do what I set out to do, Process Evaluation and did it make a difference? ” Impact/ Outcome Evaluation
 Process Evaluation Defined Process Evaluation asks: – What was actually done? – Where and when was it done? – How often was it done? – Who did it, and who did they do it for?
Process Evaluation Defined Process Evaluation asks: – What was actually done? – Where and when was it done? – How often was it done? – Who did it, and who did they do it for?
 Process Evaluation When its Used • Process evaluation planning takes place during project planning and before formative evaluation starts. • Begins immediately after your project is implemented. • Continues throughout the life of your project.
Process Evaluation When its Used • Process evaluation planning takes place during project planning and before formative evaluation starts. • Begins immediately after your project is implemented. • Continues throughout the life of your project.
 Process Evaluation Why it’s Used • Allows you to make adjustments in a timely manner. • Needs of target population might change, and project may need to adapt. • Identifies any problems that occur in reaching the target population.
Process Evaluation Why it’s Used • Allows you to make adjustments in a timely manner. • Needs of target population might change, and project may need to adapt. • Identifies any problems that occur in reaching the target population.
 Process Evaluation Why it’s Used • Can be used to show funding agencies the project’s level of activity. • Tells you how well your project is being implemented. • Tells other interested programs, the “how” and “why” your program works.
Process Evaluation Why it’s Used • Can be used to show funding agencies the project’s level of activity. • Tells you how well your project is being implemented. • Tells other interested programs, the “how” and “why” your program works.
 Process Evaluation Limitations • Is necessary but not sufficient in evaluating a program’s effectiveness. • Depends upon accurate record keeping and effective communication.
Process Evaluation Limitations • Is necessary but not sufficient in evaluating a program’s effectiveness. • Depends upon accurate record keeping and effective communication.
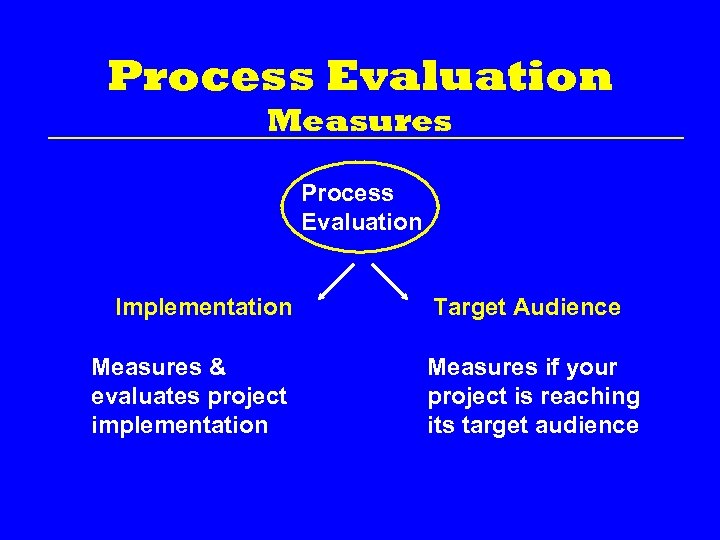 Process Evaluation Measures Process Evaluation Implementation Measures & evaluates project implementation Target Audience Measures if your project is reaching its target audience
Process Evaluation Measures Process Evaluation Implementation Measures & evaluates project implementation Target Audience Measures if your project is reaching its target audience
 Process Evaluation Implementation activities: • • • Developing project’s goals and objectives Creation of an implementation protocol Monitoring daily operations Data collection Coalition building Ensuring staffing is at proper level to meet program needs • Ensuring that staff are sufficiently trained
Process Evaluation Implementation activities: • • • Developing project’s goals and objectives Creation of an implementation protocol Monitoring daily operations Data collection Coalition building Ensuring staffing is at proper level to meet program needs • Ensuring that staff are sufficiently trained
 Process Evaluation Implementation Questions • • • What was actually done? When and where was it done? Who did it? Who did they do it for? Were any materials distributed? What barriers or challenges were discovered? • What was the cost?
Process Evaluation Implementation Questions • • • What was actually done? When and where was it done? Who did it? Who did they do it for? Were any materials distributed? What barriers or challenges were discovered? • What was the cost?
 Process Evaluation Target Audience Reaching the Target Audience activities: • Ensuring the target pop. is being reached • Measuring program participation by target pop. • Making materials and resources available and understood by target pop. • Determining if program is relevant to target pop. • Tracking the distribution of materials
Process Evaluation Target Audience Reaching the Target Audience activities: • Ensuring the target pop. is being reached • Measuring program participation by target pop. • Making materials and resources available and understood by target pop. • Determining if program is relevant to target pop. • Tracking the distribution of materials
 Process Evaluation Target Audience Questions • Is the target population being reached? • What was the nature of this contact? • How often and for how long was the target population involved? • Are the project’s messages and materials appropriate for the target population?
Process Evaluation Target Audience Questions • Is the target population being reached? • What was the nature of this contact? • How often and for how long was the target population involved? • Are the project’s messages and materials appropriate for the target population?
 Process Evaluation Data Collection Techniques A. B. C. D. E. Project Exposure Progress Review Internal Audit Target Population Survey Project Site Survey
Process Evaluation Data Collection Techniques A. B. C. D. E. Project Exposure Progress Review Internal Audit Target Population Survey Project Site Survey
 Process Evaluation Data Collection Techniques A. Project Exposure • • Monitors all project contacts (telephone, email, classes, etc. ) and materials distributed (brochures, products, etc. ) Monitors who utilizes project information (e. g. , sign-in sheets)
Process Evaluation Data Collection Techniques A. Project Exposure • • Monitors all project contacts (telephone, email, classes, etc. ) and materials distributed (brochures, products, etc. ) Monitors who utilizes project information (e. g. , sign-in sheets)
 Process Evaluation Data Collection Techniques B. Progress Review • • • Reviews program activities to determine if goals and objectives are being met (e. g. , meetings with coalition, tribal members, courses provided) Conducts interviews with staff and coalition members Conducted by project staff and interested parties
Process Evaluation Data Collection Techniques B. Progress Review • • • Reviews program activities to determine if goals and objectives are being met (e. g. , meetings with coalition, tribal members, courses provided) Conducts interviews with staff and coalition members Conducted by project staff and interested parties
 Process Evaluation Data Collection Techniques C. Internal Audit • • • Compares implementation plan to actual activities Documents staff efforts, resources, amount of time devoted to each task, and date of task completion E. g. , Sleep Safe Coordinator’s quarterly reports
Process Evaluation Data Collection Techniques C. Internal Audit • • • Compares implementation plan to actual activities Documents staff efforts, resources, amount of time devoted to each task, and date of task completion E. g. , Sleep Safe Coordinator’s quarterly reports
 Process Evaluation Data Collection Techniques D. Target Population Survey • • Measures whether program is reaching target audience Describes target population’s awareness of project, level of interest in the project, number who utilize project
Process Evaluation Data Collection Techniques D. Target Population Survey • • Measures whether program is reaching target audience Describes target population’s awareness of project, level of interest in the project, number who utilize project
 Process Evaluation Data Collection Techniques E. Project Site Survey • • • Determines if materials are being distributed effectively Monitors the number of materials used over a certain period of time E. g. , Sleep Safe smoke alarm follow-up data collection form
Process Evaluation Data Collection Techniques E. Project Site Survey • • • Determines if materials are being distributed effectively Monitors the number of materials used over a certain period of time E. g. , Sleep Safe smoke alarm follow-up data collection form
 Process Evaluation Interpreting the Data The 5 process evaluation methods are now producing results… Results of Internal Audit are used to inform project staff No problems discovered: status-quo Problems discovered: timely revisions to project May require Formative evaluation to determine the problem’s cause
Process Evaluation Interpreting the Data The 5 process evaluation methods are now producing results… Results of Internal Audit are used to inform project staff No problems discovered: status-quo Problems discovered: timely revisions to project May require Formative evaluation to determine the problem’s cause
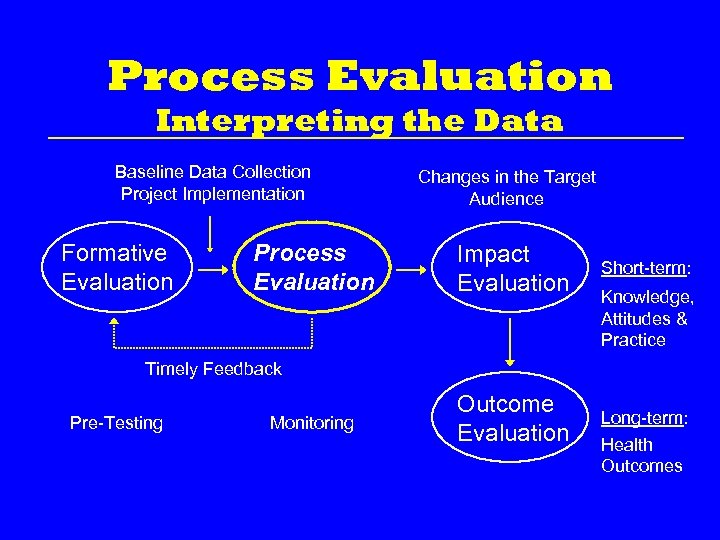 Process Evaluation Interpreting the Data Baseline Data Collection Project Implementation Formative Evaluation Process Evaluation Changes in the Target Audience Impact Evaluation Short-term: Knowledge, Attitudes & Practice Timely Feedback Pre-Testing Monitoring Outcome Evaluation Long-term: Health Outcomes
Process Evaluation Interpreting the Data Baseline Data Collection Project Implementation Formative Evaluation Process Evaluation Changes in the Target Audience Impact Evaluation Short-term: Knowledge, Attitudes & Practice Timely Feedback Pre-Testing Monitoring Outcome Evaluation Long-term: Health Outcomes
 Process Evaluation Conclusion • Process evaluation is a management tool that is used to make sure that your project is implemented as planned and on schedule. • Information collected during process evaluation can be used to make adjustments to your project. • Tells you how well your project is being implemented.
Process Evaluation Conclusion • Process evaluation is a management tool that is used to make sure that your project is implemented as planned and on schedule. • Information collected during process evaluation can be used to make adjustments to your project. • Tells you how well your project is being implemented.
 Process Evaluation Conclusion “The only difference between stumbling blocks and stepping stones is how you use them. ” (And your ability to recognize them. )
Process Evaluation Conclusion “The only difference between stumbling blocks and stepping stones is how you use them. ” (And your ability to recognize them. )
 Process Evaluation Exercise • Using the provided goal & objectives and the Process Evaluation worksheet, your group should: – Select an objective. – Describe one way you will measure how well your project is implemented and how it will reach the target audience. – Describe how you will measure the objective using one of the process evaluation data collection techniques. Time allowed: 15 minutes
Process Evaluation Exercise • Using the provided goal & objectives and the Process Evaluation worksheet, your group should: – Select an objective. – Describe one way you will measure how well your project is implemented and how it will reach the target audience. – Describe how you will measure the objective using one of the process evaluation data collection techniques. Time allowed: 15 minutes
 Child Passenger Safety • Goal: . . to increase the use of child passenger safety seats & correct use of seats • Objectives: – Coalition to increase number of CPST and Instructors by end of this year. – Media advertisement of clinics, checkpoints, and importance of car seats by March 2007. – Conduct a clinic & checkpoint per community yearly, starting next year.
Child Passenger Safety • Goal: . . to increase the use of child passenger safety seats & correct use of seats • Objectives: – Coalition to increase number of CPST and Instructors by end of this year. – Media advertisement of clinics, checkpoints, and importance of car seats by March 2007. – Conduct a clinic & checkpoint per community yearly, starting next year.
 The 4 Stages of Evaluation Baseline Data Collection Project Implementation Formative Evaluation Process Evaluation Changes in the Target Audience Impact Evaluation Short-term: Knowledge, Attitudes & Practice Timely Feedback Pre-Testing Monitoring Outcome Evaluation Long-term: Health Outcomes
The 4 Stages of Evaluation Baseline Data Collection Project Implementation Formative Evaluation Process Evaluation Changes in the Target Audience Impact Evaluation Short-term: Knowledge, Attitudes & Practice Timely Feedback Pre-Testing Monitoring Outcome Evaluation Long-term: Health Outcomes
 Impact Evaluation • Collects baseline information of people’s knowledge, attitudes, beliefs or behaviors. • Long-term data collection (3 to 5 years) to measure and reduce morbidity mortality.
Impact Evaluation • Collects baseline information of people’s knowledge, attitudes, beliefs or behaviors. • Long-term data collection (3 to 5 years) to measure and reduce morbidity mortality.
 Impact Evaluation • Changes in elders use (observed, selfreported) of walkers. • Changes in community members behavior in using occupant restraints (seat belt wearing for adults or car seats for children.
Impact Evaluation • Changes in elders use (observed, selfreported) of walkers. • Changes in community members behavior in using occupant restraints (seat belt wearing for adults or car seats for children.
 Impact Evaluation • Children bicycle helmet use (observed, selfreported) before/after a bicycle campaign. • Changes in elders use (observed, selfreported) of walkers. • Changes in number of operable smoke detectors installed/maintained in homes after a comprehensive fire prevention campaign.
Impact Evaluation • Children bicycle helmet use (observed, selfreported) before/after a bicycle campaign. • Changes in elders use (observed, selfreported) of walkers. • Changes in number of operable smoke detectors installed/maintained in homes after a comprehensive fire prevention campaign.
 Impact Evaluation Example: Alaska PFD Promotion Project • Drowning rate in Alaska’s YK Delta more than 3 times greater than the State average • PFD promotion project began in YK Delta • Observational surveys of PFD use were conducted after baseline data was collected • Timely changes made to increase sales and PFD use
Impact Evaluation Example: Alaska PFD Promotion Project • Drowning rate in Alaska’s YK Delta more than 3 times greater than the State average • PFD promotion project began in YK Delta • Observational surveys of PFD use were conducted after baseline data was collected • Timely changes made to increase sales and PFD use
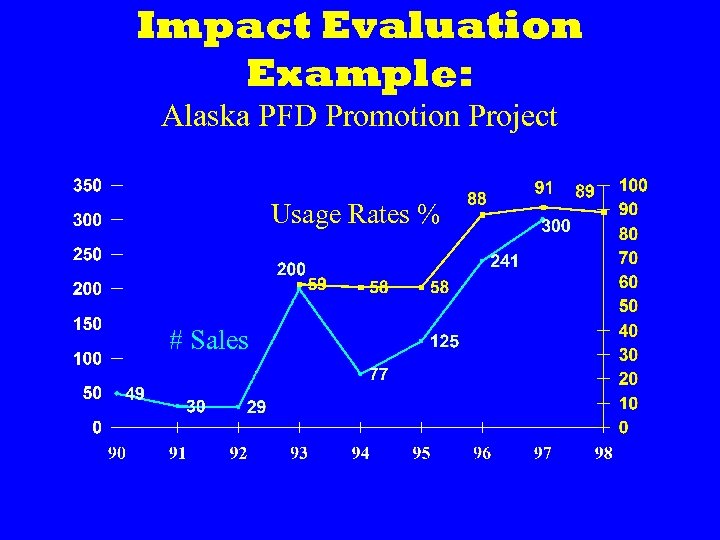 Impact Evaluation Example: Alaska PFD Promotion Project Usage Rates % # Sales
Impact Evaluation Example: Alaska PFD Promotion Project Usage Rates % # Sales
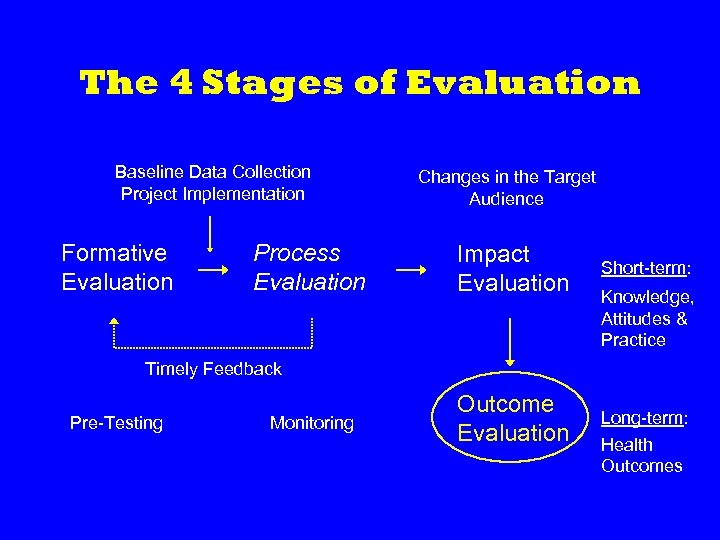 The 4 Stages of Evaluation Baseline Data Collection Project Implementation Formative Evaluation Process Evaluation Changes in the Target Audience Impact Evaluation Short-term: Knowledge, Attitudes & Practice Timely Feedback Pre-Testing Monitoring Outcome Evaluation Long-term: Health Outcomes
The 4 Stages of Evaluation Baseline Data Collection Project Implementation Formative Evaluation Process Evaluation Changes in the Target Audience Impact Evaluation Short-term: Knowledge, Attitudes & Practice Timely Feedback Pre-Testing Monitoring Outcome Evaluation Long-term: Health Outcomes
 Outcome Evaluation • Usually requires significant resources, long periods of time, and ongoing data monitoring. • Used less frequently than impact evaluation in NA injury prevention programs. • Focuses on the program’s long-term effect on its target audience. • Conducted after a program has been completed
Outcome Evaluation • Usually requires significant resources, long periods of time, and ongoing data monitoring. • Used less frequently than impact evaluation in NA injury prevention programs. • Focuses on the program’s long-term effect on its target audience. • Conducted after a program has been completed
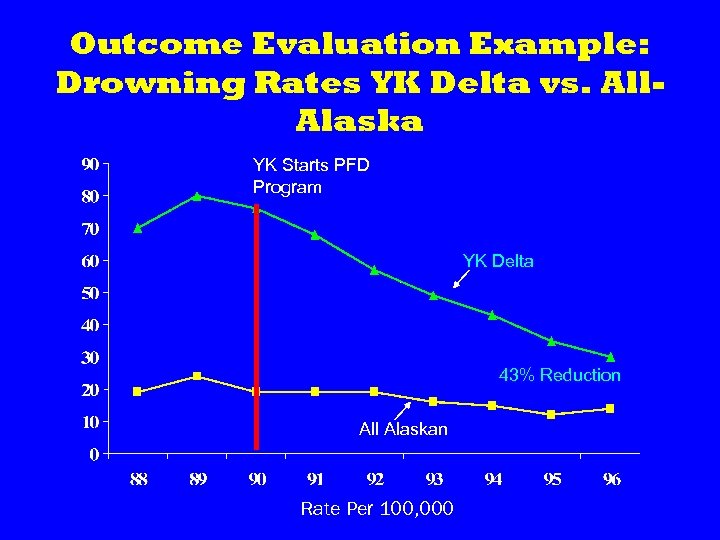 Outcome Evaluation Example: Drowning Rates YK Delta vs. All. Alaska YK Starts PFD Program YK Delta 43% Reduction All Alaskan Rate Per 100, 000
Outcome Evaluation Example: Drowning Rates YK Delta vs. All. Alaska YK Starts PFD Program YK Delta 43% Reduction All Alaskan Rate Per 100, 000
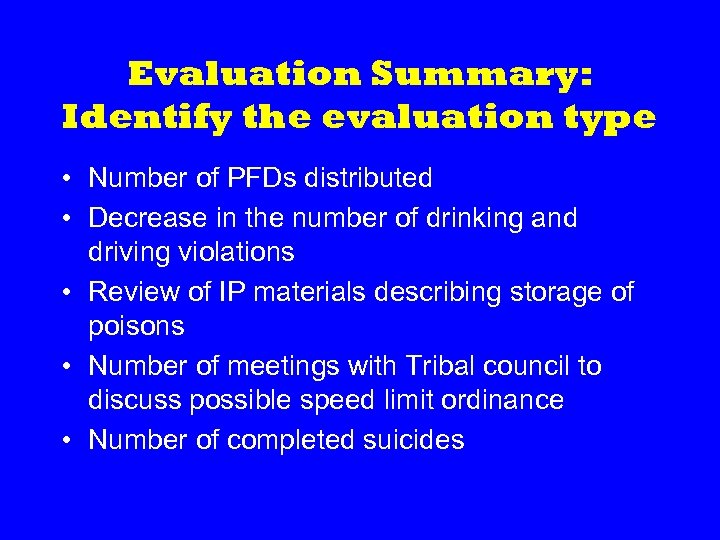 Evaluation Summary: Identify the evaluation type • Number of PFDs distributed • Decrease in the number of drinking and driving violations • Review of IP materials describing storage of poisons • Number of meetings with Tribal council to discuss possible speed limit ordinance • Number of completed suicides
Evaluation Summary: Identify the evaluation type • Number of PFDs distributed • Decrease in the number of drinking and driving violations • Review of IP materials describing storage of poisons • Number of meetings with Tribal council to discuss possible speed limit ordinance • Number of completed suicides
 Additional Resources www. nhtsa. dot. gov www. cdc. gov/eval/resources. htm
Additional Resources www. nhtsa. dot. gov www. cdc. gov/eval/resources. htm


