5d3cdd7010d6c75d13023b04af666e39.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 26

Process Definition and Rollout A Better Approach © 1998 pragma SYSTEMS CORPORATION 849 Lincoln Avenue Glen Rock NJ 07452 201 -612 -7451 Business 201 -612 -6117 Facsimile cbuchman@pragmasystems. com

SW-CMM Characteristics SW-C M M Written in passive voice to support auditors Software Development and Maintenance Organization Auditor © 1998 pragma SYSTEMS CORPORATION 2 Serverpc: process. Max Release Baseline: Collateral Materials: Spin pmax. ppt
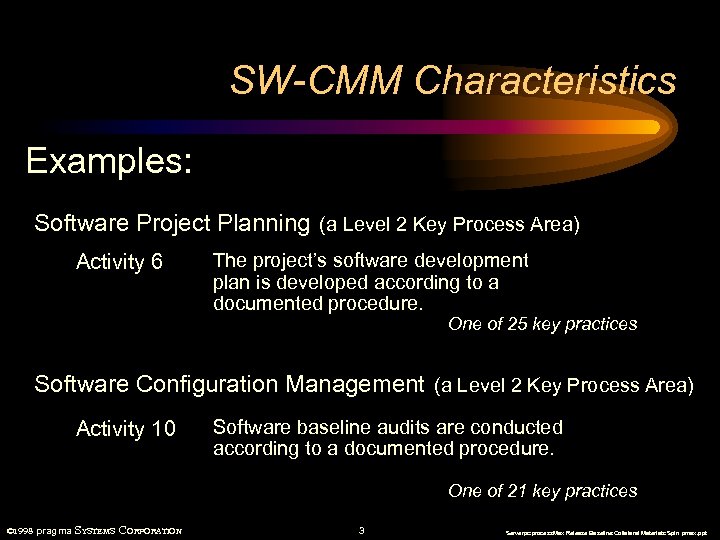
SW-CMM Characteristics Examples: Software Project Planning (a Level 2 Key Process Area) Activity 6 The project’s software development plan is developed according to a documented procedure. One of 25 key practices Software Configuration Management (a Level 2 Key Process Area) Activity 10 Software baseline audits are conducted according to a documented procedure. One of 21 key practices © 1998 pragma SYSTEMS CORPORATION 3 Serverpc: process. Max Release Baseline: Collateral Materials: Spin pmax. ppt
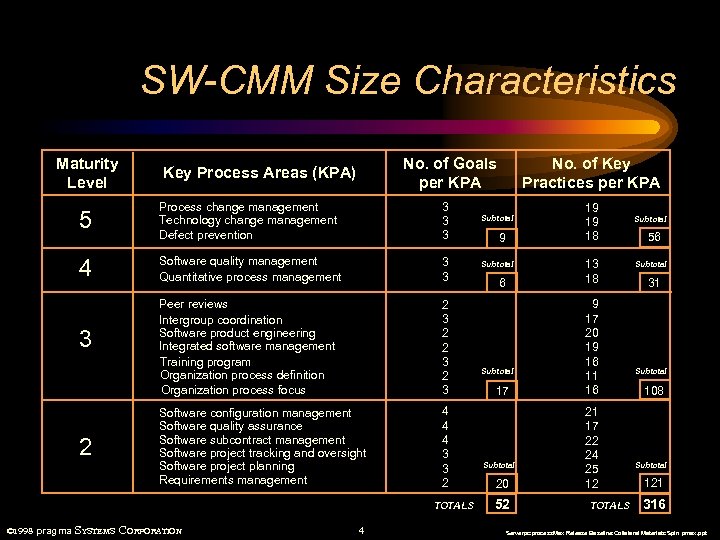
SW-CMM Size Characteristics Maturity Level No. of Goals per KPA Key Process Areas (KPA) 5 Process change management Technology change management Defect prevention 3 3 3 4 Software quality management Quantitative process management 3 3 Peer reviews Intergroup coordination Software product engineering Integrated software management Training program Organization process definition Organization process focus 2 3 2 3 Software configuration management Software quality assurance Software subcontract management Software project tracking and oversight Software project planning Requirements management 4 4 4 3 3 2 TOTALS © 1998 pragma SYSTEMS CORPORATION 4 No. of Key Practices per KPA Subtotal 9 Subtotal 6 Subtotal 17 Subtotal 20 52 19 19 18 13 18 9 17 20 19 16 11 16 21 17 22 24 25 12 TOTALS Subtotal 56 Subtotal 31 Subtotal 108 Subtotal 121 316 Serverpc: process. Max Release Baseline: Collateral Materials: Spin pmax. ppt

Key Process Areas 18 Key Process Areas 5 major sections in each Key Process Area Several people are required to initiate action in each Key Process Area No one person can fully satisfy any one Key Process Area © 1998 pragma SYSTEMS CORPORATION 5 Serverpc: process. Max Release Baseline: Collateral Materials: Spin pmax. ppt
SW-CMM Characteristics Not written to support process definers/ documenters Especially not written to support software development and maintenance project personnel © 1998 pragma SYSTEMS CORPORATION 6 Serverpc: process. Max Release Baseline: Collateral Materials: Spin pmax. ppt
Process Improvement Industry Solution space for Internal Business Challenges People Process Technology © 1998 pragma SYSTEMS CORPORATION 7 Serverpc: process. Max Release Baseline: Collateral Materials: Spin pmax. ppt

Process Improvement Industry Usual approach: Internal staff, facilitated sessions, and the SW-CMM, starting with page 1 of Level 2 Result: Many false starts and if successful, a Key Process Area by Key Process Area solution © 1998 pragma SYSTEMS CORPORATION 8 Serverpc: process. Max Release Baseline: Collateral Materials: Spin pmax. ppt

KPA by KPA Approach Customized Key Process Area solutions are more familiar and easier to understand than the SW-CMM, but still require a significant study and interpretation effort by each project. Easy to define, hard to rollout © 1998 pragma SYSTEMS CORPORATION 9 Serverpc: process. Max Release Baseline: Collateral Materials: Spin pmax. ppt

Scenario of the 1990 s © 1998 pragma SYSTEMS CORPORATION

SPI Project Initiation Process-oriented informal group begins meeting over brown bag lunches. At least one of them has an urgent proposal deadline and 2 or 3 have been to a processrelated conference. One of them gets appointed SEPG Leader and is allowed to charge 1 day per week for this work. Process Action Teams (PAT) are formed, with Key Process Area-type names and PAT Leaders are appointed. PATs are allowed to meet and charge overhead 4 hours per week person usually on Friday afternoons. © 1998 pragma SYSTEMS CORPORATION 11 Serverpc: process. Max Release Baseline: Collateral Materials: Spin pmax. ppt

Wild Enthusiasm Appoint a full-time SEPG Leader. Increase the budget for the PATs. Write the charters for the PATs and the SEPG. Replace some of the PAT Leaders and some of the PAT membership. Exit Criteria for Wild Enthusiasm: $250 K to $1 M must have been spent and 6 to 18 months must have past. © 1998 pragma SYSTEMS CORPORATION 12 Serverpc: process. Max Release Baseline: Collateral Materials: Spin pmax. ppt

Mild Enthusiasm A Software Process Improvement Plan is developed (revised) by the SEPG Leader. Reform the PATs with 1 or 2 full-time people on each PAT and replace some of the PAT Leaders and membership. SEPG Leader tracks progress against the Plan. One or two strong PAT leaders get promoted into line management or otherwise get pulled back onto project or proposal work. The SEPG Leader leaves or is removed. Exit Criteria for Mild Enthusiasm: $500 K to $2 M must have been spent and At least 24 months must have past. © 1998 pragma SYSTEMS CORPORATION 13 Serverpc: process. Max Release Baseline: Collateral Materials: Spin pmax. ppt

Disillusionment Pressure intensifies from the sponsor to get an official assessment. Panic sets in. No one has actually used the processes yet. Get PAT members to pilot the processes on their projects. Hopefully, these projects have a compelling business need to achieve Level 2. Conduct brown bag lunches to teach the CMM to potential assessment interviewees. Conduct a pre-assessment. © 1998 pragma SYSTEMS CORPORATION 14 Serverpc: process. Max Release Baseline: Collateral Materials: Spin pmax. ppt

Chaos Panic intensifies. The processes are not fully compliant with the CMM, even if they are used. Rework and reinstall the processes on the pilot projects. Accelerate the CMM lunches for potential assessment interviewees. © 1998 pragma SYSTEMS CORPORATION 15 Serverpc: process. Max Release Baseline: Collateral Materials: Spin pmax. ppt

Gaming the Assessment We no longer talk about how much money has been spent or how much time has past. We are solely focused on the impending assessment. Stack the assessment team with PAT members and the SEPG Leader. Overwhelm the assessment team with paper and interviewees who “speak” the CMM. At the Findings Briefout the sponsor congratulates everyone on the great work and says s/he wants Level 3 in fewer than 12 months. © 1998 pragma SYSTEMS CORPORATION 16 Serverpc: process. Max Release Baseline: Collateral Materials: Spin pmax. ppt

Post-Assessment Fallout–Part 1 After the assessment, the pilot projects go back to business as usual and all other projects are not interested in the agony the pilot projects endured. Twelve months later, can’t conduct an assessment because organization would probably fail Level 2. © 1998 pragma SYSTEMS CORPORATION 17 Serverpc: process. Max Release Baseline: Collateral Materials: Spin pmax. ppt

Post-Assessment Fallout –Part 2 Search for the guilty. Punish the innocent. Promote the nonparticipants. If the business need for the SW-CMM still exists, define the requirements. © 1998 pragma SYSTEMS CORPORATION 18 Serverpc: process. Max Release Baseline: Collateral Materials: Spin pmax. ppt

The Project Perspective Process people consume a lot of overhead $$. Process people produce a lot of binders filled with pictures of boxes and arrows. © 1998 pragma SYSTEMS CORPORATION 19 Serverpc: process. Max Release Baseline: Collateral Materials: Spin pmax. ppt

Pithy (but not useful or accurate) Sayings from the Field You can’t buy a process for intellectual work, you must create it yourself. You must document the as-is process first. Document what you do and you are a Level 2. © 1998 pragma SYSTEMS CORPORATION 20 Serverpc: process. Max Release Baseline: Collateral Materials: Spin pmax. ppt
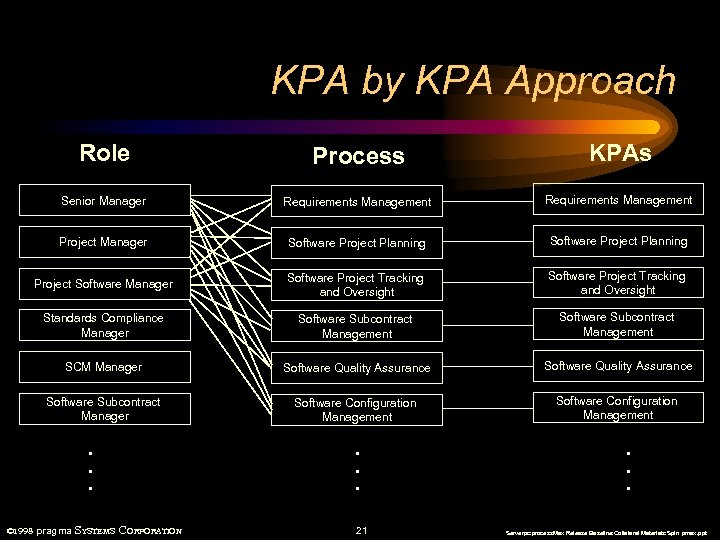
KPA by KPA Approach Role Process KPAs Senior Manager Requirements Management Project Manager Software Project Planning Project Software Manager Software Project Tracking and Oversight Standards Compliance Manager Software Subcontract Management SCM Manager Software Quality Assurance Software Subcontract Manager Software Configuration Management . . . © 1998 pragma SYSTEMS CORPORATION . . . 21 . . . Serverpc: process. Max Release Baseline: Collateral Materials: Spin pmax. ppt
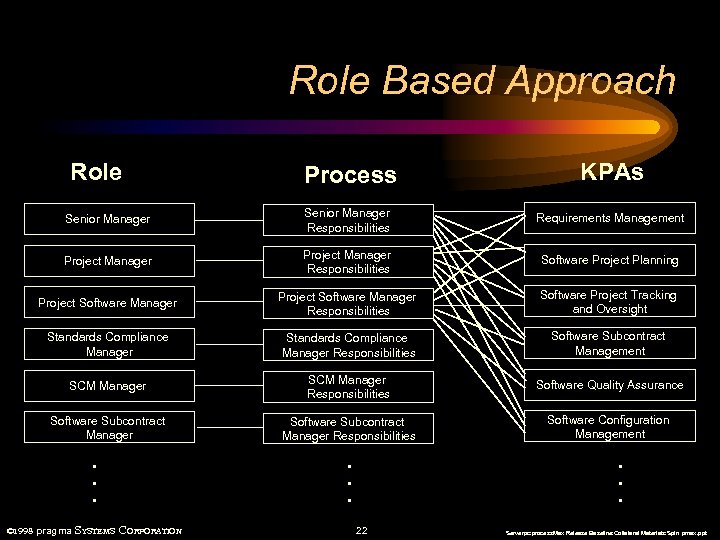
Role Based Approach Role Process KPAs Senior Manager Responsibilities Requirements Management Project Manager Responsibilities Software Project Planning Project Software Manager Responsibilities Software Project Tracking and Oversight Standards Compliance Manager Responsibilities Software Subcontract Management SCM Manager Responsibilities Software Quality Assurance Software Subcontract Manager Responsibilities Software Configuration Management . . . © 1998 pragma SYSTEMS CORPORATION . . . 22 Serverpc: process. Max Release Baseline: Collateral Materials: Spin pmax. ppt
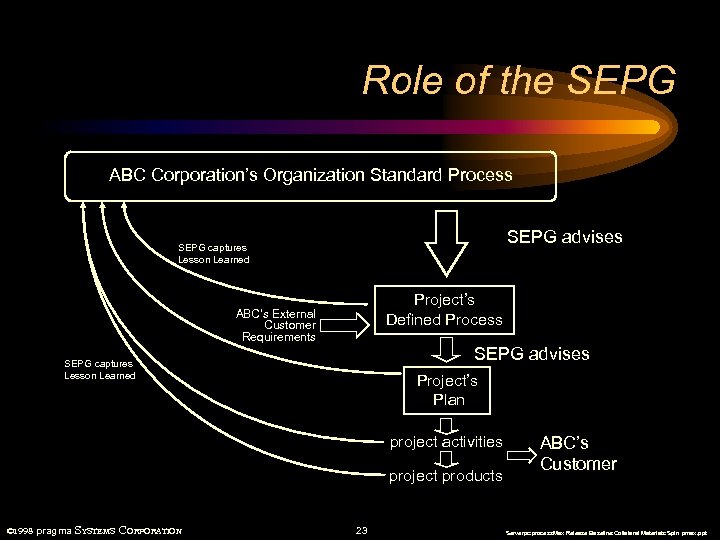
Role of the SEPG ABC Corporation’s Organization Standard Process SEPG advises SEPG captures Lesson Learned Project’s Defined Process ABC’s External Customer Requirements SEPG advises SEPG captures Lesson Learned Project’s Plan project activities project products © 1998 pragma SYSTEMS CORPORATION 23 ABC’s Customer Serverpc: process. Max Release Baseline: Collateral Materials: Spin pmax. ppt

Software Engineering Process Group Develop the SPI Project Plan Monitor Progress in Preparation for Progress and Strategic Reviews with the Sponsor Provide Consulting to Project Personnel in the Use of the Processes Identify Needs for New Tools and Processes Document Requirements for New Tools and Processes Evaluate and Select Good Worked Examples of Software Work Products for Reference by Other Projects Prepare Process Change Requests Implement Approved Change Requests to the Processes © 1998 pragma SYSTEMS CORPORATION 24 Serverpc: process. Max Release Baseline: Collateral Materials: Spin pmax. ppt

Software Process Improvement Sponsor Approve the Software Process Improvement Plan Approve Organizational Software Process Policies Conduct SPI Project Strategic Reviews Conduct SPI Project Progress Reviews Communicate SPI Objectives Create Incentives for use of the Processes Approve Changes to the Organization’s Process Enforce the use of Processes with his/her Direct Reports © 1998 pragma SYSTEMS CORPORATION 25 Serverpc: process. Max Release Baseline: Collateral Materials: Spin pmax. ppt

Lessons Learned from the Role-Based Approach Study and interpretation of the SW-CMM is removed from the critical path for project personnel. Processes look familiar and business-oriented. Learning curve for role-based processes is much shorter and less frustrating than for KPA-based processes. Individual and organizational resistance is much less than with the KPA-based approach. © 1998 pragma SYSTEMS CORPORATION 26 Serverpc: process. Max Release Baseline: Collateral Materials: Spin pmax. ppt
5d3cdd7010d6c75d13023b04af666e39.ppt