0ff710e60a2715a71d5a156b0fad68b3.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 22
 Process Control: Quality Control of Qualitative and Semi-Quantitative Procedures 1
Process Control: Quality Control of Qualitative and Semi-Quantitative Procedures 1
 Learning Objectives n n At the end of this module, participants should be able to: Differentiate between built-in and traditional controls. Describe how to use stock cultures for microbiology QC. Discuss the use of quality control procedures for stains used in microscopic examination. Describe methods for verifying performance of microbiological media. Process Control: Qualitative and Semi-Quantitative QC-Module 8
Learning Objectives n n At the end of this module, participants should be able to: Differentiate between built-in and traditional controls. Describe how to use stock cultures for microbiology QC. Discuss the use of quality control procedures for stains used in microscopic examination. Describe methods for verifying performance of microbiological media. Process Control: Qualitative and Semi-Quantitative QC-Module 8
 Scenario Laboratory A performs a culture, and Pseudomonas aeruginosa is identified. What QC measures can you use to confirm that the isolate is correctly identified? Process Control: Qualitative and Semi-Quantitative QC-Module 8 3
Scenario Laboratory A performs a culture, and Pseudomonas aeruginosa is identified. What QC measures can you use to confirm that the isolate is correctly identified? Process Control: Qualitative and Semi-Quantitative QC-Module 8 3
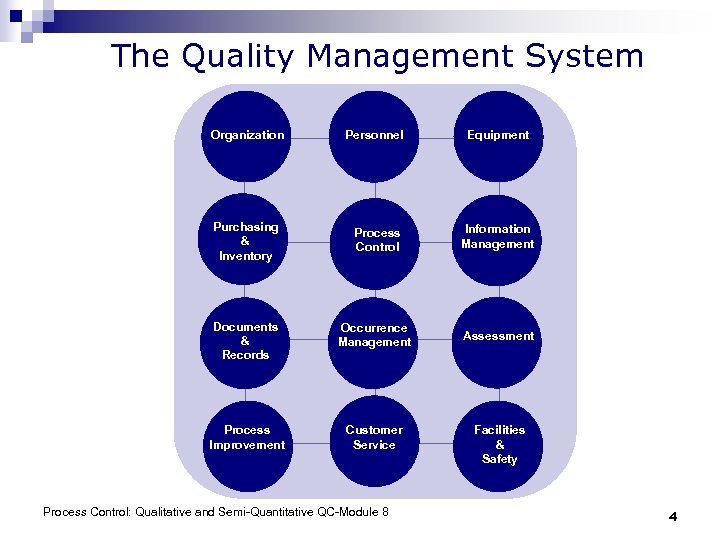 The Quality Management System Organization Personnel Equipment Purchasing & Inventory Process Control Information Management Documents & Records Occurrence Management Assessment Process Improvement Customer Service Process Control: Qualitative and Semi-Quantitative QC-Module 8 Facilities & Safety 4
The Quality Management System Organization Personnel Equipment Purchasing & Inventory Process Control Information Management Documents & Records Occurrence Management Assessment Process Improvement Customer Service Process Control: Qualitative and Semi-Quantitative QC-Module 8 Facilities & Safety 4
 Qualitative or semi-quantitative tests Examples n n n microscopic examinations dipsticks serologic procedures microbiological procedures any reaction that produces non-numeric results Process Control: Qualitative and Semi-Quantitative QC-Module 8
Qualitative or semi-quantitative tests Examples n n n microscopic examinations dipsticks serologic procedures microbiological procedures any reaction that produces non-numeric results Process Control: Qualitative and Semi-Quantitative QC-Module 8
 Important Concepts sample management n staff competency n equipment maintenance n control materials n stains, media and reagents management n record keeping n Process Control: Qualitative and Semi-Quantitative QC-Module 8
Important Concepts sample management n staff competency n equipment maintenance n control materials n stains, media and reagents management n record keeping n Process Control: Qualitative and Semi-Quantitative QC-Module 8
 Quality Control Materials n built-in controls n control materials that mimic patient samples n reference organisms Process Control: Qualitative and Semi-Quantitative QC-Module 8 7
Quality Control Materials n built-in controls n control materials that mimic patient samples n reference organisms Process Control: Qualitative and Semi-Quantitative QC-Module 8 7
 Built-in Controls integrated into the design of a test kit device n automatically run with each test performed n assess certain aspects of kit performance n may not assess entire testing process n Process Control: Qualitative and Semi-Quantitative QC-Module 8 8
Built-in Controls integrated into the design of a test kit device n automatically run with each test performed n assess certain aspects of kit performance n may not assess entire testing process n Process Control: Qualitative and Semi-Quantitative QC-Module 8 8
 Traditional Controls n materials with known reactivity n mimic patient samples n assess the integrity of the entire test system Process Control: Qualitative and Semi-Quantitative QC-Module 8 9
Traditional Controls n materials with known reactivity n mimic patient samples n assess the integrity of the entire test system Process Control: Qualitative and Semi-Quantitative QC-Module 8 9
 Using Traditional Controls n n n test as per patient samples use a positive and negative control include a weak positive control for immunological procedures choose positive controls close to the cutoff value include control to monitor extraction phase Process Control: Qualitative and Semi-Quantitative QC-Module 8
Using Traditional Controls n n n test as per patient samples use a positive and negative control include a weak positive control for immunological procedures choose positive controls close to the cutoff value include control to monitor extraction phase Process Control: Qualitative and Semi-Quantitative QC-Module 8
 Stock Cultures for QC n n reference strains in-house developed strains predictable reactions in stains and media ensure media, reagents and supplies work as intended Process Control: Qualitative and Semi-Quantitative QC-Module 8
Stock Cultures for QC n n reference strains in-house developed strains predictable reactions in stains and media ensure media, reagents and supplies work as intended Process Control: Qualitative and Semi-Quantitative QC-Module 8
 Sources for Obtaining Reference Strains § ATCC-American Type Culture Collection § NTCC-National Type Culture Collection (UK) § CIP- Pasteur Institute Collection (France) Process Control: Qualitative and Semi-Quantitative QC-Module 8
Sources for Obtaining Reference Strains § ATCC-American Type Culture Collection § NTCC-National Type Culture Collection (UK) § CIP- Pasteur Institute Collection (France) Process Control: Qualitative and Semi-Quantitative QC-Module 8
 Stains are important— take care of them! Continued Attention Process Control: Qualitative and Semi-Quantitative QC-Module 8 No Attention 13 13
Stains are important— take care of them! Continued Attention Process Control: Qualitative and Semi-Quantitative QC-Module 8 No Attention 13 13
 Stain Management n use established procedure for preparation or reconstitution n label: content, concentration, date prepared and placed in service, expiration, initials n store appropriately Process Control: Qualitative and Semi-Quantitative QC-Module 8 14 14
Stain Management n use established procedure for preparation or reconstitution n label: content, concentration, date prepared and placed in service, expiration, initials n store appropriately Process Control: Qualitative and Semi-Quantitative QC-Module 8 14 14
 Quality Control for Stains As appropriate for particular stain: § check with known organisms or cells § examine for crystal shards or for precipitation § examine for contaminants such as bacteria and fungi Left: Wright stain Right: Gram stain Process Control: Qualitative and Semi-Quantitative QC-Module 8 15 15
Quality Control for Stains As appropriate for particular stain: § check with known organisms or cells § examine for crystal shards or for precipitation § examine for contaminants such as bacteria and fungi Left: Wright stain Right: Gram stain Process Control: Qualitative and Semi-Quantitative QC-Module 8 15 15
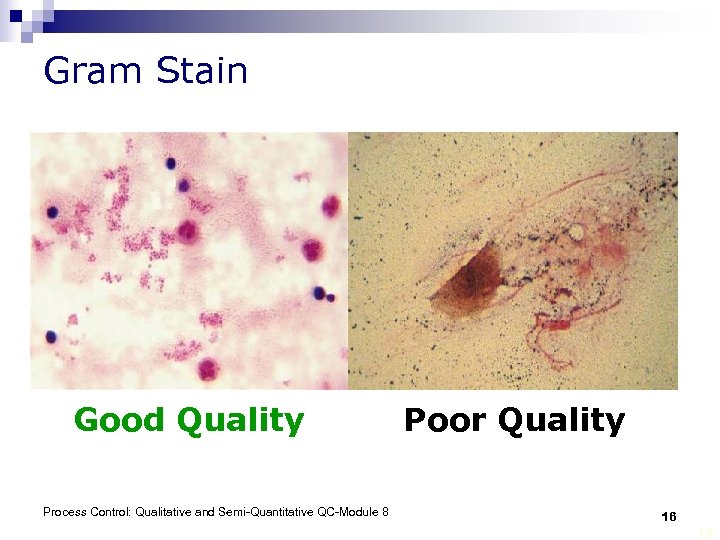 Gram Stain Good Quality Process Control: Qualitative and Semi-Quantitative QC-Module 8 Poor Quality 16 16
Gram Stain Good Quality Process Control: Qualitative and Semi-Quantitative QC-Module 8 Poor Quality 16 16
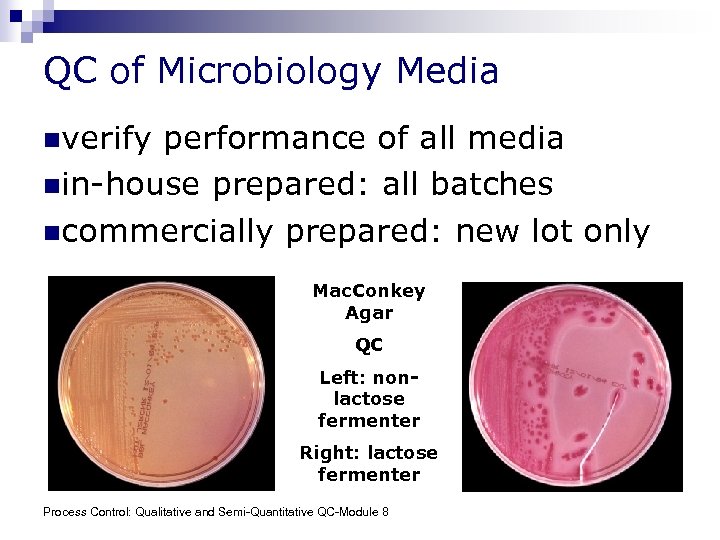 QC of Microbiology Media nverify performance of all media nin-house prepared: all batches ncommercially prepared: new lot only Mac. Conkey Agar QC Left: nonlactose fermenter Right: lactose fermenter Process Control: Qualitative and Semi-Quantitative QC-Module 8
QC of Microbiology Media nverify performance of all media nin-house prepared: all batches ncommercially prepared: new lot only Mac. Conkey Agar QC Left: nonlactose fermenter Right: lactose fermenter Process Control: Qualitative and Semi-Quantitative QC-Module 8
 Media Problems to Avoid § out-dated § dried-out § contaminated Human blood should not be used because: § too much batch to batch variation §may include inhibitory substances, including antimicrobials §may contain biohazards (e. g. , hepatitis virus) Process Control: Qualitative and Semi-Quantitative QC-Module 8
Media Problems to Avoid § out-dated § dried-out § contaminated Human blood should not be used because: § too much batch to batch variation §may include inhibitory substances, including antimicrobials §may contain biohazards (e. g. , hepatitis virus) Process Control: Qualitative and Semi-Quantitative QC-Module 8
 Quality Control of Growth Media n keep records for media prepared inhouse n record outcomes in a dedicated media logbook for: ¨ n p. H, sterility, ability to support growth using stock cultures, biochemical response of stock cultures frequency ¨ test each new batch or lot number Process Control: Qualitative and Semi-Quantitative QC-Module 8
Quality Control of Growth Media n keep records for media prepared inhouse n record outcomes in a dedicated media logbook for: ¨ n p. H, sterility, ability to support growth using stock cultures, biochemical response of stock cultures frequency ¨ test each new batch or lot number Process Control: Qualitative and Semi-Quantitative QC-Module 8
 Summary § qualitative tests produce non- numerical results § semi-quantitative tests give an estimate § establish a QC program for qualitative and semiquantitative tests Process Control: Qualitative and Semi-Quantitative QC-Module 8 20 20
Summary § qualitative tests produce non- numerical results § semi-quantitative tests give an estimate § establish a QC program for qualitative and semiquantitative tests Process Control: Qualitative and Semi-Quantitative QC-Module 8 20 20
 Key Messages n QC procedures followed by ALL staff n always record QC results and corrective actions n If QC results are not acceptable, do not report patient results! Process Control: Qualitative and Semi-Quantitative QC-Module 8
Key Messages n QC procedures followed by ALL staff n always record QC results and corrective actions n If QC results are not acceptable, do not report patient results! Process Control: Qualitative and Semi-Quantitative QC-Module 8
 Organization Personnel Equipment Questions? Purchasing & Inventory Process Control Documents & Records Occurrence Management Process Improvement Customer Service Information Management Comments? Assessment Facilities & Safety Process Control: Qualitative and Semi-Quantitative QC-Module 8 22
Organization Personnel Equipment Questions? Purchasing & Inventory Process Control Documents & Records Occurrence Management Process Improvement Customer Service Information Management Comments? Assessment Facilities & Safety Process Control: Qualitative and Semi-Quantitative QC-Module 8 22


