Problem-Based Learning Creating opportunities for inquiry, investigation, research,


Problem-Based Learning Creating opportunities for inquiry, investigation, research, and resolution.

What is Problem-Based Learning? An instructional method which focuses on the investigation and resolution of messy, “real world” problems as a context for students to learn critical thinking and problem solving skills “Students work individually and/or in groups to solve challenging problems that are authentic, curriculum-based, and often interdisciplinary”

A problem-based classroom lesson: Based on your reading and the statistics that you have interpreted, you are aware that Hispanic Americans face a number of challenges, culturally, emotionally, educationally, and economically.

Benefits of PBL Makes learning relevant to the real world (and answers the dreaded question…) Moves learning from a passive activity to an active activity -- learning becomes the act of discovery Increases motivation -- students are more engaged, interested, and energetic learners as they make a personal investment in the outcome of their inquiry

More Benefits of PBL Promotes an interdisciplinary approach to learning Promotes collaborative learning Requires advanced cognitive skills, higher order thinking Requires research from multiple sources Ideal for heterogeneous classrooms Reverses teacher and student roles

Comparison of teaching methods Role of Teacher: As expert: Directs Thinking Holds Knowledge Evaluates Students Role of Student: As receiver: Inert Inactive Empty Lecture

Comparison of teaching methods Role of Teacher: As conductor: Orchestrates learning Guides rehearsal Evaluates Students Role of Student: As follower: Responsive Semi-active Waiting to be lead Direct Instruction
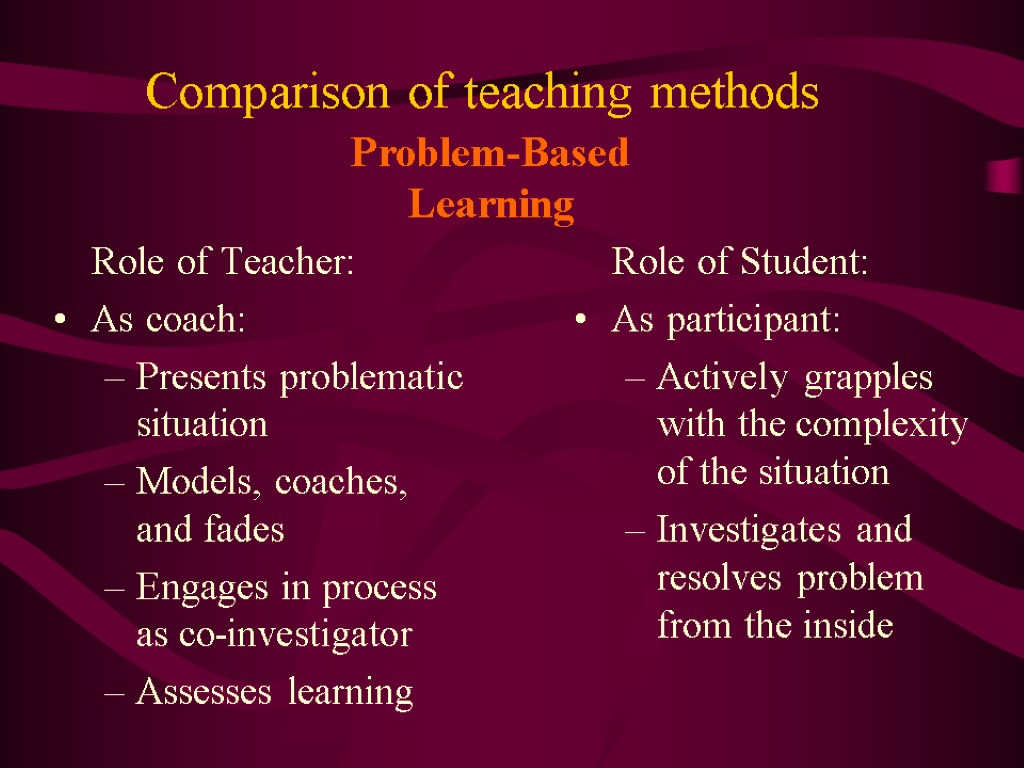
Comparison of teaching methods Role of Teacher: As coach: Presents problematic situation Models, coaches, and fades Engages in process as co-investigator Assesses learning Role of Student: As participant: Actively grapples with the complexity of the situation Investigates and resolves problem from the inside Problem-Based Learning

Teachers = Active Coaches Diagnosing needs Mentoring learning Encouraging process Questioning thinking Modeling inquiry

Step 1. Create a PROBLEM Find a real life situation with multiple solutions that interests the students Organize the students into teams

Step2. Problem analysis Students list known facts List unknowns Research unknowns

Step3. Test theories Students must model the situation to test their theories Students generate possible solutions

Step 4. PRESENTING Students select the solution that best fits Students present their solutions and methods

5. Generate Solutions Learners begin to recommend solutions based on the information they have gathered Students’ goal is to develop best solution according to problem conditions Responsible thinkers are able to justify solution(s) with supportive evidence

6. Performance Assessment Goal is for teacher to assess LEARNING Ongoing assessments throughout process are ideal -good for assessing both individual and group accountability Teachers embed instruction to help students explore important information related to the problem Teacher typically assesses culminating performance via a rubric -- on content, presentation skills, teamwork, and fit of solution.

Assessment Options Video Presentation Panel Discussion Patient Consultation Poster Session Letter to a committee Web page Report Map Expert Panel Debate Charts Proposal

7. Debriefing the problem Even after final product is complete, more opportunities for learning exist. Consider the following questions as a way of providing closure: Were the strategies you used to solve the problem effective? What would you do differently? What is the foundational or “big” issue at stake? What did you learn academically? What can you do now that you didn’t think you could do before?

Anti-Americanism Why are anti-American feelings prevalent around the world? What can the United States do to change this perception in the eyes of the world and improve foreign relations?

Role of the Student You are a United Nations representative for the country of ___________. At your next meeting, you will need to discuss the grievances your country has with the United States. You will also need to include a list of recommendations for the U.S. on how they can work to remedy these problems.

Questions to Think About Why do many nations/people have anti-American feelings? Did the U.S. do anything to provoke these sentiments? Has the U.S. tried to fix past actions that caused ill feelings among nations? Specifically, what grievances does your nation have with the U.S.?

Problem Statement How can we ______ so that _________? How can we, as nations, inform the President of the U.S. of past actions against us so that we can move toward a more peaceful relationship?
pbl_presentation.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 21

