sudno_na_vozdushnoy_podushke.pptx
- Количество слайдов: 17

Problem № 9 Hovercraft Done by: student of 9 grade Nevsky Dmitry Team “название” IYPT-2015

Problem formulation A simple model hovercraft can be built using a CD and a balloon filled with air attached via a tube. Exiting air can lift the device making it float over a surface with low friction. Investigate how the relevant parameters influence the time of the 'low-friction' state. 2

Objectives 1) Make experimental setup 2) Do an experiment - run “Hovercraft" 3) Find the parameters that determine the time and altitude 4) Try to change the diameter of the hole and the mass of the structure 5) Optimize the construction 6) Draw conclusions about the work done 3

Setup 1) ball 2)stopper with a lid 3)Disk 4
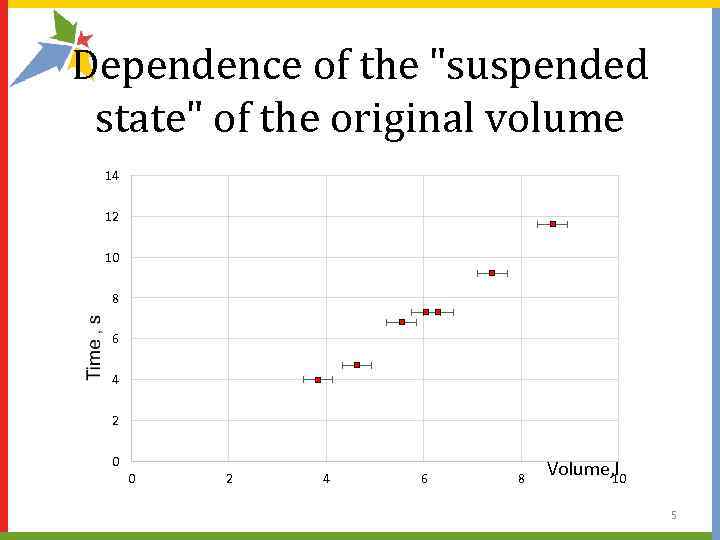
Dependence of the "suspended state" of the original volume 14 12 10 8 6 4 2 0 0 2 4 6 8 Volume, l 10 5
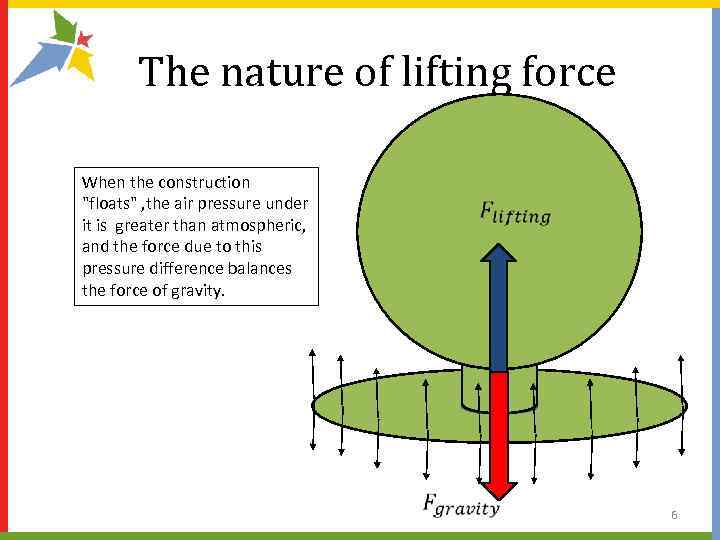
The nature of lifting force When the construction "floats" , the air pressure under it is greater than atmospheric, and the force due to this pressure difference balances the force of gravity. 6
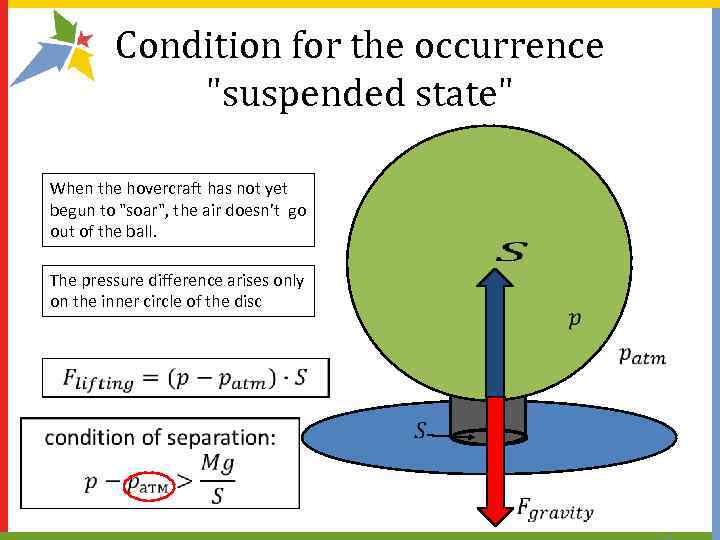
Condition for the occurrence "suspended state" When the hovercraft has not yet begun to "soar", the air doesn’t go out of the ball. The pressure difference arises only on the inner circle of the disc

Measurement of the parameters of the ball The ball was blown away through a narrow opening, starred dependence of the pressure inside the ball from time to time. 8
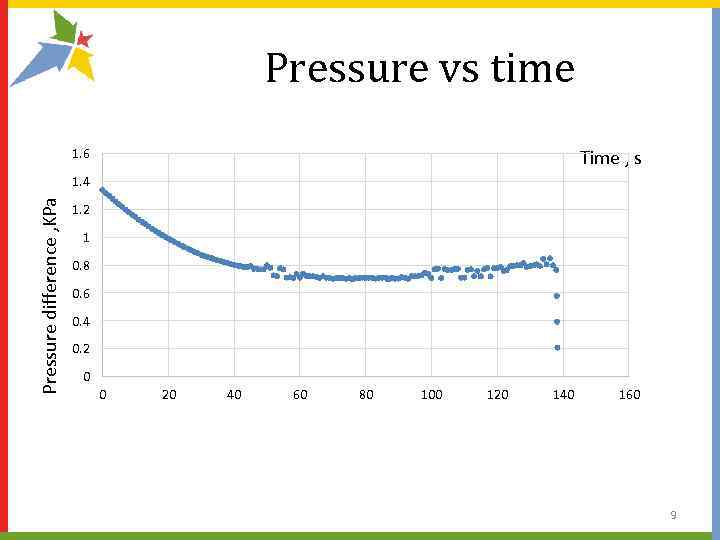
Pressure vs time Time , s 1. 6 Pressure difference , KPa 1. 4 1. 2 1 0. 8 0. 6 0. 4 0. 2 0 0 20 40 60 80 100 120 140 160 9

Getting pressure dependence of the volume of the ball The frictional force acting on the air in the tube is proportional to its velocity. The tube is thin, so the friction force is the force due to the pressure difference inside and outside. Air velocity is directly proportional to pressure difference Δ . Knowing ( = 0) and the volume of the inflated ball, you can find the coefficient α and dependence ( ). With the volume and pressure dependence of the time can be plotted as a function of the volume of the pressure. 10
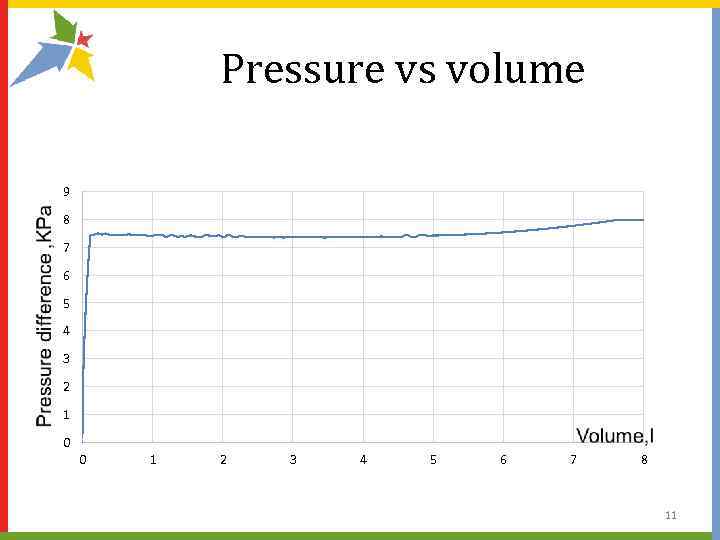
Pressure vs volume 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 11
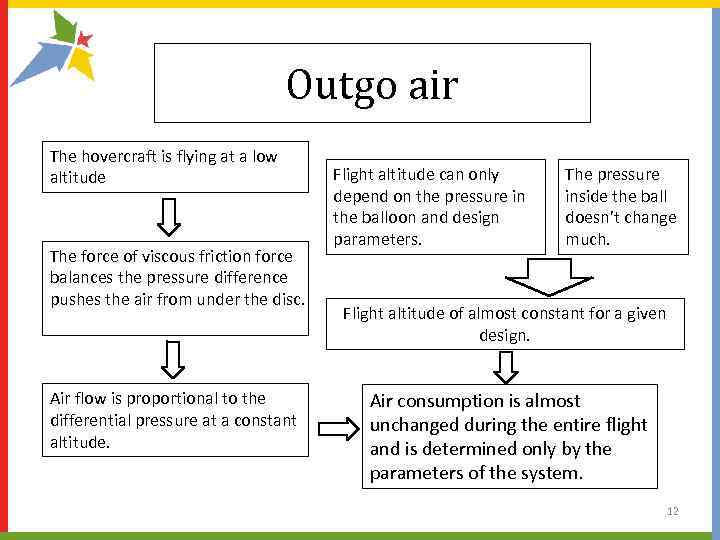
Outgo air The hovercraft is flying at a low altitude The force of viscous friction force balances the pressure difference pushes the air from under the disc. Air flow is proportional to the differential pressure at a constant altitude. Flight altitude can only depend on the pressure in the balloon and design parameters. The pressure inside the ball doesn’t change much. Flight altitude of almost constant for a given design. Air consumption is almost unchanged during the entire flight and is determined only by the parameters of the system. 12



Conclusions 1. A workable construction was made 2. Removed the dependence of the "suspended state" of the original volume of the ball. 3. Dependence of the pressure lifted the ball from its scope. 4. Found an explanation of the linear dependence of the "suspended state" of the original volume. 15

Literature 1) 2) 3) 4) Jackson Symmons “An investigation of lami” Stokes equation in a toy CD hovercraft Noundary -layer Theory IOPscience 16

Thank you!
sudno_na_vozdushnoy_podushke.pptx