a66400c6febfb25f479582d958b828bf.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 22

Problem 6. 7 Flow rate R = 150, 000 lbs/ yr Purchasing cost = $1. 50 Also add shipping cost (sh) sh: Q<10, 000 0. 17 10, 000<Q<15, 000 0. 15 Q>15, 000 0. 13 Inventory cost of capital H = 0. 15 (? ? ) H = 0. 15 (1. 5+sh) S 1 = $50 paper work S 2 = $350 forklift S = 400 or 50
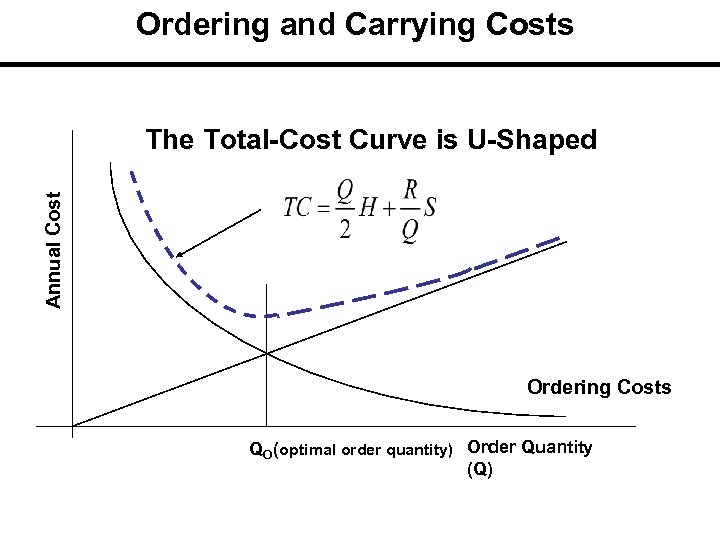
Ordering and Carrying Costs Annual Cost The Total-Cost Curve is U-Shaped Ordering Costs QO (optimal order quantity) Order Quantity (Q)
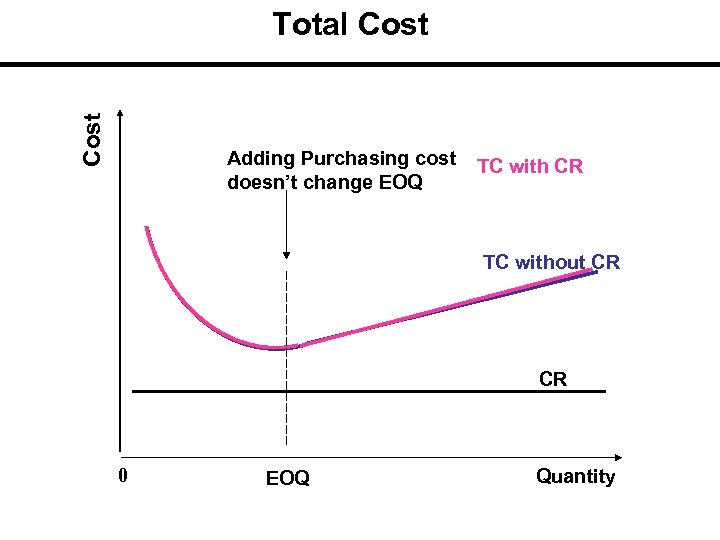
Cost Total Cost Adding Purchasing cost doesn’t change EOQ TC with CR TC without CR CR 0 EOQ Quantity

a) What is the optimal EOQ Wish for the best. Hope EOQ > 15, 000 Then take advantage of both 1) EOQ minimal carrying + ordering costs 2) Minimal shipping cost Therefore approach the problem using H= 1. 5 +. 13 = 0. 15(1. 63) = 0. 2445 S = 400 R = 150, 000 EOQ = Problem 6. 7 Flow rate R = 150, 000 lbs/ yr Purchasing cost = $1. 50 Sh: Q<10, 000 0. 17 10, 000<Q<15, 000 0. 15 Q>15, 000 0. 13 H = 0. 15 (1. 5+sh) S 1 = $50 paper work S 2 = $350 forklift S = 400 or 50 =22, 154 We are very lucky: Q* = 22, 154 not only minimized our carrying + ordering costs, but also shipping costs Total cost = 400(150000/22154) +. 2445(22154/2) + 150000*1. 63 = 2708. 3 + 244500 = 249, 917

b) What is the optimal EOQ if we buy a forklift Wish for the best. Again, approach the problem using H= 1. 5 +. 13 = 0. 15(1. 63) = 0. 2445 But S = 50, R = 150, 000 EOQ = Problem 6. 7 Shipping (sh) Q<10, 000<Q<15, 000 Q>15, 000 H = 0. 15 (C+sh) =7, 832 But at 7, 832 H is not 0. 15(1. 5+0. 13) =. 2445 It is 0. 15(1. 5+0. 17) =. 2505 Is EOQ > or < 7, 832 If H is increases, EOQ decreases. Therefore EOQ is even smaller than 7, 832 EOQ = =7, 738 0. 17 0. 15 0. 13
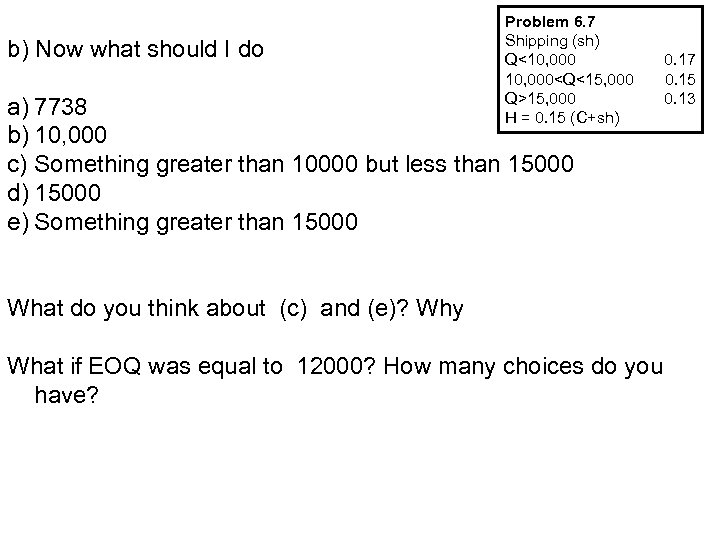
b) Now what should I do Problem 6. 7 Shipping (sh) Q<10, 000<Q<15, 000 Q>15, 000 H = 0. 15 (C+sh) a) 7738 b) 10, 000 c) Something greater than 10000 but less than 15000 d) 15000 e) Something greater than 15000 What do you think about (c) and (e)? Why What if EOQ was equal to 12000? How many choices do you have? 0. 17 0. 15 0. 13
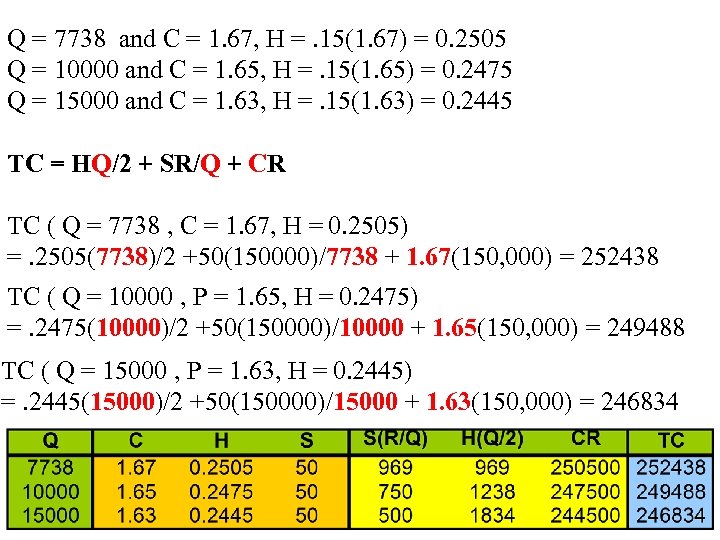
Q = 7738 and C = 1. 67, H =. 15(1. 67) = 0. 2505 Q = 10000 and C = 1. 65, H =. 15(1. 65) = 0. 2475 Q = 15000 and C = 1. 63, H =. 15(1. 63) = 0. 2445 TC = HQ/2 + SR/Q + CR TC ( Q = 7738 , C = 1. 67, H = 0. 2505) =. 2505(7738)/2 +50(150000)/7738 + 1. 67(150, 000) = 252438 TC ( Q = 10000 , P = 1. 65, H = 0. 2475) =. 2475(10000)/2 +50(150000)/10000 + 1. 65(150, 000) = 249488 TC ( Q = 15000 , P = 1. 63, H = 0. 2445) =. 2445(15000)/2 +50(150000)/15000 + 1. 63(150, 000) = 246834

Without forklift TC ( Q = 22, 154 , P = 1. 63, H = 0. 2445, S=400) =. 2445(22154)/2 +400(150000)/22154 + 1. 63(150, 000) = 249917 With forklift TC ( Q = 15000 , P = 1. 63, H = 0. 2445, S=50) =. 2445(15000)/2 +50(150000)/15000 + 1. 63(150, 000) = 246834 Saving due to buying a fork lift = 249917 -246834 = 3083 / yr Cost of capital = 15%

NPV and IRR: If I put P dollar in a bank at the start of year 1 (which is at the end of year 0) and if interest rate (or cost of capital or opportunity cost) is i. For example, i =. 2 means 20% interest rate. The value of my money at the end of year 1 is F 1 where F 1 = P + i. P P(1+i) At the end of year 1, if I put it into the same investment, then F 2 = F 1(1+i) F 2 = P(1+i)2 At the end of year 2, if I put it into the same investment F 3 = F 2(1+i) Since F 2 = P(1+i)2 therefore F 3 = P(1+i)2(1+i) F 3 = P(1+i)3 Following the same logic, at the end of year n, I have Fn = P(1+i)n Now if I have Fn at the end of year n, its present value at the start of year 1 is P = Fn/(1+i)n P = Fn(1+i)-n

Now if I get A dollars at the end of the next n years. And if S is the present value of 5 equal installments of A, then S = A(1+i) -1 + A(1+i)-2 + A(1+i)-3 + A(1+i)-4 + A(1+i)-5 If I multiply both sides by (1+i), then I will have (1+i) S = (1+i) A(1+i) -1 + (1+i) A(1+i)-2 + (1+i)A(1+i)-3 + (1+i)A(1+i)-4 + (1+i)A(1+i)-5 (1+i) S = A + A(1+i)-1 + A(1+i)-2 + A(1+i)-3 + A(1+i)-4 -S = -A(1+i) -1 - A(1+i)-2 - A(1+i)-3 - A(1+i)-4 - A(1+i)-5 i. S = A – A(1+i)-5 S= A[1 -(1+i)-5]/i For n installment S= A[1 -(1+i)-n]/i For our example A= 3083, i = 0. 15, n = 5 S= 3083 [1 -(1. 15)-5]/. 15 3083(1 -. 497177)/. 15 3083(. 502823)/. 15 S = 10335
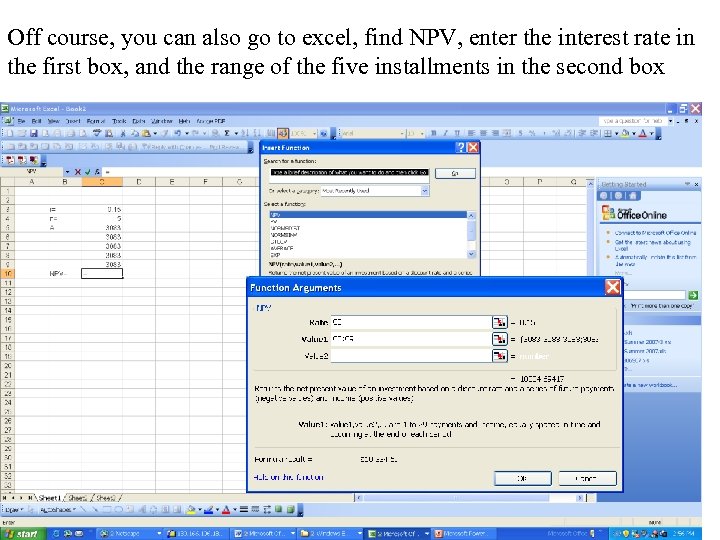
Off course, you can also go to excel, find NPV, enter the interest rate in the first box, and the range of the five installments in the second box
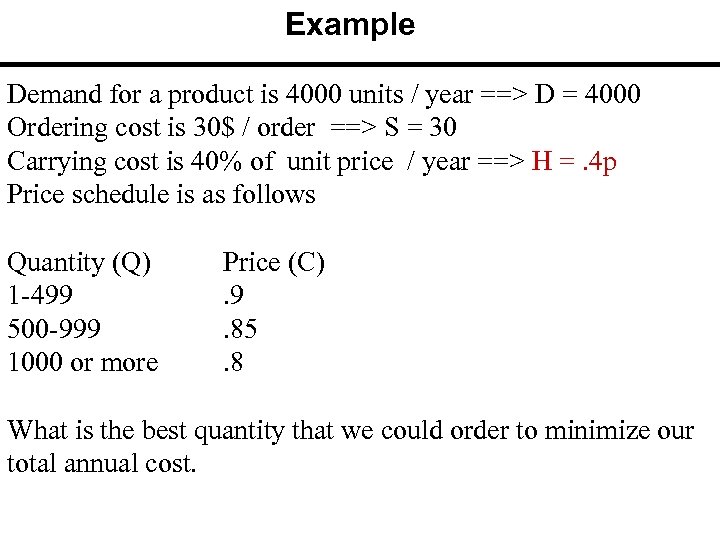
Example Demand for a product is 4000 units / year ==> D = 4000 Ordering cost is 30$ / order ==> S = 30 Carrying cost is 40% of unit price / year ==> H =. 4 p Price schedule is as follows Quantity (Q) 1 -499 500 -999 1000 or more Price (C). 9. 85. 8 What is the best quantity that we could order to minimize our total annual cost.
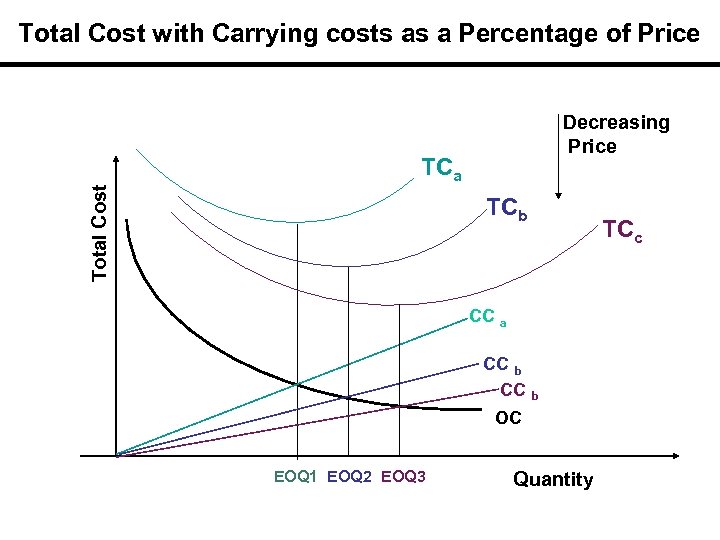
Total Cost with Carrying costs as a Percentage of Price Decreasing Price TCa TCb CC a CC b OC EOQ 1 EOQ 2 EOQ 3 Quantity TCc
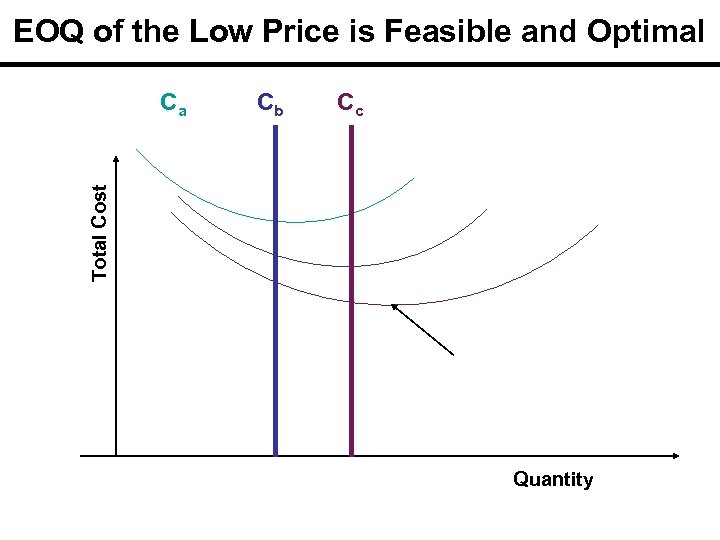
EOQ of the Low Price is Feasible and Optimal Cb Cc Total Cost Ca Quantity
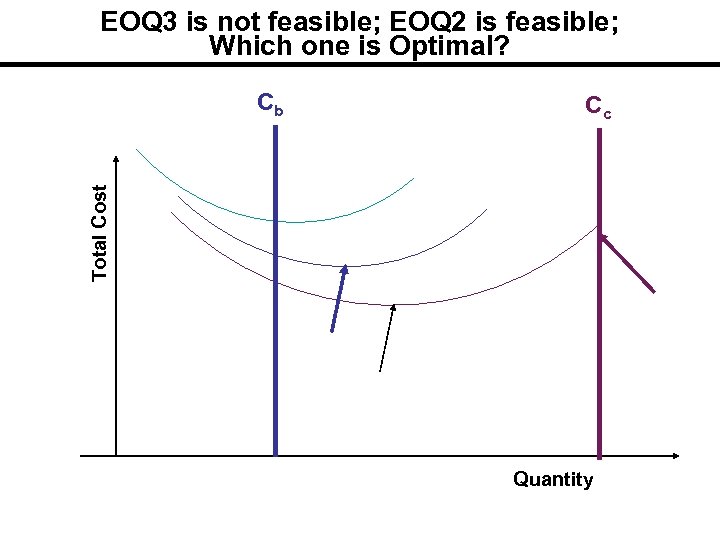
EOQ 3 is not feasible; EOQ 2 is feasible; Which one is Optimal? Cc Total Cost Cb Quantity
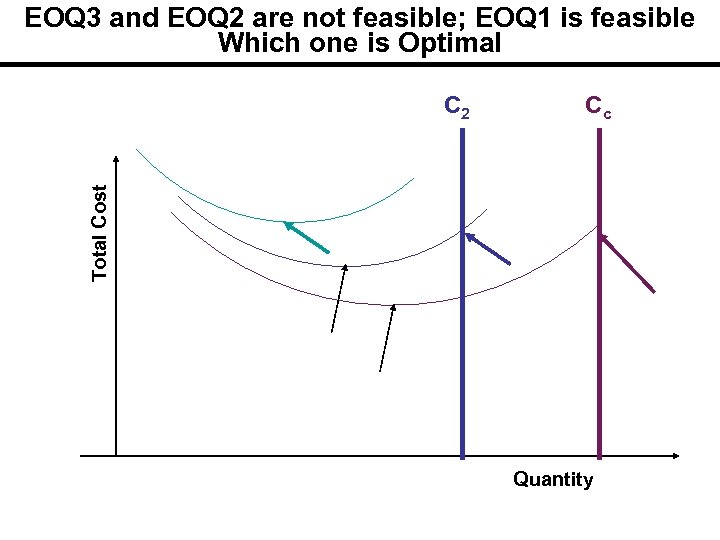
EOQ 3 and EOQ 2 are not feasible; EOQ 1 is feasible Which one is Optimal Cc Total Cost C 2 Quantity
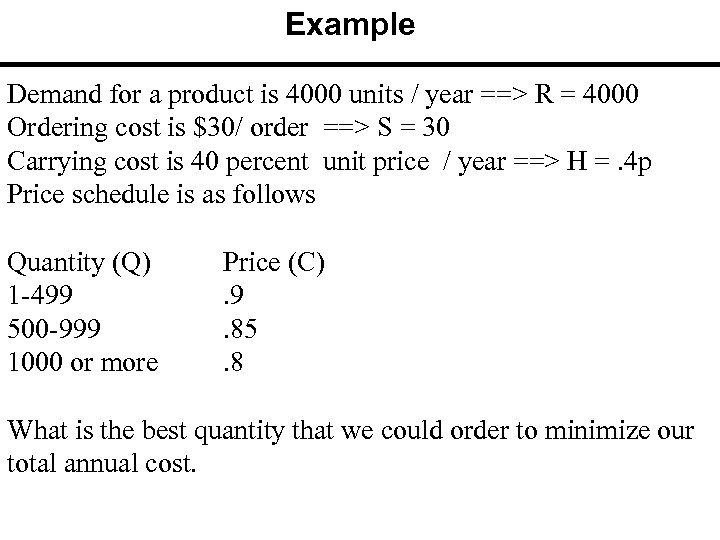
Example Demand for a product is 4000 units / year ==> R = 4000 Ordering cost is $30/ order ==> S = 30 Carrying cost is 40 percent unit price / year ==> H =. 4 p Price schedule is as follows Quantity (Q) 1 -499 500 -999 1000 or more Price (C). 9. 85. 8 What is the best quantity that we could order to minimize our total annual cost.
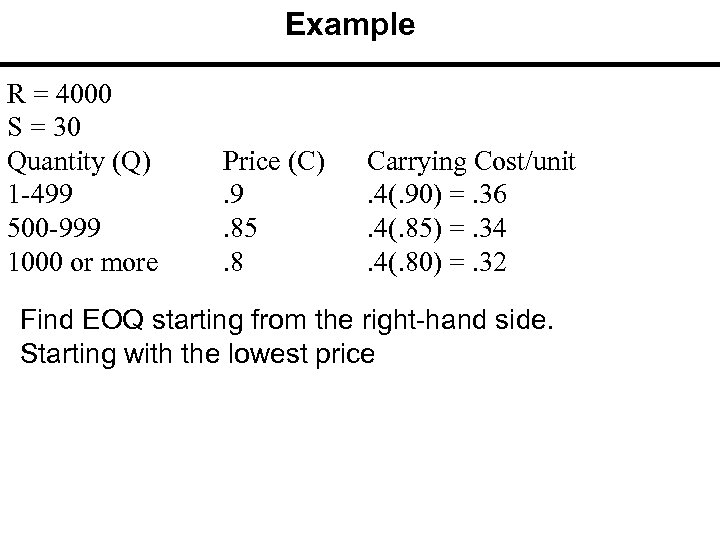
Example R = 4000 S = 30 Quantity (Q) 1 -499 500 -999 1000 or more Price (C). 9. 85. 8 Carrying Cost/unit. 4(. 90) =. 36. 4(. 85) =. 34. 4(. 80) =. 32 Find EOQ starting from the right-hand side. Starting with the lowest price

EOQ 3 not feasible; Compute Cost at 1000 Not feasible TC = HQ/2 + SR/Q + CD TC =. 32(1000)/2 + 30(4000)/1000+. 8(4000) TC = 160 + 120 + 3200= 3480 R = 4000 S = 30 Q 1 -499 500 -999 >1000 C. 9. 85. 8 H. 36. 34. 32

EOQ 2 Feasible; Compare with 1000 Feasible TC = HQ/2 + SD/Q + PD TC =. 34(840)/2 + 30(4000)/840+. 85(4000) TC = 142. 8 + 3400= 3685. 6 D = 4000 S = 30 Q 1 -499 500 -999 >1000 P. 9. 85. 8 H. 36. 34. 32
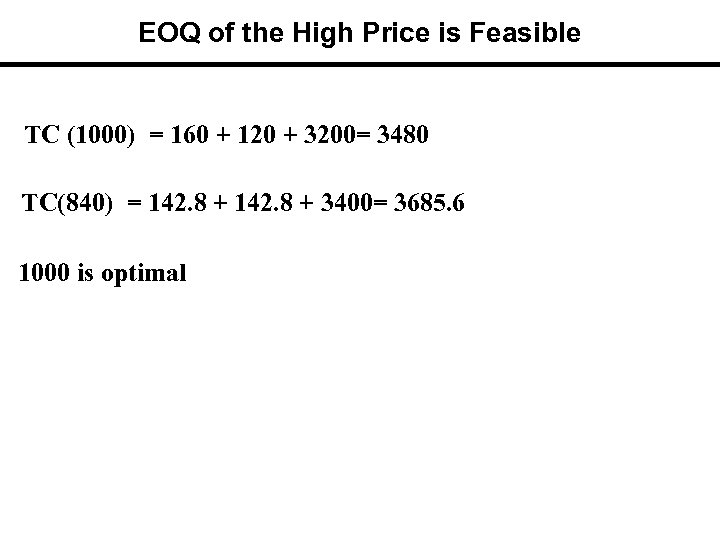
EOQ of the High Price is Feasible TC (1000) = 160 + 120 + 3200= 3480 TC(840) = 142. 8 + 3400= 3685. 6 1000 is optimal
a66400c6febfb25f479582d958b828bf.ppt