8c92923790b94186f2ee76011afd1b49.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 9

Problem 2: Moe Rd/Route 146 Intersection Examine issues related to pedestrians & lane utilization in addition to with-site conditions analyses. n Analysis Plans n 2 a: AM Existing: pedestrian effects n 2 b: PM With-site: lane utilization considerations
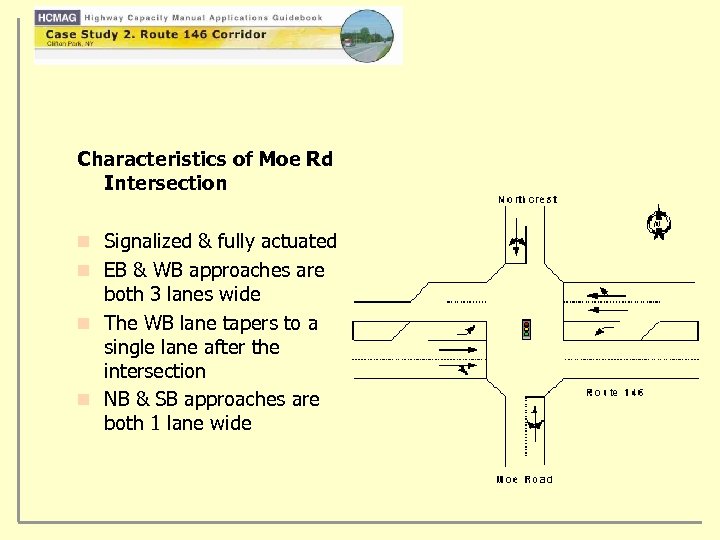
Characteristics of Moe Rd Intersection n Signalized & fully actuated n EB & WB approaches are both 3 lanes wide n The WB lane tapers to a single lane after the intersection n NB & SB approaches are both 1 lane wide

n Arrival Patterns n EB traffic arrives in platoons, discharged from the upstream intersection at the entrance to the Shenendehowa campus n WB traffic arrives in platoons, discharged by the Maxwell Drive intersection n The platoons tend to arrive on red n The NB & SB traffic arrives randomly What Arrival Type would be most appropriate for each approach? EB & WB = Arrival Type 2 NB & SB = Arrival Type 3
Factors that should be considered for this intersection: - Pedestrians - Lane Utilization Observations?

Sub-problem 2 a: Moe Road AM peak hour Existing Conditions What effects do pedestrians generally have on intersection analyses and operational requirements? n They usually conflict with the coincident right-turning vehicles n They sometimes require insertion of an all-walk phase with no vehicular movements n Consideration of them generally requires modifications to the signal timing How do each of these factors affect the Moe Road intersection analysis? Observations?
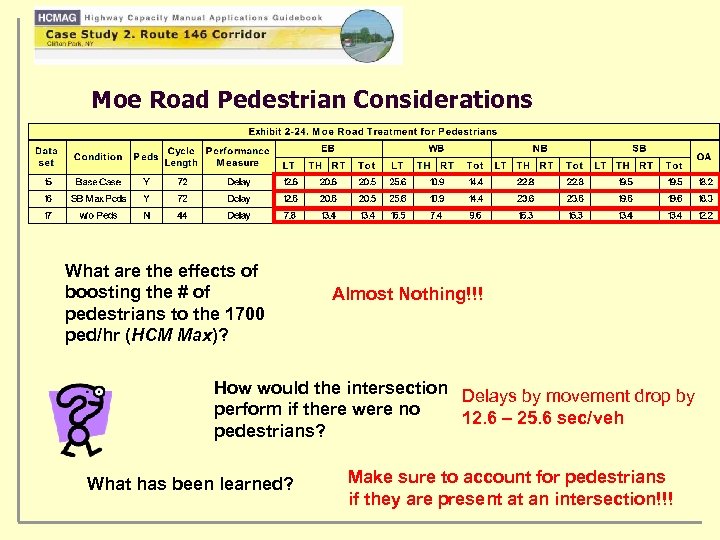
Moe Road Pedestrian Considerations What are the effects of boosting the # of pedestrians to the 1700 ped/hr (HCM Max)? Almost Nothing!!! How would the intersection Delays by movement drop by perform if there were no 12. 6 – 25. 6 sec/veh pedestrians? What has been learned? Make sure to account for pedestrians if they are present at an intersection!!!

Lane Utilization ~ 250’ from the intersection the 2 WB lanes merge into 1 What would you expect the driver tendencies to be? Many will desire to pre-position themselves in the lane that does not end (inner lane) HCM lane utilization factor, f. LU, is defined as the ratio of the average volume per lane to the volume in the heaviest-used lane
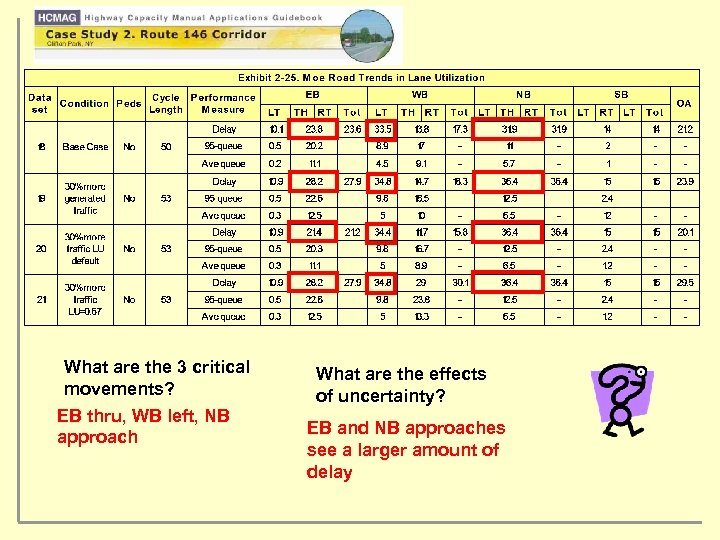
What are the 3 critical movements? EB thru, WB left, NB approach What are the effects of uncertainty? EB and NB approaches see a larger amount of delay

Findings and Additional Observations n We’ve seen that to allow for these pedestrian times, the cycle length gets longer and the vehicular delays get larger. n Pedestrian push-buttons are particularly valuable where the pedestrian volumes are light. On the cycles when the pedestrian timings aren’t invoked, the delays will be shorter and the signal will be more responsive to the vehicular flows. n For lane utilization, we’ve seen what effect it can have on estimates of delays and queue lengths. n We’ve seen that as the lane utilization gets poorer (i. e. , more traffic in just one lane), delays and queue lengths increase. n Not accounting for lane utilization, and using the defaults, can lead to overly optimistic assessments of intersection performance.
8c92923790b94186f2ee76011afd1b49.ppt