d9cc023f5948adcf3900148b2bf8a9b0.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 67

PRNFC SAFETY STANDDOWN Navy Flying Club Safety Brief May 10, 2005
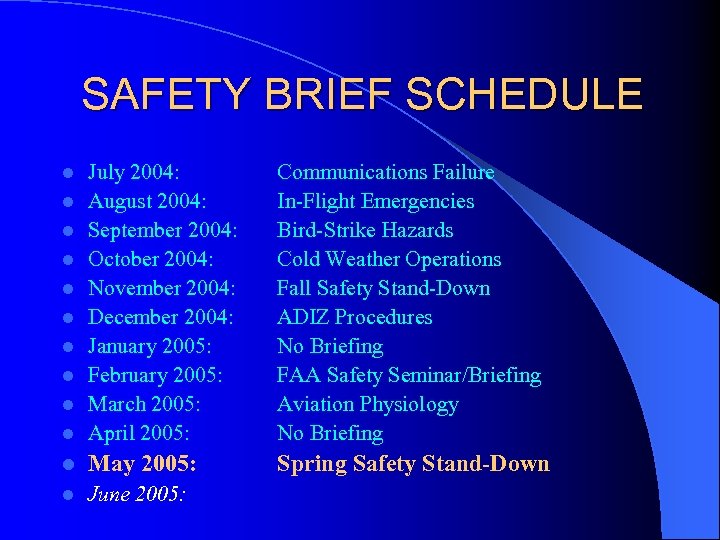
SAFETY BRIEF SCHEDULE l July 2004: August 2004: September 2004: October 2004: November 2004: December 2004: January 2005: February 2005: March 2005: April 2005: Communications Failure In-Flight Emergencies Bird-Strike Hazards Cold Weather Operations Fall Safety Stand-Down ADIZ Procedures No Briefing FAA Safety Seminar/Briefing Aviation Physiology No Briefing l May 2005: Spring Safety Stand-Down l June 2005: l l l l l
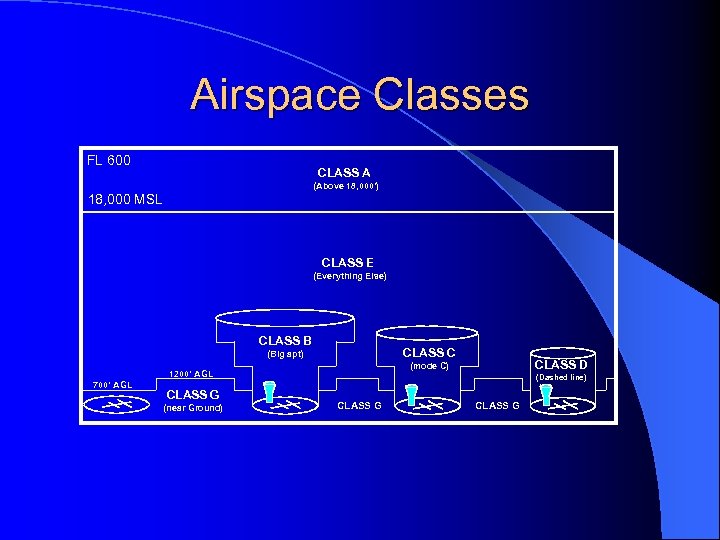
Airspace Classes FL 600 CLASS A (Above 18, 000’) 18, 000 MSL CLASS E (Everything Else) CLASS B CLASS C (Big apt) 700’ AGL CLASS G (near Ground) CLASS D (mode C) 1200’ AGL (Dashed line) CLASS G
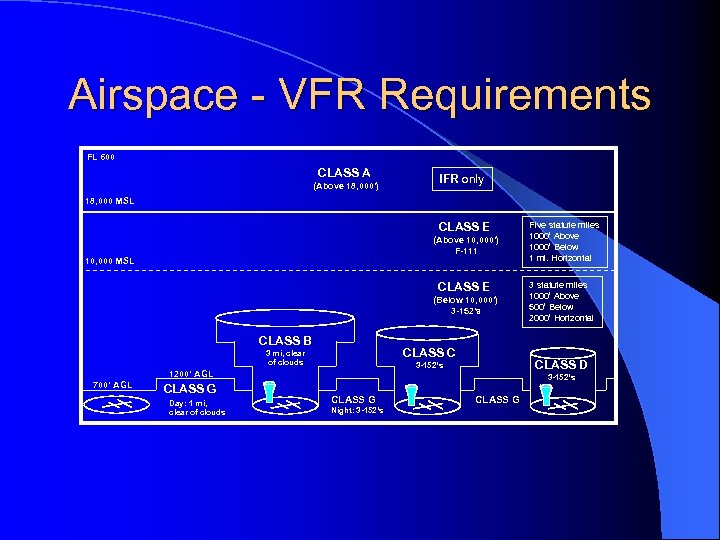
Airspace - VFR Requirements FL 600 CLASS A (Above 18, 000’) IFR only 18, 000 MSL CLASS E (Above 10, 000’) F-111 10, 000 MSL CLASS E (Below 10, 000’) 3 -152’s CLASS B CLASS C 3 mi, clear of clouds 700’ AGL CLASS G Day: 1 mi, clear of clouds 3 statute miles 1000’ Above 500’ Below 2000’ Horizontal CLASS D 3 -152’s 1200’ AGL Five statute miles 1000’ Above 1000’ Below 1 mi. Horizontal 3 -152’s CLASS G Night: 3 -152’s CLASS G

Class A Airspace l Begins at 18, 000 feet MSL up to FL 600 l Instrument Flight Plan, Mode C Transponder and IFR Clearance Required l VFR Weather Minimums – not applicable

Class B Airspace l Clearance required to enter l Required Equipment – 2 -way radio – Mode C Transponder – VOR or TACAN (IFR only) l VFR Weather Minimums – 3 statute miles, clear of clouds

Class C Airspace l Establish 2 -way radio communication before entering l Required Equipment – 2 -way radio – Mode C Transponder l VFR Weather Minimums: 3 -152’s – 3 s. m. , 500’ below, 1000’ above, 2000’ Horizontal

Class D Airspace l Need operating control tower to be in effect l 2 -way radio comm. required before entering l Extends 4. 4 nm (5 sm) radius from airport l Extends up to, not including 2, 500’ AGL – other altitudes may apply l VFR Weather Minimums: 3 -152’s – 3 s. m. , 500’ below, 1000’ above, 2000’ Horizontal

Class E Airspace l Everything except A, B, C, D and G airspace l Normally extends from 1200’ to 18, 000’ – magenta bar indicates floor of 700’ – magenta dashed line indicates floor to surface l VFR Minimums (below 10, 000’): 3 -152’s – 3 s. m. , 500’ below, 1000’ above, 2000’ Horizontal l VFR Minimums (above 10, 000’): F-111 – 5 s. m. , 1000’ below, 1000’ above, 1 s. m. Horizontal

Class G Airspace l VFR Weather Minimums (day) – 1 statute mile, clear of clouds l VFR Weather Minimums (night): 3 -152’s – 3 s. m. , 500’ below, 1000’ above, 2000’ Horizontal l Other VFR min. apply above 1200’ AGL

VFR Weather Minimums l Usually 3 -152’s – 3 s. m. , 500’ below, 1000’ above, 2000’ Horizontal l VFR Weather Min. other than 3 -152’s – Class A: IFR only – Class B: 3 statute miles, clear of clouds – Class E (above 10, 000’): F-111 – Class G (day): 1 statute mile, clear of clouds – Special VFR: 1 s. m. , clear of clouds

Mode C Transponder Required l Class A, B, and C l Within 30 n. m. of Class B (mode C veil) l Above Class B, Above Class C l Above 10, 000’ MSL and above 2500’ AGL l Into or Across U. S. ADIZ l 10 nm apt in FAR Part 91, Apndx D Sect 2 l In all controlled airspace if equipped

Prohibited Area Permission Required to Enter Always Active

Restricted Area l Activities – Artillery – Aerial Gunnery – Guided Missiles l If active, permission from controlling agency required to enter

Warning Area l Activities – Artillery – Aerial Gunnery – Guided Missiles l Located outside 3 mi. limit, over international water l Permission not required to enter, but Exercise Extreme Caution

Military Operating Area l Aerobatic flying and abrupt maneuvers l Purpose: Separate IFR and military traffic l FSS within 100 nm can provide info. l Permission is not required to enter MOA

Alert Area l Activities – High volume of pilot training – Unusual aerial activity l Exercise caution when operating in an Alert Area l Permission is not required to enter an Alert Area

FAR’s - Speed Restrictions l Aircraft may not exceed 250 knots below 10, 000 feet MSL (unless authorized by the FAA Administrator) l Aircraft may not exceed 200 knots below a Class B Airspace (Terminal Control Area) l Unless authorized or required by ATC, aircraft may not exceed 200 knots within an Class D Airspace (Airport Traffic Area)

FAR’s - Seat Belts l Pilot must wear seat belt and shoulder harness (if equipped) while at duty station – pilot may remove shoulder harness if unable to perform required duties l All passengers must wear seat belt and shoulder harness (if equipped) during takeoff and landing

FAR’s - Aircraft Documents A = Airworthiness Certificate R = Registration Certificate R = Radio Operating License (no longer required in USA, Canada) O = Operating Limitations W = Weight and Balance These documents must be on board the aircraft during all periods of operation.

Emergency Locator Transmitter (ELT) l ELT’s transmit on 121. 5 and 243. 0 Mhz l Test/inspection required every 12 months – Only during the first 5 minutes of every hour – Limited to 3 audio sweeps l Battery – Must be marked with an expiration date – Must be replaced after 1 hour cumulative use or after 1/2 battery life has expired

Oxygen Requirements Non-Pressurized Aircraft l 12, 500 - 14, 000 feet MSL – Flight crew must use oxygen for all portions of flight over 30 minutes between these altitudes l Above 14, 000 feet MSL – Flight crew must use oxygen at all times l Above 15, 000 feet MSL – All passengers must be provided with oxygen
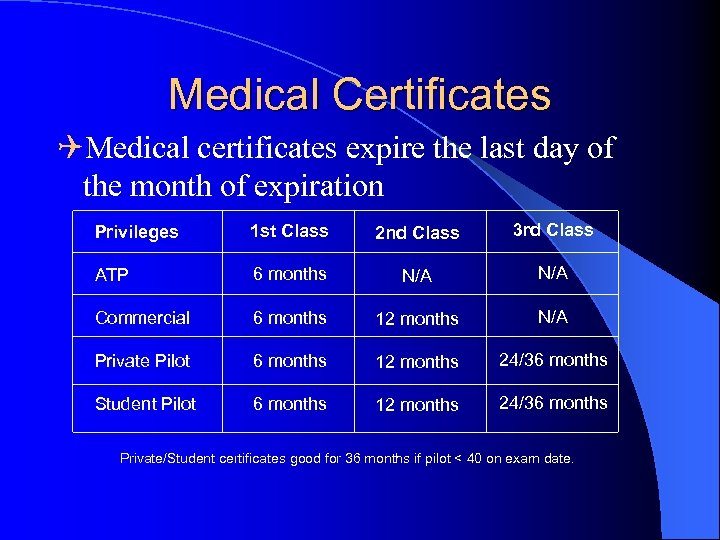
Medical Certificates QMedical certificates expire the last day of the month of expiration Privileges 1 st Class 2 nd Class 3 rd Class ATP 6 months N/A Commercial 6 months 12 months N/A Private Pilot 6 months 12 months 24/36 months Student Pilot 6 months 12 months 24/36 months Private/Student certificates good for 36 months if pilot < 40 on exam date.

Aerobatic Flight l Not allowed – Below 1, 500 feet AGL – Flight visibility less than 3 statute miles – Within Class B, C or D Airspace – Within Class E Airspace designated for an apt. – On federal airways – Over congested areas – Over open assemblies of people

Pilot Currency Required for Passenger Transportation l Within the past 90 days l Same category and class l Daytime – Three takeoffs and landings l Conventional Landing Gear (Taildragger) – Three takeoffs and landings to full stop l Nighttime – Three takeoffs and landings to full stop

Night Flight l Night - Definition: – the time between the end of evening civil twilight and the beginning of morning civil twilight, as published in the American Air Almanac, converted to local time l Twilight ends/begins when the center of the sun’s disk is 6 degrees below the horizon – In Florida, 23 -27 min after/before sunset/rise – In Maine, 29 -35 min after/before sunset/rise

Night Flight Position lights required from sunset to sunrise l Currency requirements for passenger transportation at night l – During the period from 1 hour after sunset to 1 hour before sunrise – Within preceding 90 days – Three takeoffs, three landings to a full stop – Same category and class aircraft

Special VFR l Class D & E Airspace, some – Ceiling Below 1, 000’ AGL – Visibility Less then 3 miles Class B & C l Required for SVFR – 1 statute mile visibility, clear of clouds l Required for SVFR at night – Pilot must be instrument rated – Aircraft must be instrument equipped

Transponder Codes l 7700 = Emergency l 7600 = Lost communications l 7500 = Hijack l 1200 = Standard VFR l 7777 = Military interceptor operations l 4000 = Military in restricted/warning areas l 0000 = Target drones

Maintenance l All aircraft must have an Annual Inspection l Commercial aircraft must have 100 hr insp. l Transponder check every two years l Pitot/Static check every two years (IFR) l ELT Battery replacement every two years l ELT Inspection every 12 calendar months l AD compliance mandatory

Required Equipment (VFR) l l l T = Tachometer O = Oil Pressure Gauge M = Magnetic Compass A = Altimeter T = Temp. Gauge (if liquid cooled) O = Oil Temperature Gauge

Required Equipment (VFR) l l l F = Fuel Gauge For Each Tank L = Landing Gear Position Indicator A = Airspeed Indicator M = Manifold Pressure Indicator E = Emergency Locator Transmitter S = Seat Belts (>=2 years old)

Required Equipment (Night VFR) l l l F = Fuses (Spare Set or 3 of Each Type) L = Landing Light (Commercial Ops. ) A = Anti-Collision Light P = Position Lights S = Source of Electrical Power

ATC Light Signals

Minimum Altitudes l 1, 000’ above, 2, 000’ horizontal from any object over congested area l 500’ above non-congested area l Sparsely populated area, 500’ from any – person – vessel – property

VFR Cruising Altitudes l Based upon magnetic course, not magnetic heading l Starts at 3, 000 feet AGL l 0°-179° – maintain odd thousands plus 500’ MSL l 180°-359° – maintain even thousands plus 500’ MSL l Remember “Odd Geese Fly East”

Right of Way l Aircraft in distress has ROW over all others l Balloon has ROW over any aircraft l Glider has ROW over airships, airplanes and rotorcraft l Airship has ROW over airplanes, rotorcraft

Right of Way l When two aircraft are approaching head on, both should turn to the right l When two aircraft (same category) are converging, the on the others right has the ROW l An aircraft being overtaken has the ROW l While landing, the lowest aircraft has ROW

Pre-Flight Action l Pilot must be free from alcoholic beverages for eight hours prior to flight – “Eight hours from bottle to throttle” l Pilot must acquire current and forecast weather l Pilot must check runway lengths of the destination airport

Pre-Flight Action l Pilot must have alternate course of action if flight can not be completed to destination l Pilot must check if there are ATC delays l Pilot must concern herself with all available information regarding the flight

Fuel Requirements l VFR Daytime l VFR Nighttime – Fuel to destination – plus 30 minutes l – Fuel to destination – plus 45 minutes IFR – Fuel to destination or alternate apt. if required – plus 45 minutes l IFR Alternate Airport not required if, 1 hour before/after, more than 2000’ and 3 sm visibility

Hyperventilation l Hyperventilation: an excessive increase in breathing rate or depth l Occurs as a result of – Emotional tension – Anxiety – Apprehension

Hyperventilation l Symptoms – Sensation of being warm – Nausea – Tingling of fingers and toes – Muscle spasms l Can lead to unconsciousness
Hyperventilation l Treatment – Try to get the person to breathe slowly – Breathe into a paper bag l Try to re-establish proper amount of carbon dioxide in the blood

Vertigo l Caused by loss of visual references l Leads to spatial disorientation l Overcome vertigo by relying on the flight instruments

Hypoxia l Occurs when an insufficient quantity of oxygen is available in the blood l Symptoms occur at approx. 10, 000 feet l Symptoms at lower altitudes for – Heavy smokers – People in poor physical condition l Hypoxia can lead to unconsciousness

Hypoxia l The most dangerous symptom is a feeling of well being l Treatment – Provide supplemental oxygen – Descend to a lower altitude
METAR/TAF l METAR – Aviation Routine Weather Report – replaces Surface Aviation Observation (SA) l TAF – Aerodrome Forecast – replaces Terminal Forecast (FT)

Sigmet l Significant Meteorology – Severe/Extreme turbulence – Severe Icing – Widespread dust and sandstorms with visibility less than three miles l Available from FAA and HIWAS stations

Convective Sigmet l Tornadoes l Lines of thunderstorms l Embedded thunderstorms l Intense thunderstorms – affecting 40% or more of area – of at least 3, 000 square feet l Hail 3/4 of and inch or greater in diameter

Airmet l Concerns small aircraft and aircraft with lack of instruments or equipment l Airmet covers – Moderate icing & severe turbulence over an extensive area – Extensive area of visibility less then 3 miles and/or ceilings lower then 1, 000’ – Winds 30 kts or more within 2, 000’ of surface

Surface Analysis Chart l Issued every three hours l Provides a general picture of atmospheric pressure patterns by showing highs, lows and fronts
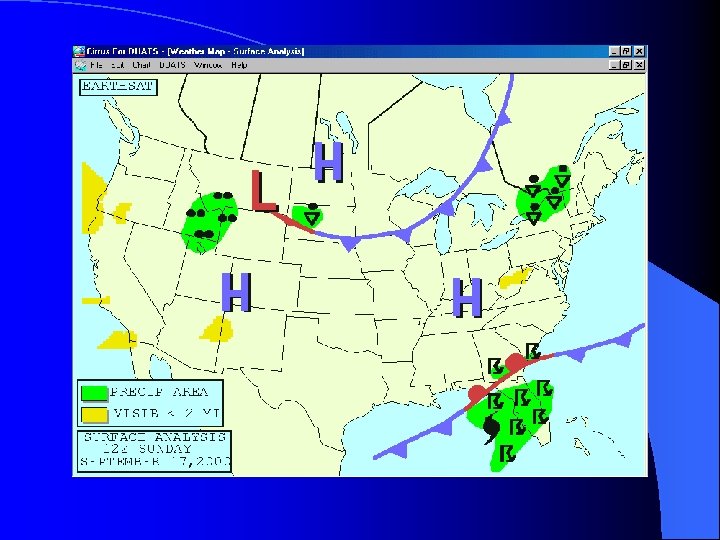

Surface Forecast Chart l Issued four times a day l Forecast of Surface Analysis Chart l Provides a general picture of atmospheric pressure patterns by showing highs, lows and fronts
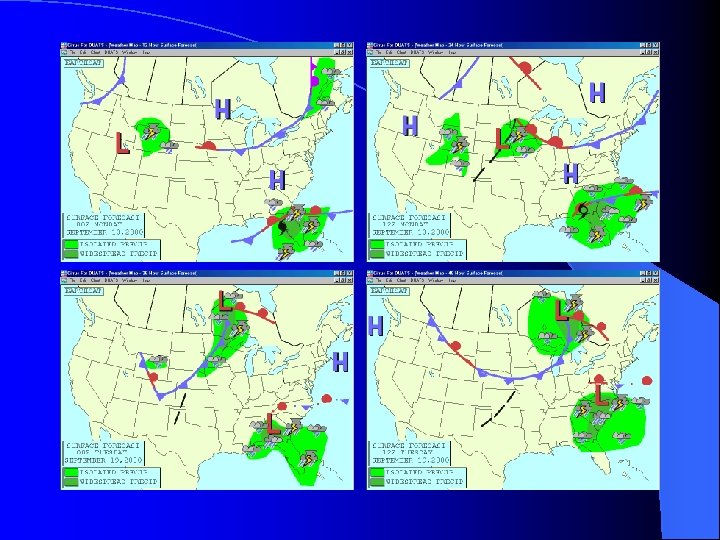

Weather Depiction Chart l Issued every three hours l Provides a picture of areas with – IFR – MVFR – VFR
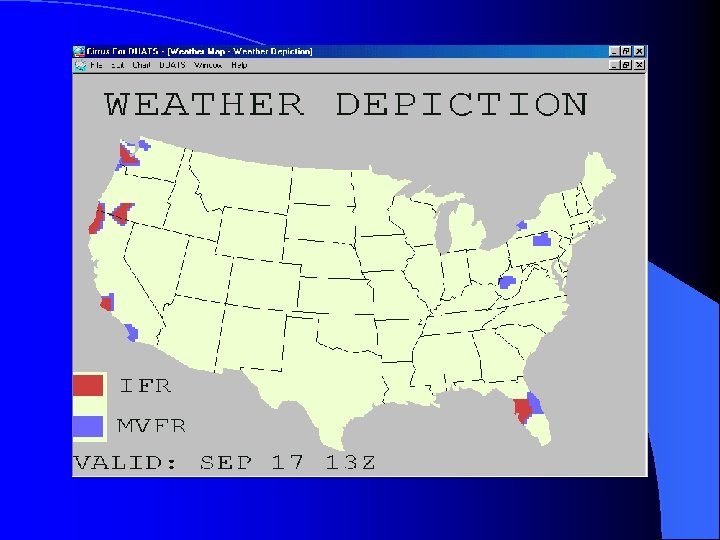

Radar Summary Chart l Normally issued every hour l Provides location and movement of thunderstorms, tornadoes, hurricanes and their intensity l Shows weather associated with rain, hail, icing and turbulence
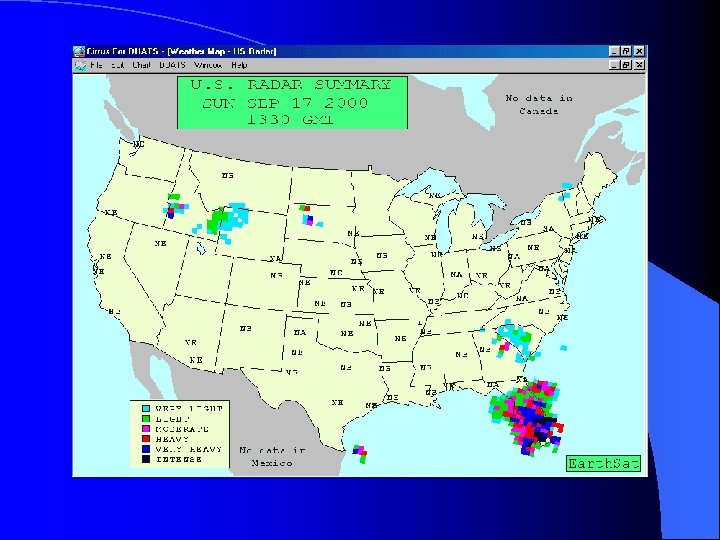

Satellite Weather Views l Issued every hour l Available on DUATS l Infrared available 24 hours/day l Visual available during daylight hours
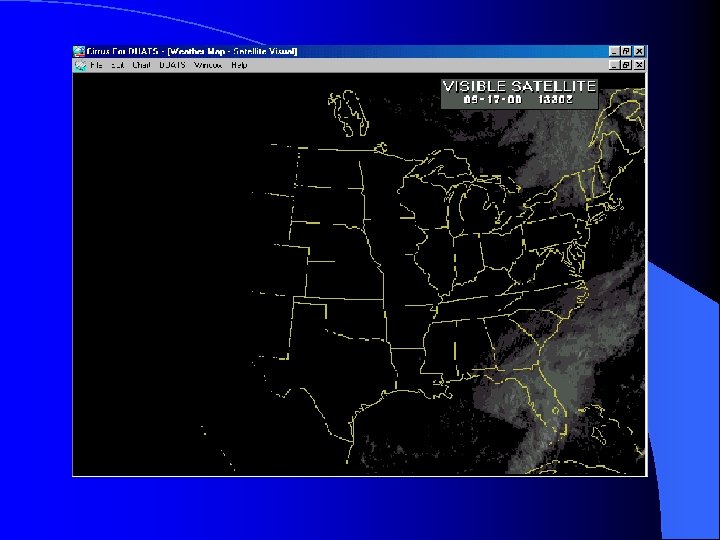

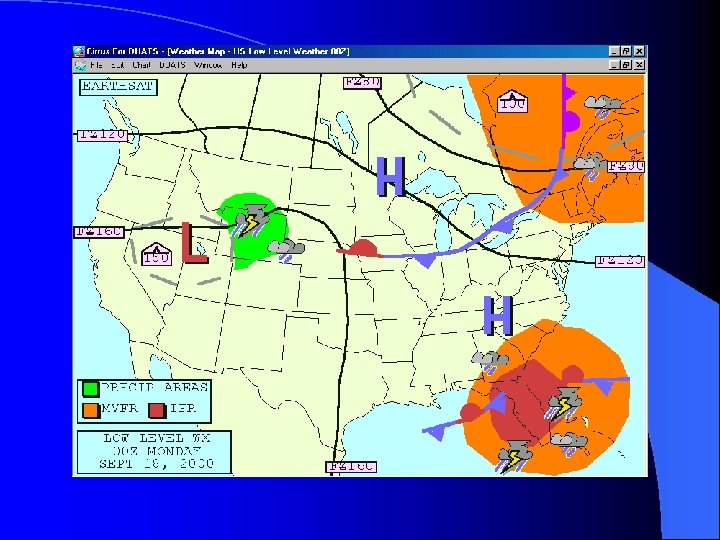
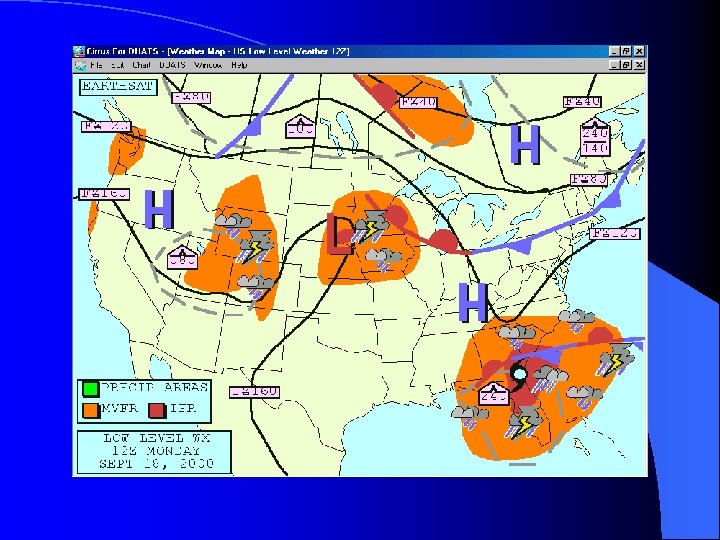
Low Level Weather l Issued every six hours l Provides – – – freezing levels areas and levels of turbulence locations of fronts pressure systems areas of precipitation VFR/MVFR/IFR areas

QUESTIONS?
d9cc023f5948adcf3900148b2bf8a9b0.ppt