bbb381b84b9ed9205009072ad4ed0ffe.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 44
 Private Equity and M&A – Middle East Perspective Presented to: In-House Congress United Arab Emirates 2007 20 March 2007 By: Rindala Beydoun
Private Equity and M&A – Middle East Perspective Presented to: In-House Congress United Arab Emirates 2007 20 March 2007 By: Rindala Beydoun
 Table of Contents • • • Acquisition Process Letter of Intent Due Diligence Transaction Structure Fact Situation Some of the Factors in Determining the Form of Acquisition Covering Stock Purchase Agreement Only Purchaser’s Goals Seller’s Goals The Acquisition Agreement – – – – – • • Overview Definitions Sale and closing Seller’s Representations Purchaser’s Representations Seller’s Covenants Purchaser’s Covenants Termination Post-Closing Matters Post-Closing Liability Middle East Acquisition Issues Private Equity Funds © 2007 Vinson & Elkins LLP 2
Table of Contents • • • Acquisition Process Letter of Intent Due Diligence Transaction Structure Fact Situation Some of the Factors in Determining the Form of Acquisition Covering Stock Purchase Agreement Only Purchaser’s Goals Seller’s Goals The Acquisition Agreement – – – – – • • Overview Definitions Sale and closing Seller’s Representations Purchaser’s Representations Seller’s Covenants Purchaser’s Covenants Termination Post-Closing Matters Post-Closing Liability Middle East Acquisition Issues Private Equity Funds © 2007 Vinson & Elkins LLP 2
 Acquisition Process • • • Bid Process vs. Private Negotiation Confidentiality Agreement Due Diligence Letter of Intent Negotiation of Definitive Stock Purchase Agreement or Asset Purchase Agreement • Closing – Deferred Closing vs. Simultaneous Closing • Post-Closing © 2007 Vinson & Elkins LLP 3
Acquisition Process • • • Bid Process vs. Private Negotiation Confidentiality Agreement Due Diligence Letter of Intent Negotiation of Definitive Stock Purchase Agreement or Asset Purchase Agreement • Closing – Deferred Closing vs. Simultaneous Closing • Post-Closing © 2007 Vinson & Elkins LLP 3
 Letter of Intent • Advantages – Memorialize “the deal” and address major structural issues (e. g. foreign ownership issues) – Come to agreement on major points before investing further time & money – Facilitate acquisition financing – Facilitate regulatory filings • Disadvantages – Timing: Often quicker to proceed with full acquisition agreement – Risk in the event of failed transaction (Texaco vs. Pennzoil) © 2007 Vinson & Elkins LLP 4
Letter of Intent • Advantages – Memorialize “the deal” and address major structural issues (e. g. foreign ownership issues) – Come to agreement on major points before investing further time & money – Facilitate acquisition financing – Facilitate regulatory filings • Disadvantages – Timing: Often quicker to proceed with full acquisition agreement – Risk in the event of failed transaction (Texaco vs. Pennzoil) © 2007 Vinson & Elkins LLP 4
 Letter of Intent • Contents – General description of transaction, structure and timetable – Purchase price – Basic description of other terms – Extent of indemnification – Conditions – Statement the LOI is “non-binding” – Other special provisions (e. g. , due diligence access, confidentiality, exclusivity) • These provisions can be made binding © 2007 Vinson & Elkins LLP 5
Letter of Intent • Contents – General description of transaction, structure and timetable – Purchase price – Basic description of other terms – Extent of indemnification – Conditions – Statement the LOI is “non-binding” – Other special provisions (e. g. , due diligence access, confidentiality, exclusivity) • These provisions can be made binding © 2007 Vinson & Elkins LLP 5
 Due Diligence • Purpose – Assess risks – Gain understanding of Target’s business • Team Effort – – – – Commercial Accounting Tax Legal Environmental Technical Other © 2007 Vinson & Elkins LLP 6
Due Diligence • Purpose – Assess risks – Gain understanding of Target’s business • Team Effort – – – – Commercial Accounting Tax Legal Environmental Technical Other © 2007 Vinson & Elkins LLP 6
 Due Diligence • Process – – Checklist Review Internal Meetings Feedback to Commercial Team • Role of the Legal Team – – – Focus on Risk Assessment Corporate Matters Debt Obligations and Material Contracts Title to Property Litigation Legal Compliance © 2007 Vinson & Elkins LLP 7
Due Diligence • Process – – Checklist Review Internal Meetings Feedback to Commercial Team • Role of the Legal Team – – – Focus on Risk Assessment Corporate Matters Debt Obligations and Material Contracts Title to Property Litigation Legal Compliance © 2007 Vinson & Elkins LLP 7
 Transaction Structure • Asset Purchase • Stock Purchase • Merger Consider foreign ownership restrictions in some GCC jurisdictions including the UAE, Saudi Arabia and Kuwait. © 2007 Vinson & Elkins LLP 8
Transaction Structure • Asset Purchase • Stock Purchase • Merger Consider foreign ownership restrictions in some GCC jurisdictions including the UAE, Saudi Arabia and Kuwait. © 2007 Vinson & Elkins LLP 8
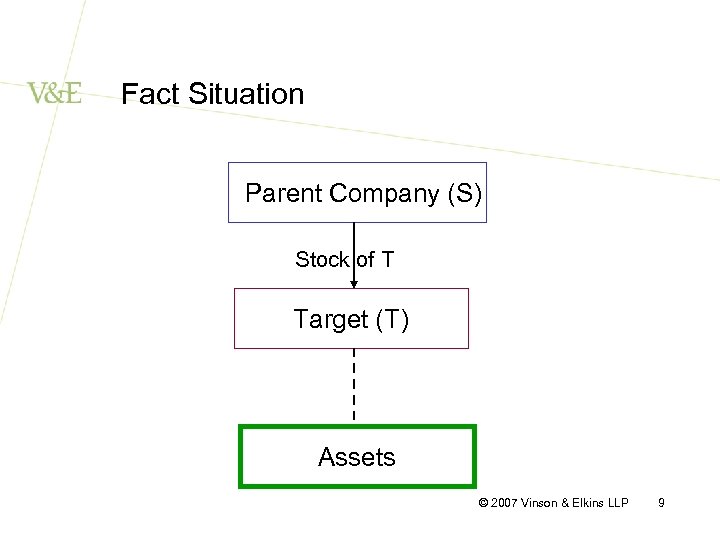 Fact Situation Parent Company (S) Stock of T Target (T) Assets © 2007 Vinson & Elkins LLP 9
Fact Situation Parent Company (S) Stock of T Target (T) Assets © 2007 Vinson & Elkins LLP 9
 Fact Situation – Cont’d • Stock Purchase Agreement: Purchaser (P) enters into SPA with S covering the sale of the stock of T • Asset Purchase Agreement: P enters into APA with T covering the sale of the assets of T • Merger Forward Merger –T merges into P or a subsidiary of P Reverse Merger – P or a subsidiary of P merges into T © 2007 Vinson & Elkins LLP 10
Fact Situation – Cont’d • Stock Purchase Agreement: Purchaser (P) enters into SPA with S covering the sale of the stock of T • Asset Purchase Agreement: P enters into APA with T covering the sale of the assets of T • Merger Forward Merger –T merges into P or a subsidiary of P Reverse Merger – P or a subsidiary of P merges into T © 2007 Vinson & Elkins LLP 10
 Some of the Factors in Determining the Form of Acquisition • Will P assume or be subject to all of T’s liabilities or only specific ones? • Can T’s assets be transferred to P without third party approvals? • Are the shares of T widely held? • Many tax and accounting issues, including whether P will obtain a new cost basis in T’s assets or P will take a carryover basis © 2007 Vinson & Elkins LLP 11
Some of the Factors in Determining the Form of Acquisition • Will P assume or be subject to all of T’s liabilities or only specific ones? • Can T’s assets be transferred to P without third party approvals? • Are the shares of T widely held? • Many tax and accounting issues, including whether P will obtain a new cost basis in T’s assets or P will take a carryover basis © 2007 Vinson & Elkins LLP 11
 Covering Stock Purchase Agreement Only • SPA generally covers everything an APA does, plus other items • A merger, like a stock purchase, involves P’s assumption of all of T’s liabilities © 2007 Vinson & Elkins LLP 12
Covering Stock Purchase Agreement Only • SPA generally covers everything an APA does, plus other items • A merger, like a stock purchase, involves P’s assumption of all of T’s liabilities © 2007 Vinson & Elkins LLP 12
 Purchaser’s Goals • Get what it paid for • Be able to get compensation if it does not get what it paid for • Have an out from closing if assumptions prove to be incorrect • Minimize obligations to take harmful steps to get the deal done • Certainty of the deal © 2007 Vinson & Elkins LLP 13
Purchaser’s Goals • Get what it paid for • Be able to get compensation if it does not get what it paid for • Have an out from closing if assumptions prove to be incorrect • Minimize obligations to take harmful steps to get the deal done • Certainty of the deal © 2007 Vinson & Elkins LLP 13
 Seller’s Goals • Obtain maximum value • Minimize residual risks • Certainty of the deal © 2007 Vinson & Elkins LLP 14
Seller’s Goals • Obtain maximum value • Minimize residual risks • Certainty of the deal © 2007 Vinson & Elkins LLP 14
 The Acquisition Agreement – Overview • • • Parties Recitals Definitions Sale and Closing Seller’s Representations and Warranties Purchaser’s Representations and Warranties Covenants Conditions Termination Post-Closing Remedies We will focus on key definitions, representations and warranties, covenants, termination and post-closing remedies © 2007 Vinson & Elkins LLP 15
The Acquisition Agreement – Overview • • • Parties Recitals Definitions Sale and Closing Seller’s Representations and Warranties Purchaser’s Representations and Warranties Covenants Conditions Termination Post-Closing Remedies We will focus on key definitions, representations and warranties, covenants, termination and post-closing remedies © 2007 Vinson & Elkins LLP 15
 The Acquisition Agreement - Definitions • Definitions are perhaps the most crucial part of any complex contract. It’s convenient to accumulate them in one section of the SPA, usually Section 1 • It’s impossible here to discuss all definitions, but here a few to focus on: – “Best Efforts” • This term is often used in covenants the parties agree to perform. It’s often defined as reasonable commercial efforts under all the circumstances. Most obligations are on S, so it’s dangerous for S to agree to use best efforts without definition. © 2007 Vinson & Elkins LLP 16
The Acquisition Agreement - Definitions • Definitions are perhaps the most crucial part of any complex contract. It’s convenient to accumulate them in one section of the SPA, usually Section 1 • It’s impossible here to discuss all definitions, but here a few to focus on: – “Best Efforts” • This term is often used in covenants the parties agree to perform. It’s often defined as reasonable commercial efforts under all the circumstances. Most obligations are on S, so it’s dangerous for S to agree to use best efforts without definition. © 2007 Vinson & Elkins LLP 16
 The Acquisition Agreement - Definitions – “Knowledge” • • This term is often used to limit S’s representations to its Knowledge Some of the issues: – Is it limited to actual knowledge? – What about things that would have discovered by reasonable investigation? – What about that which “should have been” known? – The case of a corporation, whose knowledge should count? Officers and directors? Non-officer employees with management responsibilities? All employees? © 2007 Vinson & Elkins LLP 17
The Acquisition Agreement - Definitions – “Knowledge” • • This term is often used to limit S’s representations to its Knowledge Some of the issues: – Is it limited to actual knowledge? – What about things that would have discovered by reasonable investigation? – What about that which “should have been” known? – The case of a corporation, whose knowledge should count? Officers and directors? Non-officer employees with management responsibilities? All employees? © 2007 Vinson & Elkins LLP 17
 The Acquisition Agreement - Definitions – “Material Adverse Change” • If a MAC in the business or prospects of T occurs, P will probably not be obligated to close. Issues include whether the following changes are excluded from being a MAC: – General economic conditions – General industry conditions – War/Hostilities – Decline in the stock market generally – Changes in law or accounting practices © 2007 Vinson & Elkins LLP 18
The Acquisition Agreement - Definitions – “Material Adverse Change” • If a MAC in the business or prospects of T occurs, P will probably not be obligated to close. Issues include whether the following changes are excluded from being a MAC: – General economic conditions – General industry conditions – War/Hostilities – Decline in the stock market generally – Changes in law or accounting practices © 2007 Vinson & Elkins LLP 18
 The Acquisition Agreement – Sale and Closing This Section typically covers • Obligation of S and P to sell and buy stock • Payment of purchase price (form of payment (cash, note or shares), escrow arrangements and adjusted price) • Timing of closing – certain number of days after Closing conditions satisfied • Delivery of required Closing documents • • • Share Certificates & Stock Transfer Instruments Officer’s Certificates Legal Opinions © 2007 Vinson & Elkins LLP 19
The Acquisition Agreement – Sale and Closing This Section typically covers • Obligation of S and P to sell and buy stock • Payment of purchase price (form of payment (cash, note or shares), escrow arrangements and adjusted price) • Timing of closing – certain number of days after Closing conditions satisfied • Delivery of required Closing documents • • • Share Certificates & Stock Transfer Instruments Officer’s Certificates Legal Opinions © 2007 Vinson & Elkins LLP 19
 The Acquisition Agreement – Seller’s Representations • S’s representations serve three functions: – Device for obtaining disclosure about T before signing SPA – Basis for P’s right to terminate before Closing if representations breached – Grounds for P’s obtaining indemnity after Closing • Usual format is that a single section contains all of S’s representations, both those concerning S (e. g. , it owns beneficially and of record all T’s stock) and those concerning T (e. g. , its financial statements fairly present its financial condition) • Representations have to be true at signing and also at Closing © 2007 Vinson & Elkins LLP 20
The Acquisition Agreement – Seller’s Representations • S’s representations serve three functions: – Device for obtaining disclosure about T before signing SPA – Basis for P’s right to terminate before Closing if representations breached – Grounds for P’s obtaining indemnity after Closing • Usual format is that a single section contains all of S’s representations, both those concerning S (e. g. , it owns beneficially and of record all T’s stock) and those concerning T (e. g. , its financial statements fairly present its financial condition) • Representations have to be true at signing and also at Closing © 2007 Vinson & Elkins LLP 20
 The Acquisition Agreement – Seller’s Representations • Common to have a single Exhibit or Disclosure Schedule mentioned in the lead-in that contains all exceptions to the representations • Whether representations are limited to S’s Knowledge is a major issue. Clearly some representations should not be so limited (e. g. , S and T are validly existing; the SPA is a legal and binding obligation of S; S owns the stock of T; and T has no obligation to pay a brokerage fee concerning the Closing). Many others may or may not be so limited – arguments can be made on both sides. © 2007 Vinson & Elkins LLP 21
The Acquisition Agreement – Seller’s Representations • Common to have a single Exhibit or Disclosure Schedule mentioned in the lead-in that contains all exceptions to the representations • Whether representations are limited to S’s Knowledge is a major issue. Clearly some representations should not be so limited (e. g. , S and T are validly existing; the SPA is a legal and binding obligation of S; S owns the stock of T; and T has no obligation to pay a brokerage fee concerning the Closing). Many others may or may not be so limited – arguments can be made on both sides. © 2007 Vinson & Elkins LLP 21
 The Acquisition Agreement – Seller’s Representations • Another major issue is whether S’s representations should be qualified as to materiality • The approach that we often suggest is not to have materiality qualifiers in most individual representations and instead limit P’s rights with respect to breaches of S’s representations to the following: – P has the right to terminate before Closing only in the case of material breaches – P’s rights of indemnity after Closing for breaches of representations only apply after a deductible or basket dollar amount has occurred © 2007 Vinson & Elkins LLP 22
The Acquisition Agreement – Seller’s Representations • Another major issue is whether S’s representations should be qualified as to materiality • The approach that we often suggest is not to have materiality qualifiers in most individual representations and instead limit P’s rights with respect to breaches of S’s representations to the following: – P has the right to terminate before Closing only in the case of material breaches – P’s rights of indemnity after Closing for breaches of representations only apply after a deductible or basket dollar amount has occurred © 2007 Vinson & Elkins LLP 22
 The Acquisition Agreement – Seller’s Representations • Key Representations by Seller: – – – – Organization, Good Standing and Authority T’s financial statements No “Material Adverse Effect” No undisclosed liabilities Due Authorization Capitalization and Title to Shares No Violations Litigation Compliance with Law; Environmental Matters Regulatory Assets Taxes Material Contracts Labor & Benefits No Misleading Statements Etc. © 2007 Vinson & Elkins LLP 23
The Acquisition Agreement – Seller’s Representations • Key Representations by Seller: – – – – Organization, Good Standing and Authority T’s financial statements No “Material Adverse Effect” No undisclosed liabilities Due Authorization Capitalization and Title to Shares No Violations Litigation Compliance with Law; Environmental Matters Regulatory Assets Taxes Material Contracts Labor & Benefits No Misleading Statements Etc. © 2007 Vinson & Elkins LLP 23
 The Acquisition Agreement – Purchaser’s Representations • Much less extensive than Seller’s representations • The only typical P representations cover organization, authorization, investment intent, no adverse proceedings and no brokers • Different scenario if P is paying for T’s stock with P’s stock or if P’s obligation to close is subject to obtaining financing © 2007 Vinson & Elkins LLP 24
The Acquisition Agreement – Purchaser’s Representations • Much less extensive than Seller’s representations • The only typical P representations cover organization, authorization, investment intent, no adverse proceedings and no brokers • Different scenario if P is paying for T’s stock with P’s stock or if P’s obligation to close is subject to obtaining financing © 2007 Vinson & Elkins LLP 24
 The Acquisition Agreement – Seller’s Covenants • Covenants Relating to the Transaction Process • Covenants Relating to the Operation of T’s Business © 2007 Vinson & Elkins LLP 25
The Acquisition Agreement – Seller’s Covenants • Covenants Relating to the Transaction Process • Covenants Relating to the Operation of T’s Business © 2007 Vinson & Elkins LLP 25
 The Acquisition Agreement – Seller’s Covenants • Covenants relating to the transaction Process: – Access of P and its lenders to T’s personnel, properties and books – “Best Efforts” to obtain any necessary third party consents – Make necessary regulatory filings – Ensure that representations and warranties remain true until closing – Release of liens – Update disclosure schedules – Tax matters (filing, payment, collection of refunds) – “Best Efforts” to satisfy conditions to Closing – “No shop” provision – Public announcements © 2007 Vinson & Elkins LLP 26
The Acquisition Agreement – Seller’s Covenants • Covenants relating to the transaction Process: – Access of P and its lenders to T’s personnel, properties and books – “Best Efforts” to obtain any necessary third party consents – Make necessary regulatory filings – Ensure that representations and warranties remain true until closing – Release of liens – Update disclosure schedules – Tax matters (filing, payment, collection of refunds) – “Best Efforts” to satisfy conditions to Closing – “No shop” provision – Public announcements © 2007 Vinson & Elkins LLP 26
 The Acquisition Agreement – Seller’s Covenants • Covenants relating to the operation of T’s business – Operate T’s business only “in the ordinary course, consistent with past practice” – Long list of “negative covenants” • No amendment to charter or bylaws • No sale, issuance or redemption of stock, options, etc. • No dividends or stock splits • No investments or acquisitions • No change of business practice or entry into new lines of business © 2007 Vinson & Elkins LLP 27
The Acquisition Agreement – Seller’s Covenants • Covenants relating to the operation of T’s business – Operate T’s business only “in the ordinary course, consistent with past practice” – Long list of “negative covenants” • No amendment to charter or bylaws • No sale, issuance or redemption of stock, options, etc. • No dividends or stock splits • No investments or acquisitions • No change of business practice or entry into new lines of business © 2007 Vinson & Elkins LLP 27
 The Acquisition Agreement – Seller’s Covenants – More “negative covenants” • No borrowing or assumption/guarantee of debt • No capital expenditures larger than specified amount • No settling claims • No increases in compensation or benefits • No changing accounting practices • No taking any action that would result in a default under any commitment by T • No taking any action that would result in a breach of a covenant or a failure of a representation to be true at closing • Etc, etc. © 2007 Vinson & Elkins LLP 28
The Acquisition Agreement – Seller’s Covenants – More “negative covenants” • No borrowing or assumption/guarantee of debt • No capital expenditures larger than specified amount • No settling claims • No increases in compensation or benefits • No changing accounting practices • No taking any action that would result in a default under any commitment by T • No taking any action that would result in a breach of a covenant or a failure of a representation to be true at closing • Etc, etc. © 2007 Vinson & Elkins LLP 28
 The Acquisition Agreement – Purchaser’s Covenants • These are very limited, usually covering only seeking of required governmental approvals and a Best Efforts obligation to seek to close © 2007 Vinson & Elkins LLP 29
The Acquisition Agreement – Purchaser’s Covenants • These are very limited, usually covering only seeking of required governmental approvals and a Best Efforts obligation to seek to close © 2007 Vinson & Elkins LLP 29
 The Acquisition Agreement - Termination • By notice given before Closing, either party can terminate the SPA – Because of a material breach by the other party – If any of the terminating party’s conditions to Closing have not been satisfied (other than through the failure of that party to comply with its obligations) – If Closing has not occurred by a specified date (the “dropdead date”) (other than through the failure of the terminating party to comply with its obligations) © 2007 Vinson & Elkins LLP 30
The Acquisition Agreement - Termination • By notice given before Closing, either party can terminate the SPA – Because of a material breach by the other party – If any of the terminating party’s conditions to Closing have not been satisfied (other than through the failure of that party to comply with its obligations) – If Closing has not occurred by a specified date (the “dropdead date”) (other than through the failure of the terminating party to comply with its obligations) © 2007 Vinson & Elkins LLP 30
 The Acquisition Agreement - Termination • Termination by a party is not an election of remedies, and if a party terminates because of a breach by the other, the terminating party can seek all legal remedies • All obligations under the SPA cease upon termination; possible exceptions include paying one’s own expenses, confidentiality, protection against brokers and jurisdiction and venue © 2007 Vinson & Elkins LLP 31
The Acquisition Agreement - Termination • Termination by a party is not an election of remedies, and if a party terminates because of a breach by the other, the terminating party can seek all legal remedies • All obligations under the SPA cease upon termination; possible exceptions include paying one’s own expenses, confidentiality, protection against brokers and jurisdiction and venue © 2007 Vinson & Elkins LLP 31
 The Acquisition Agreement – Post-Closing Matters • Post-Closing Liability • Resolution of Purchase Price Adjustments • Earn-Outs © 2007 Vinson & Elkins LLP 32
The Acquisition Agreement – Post-Closing Matters • Post-Closing Liability • Resolution of Purchase Price Adjustments • Earn-Outs © 2007 Vinson & Elkins LLP 32
 The Acquisition Agreement – Post-Closing Liability • Redress for Purchaser if assumptions relating to value of T (as reflected in S’s representations) prove to be incorrect • Generally tied to breaches of representations and covenants or to periods of ownership © 2007 Vinson & Elkins LLP 33
The Acquisition Agreement – Post-Closing Liability • Redress for Purchaser if assumptions relating to value of T (as reflected in S’s representations) prove to be incorrect • Generally tied to breaches of representations and covenants or to periods of ownership © 2007 Vinson & Elkins LLP 33
 The Acquisition Agreement – Post-Closing Liability • Limitations of Liability – Seller will generally negotiate for limitations of its postclosing liability • Survival Periods • Caps on Damages • Baskets and Thresholds • Effect of Tax Benefits and Insurance © 2007 Vinson & Elkins LLP 34
The Acquisition Agreement – Post-Closing Liability • Limitations of Liability – Seller will generally negotiate for limitations of its postclosing liability • Survival Periods • Caps on Damages • Baskets and Thresholds • Effect of Tax Benefits and Insurance © 2007 Vinson & Elkins LLP 34
 The Acquisition Agreement – Post-Closing Liability • Survival Period – Generally 1 – 3 years after closing for most matters – Some matters may be subject to longer periods • Environmental claims • Tax matters • Employee benefits • Title to shares © 2007 Vinson & Elkins LLP 35
The Acquisition Agreement – Post-Closing Liability • Survival Period – Generally 1 – 3 years after closing for most matters – Some matters may be subject to longer periods • Environmental claims • Tax matters • Employee benefits • Title to shares © 2007 Vinson & Elkins LLP 35
 The Acquisition Agreement – Post-Closing Liability • Caps on Seller’s Post-Closing Liability – Typically 50% - 100% of the Purchase Price – Exceptions • Environmental matters • Tax matters • Employee benefits • Product liability claims • Title to shares © 2007 Vinson & Elkins LLP 36
The Acquisition Agreement – Post-Closing Liability • Caps on Seller’s Post-Closing Liability – Typically 50% - 100% of the Purchase Price – Exceptions • Environmental matters • Tax matters • Employee benefits • Product liability claims • Title to shares © 2007 Vinson & Elkins LLP 36
 The Acquisition Agreement – Post-Closing Liability • Baskets and Thresholds – Baskets • Functions like a deductible under an insurance policy • Typically < 1% of Purchase Price – Thresholds • Different from basket in that once threshold is crossed, Purchaser entitled to indemnification from the first dollar of losses © 2007 Vinson & Elkins LLP 37
The Acquisition Agreement – Post-Closing Liability • Baskets and Thresholds – Baskets • Functions like a deductible under an insurance policy • Typically < 1% of Purchase Price – Thresholds • Different from basket in that once threshold is crossed, Purchaser entitled to indemnification from the first dollar of losses © 2007 Vinson & Elkins LLP 37
 Middle East Acquisition Issues • Foreign Ownership Restrictions • • • Free zones Sector-specific exemptions Limited “negative lists” Transfer of technology and Know-how Transfer of Assets Use of security agents (issues) © 2007 Vinson & Elkins LLP 38
Middle East Acquisition Issues • Foreign Ownership Restrictions • • • Free zones Sector-specific exemptions Limited “negative lists” Transfer of technology and Know-how Transfer of Assets Use of security agents (issues) © 2007 Vinson & Elkins LLP 38
 Middle East Acquisition Issues • Domicile of Acquisition Vehicles • • • Foreign ownership issues Tax and regulatory considerations Practicality and documentation Selling-down to investors Growing-use of private equity fund vehicles © 2007 Vinson & Elkins LLP 39
Middle East Acquisition Issues • Domicile of Acquisition Vehicles • • • Foreign ownership issues Tax and regulatory considerations Practicality and documentation Selling-down to investors Growing-use of private equity fund vehicles © 2007 Vinson & Elkins LLP 39
 Middle East Acquisition Issues • Sharia Private Equity Considerations • • • Sharia audit considerations Debt-to-equity ratio & restructuring of debt Choice of law and forum Structure of acquisition Domicile of T (non-Islamic jurisdictions) © 2007 Vinson & Elkins LLP 40
Middle East Acquisition Issues • Sharia Private Equity Considerations • • • Sharia audit considerations Debt-to-equity ratio & restructuring of debt Choice of law and forum Structure of acquisition Domicile of T (non-Islamic jurisdictions) © 2007 Vinson & Elkins LLP 40
 Middle East Acquisition Issues • Regulatory and Licensing Issues • • • Disclosure requirements for listing companies - PIPEs Acquisition of financial institutions Permitting issues Local partner considerations Employment matters Etc. © 2007 Vinson & Elkins LLP 41
Middle East Acquisition Issues • Regulatory and Licensing Issues • • • Disclosure requirements for listing companies - PIPEs Acquisition of financial institutions Permitting issues Local partner considerations Employment matters Etc. © 2007 Vinson & Elkins LLP 41
 Middle East Acquisition Issues • Choice of law and forum • • • Choice of law considerations Choice of forum considerations The New York Convention Dispute settlement mechanisms Choice of law issues in connections with acquisitions by Islamic institutions © 2007 Vinson & Elkins LLP 42
Middle East Acquisition Issues • Choice of law and forum • • • Choice of law considerations Choice of forum considerations The New York Convention Dispute settlement mechanisms Choice of law issues in connections with acquisitions by Islamic institutions © 2007 Vinson & Elkins LLP 42
 Private Equity Funds • • Issue of fund domicile; the GCC option? Issue of structure: corporate vs. partnership “Look through” analysis Tax treaties Key documentation Private Placement vs. Public Offering Acquisition vehicles Regulatory considerations: filings, reporting, etc. © 2007 Vinson & Elkins LLP 43
Private Equity Funds • • Issue of fund domicile; the GCC option? Issue of structure: corporate vs. partnership “Look through” analysis Tax treaties Key documentation Private Placement vs. Public Offering Acquisition vehicles Regulatory considerations: filings, reporting, etc. © 2007 Vinson & Elkins LLP 43
 Contact Details Ayman H. A. Khaleq – Dubai Christopher B. Strong – Dubai Tel: +971 4 403 6216 akhaleq@velaw. com Tel: +971 4 403 6219 cstrong@velaw. com Rindala Beydoun – Dubai Tel: +971 4 403 6210 rbeydoun@velaw. com © 2007 Vinson & Elkins LLP 44
Contact Details Ayman H. A. Khaleq – Dubai Christopher B. Strong – Dubai Tel: +971 4 403 6216 akhaleq@velaw. com Tel: +971 4 403 6219 cstrong@velaw. com Rindala Beydoun – Dubai Tel: +971 4 403 6210 rbeydoun@velaw. com © 2007 Vinson & Elkins LLP 44


