 Private Equity An Overview Clark L. Maxam, Ph. D. Director of Research – Braddock Financial Corporation and El Pomar Professor of Entrepreneurial Finance – University of Colorado, Colorado Springs
Private Equity An Overview Clark L. Maxam, Ph. D. Director of Research – Braddock Financial Corporation and El Pomar Professor of Entrepreneurial Finance – University of Colorado, Colorado Springs
 Private Equity – Broadly Defined • Technically refers to any type of equity investment in an asset in which the equity is not freely tradable on a public market. • Less liquid • Long Term in nature
Private Equity – Broadly Defined • Technically refers to any type of equity investment in an asset in which the equity is not freely tradable on a public market. • Less liquid • Long Term in nature
 Private Equity – Categories and Players • Angel – Early Stage: Seed, Start-up • Professional Venture Capital – Early Stage, Expansion, Later Stage • Private Equity – Later Stage, Buyout, Special Situations • Hedge Funds – All Stages
Private Equity – Categories and Players • Angel – Early Stage: Seed, Start-up • Professional Venture Capital – Early Stage, Expansion, Later Stage • Private Equity – Later Stage, Buyout, Special Situations • Hedge Funds – All Stages
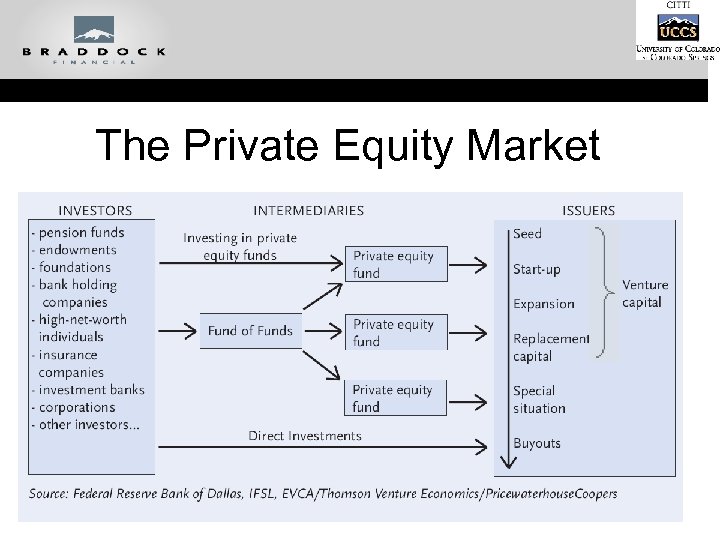 The Private Equity Market
The Private Equity Market
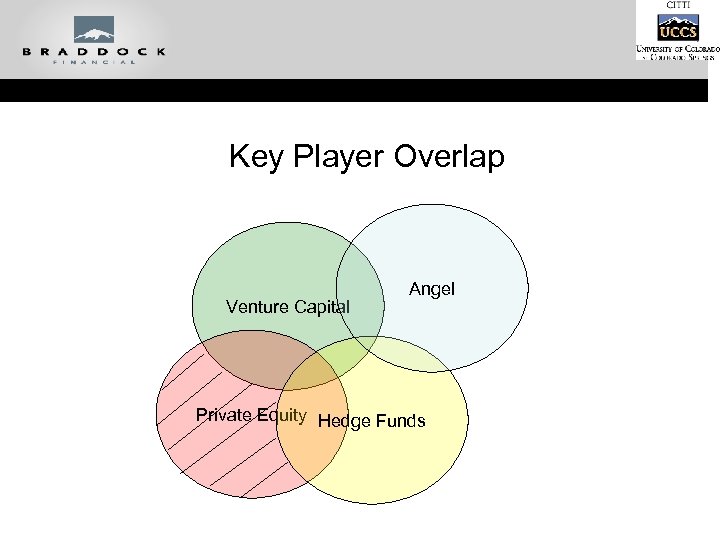 Key Player Overlap Venture Capital Angel Private Equity Hedge Funds
Key Player Overlap Venture Capital Angel Private Equity Hedge Funds
 Traditional Private Equity – Primary Activity • Professional pools of capital that buy all the publicly traded equity of target companies = “Go Private” • Usually done with borrowed money – High degree of leverage • Aka : Leveraged Buyout
Traditional Private Equity – Primary Activity • Professional pools of capital that buy all the publicly traded equity of target companies = “Go Private” • Usually done with borrowed money – High degree of leverage • Aka : Leveraged Buyout
 The Basic Value Creation Formula Fundamental Ideas 1) 2) 3) Re-focuses acquired businesses resulting in lower costs and improved efficiency. Value is created through basic finance that says debt can increase firm value if you can afford it! • Exploits corporate aversion to debt (Henry Mc. Vey, Morgan Stanley). Regulatory Arbitrage – Sarbanes-Oxley
The Basic Value Creation Formula Fundamental Ideas 1) 2) 3) Re-focuses acquired businesses resulting in lower costs and improved efficiency. Value is created through basic finance that says debt can increase firm value if you can afford it! • Exploits corporate aversion to debt (Henry Mc. Vey, Morgan Stanley). Regulatory Arbitrage – Sarbanes-Oxley
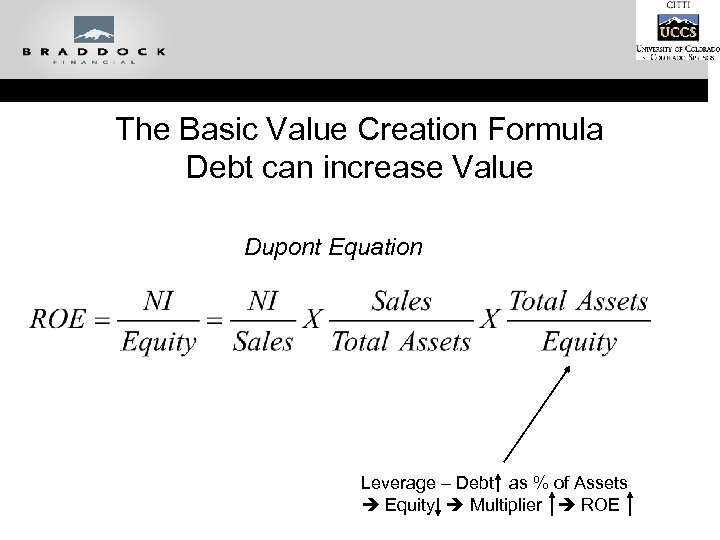 The Basic Value Creation Formula Debt can increase Value Dupont Equation Leverage – Debt as % of Assets Equity Multiplier ROE
The Basic Value Creation Formula Debt can increase Value Dupont Equation Leverage – Debt as % of Assets Equity Multiplier ROE
 The Basic Value Creation Formula Debt can increase Value Consider a company that takes on debt at a cost of $3 in Net Income, but changes NOTHING ELSE. Could drop NI to 4. 8 and still match the previous ROE!!
The Basic Value Creation Formula Debt can increase Value Consider a company that takes on debt at a cost of $3 in Net Income, but changes NOTHING ELSE. Could drop NI to 4. 8 and still match the previous ROE!!
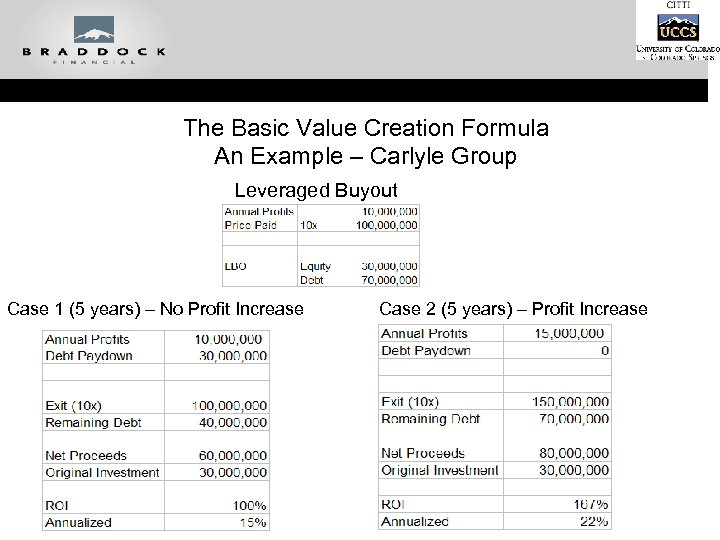 The Basic Value Creation Formula An Example – Carlyle Group Leveraged Buyout Case 1 (5 years) – No Profit Increase Case 2 (5 years) – Profit Increase
The Basic Value Creation Formula An Example – Carlyle Group Leveraged Buyout Case 1 (5 years) – No Profit Increase Case 2 (5 years) – Profit Increase
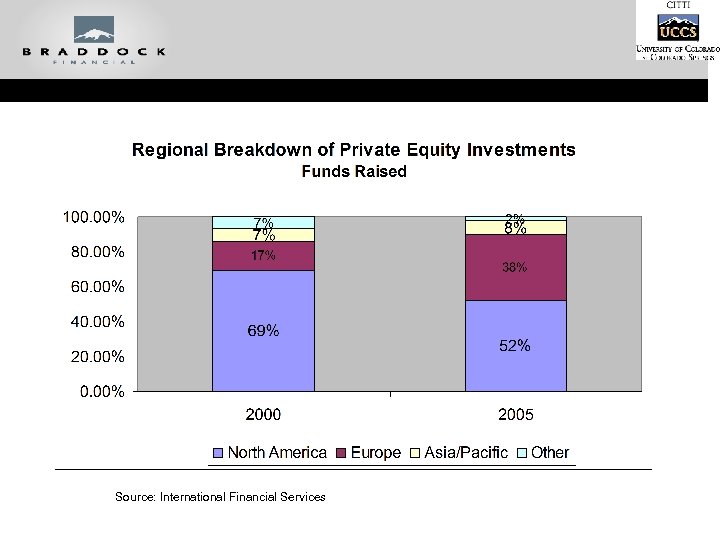 Source: International Financial Services
Source: International Financial Services
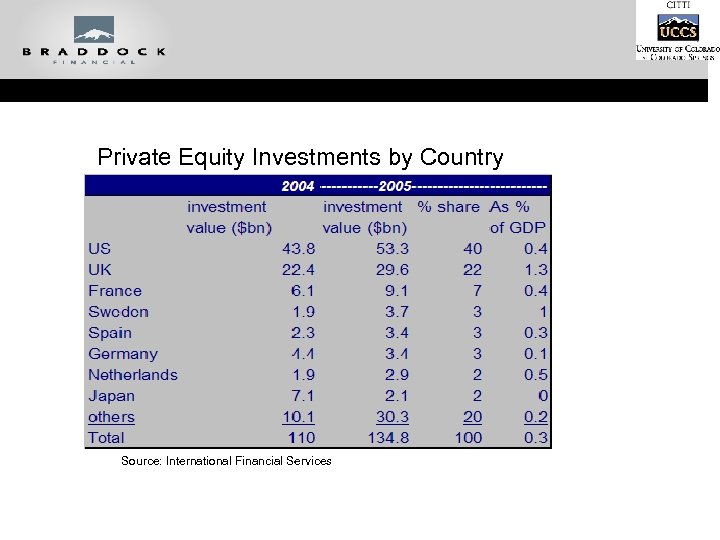 Private Equity Investments by Country Source: International Financial Services
Private Equity Investments by Country Source: International Financial Services
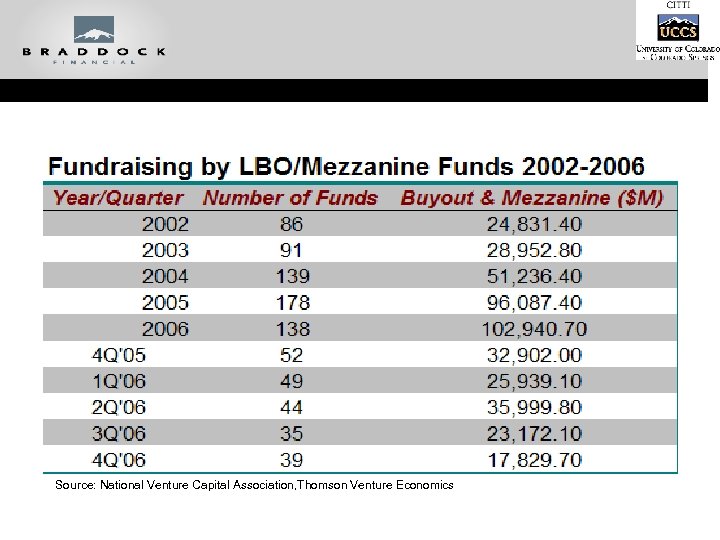 Source: National Venture Capital Association, Thomson Venture Economics
Source: National Venture Capital Association, Thomson Venture Economics
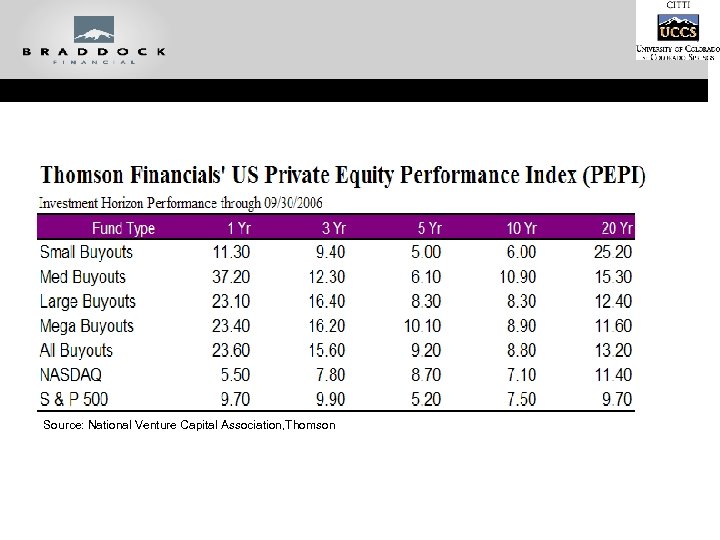 Source: National Venture Capital Association, Thomson
Source: National Venture Capital Association, Thomson
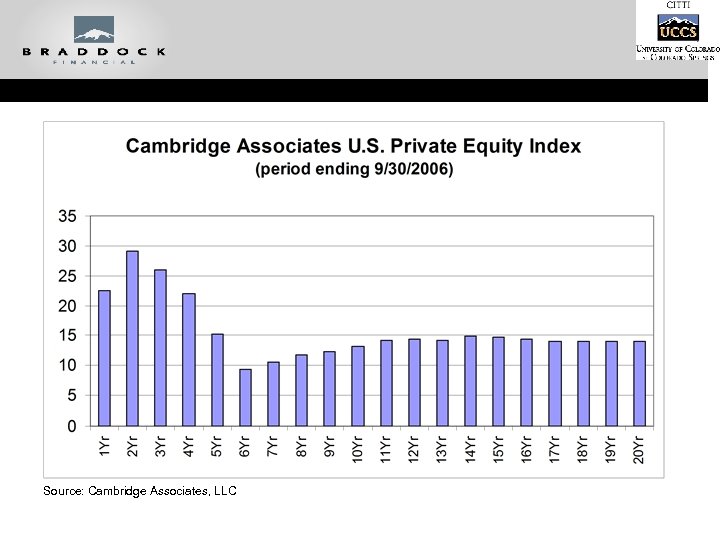 Source: Cambridge Associates, LLC
Source: Cambridge Associates, LLC
 Private Equity Issues Going Forward • PE as a new Model of General Management (Jensen) – Overcomes entrenched thinking, management and disjoint between manager incentives and capital markets. – Problematic Trends • Publicly held Private Equity – oxymoron • Fee Structures not tied to exit • Hedge funds in the PE business – not a transaction business.
Private Equity Issues Going Forward • PE as a new Model of General Management (Jensen) – Overcomes entrenched thinking, management and disjoint between manager incentives and capital markets. – Problematic Trends • Publicly held Private Equity – oxymoron • Fee Structures not tied to exit • Hedge funds in the PE business – not a transaction business.
 Private Equity Issues Going Forward • 2007 estimate of$160 B in dry powder $750 B $590 B in debt appetite. – Banking capacity is finite and already extended. – Potential regulatory limits
Private Equity Issues Going Forward • 2007 estimate of$160 B in dry powder $750 B $590 B in debt appetite. – Banking capacity is finite and already extended. – Potential regulatory limits
 Private Equity Issues Going Forward • PE Boom has been fueled by – Historically low rates – Regulatory arbitrage • Both could reverse quickly and change the metrics dramatically
Private Equity Issues Going Forward • PE Boom has been fueled by – Historically low rates – Regulatory arbitrage • Both could reverse quickly and change the metrics dramatically