6db1542700715e65b02307f86727ec48.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 43

PRIORITY 1 Life sciences, genomics and biotechnology for health From Expressions of Interest to a Workprogramme for 2003 Slide 1
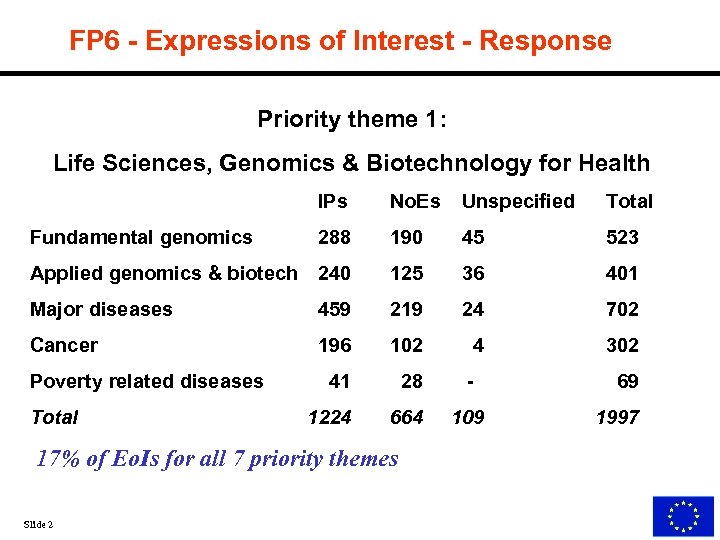
FP 6 - Expressions of Interest - Response Priority theme 1: Life Sciences, Genomics & Biotechnology for Health IPs No. Es Unspecified Total 288 190 45 523 Applied genomics & biotech 240 125 36 401 Major diseases 459 219 24 702 Cancer 196 102 4 302 41 28 - 1224 664 109 Fundamental genomics Poverty related diseases Total 17% of Eo. Is for all 7 priority themes Slide 2 69 1997
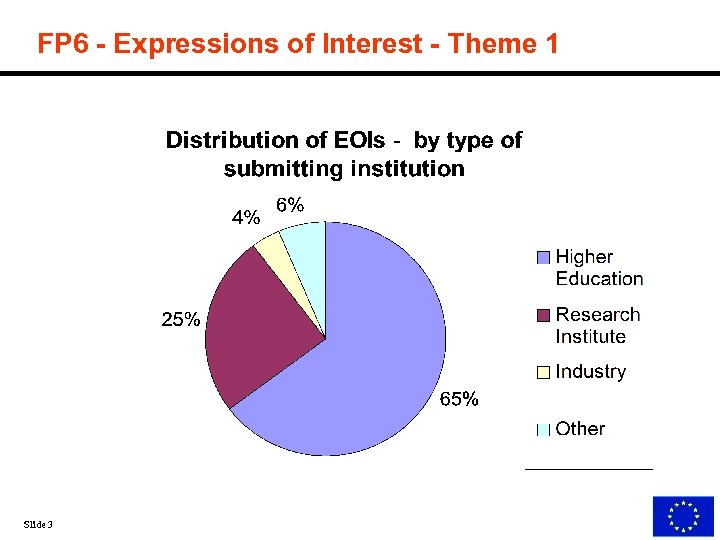
FP 6 - Expressions of Interest - Theme 1 Slide 3
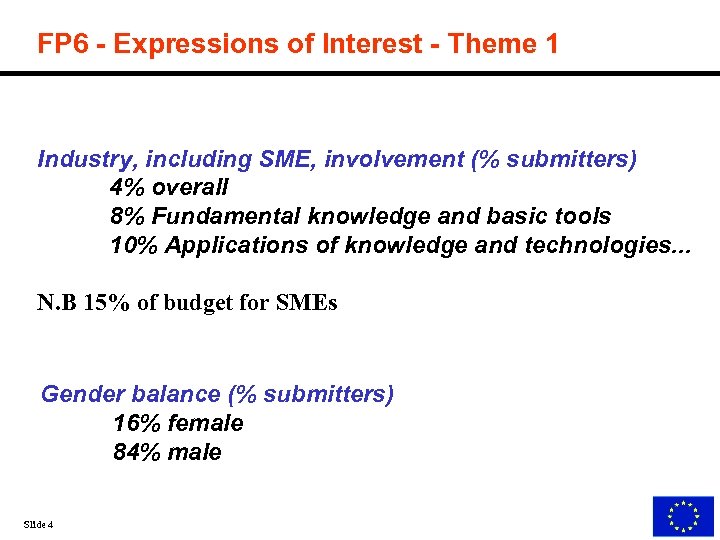
FP 6 - Expressions of Interest - Theme 1 Industry, including SME, involvement (% submitters) 4% overall 8% Fundamental knowledge and basic tools 10% Applications of knowledge and technologies. . . N. B 15% of budget for SMEs Gender balance (% submitters) 16% female 84% male Slide 4
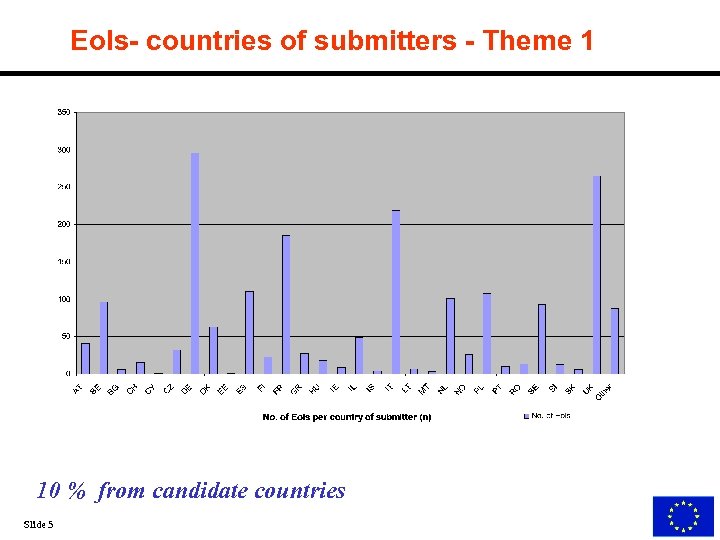
Eo. Is- countries of submitters - Theme 1 10 % from candidate countries Slide 5

FP 6 - Expressions of Interest - Theme 1 Outcome of the panel meeting Categories of scientific topics - all panels 1. Strategic importance for Europe & thematic priority; ready for implementation through an IP or No. E 2. Not-relevant to thematic priority; less obvious strategic importance for Europe Some panels 3. Strategic importance for Europe & thematic priority; BUT not yet mature for an IP or No. E (based on the Eo. Is received) 4. Strategic importance but not covered by any Eo. Is or the Eo. Is were not well argued Slide 6

FP 6 - Expressions of Interest - Theme 1 Analysis Methodology At the panel meeting in Bussels “Citation list” of Eo. Is to start the discussion - cited Eo. Is - non-cited Eo. Is - expert rapporteur for every Eo. I Some Eo. Is analysed by more than one panel (broad scope) Definition of topics for IP and No. E - no pre-selection of particular Eo. I or consortium Slide 7

Fundamental knowledge and basic tools for functional genomics in all organisms • In total, 30 recommended topics • 15 topics will be published in first call; 15 in second call • The selected topics will be open only for the call indicated • It is envisaged that no more than 1 project utilising a new instrument will be funded for each topic • There will be competition between topics as well as within topic areas • This will result in some topic areas not being supported Slide 8
Gene expression and Proteomics Examples • Advanced array technologies • High throughput proteomics for large data set of protein interactions • In situ gene expression analysis in mouse and human tissues Structural genomics Examples • Membrane proteins • Viral replication • Supramolecular analysis (No. E) • Large protein complexes • Hardware and software for automated technologies at synchrotron sites (IP) Slide 9
Comparative genomics & Population genetics Examples • Non-mammalian vertebrate models (IP) • In-vivo imaging for phenotyping and functional analysis • RNA interference screening in Arabidopsis for processes relevant to health • Phenotyping human populations • Bacterial diversity with relevance to human health (No. E) • High throughput genotyping in human populations (No. E) Bioinformatics Examples • Annotation of human and other genomes (No. E) Slide 10 • Genomics grid for European research (No. E) • Software platform to tackle sequence-structure-function relationships
Basic biological processes Examples: • Cell cycle • Kidney disease • Non-human embryonic stem • Peroxisomes cell differentiation • Erythroid development (IP) • Lymphangiogenesis • Inflammation processes (No. E) • Ubiquitin-proteasome (No. E) • Epigenetics (No. E) Slide 11 • Inner ear or retina development • DNA damage and repair • Disease of the immune system or of the muscle • X-linked syndromes
Traditional instruments Examples: • Transcription activation • Signal transduction • Intracellular communication • Non-coding genomic information • Integration of genes • In silico prediction of gene function • Simulation of complex regulatory networks • New tools and approaches, standard protocols producing knowledge in functional and structural genomics Slide 12

Applications of knowledge and technologies in the field of genomics and biotechnology for health Strategic Objective: To foster the competitiveness of Europe’s biotechnology industry by exploiting the wealth of biological data produced by genomics and advances in biotechnology Slide 13
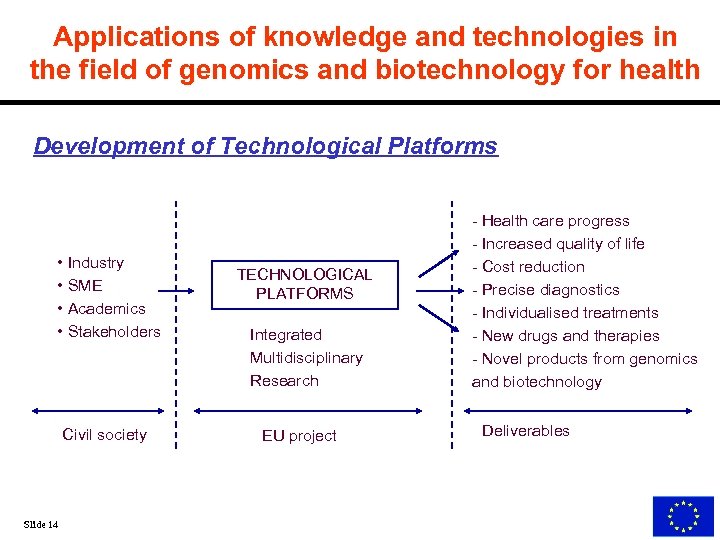
Applications of knowledge and technologies in the field of genomics and biotechnology for health Development of Technological Platforms • Industry • SME • Academics • Stakeholders Civil society Slide 14 TECHNOLOGICAL PLATFORMS Integrated Multidisciplinary Research EU project - Health care progress - Increased quality of life - Cost reduction - Precise diagnostics - Individualised treatments - New drugs and therapies - Novel products from genomics and biotechnology Deliverables

Applications of knowledge and technologies in the field of genomics and biotechnology for health Technology Platforms will focus their research activities on: • New, safer and more effective drugs including pharmacogenomics approaches • New diagnostics • New in vitro tests to replace animal experimentation • New preventive and therapeutic tools such as somatic gene and cell therapies (in particular stem cell therapies) and immunotherapies • Innovative research in post-genomics (novel products from genomics and biotechnology) Slide 15

STEM CELL Therapies • Detailed implementing provisions concerning research activities involving the use of human embryos and human embryonic stem cells which may be funded under the 6 th Framework Programme shall be established by 31 December 2003. • During that period and pending establishment of the detailed implementing provision, the Commission will not propose to fund such research, with the exception of the study of banked or isolated human embryonic stem cells in culture. Slide 16

New, safer and more effective drugs including pharmacogenomics approaches Examples • • Drugs for aberrant molecular signalling in protein phosphorylation pathways (IP) Genome-based individualised medicine Drugs for psychiatric disorders (No. E) Antiviral therapies (IP) • Medicines for paediatrics • Computer-assisted modelling for drugs • Therapeutics for neurodegenerative diseases Development of new diagnostics Examples • • Non-invasive diagnostics: Development of markets for anteand neonatal screening (No. E) • Genetic tests allowing for harmonisation, validation and standardisation In-vivo molecular imaging Development of new in vitro tests Examples • Combined in vitro cell and sensor technologies for animal toxicology (IP) Slide 17 • Test batteries for human acute toxicity

New preventive and therapeutic tools Examples • • • New cell lines for cellbased therapies (IP) • Gene delivery systems against severe acquired diseases • Gene therapy of inherited diseases Allogenic stem cell • transplantation for haematological and neoplastic diseases (IP) • Safety, quality, standardisation of stem cells (European registry) Cell-based therapies for • regeneration of connective tissue (IP) • Vaccine delivery systems (bacterial, synthetic, aimed at dendritic cells, etc…) Regeneration therapies for vital organs New chemokine modulators in autoimmune diseases Innovative research in Post-Genomics Examples • Post-genomic approaches against asthma and autoimmune diseases (IP) • Plant platforms for immunotherapeutic biomolecule production (IP) Slide 18 • RNA as human therapeutic tool • Post-genomic approaches to study human pathogens Pre-clinical and clinical applications •

New, safer and more effective drugs including pharmacogenomics approaches Examples: Blood substitutes (e. g. oxygen carriers), G-Protein coupled receptors Development of new diagnostics Examples: Non-invasive diagnostics using bioinformatics tools, Diagnostics for prion diseases Development of new in vitro tests Examples: Competitive product screening & development process stages lead compounds by introduction of alternative testing New preventive and therapeutic tools Examples: Vaccine technologies targeted to dendritic cells Databank on immuno therapies, comprising advances from genomics, proteomics and cell biology Stem cell products for myocardial repair Innovative research in post-genomics Examples: Slide 19 Combinatorial biosynthesis, Optically-active therapeutic biomolecules by biocatalysis, Precision technology platforms from post-genomics
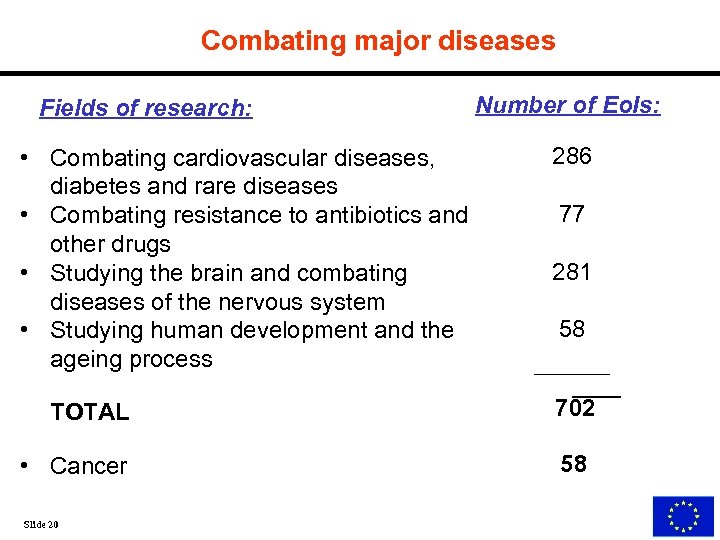
Combating major diseases Fields of research: • Combating cardiovascular diseases, diabetes and rare diseases • Combating resistance to antibiotics and other drugs • Studying the brain and combating diseases of the nervous system • Studying human development and the ageing process TOTAL • Cancer Slide 20 Number of Eo. Is: 286 77 281 58 702 58
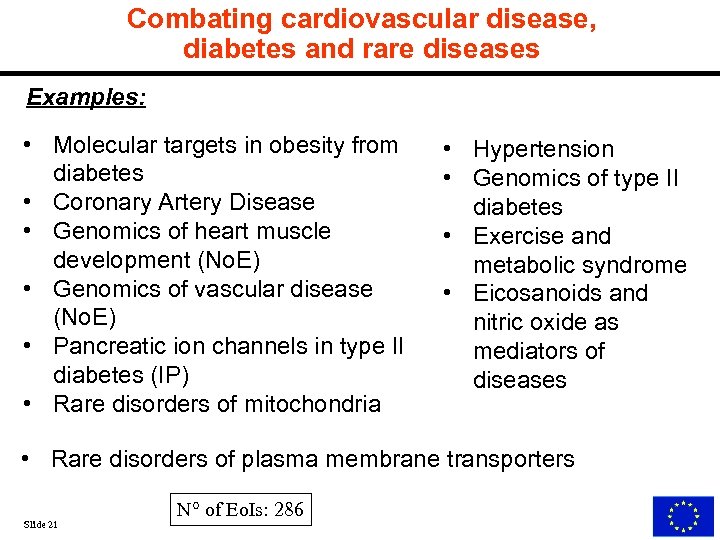
Combating cardiovascular disease, diabetes and rare diseases Examples: • Molecular targets in obesity from diabetes • Coronary Artery Disease • Genomics of heart muscle development (No. E) • Genomics of vascular disease (No. E) • Pancreatic ion channels in type II diabetes (IP) • Rare disorders of mitochondria • Hypertension • Genomics of type II diabetes • Exercise and metabolic syndrome • Eicosanoids and nitric oxide as mediators of diseases • Rare disorders of plasma membrane transporters Slide 21 N° of Eo. Is: 286

Combating resistance to antibiotics and other drugs Examples: • Upper Respiratory Tract Infections (No. E) • Anti-viral drug resistance • Antibiotics producing organisms • New targets for drugs - the ribosome • Anti-fungal resistance • Microbial ecology epidemiology • Control of hospital acquired infections • Broadening the knowledge base on molecular mechanisms behind resistance • Non antimicrobial therapies Slide 22
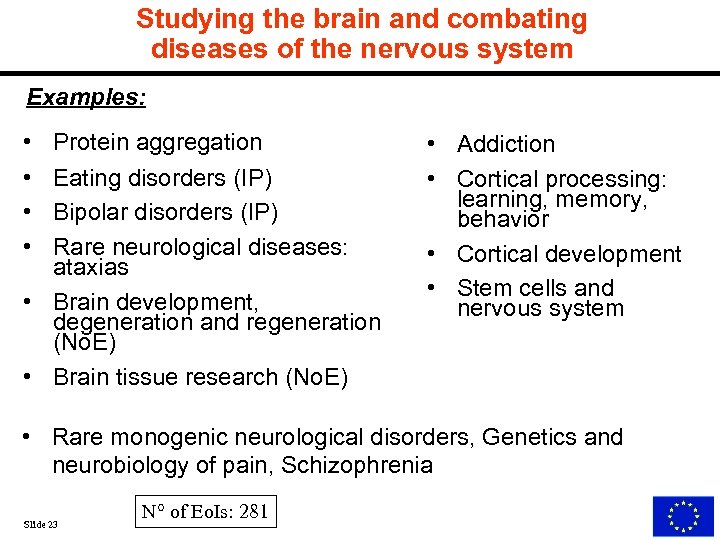
Studying the brain and combating diseases of the nervous system Examples: • • Protein aggregation Eating disorders (IP) Bipolar disorders (IP) Rare neurological diseases: ataxias • Brain development, degeneration and regeneration (No. E) • Brain tissue research (No. E) • Addiction • Cortical processing: learning, memory, behavior • Cortical development • Stem cells and nervous system • Rare monogenic neurological disorders, Genetics and neurobiology of pain, Schizophrenia Slide 23 N° of Eo. Is: 281
Human Development and Ageing Examples: • Longevity • Mesodermal organ system (No. E) • Mitochondrial dysfunction • Embryo implantation • Congenital anomalies Markers • Aberrant Steroid signalling • Biochemistry of Reactive Oxygen Species • Molecular mechanisms of bone homeostasis N° of Eo. Is: 58 Slide 24

Cancer Selected 6 out of 14 topics for first call in order to ensure: Þ Potential co-ordination of complementary areas (e. g. molecular targets - molecular imaging) Þ Balanced coverage of the main WP areas: A. Establishing facilities for exploitation of research • Registries and repositories B. Clinical research • European networks for clinical trials • Molecular imaging for early detection • Radiation therapy C. Translational research • Functional oncogenomics • Molecular targets Slide 25
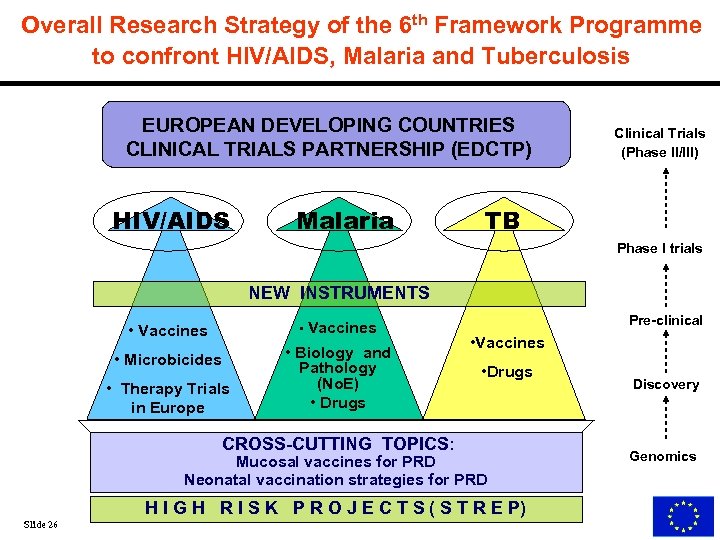
Overall Research Strategy of the 6 th Framework Programme to confront HIV/AIDS, Malaria and Tuberculosis EUROPEAN DEVELOPING COUNTRIES CLINICAL TRIALS PARTNERSHIP (EDCTP) HIV/AIDS Malaria Clinical Trials (Phase II/III) TB Phase I trials NEW INSTRUMENTS • Vaccines • Microbicides • Therapy Trials in Europe • Biology and Pathology (No. E) • Drugs Pre-clinical • Vaccines • Drugs CROSS-CUTTING TOPICS: Mucosal vaccines for PRD Neonatal vaccination strategies for PRD H I G H R I S K P R O J E C T S ( S T R E P) Slide 26 Discovery Genomics
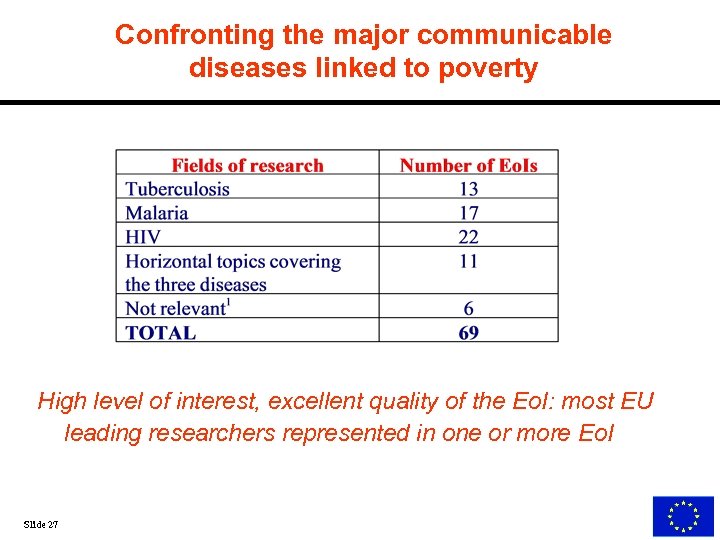
Confronting the major communicable diseases linked to poverty High level of interest, excellent quality of the Eo. I: most EU leading researchers represented in one or more Eo. I Slide 27

Eo. I’s Panel main recommendations • Encourage participation of partners from DC • Stimulate the training component both for the North and the South • Increase the professionalism of management • Include in the projects pre-clinical testing in nonhuman primates and GMP production of candidate drugs or vaccines Slide 28

PRIORITY 5 Food Quality & Safety From Expressions of Interest to a Workprogramme for 2003 Slide 29
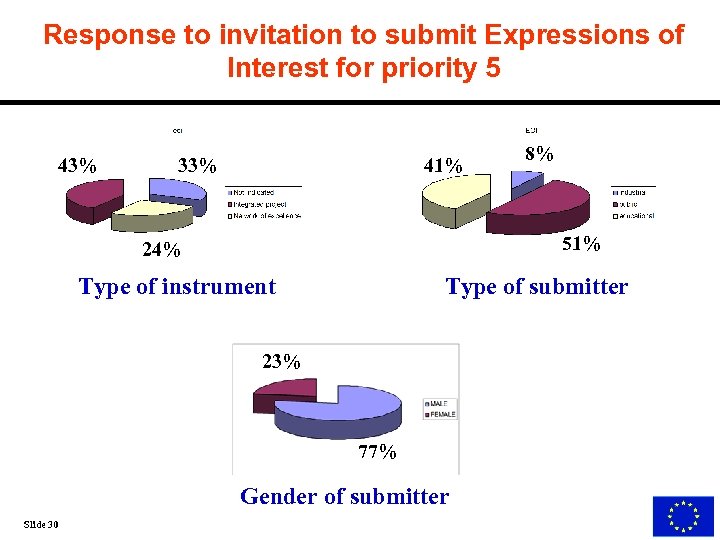
Response to invitation to submit Expressions of Interest for priority 5 43% 41% 33% 51% 24% Type of instrument Type of submitter 23% 77% Gender of submitter Slide 30 8%

Expert comments on nonselected Eo. I • Very many EOIs on similar subjects • Many were technical skills looking for funds • Many were on a very large scale with little indication of management skills • Need for a “Development Bank” business plan approach • Lack of analysis on the importance of the problems to be addressed and of any potential benefits • No gender balance awareness • IP management was weak • No gender balance awareness and IP management was weak Slide 31

From Eo. I to Workprogramme • Budget: 149 M€ in 2003 • Focussing: from 53 topics through Eo. Is down to. . . • Consultation of AG and committee • Maturity of the topic • Readiness of the topics for new instruments or traditional instruments • Urgency of the issue: 2003 or 2004 Slide 32

Format of the Draft Workprogramme (1) • Common format for all Thematic Priorities • Follows the specific programme • Introduction to each area: clear signals • NI (NE/ IP) or TI (STREP/ CA) Slide 33

Format of the Draft Workprogramme (2) • 2003: - selected topics - detailed description (objectives/disciplines/expected outcome) • 2004: - indicative areas - outline description • Objectives for Specific Support Measures Slide 34
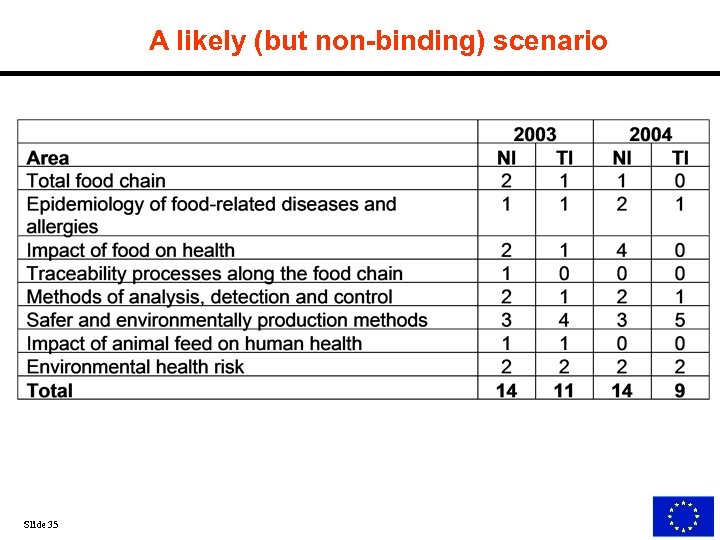
A likely (but non-binding) scenario Slide 35

Total Food Chain Examples: · Food from low input and organic production systems: Ensuring the safety and improving quality along the whole chain · Quality seafood for improved consumer health and wellbeing · Improving the quality and safety of beef for the consumer · Pathogen free production systems Slide 36

Epidemiology of food-related diseases and allergies Examples: · Validated food information database for Europe (No. E) · Epidemiology of food allergy · Influence of gene-nutrient interaction on the development of chronic diseases · Influence of nutrition and lifestyle on healthy ageing aimed at preventing adult degenerative disease · Nutritional and lifestyle habits of adolescents throughout Europe, including production of functional foods with sensory properties attractive to adolescents Slide 37

Impact of food on health Examples: · Functional genomics in relation to food, nutrition and health (No. E) · Lipid metabolism and the metabolic syndrome · Food safety, risk assessment and communication · Programming effects of early nutrition on long-term health · Microbes, the immune system and gut health · Improving and enhancing the nutritional value and health benefits of cereals · Health risks from heat-treated foods and food products Slide 38
“Traceability” processes along the production chain · Development of reliable traceability methods and systems to establish the origin/mode of productin of food products Slide 39

Methods of analysis, detection and control Examples: · · Zoonoses including food borne diseases (No. E) Prion diseases (No. E) Chemical contaminants in food products Emerging and future food borne pathogenic microorganisms throughout the food chain · Quantitative risk assessment strategies based on probabilistic, genomic and profiling approaches including a risk-benefit analysis for novel foods · Cost-effective tools for risk management and traceability systems for zoonotic agents and phycotoxins in seafood Slide 40

Safer and environmentally friendly production methods and healthier foodstuffs Examples: · · · High throughput analysis of plant composition and metabolism for optimising end-product quality Animal welfare for improved food quality Genomics of host-pathogen interactions in animals (No. E) · · · Soil microbial community management for safe production under stress conditions Plant biodiversity to reduce pesticide application Immunological basis for protection against animal disease Antibiotic resistance Crop protection systems based on biological control agents and semiochemicals Modelling of improved crop establishment in low input systems Plant flavonoids Recycled organic wastes from the food chain Sustainable aquaculture GMO co-existence analysis Use of genetic resistance to control plant viruses Disease risk from alternative and enriched cage and free-range systems Slide 41

Impact of animal feed on human health · New strategies to improve grain legumes for food and feed · Alternatives to antimicrobials in feeds Slide 42

Environmental health risks Examples: · · Allergy and asthma network Exposure to chemical residues in the environment Environmental factors and puberty onset Cancer risk from environment, diet and genetic · · Human pathogens in drinking water Food and fertility Neurotoxic effects of environmental contamineants Exposure to complex chemical mixtures Slide 43
6db1542700715e65b02307f86727ec48.ppt