9ab7df89a69581a775e239fbd1a29425.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 20
 Printing q Some printer jargon m Spooler • A piece of software m Dpi • Dots per inch m PDL • Page description languages m Bitmap • Common bitmap formats include JPEG, PNG, TIFF and GIF Introduction 1
Printing q Some printer jargon m Spooler • A piece of software m Dpi • Dots per inch m PDL • Page description languages m Bitmap • Common bitmap formats include JPEG, PNG, TIFF and GIF Introduction 1
 Printing q Some printer jargon (cont) m RIP • Raster Image Processor • Converts PDL documents to a bitmap m Filters • Programs that modify jobs en route from the spooler to the printer m Postscript • The most common PDL found on Unix m PCL • Exclusively on Hp printers and quite common in PC world Introduction 2
Printing q Some printer jargon (cont) m RIP • Raster Image Processor • Converts PDL documents to a bitmap m Filters • Programs that modify jobs en route from the spooler to the printer m Postscript • The most common PDL found on Unix m PCL • Exclusively on Hp printers and quite common in PC world Introduction 2
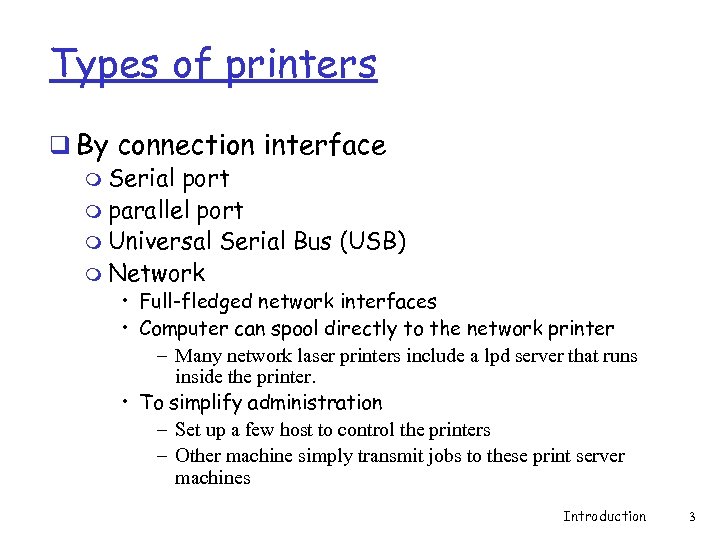 Types of printers q By connection interface m Serial port m parallel port m Universal Serial Bus (USB) m Network • Full-fledged network interfaces • Computer can spool directly to the network printer – Many network laser printers include a lpd server that runs inside the printer. • To simplify administration – Set up a few host to control the printers – Other machine simply transmit jobs to these print server machines Introduction 3
Types of printers q By connection interface m Serial port m parallel port m Universal Serial Bus (USB) m Network • Full-fledged network interfaces • Computer can spool directly to the network printer – Many network laser printers include a lpd server that runs inside the printer. • To simplify administration – Set up a few host to control the printers – Other machine simply transmit jobs to these print server machines Introduction 3
 BSD Printing q Redhat and Free. BSD use BSD printing system. q Daemon lpd m Accepts print jobs from users or other (remote) lpds m Processes the jobs m Sends jobs to an actual printer m reads /etc/printcap and is started at boot time q Program lpr allow users to submit print jobs to lpd. m Lpr and lpd communicate through the unix socket /dev/printer m Which printer to use • Option -Pprinter • Env $PRINTER • Default printer lp, or the first one in /etc/printcap Introduction 4
BSD Printing q Redhat and Free. BSD use BSD printing system. q Daemon lpd m Accepts print jobs from users or other (remote) lpds m Processes the jobs m Sends jobs to an actual printer m reads /etc/printcap and is started at boot time q Program lpr allow users to submit print jobs to lpd. m Lpr and lpd communicate through the unix socket /dev/printer m Which printer to use • Option -Pprinter • Env $PRINTER • Default printer lp, or the first one in /etc/printcap Introduction 4
 BSD Printing m Spool • Lpr create two files under the printer’s spool dir /var/spool/lpd/printername control file started with cf data file started with df m Lpr notifies lpd of the job’s existence m Lpd then check printcap to determine if the destination is local or remote • If remote, lpd opens a connection to the remote machines’ lpd, transfer the cf and df file, and delete the local copy • If local, lpd creates a series of UNIX pipes between the spool file and hardware to transport the data – filter processes Introduction 5
BSD Printing m Spool • Lpr create two files under the printer’s spool dir /var/spool/lpd/printername control file started with cf data file started with df m Lpr notifies lpd of the job’s existence m Lpd then check printcap to determine if the destination is local or remote • If remote, lpd opens a connection to the remote machines’ lpd, transfer the cf and df file, and delete the local copy • If local, lpd creates a series of UNIX pipes between the spool file and hardware to transport the data – filter processes Introduction 5
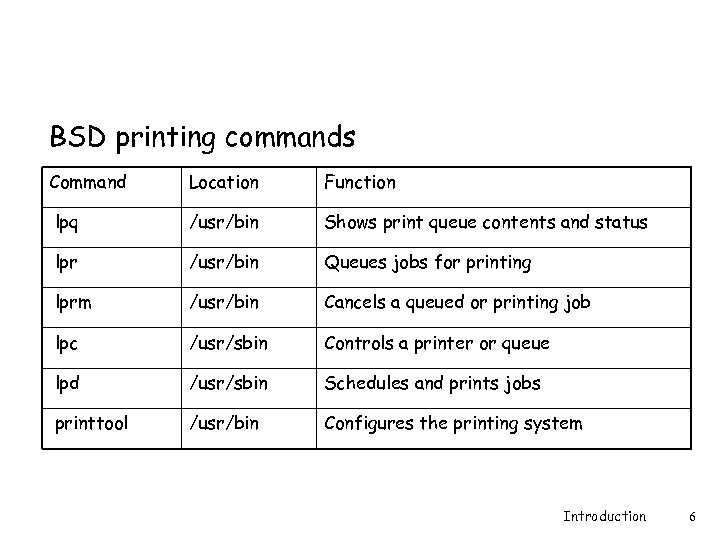 BSD printing commands Command Location Function lpq /usr/bin Shows print queue contents and status lpr /usr/bin Queues jobs for printing lprm /usr/bin Cancels a queued or printing job lpc /usr/sbin Controls a printer or queue lpd /usr/sbin Schedules and prints jobs printtool /usr/bin Configures the printing system Introduction 6
BSD printing commands Command Location Function lpq /usr/bin Shows print queue contents and status lpr /usr/bin Queues jobs for printing lprm /usr/bin Cancels a queued or printing job lpc /usr/sbin Controls a printer or queue lpd /usr/sbin Schedules and prints jobs printtool /usr/bin Configures the printing system Introduction 6
 BSD Printing q lpc : make administrative changes m Enable or disable queuing for a particular printer • enable/disable printer m Enable or disable printing on a particular printer • start/stop printer m Remove all jobs from a printer’s queue • clean printer m Move a job to the top of a printer’s queue • topq printer jobid • topq printer username m Start, stop or restart the lpd daemon • restart printer m Get printer status information • status printer Introduction 7
BSD Printing q lpc : make administrative changes m Enable or disable queuing for a particular printer • enable/disable printer m Enable or disable printing on a particular printer • start/stop printer m Remove all jobs from a printer’s queue • clean printer m Move a job to the top of a printer’s queue • topq printer jobid • topq printer username m Start, stop or restart the lpd daemon • restart printer m Get printer status information • status printer Introduction 7
 BSD Printing q /etc/printcap file m BSD printing system’s master database m A printer must be described in the printcap file before jobs can be submitted it. m Printcap format • Name: xx=string: xx#number: xx=string… … Introduction 8
BSD Printing q /etc/printcap file m BSD printing system’s master database m A printer must be described in the printcap file before jobs can be submitted it. m Printcap format • Name: xx=string: xx#number: xx=string… … Introduction 8
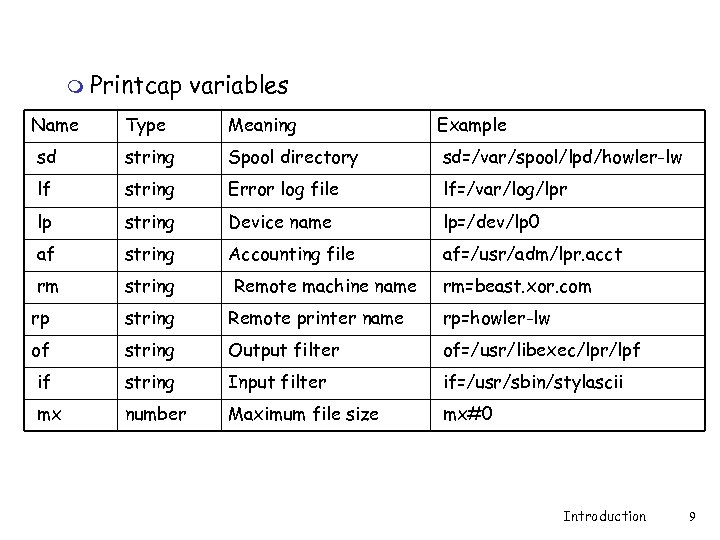 m Printcap variables Name Type Meaning Example sd string Spool directory sd=/var/spool/lpd/howler-lw lf string Error log file lf=/var/log/lpr lp string Device name lp=/dev/lp 0 af string Accounting file af=/usr/adm/lpr. acct rm string Remote machine name rm=beast. xor. com rp string Remote printer name rp=howler-lw of string Output filter of=/usr/libexec/lpr/lpf if string Input filter if=/usr/sbin/stylascii mx number Maximum file size mx#0 Introduction 9
m Printcap variables Name Type Meaning Example sd string Spool directory sd=/var/spool/lpd/howler-lw lf string Error log file lf=/var/log/lpr lp string Device name lp=/dev/lp 0 af string Accounting file af=/usr/adm/lpr. acct rm string Remote machine name rm=beast. xor. com rp string Remote printer name rp=howler-lw of string Output filter of=/usr/libexec/lpr/lpf if string Input filter if=/usr/sbin/stylascii mx number Maximum file size mx#0 Introduction 9
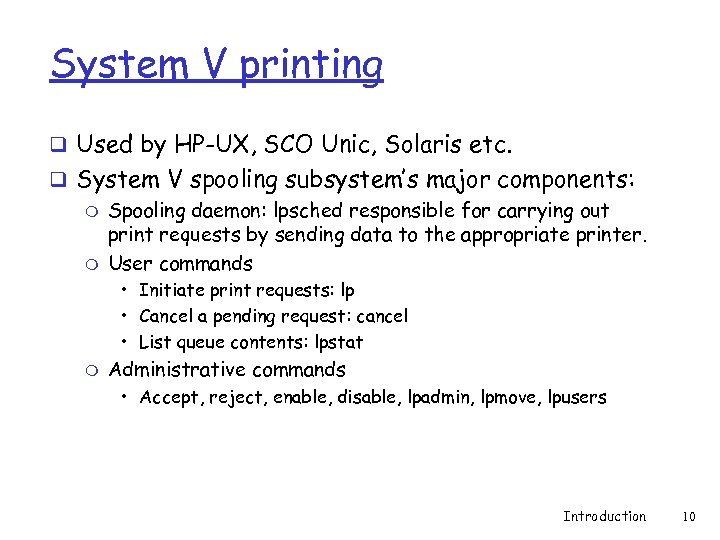 System V printing q Used by HP-UX, SCO Unic, Solaris etc. q System V spooling subsystem’s major components: m Spooling daemon: lpsched responsible for carrying out print requests by sending data to the appropriate printer. m User commands • Initiate print requests: lp • Cancel a pending request: cancel • List queue contents: lpstat m Administrative commands • Accept, reject, enable, disable, lpadmin, lpmove, lpusers Introduction 10
System V printing q Used by HP-UX, SCO Unic, Solaris etc. q System V spooling subsystem’s major components: m Spooling daemon: lpsched responsible for carrying out print requests by sending data to the appropriate printer. m User commands • Initiate print requests: lp • Cancel a pending request: cancel • List queue contents: lpstat m Administrative commands • Accept, reject, enable, disable, lpadmin, lpmove, lpusers Introduction 10
 System V printing m Spooling directories under /var/spool/lp/request named for each printer • By default the actual file to print is not copied. The changing or deleting a file before it is printed affects the final output. • Use –c option to lp to copy the file to the spool area q Device classes m Group similar devices and declare them to be equivalent to and substitutable for one another. q Setting the system default destination m Use the –d option to the lpadmin command • #lpadmin –dprinter 2 • #lpstat –d m User may set the env LPDEST Introduction 11
System V printing m Spooling directories under /var/spool/lp/request named for each printer • By default the actual file to print is not copied. The changing or deleting a file before it is printed affects the final output. • Use –c option to lp to copy the file to the spool area q Device classes m Group similar devices and declare them to be equivalent to and substitutable for one another. q Setting the system default destination m Use the –d option to the lpadmin command • #lpadmin –dprinter 2 • #lpstat –d m User may set the env LPDEST Introduction 11
 System V printing q Obtaining Destination Status Information m Lpstat command • • Accept job or not: -alist Display the members: -clist List print requests: -olist Display the current status: -plist Display users’ jobs: -ulist Display the special files: -vlist Display summary: -s Display all status info: -t Introduction 12
System V printing q Obtaining Destination Status Information m Lpstat command • • Accept job or not: -alist Display the members: -clist List print requests: -olist Display the current status: -plist Display users’ jobs: -ulist Display the special files: -vlist Display summary: -s Display all status info: -t Introduction 12
 System V printing q Controlling print queues m Use accept and reject commands to permit and inhibit spooling to a print queue. m Example: # reject –r “ There is no paper in the entire building …” laserprinter #accept laserprinter q Controlling the status of a particular printing device m m Use enable and disable commands followed by a device Example: #disable –r “ changing toner cartridge; back by 11” laserpritner #enable laserprinter Introduction 13
System V printing q Controlling print queues m Use accept and reject commands to permit and inhibit spooling to a print queue. m Example: # reject –r “ There is no paper in the entire building …” laserprinter #accept laserprinter q Controlling the status of a particular printing device m m Use enable and disable commands followed by a device Example: #disable –r “ changing toner cartridge; back by 11” laserpritner #enable laserprinter Introduction 13
 System V printing q Starting and stopping the print service m Started automatically at system boottime • Such as /etc/rc 2. d/S 80 lp m Check if the scheduler is running • #lpstat –r m Stop and start printing service manually • #lpshut • #/etc/rc 2. d/S 80 lp start q Managing printers and destination classes m Use lpadmin command to define and modify characteristics of printer devices and classes • Stop lpsched first Introduction 14
System V printing q Starting and stopping the print service m Started automatically at system boottime • Such as /etc/rc 2. d/S 80 lp m Check if the scheduler is running • #lpstat –r m Stop and start printing service manually • #lpshut • #/etc/rc 2. d/S 80 lp start q Managing printers and destination classes m Use lpadmin command to define and modify characteristics of printer devices and classes • Stop lpsched first Introduction 14
 System V printing • Adding a printer #lpadmin –p printer –v special-files interface-option Where interface_option can be » -e printer » -m model » -i interface-path Example: #lpadmin –p. PS 4 –v /dev/tty 02 –e. PS 3 • Modifying and deleting printers – Option –x removes a printer – Option –P changes a printer if it is existed. • Managing Device class – Use –c option to place a printer into a class » #lpadmin –p. PS 2 -claser Introduction 15
System V printing • Adding a printer #lpadmin –p printer –v special-files interface-option Where interface_option can be » -e printer » -m model » -i interface-path Example: #lpadmin –p. PS 4 –v /dev/tty 02 –e. PS 3 • Modifying and deleting printers – Option –x removes a printer – Option –P changes a printer if it is existed. • Managing Device class – Use –c option to place a printer into a class » #lpadmin –p. PS 2 -claser Introduction 15
 System V printing q Adding a New printer m Physically connect the printer m Change the ownership of the special file to the user lp and change its mode to 600 m Check startup file (s file and K file) • Make links if they do not exist m Shutdown printing service with lpshut if running, and then use lpadmin to add the printer m Start the printer and its queue • #accept PS 3 • #enable PS 3 m Test the new printer by spooling a small file. Introduction 16
System V printing q Adding a New printer m Physically connect the printer m Change the ownership of the special file to the user lp and change its mode to 600 m Check startup file (s file and K file) • Make links if they do not exist m Shutdown printing service with lpshut if running, and then use lpadmin to add the printer m Start the printer and its queue • #accept PS 3 • #enable PS 3 m Test the new printer by spooling a small file. Introduction 16
 Network Printing q Sharing printers among systems within a local area network m m Print server: allow users on other hosts send jobs to one or more of its printers Clients: send the jobs to remote hosts. q Between BSD System m Outgoing • Set up printcap entry to specify – the destination host (rm) – The target printer (rp) m Incoming • Allow a remote system to print – /etc/hosts. lpd or /etc/hosts. equiv Introduction 17
Network Printing q Sharing printers among systems within a local area network m m Print server: allow users on other hosts send jobs to one or more of its printers Clients: send the jobs to remote hosts. q Between BSD System m Outgoing • Set up printcap entry to specify – the destination host (rm) – The target printer (rp) m Incoming • Allow a remote system to print – /etc/hosts. lpd or /etc/hosts. equiv Introduction 17
 Network printing q Remote printing under Solaris m Outgoing • Register the remote system name using lpsystem • Set up a queue using lpadmin m Incoming • Handled by the Service Access Facility – Configure the local listen port monitor using pmadm Introduction 18
Network printing q Remote printing under Solaris m Outgoing • Register the remote system name using lpsystem • Set up a queue using lpadmin m Incoming • Handled by the Service Access Facility – Configure the local listen port monitor using pmadm Introduction 18
 Practice q Let’s configure the printer on Solaris m Connect the printer to the network m Set the printer IP address/netmask m Define the printer on your Solaris box • Use lpadmin sun as #lpadmin –p printername –s systemname • Or use /usr/sadm/admin/bin/printmgr m Enable the printer m Print a test page Introduction 19
Practice q Let’s configure the printer on Solaris m Connect the printer to the network m Set the printer IP address/netmask m Define the printer on your Solaris box • Use lpadmin sun as #lpadmin –p printername –s systemname • Or use /usr/sadm/admin/bin/printmgr m Enable the printer m Print a test page Introduction 19
 Exercise q Configure the printer on Linux with CUPS m CUPS: common Unix printing system • Dynamic printer detection – Broadcasts the printer available • Grouping printers • Integrating with Windows m Configure it via localhost: 631 m Disable the queue m Disable the printer m Cancel a job m Check the print queue Introduction 20
Exercise q Configure the printer on Linux with CUPS m CUPS: common Unix printing system • Dynamic printer detection – Broadcasts the printer available • Grouping printers • Integrating with Windows m Configure it via localhost: 631 m Disable the queue m Disable the printer m Cancel a job m Check the print queue Introduction 20


