f1db8be581f82817b8b5116deb1eb749.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 35
 Principles of Integrated Pest Management and Safe Use of Pesticides Capacity Building Course on Conservation Agriculture Based Crop Management in Bangladesh. June 11 -15, 2012. RWRC, Rajshahi, Bangladesh. Dr. Timothy J. Krupnik. Cropping Systems Agronomist. CIMMYT.
Principles of Integrated Pest Management and Safe Use of Pesticides Capacity Building Course on Conservation Agriculture Based Crop Management in Bangladesh. June 11 -15, 2012. RWRC, Rajshahi, Bangladesh. Dr. Timothy J. Krupnik. Cropping Systems Agronomist. CIMMYT.
 Presentation Outline 1. Consequences of misuse of pesticides 2. Principles of Integrated pest management (IPM) 3. Safe use of pesticides 4. What to do if poisoning occurs
Presentation Outline 1. Consequences of misuse of pesticides 2. Principles of Integrated pest management (IPM) 3. Safe use of pesticides 4. What to do if poisoning occurs
 What is a pesticide? • Control, prevention, destruction of pests. • Poison. • Target: Nervous system • When used in an integrated way, pesticides can benefit. • When not integrated, they can cause harm.
What is a pesticide? • Control, prevention, destruction of pests. • Poison. • Target: Nervous system • When used in an integrated way, pesticides can benefit. • When not integrated, they can cause harm.
 This presentation focuses on principles, not crop specific tools. Why?
This presentation focuses on principles, not crop specific tools. Why?
 Over use of insecticides in an agricultural ecosystem 1. Resistance 2. Resurgence 1. Replacement 2. Residues
Over use of insecticides in an agricultural ecosystem 1. Resistance 2. Resurgence 1. Replacement 2. Residues
 Pest Resistance Evolution of resistance to insecticides in an agricultural ecosystem
Pest Resistance Evolution of resistance to insecticides in an agricultural ecosystem
 Pest Resurgence Explosion of pests after insecticides. Caused by the loss of natural enemies. Lycosidae spp. Nilaparvata lugens
Pest Resurgence Explosion of pests after insecticides. Caused by the loss of natural enemies. Lycosidae spp. Nilaparvata lugens
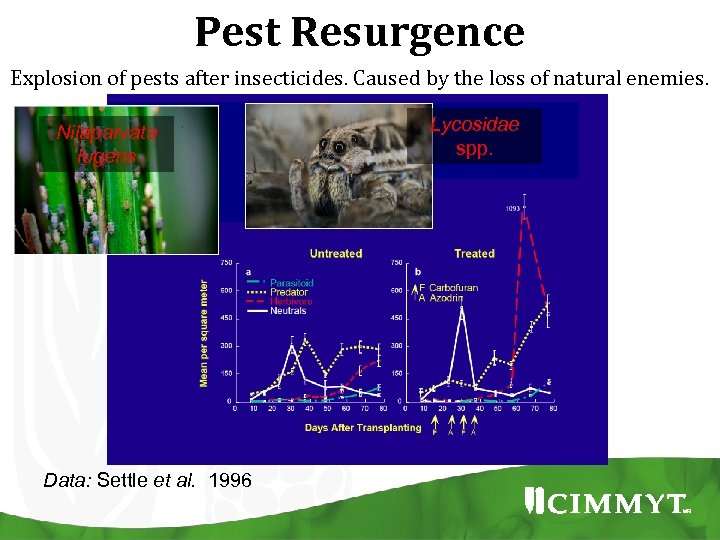 Pest Resurgence Explosion of pests after insecticides. Caused by the loss of natural enemies. Nilaparvata lugens Data: Settle et al. 1996 Lycosidae spp.
Pest Resurgence Explosion of pests after insecticides. Caused by the loss of natural enemies. Nilaparvata lugens Data: Settle et al. 1996 Lycosidae spp.
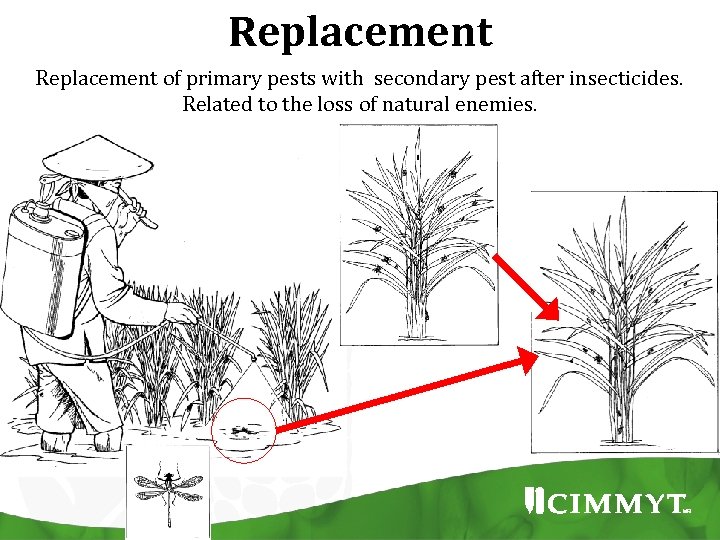 Replacement of primary pests with secondary pest after insecticides. Related to the loss of natural enemies.
Replacement of primary pests with secondary pest after insecticides. Related to the loss of natural enemies.
 Residues Pesticide residues easily enter the environment and can cause health concerns.
Residues Pesticide residues easily enter the environment and can cause health concerns.
 Integrated Pest Management A tool to provide long-term, economic suppression of pests. Builds on cultural management and ecological interactions to keep pest pressures low. Pesticides are applied to pose least possible risk as a 'last resort’ IPM is USAID policy.
Integrated Pest Management A tool to provide long-term, economic suppression of pests. Builds on cultural management and ecological interactions to keep pest pressures low. Pesticides are applied to pose least possible risk as a 'last resort’ IPM is USAID policy.
 Integrated Pest Management
Integrated Pest Management
 Biological Control of Pests • Predators, parasites and pathogens : “natural enemies”. Trichogramma spp. • Encourage habitat • “Mass release” 1. Inoculation - establishment 2. Dribble: Prevention of problems 3. Inundate: High release rate 4. Combinations: Knockdown + control
Biological Control of Pests • Predators, parasites and pathogens : “natural enemies”. Trichogramma spp. • Encourage habitat • “Mass release” 1. Inoculation - establishment 2. Dribble: Prevention of problems 3. Inundate: High release rate 4. Combinations: Knockdown + control
 Cultural Control • “Hygienic” fields and margins • Management of vector sources • Intercropping, mixed cropping, diversity • Resource concentration hypothesis (Root 1973) • Natural enemies hypothesis (Various researchers) • Trap cropping (applicable in Bangladesh? ) • Escape in time (planting date) • Others?
Cultural Control • “Hygienic” fields and margins • Management of vector sources • Intercropping, mixed cropping, diversity • Resource concentration hypothesis (Root 1973) • Natural enemies hypothesis (Various researchers) • Trap cropping (applicable in Bangladesh? ) • Escape in time (planting date) • Others?
 Host Plant Resistance Selection of varieties to (1) Escape pest attack or (2) tolerate pest presence 1. Escape: • Unpalatablility (tastes bad) • Leaf pubescence • Awns • Others? 2. Tolerance: • Able to withstand pest without impacting yield • Examples ?
Host Plant Resistance Selection of varieties to (1) Escape pest attack or (2) tolerate pest presence 1. Escape: • Unpalatablility (tastes bad) • Leaf pubescence • Awns • Others? 2. Tolerance: • Able to withstand pest without impacting yield • Examples ?
 Chemical Control If other options are not working 1. Chemical control: • Pheromones baits Selective Broad spectrum Bt • Selective spray always best for insect pests • Spot spray targeting often better than blanket spray for insect pests 2. Pesticide choice: • Lest harmful? 1. Affordable? 2. Available? Pheromone trapping
Chemical Control If other options are not working 1. Chemical control: • Pheromones baits Selective Broad spectrum Bt • Selective spray always best for insect pests • Spot spray targeting often better than blanket spray for insect pests 2. Pesticide choice: • Lest harmful? 1. Affordable? 2. Available? Pheromone trapping
 Observation and monitoring
Observation and monitoring
 Number of pest organisms Economic Threshold Time (in the crop season)
Number of pest organisms Economic Threshold Time (in the crop season)
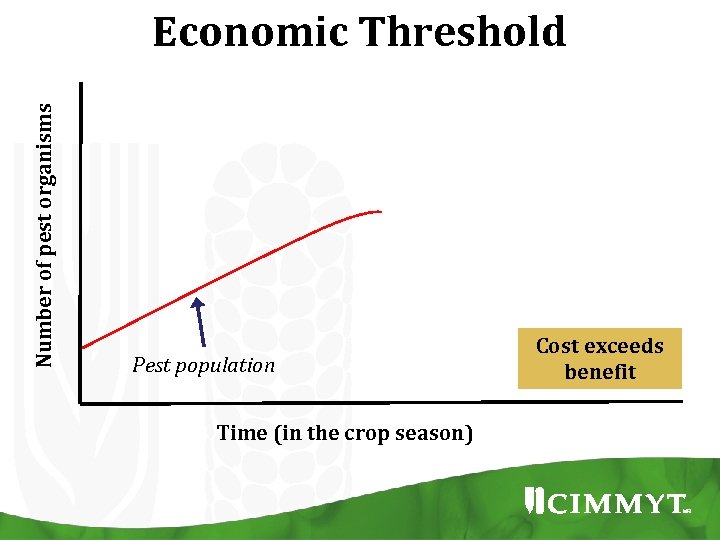 Number of pest organisms Economic Threshold Pest population Time (in the crop season) Cost exceeds benefit
Number of pest organisms Economic Threshold Pest population Time (in the crop season) Cost exceeds benefit
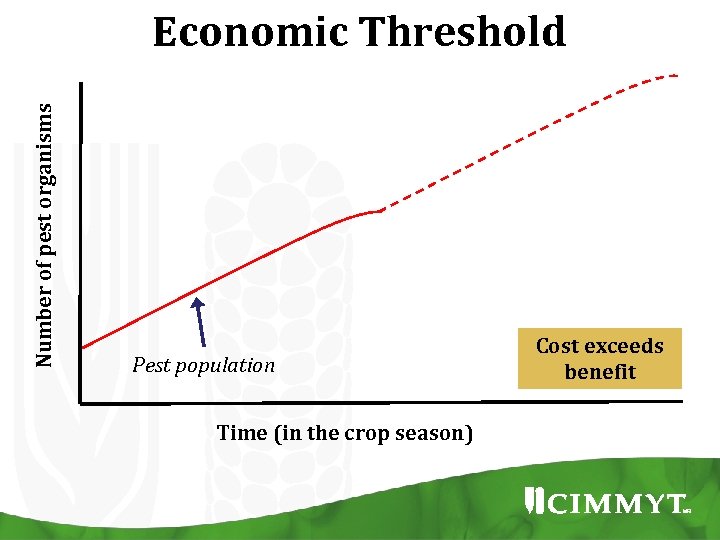 Number of pest organisms Economic Threshold Pest population Time (in the crop season) Cost exceeds benefit
Number of pest organisms Economic Threshold Pest population Time (in the crop season) Cost exceeds benefit
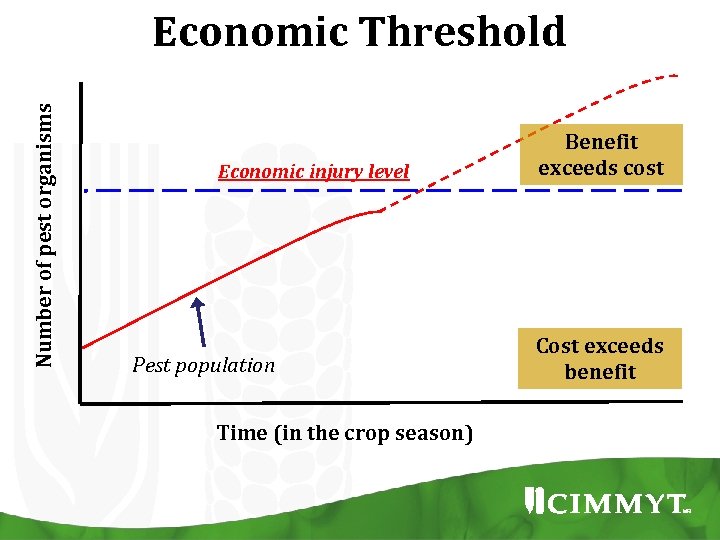 Number of pest organisms Economic Threshold Economic injury level Pest population Time (in the crop season) Benefit exceeds cost Cost exceeds benefit
Number of pest organisms Economic Threshold Economic injury level Pest population Time (in the crop season) Benefit exceeds cost Cost exceeds benefit
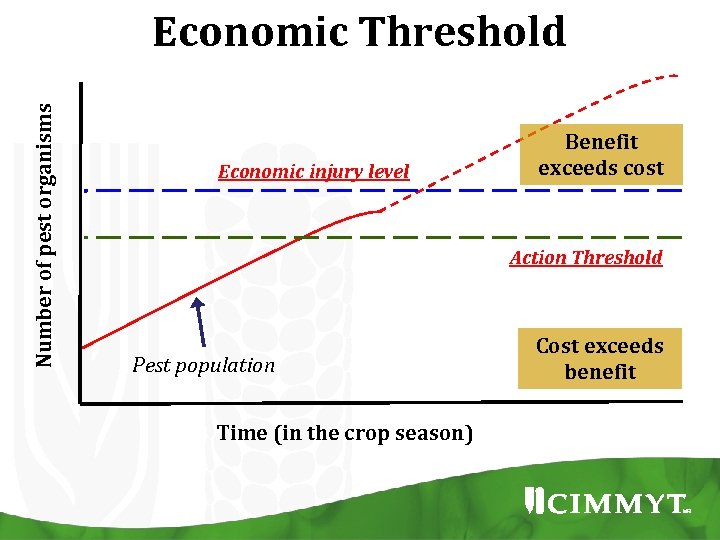 Number of pest organisms Economic Threshold Economic injury level Benefit exceeds cost Action Threshold Pest population Time (in the crop season) Cost exceeds benefit
Number of pest organisms Economic Threshold Economic injury level Benefit exceeds cost Action Threshold Pest population Time (in the crop season) Cost exceeds benefit
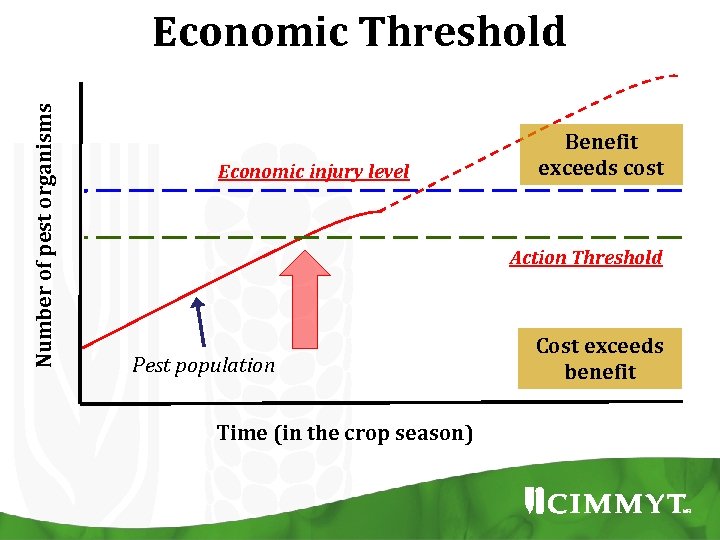 Number of pest organisms Economic Threshold Economic injury level Benefit exceeds cost Action Threshold Pest population Time (in the crop season) Cost exceeds benefit
Number of pest organisms Economic Threshold Economic injury level Benefit exceeds cost Action Threshold Pest population Time (in the crop season) Cost exceeds benefit
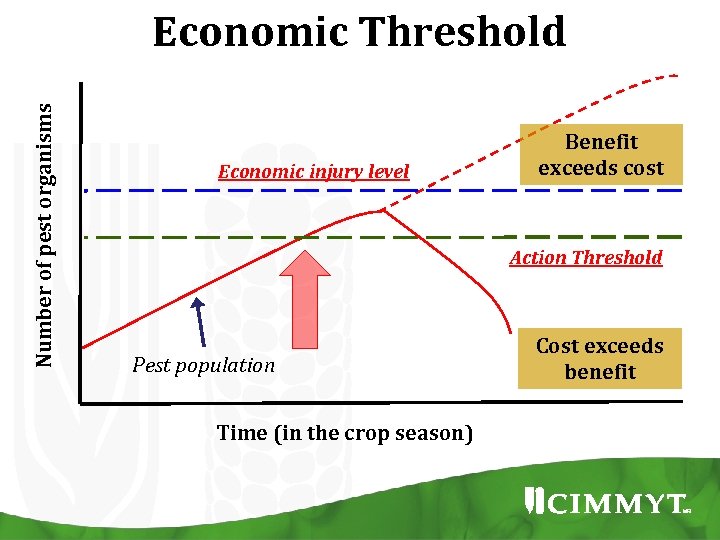 Number of pest organisms Economic Threshold Economic injury level Benefit exceeds cost Action Threshold Pest population Time (in the crop season) Cost exceeds benefit
Number of pest organisms Economic Threshold Economic injury level Benefit exceeds cost Action Threshold Pest population Time (in the crop season) Cost exceeds benefit
 Basics of pesticide safety
Basics of pesticide safety
 Know what chemical you are using 1. Dose (Dilution, frequency and timing of use) 2. Application method (Spray? Granular? Bait? Other? ) 3. Buy from a trusted dealer • Check label • Check date • Damaged container? • Good seal?
Know what chemical you are using 1. Dose (Dilution, frequency and timing of use) 2. Application method (Spray? Granular? Bait? Other? ) 3. Buy from a trusted dealer • Check label • Check date • Damaged container? • Good seal?
 Storage 1. Read label 2. Lock and don’t overstock 3. Use original container
Storage 1. Read label 2. Lock and don’t overstock 3. Use original container
 10 rules for preparing pesticides 1. Read instructions 2. Clean water 3. Don’t blow nozzles 4. Special equipment 5. Don’t fully fill containers 6. Protective clothing 7. No drinking, eating 8. Time: Just before application 9. Dispose excess in ground 10. Wash hands and equipment
10 rules for preparing pesticides 1. Read instructions 2. Clean water 3. Don’t blow nozzles 4. Special equipment 5. Don’t fully fill containers 6. Protective clothing 7. No drinking, eating 8. Time: Just before application 9. Dispose excess in ground 10. Wash hands and equipment
 Using pesticides in the field 1. Appropriate clothing 2. Washing after use
Using pesticides in the field 1. Appropriate clothing 2. Washing after use
 Using pesticides in the field 1. Appropriate clothing 2. Washing after use
Using pesticides in the field 1. Appropriate clothing 2. Washing after use
 Spray technique 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. Read the instructions Evaluate the field Avoid drift: Observe the wind. Discharge away Nozzle sizes matter! Weather considerations
Spray technique 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. Read the instructions Evaluate the field Avoid drift: Observe the wind. Discharge away Nozzle sizes matter! Weather considerations
 Recognize poisoning and act
Recognize poisoning and act
 Recognize poisoning and act 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Maintain breathing Body position Wash eyes Avoid inducing vomiting Don’t give patient anything
Recognize poisoning and act 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Maintain breathing Body position Wash eyes Avoid inducing vomiting Don’t give patient anything
 Recognize poisoning and act 1. Remove Decontaminate again
Recognize poisoning and act 1. Remove Decontaminate again
 Summary 1. Misuse of pesticides can have negative consequences. 1. IPM for insect pests relies on biological and cultural control, varietal selection, and pesticides as a last resort. 2. When used with in IPM, pesticides can offer benefits when used safely. 3. Be prepared for poisoning and know how to act.
Summary 1. Misuse of pesticides can have negative consequences. 1. IPM for insect pests relies on biological and cultural control, varietal selection, and pesticides as a last resort. 2. When used with in IPM, pesticides can offer benefits when used safely. 3. Be prepared for poisoning and know how to act.


