 PRINCIPLES OF FLE
PRINCIPLES OF FLE
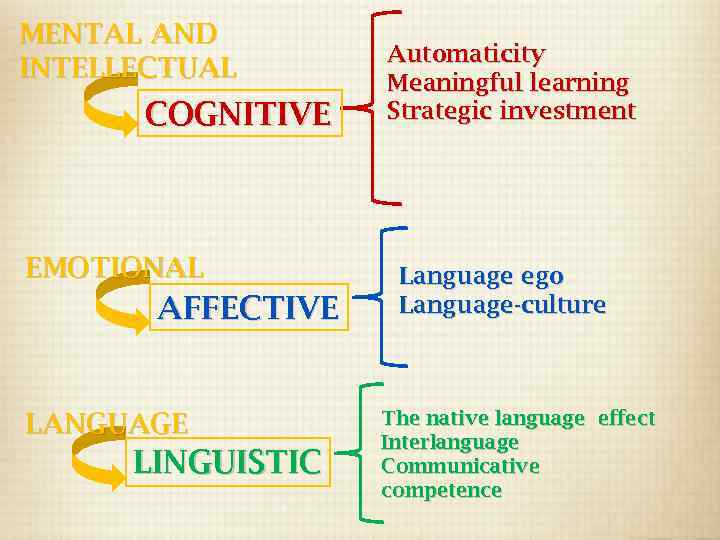 MENTAL AND INTELLECTUAL COGNITIVE EMOTIONAL AFFECTIVE LANGUAGE LINGUISTIC Automaticity Meaningful learning Strategic investment Language ego Language-culture The native language effect Interlanguage Communicative competence
MENTAL AND INTELLECTUAL COGNITIVE EMOTIONAL AFFECTIVE LANGUAGE LINGUISTIC Automaticity Meaningful learning Strategic investment Language ego Language-culture The native language effect Interlanguage Communicative competence
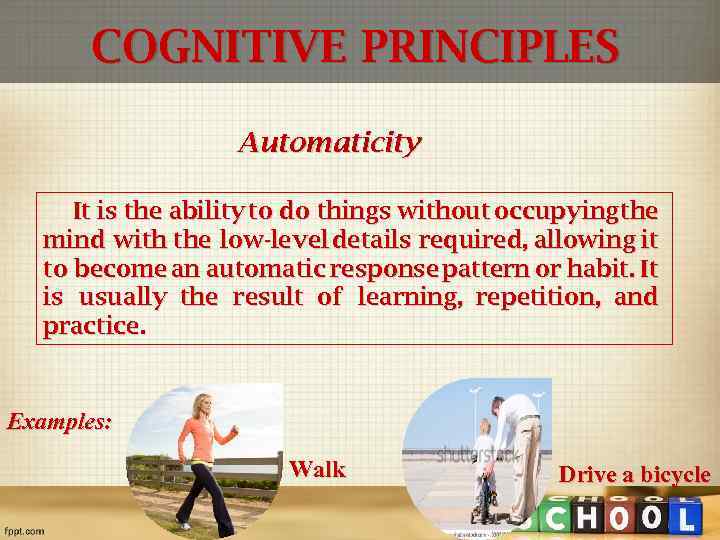 COGNITIVE PRINCIPLES Automaticity It is the ability to do things without occupyingthe mind with the low-level details required, allowing it to become an automatic response pattern or habit. It is usually the result of learning, repetition, and practice. Examples: Walk Drive a bicycle
COGNITIVE PRINCIPLES Automaticity It is the ability to do things without occupyingthe mind with the low-level details required, allowing it to become an automatic response pattern or habit. It is usually the result of learning, repetition, and practice. Examples: Walk Drive a bicycle
 Meaningful Learning Meaningful learning refers to a learning way where the new knowledge to acquire is related with previous knowledge.
Meaningful Learning Meaningful learning refers to a learning way where the new knowledge to acquire is related with previous knowledge.
 Strategic Investment of time, effort, and attention to the second language to help you to can be comprehend and produce the language.
Strategic Investment of time, effort, and attention to the second language to help you to can be comprehend and produce the language.
 AFFECTIVE PRINCIPLES Language Ego It creates within the learners a sense of fragility, a defensiveness, and a raising of inhibitions. .
AFFECTIVE PRINCIPLES Language Ego It creates within the learners a sense of fragility, a defensiveness, and a raising of inhibitions. .
 The Language-Culture Connection Wheneveryou teach a language, you also teach a complex system of cultural customs, values, and ways of thinking.
The Language-Culture Connection Wheneveryou teach a language, you also teach a complex system of cultural customs, values, and ways of thinking.
 LINGUISTIC PRINCIPLES The Native Language Effect The native language of learners exerts a strong influence on the acquisition of the target language system. While that native system will exercise both facilitating and interfering effects on the production and comprehension of the new language, the interfering effects are likely to be the most salient.
LINGUISTIC PRINCIPLES The Native Language Effect The native language of learners exerts a strong influence on the acquisition of the target language system. While that native system will exercise both facilitating and interfering effects on the production and comprehension of the new language, the interfering effects are likely to be the most salient.
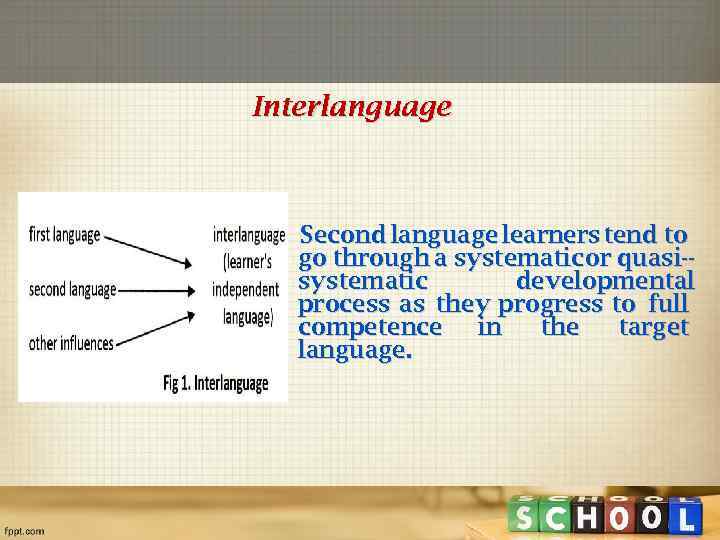 Interlanguage Second language learners tend to go through a systematic or quasi-systematic developmental process as they progress to full competence in the target language.
Interlanguage Second language learners tend to go through a systematic or quasi-systematic developmental process as they progress to full competence in the target language.
 Communicative Competence Some components of Communicative Competenc Organizational Competence Psycomotor Skills Strategic Competence Pragmatic Competence
Communicative Competence Some components of Communicative Competenc Organizational Competence Psycomotor Skills Strategic Competence Pragmatic Competence