7c9b6d7c3804cf4cfd9837e78de63800.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 20
 Principles of Engineering System Design Decision Making in System Design Dr T Asokan asok@iitm. ac. in
Principles of Engineering System Design Decision Making in System Design Dr T Asokan asok@iitm. ac. in
 Columbia Disaster • Columbia’s 28 th mission was originally scheduled for launch in January 2001. • Technical problems led to number of postponements (about 18) and finally set for 16 th Jan. 2003. • Some of the insulation tiles had come loose in the previous launches and many engineers felt that the launch should be postponed till it was rectified. • Top level management took the decision to go ahead. • During the launch few tiles ripped off and possibly damaged the wings. • Management decided to go ahead and not to interrupt the mission. • With wing temperatures over 1500 and speed exceeding mach 24, Columbia disintegrated while entering the atmosphere.
Columbia Disaster • Columbia’s 28 th mission was originally scheduled for launch in January 2001. • Technical problems led to number of postponements (about 18) and finally set for 16 th Jan. 2003. • Some of the insulation tiles had come loose in the previous launches and many engineers felt that the launch should be postponed till it was rectified. • Top level management took the decision to go ahead. • During the launch few tiles ripped off and possibly damaged the wings. • Management decided to go ahead and not to interrupt the mission. • With wing temperatures over 1500 and speed exceeding mach 24, Columbia disintegrated while entering the atmosphere.
 Decision making in Systems Design q Many important decisions are made during the development process q Most of the decisions are not made via a rational, explicit process q Many uncertainties are to be tackled while making decisions q An important point in decision making is that decisions have to be made with the best information available at the time, realizing that the outcomes associated with the decision remain uncertain when the decision is made. q Level of detail needed to make decisions in the engineering of a system and the level of detail needed to ensure proper implementation of the system’s components and CIs need to be understood clearly.
Decision making in Systems Design q Many important decisions are made during the development process q Most of the decisions are not made via a rational, explicit process q Many uncertainties are to be tackled while making decisions q An important point in decision making is that decisions have to be made with the best information available at the time, realizing that the outcomes associated with the decision remain uncertain when the decision is made. q Level of detail needed to make decisions in the engineering of a system and the level of detail needed to ensure proper implementation of the system’s components and CIs need to be understood clearly.
 Elements of decision problems • Creative generation of alternatives • Identification and quantification of multiple conflicting criteria • Assessment and analysis of uncertainty associated with the what is known and what is unknown about the decision situation.
Elements of decision problems • Creative generation of alternatives • Identification and quantification of multiple conflicting criteria • Assessment and analysis of uncertainty associated with the what is known and what is unknown about the decision situation.
 Two approaches • Lateral Thinking • Vertical Thinking
Two approaches • Lateral Thinking • Vertical Thinking
 Decision Making by Search Process
Decision Making by Search Process
 Axioms of Decision Analysis • Probability: A common approach in engineering • Order rule: Our preferences are well defined that any possible list of outcomes associated with the alternatives can be ordered from least preferred to most preferred on each objective in the fundamental objectives hierarchy. The ordered list must be transitive. • Substitution rule: Willing to substitute any combination of outcomes if we are indifferent between them.
Axioms of Decision Analysis • Probability: A common approach in engineering • Order rule: Our preferences are well defined that any possible list of outcomes associated with the alternatives can be ordered from least preferred to most preferred on each objective in the fundamental objectives hierarchy. The ordered list must be transitive. • Substitution rule: Willing to substitute any combination of outcomes if we are indifferent between them.
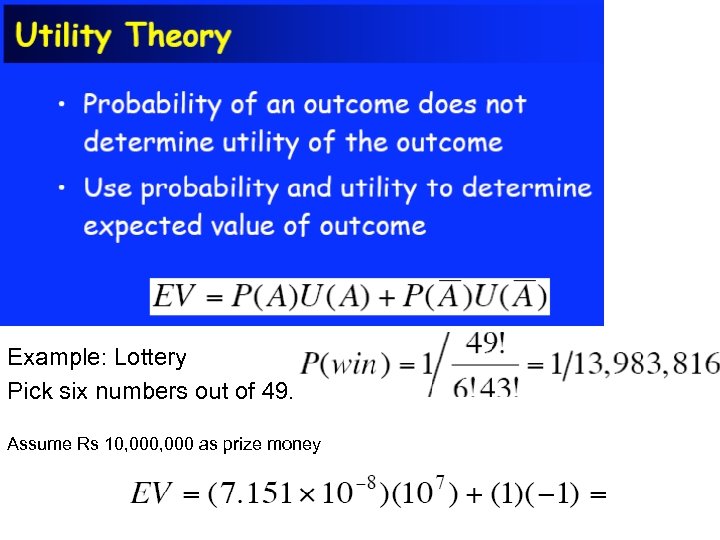 Example: Lottery Pick six numbers out of 49. Assume Rs 10, 000 as prize money
Example: Lottery Pick six numbers out of 49. Assume Rs 10, 000 as prize money
 Influence Diagrams and Decision Tree
Influence Diagrams and Decision Tree
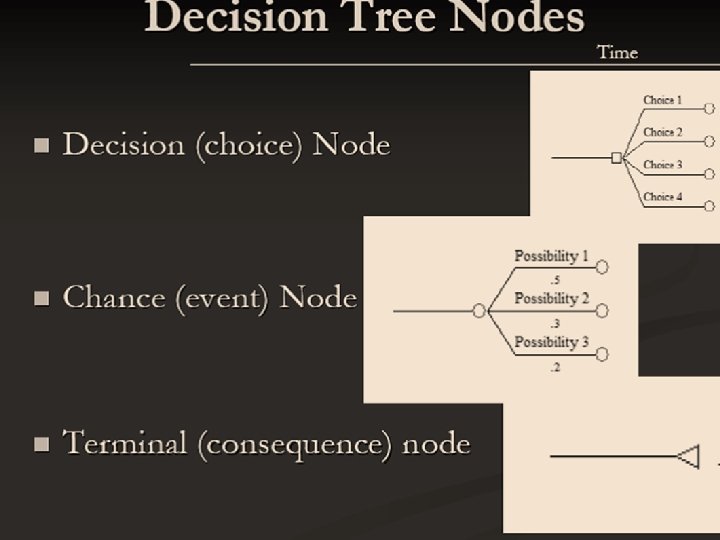
 Decision Trees
Decision Trees
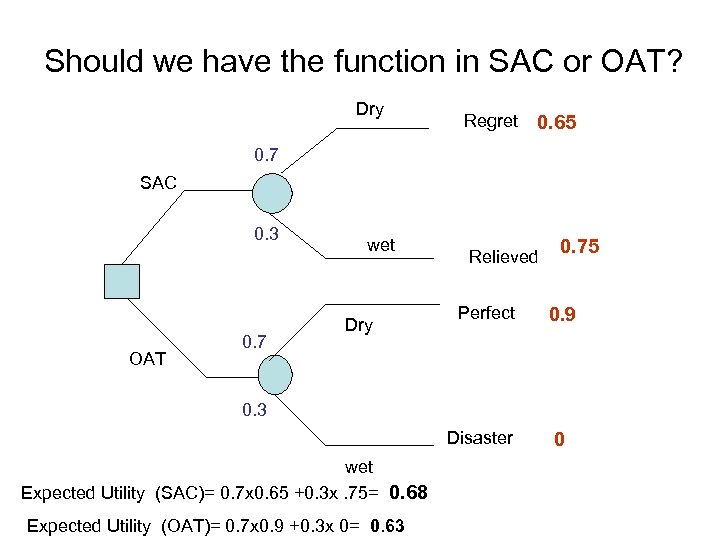 Should we have the function in SAC or OAT? Dry Regret 0. 65 0. 7 SAC 0. 3 OAT 0. 7 wet Dry Relieved Perfect 0. 75 0. 9 0. 3 Disaster wet Expected Utility (SAC)= 0. 7 x 0. 65 +0. 3 x. 75= 0. 68 Expected Utility (OAT)= 0. 7 x 0. 9 +0. 3 x 0= 0. 63 0
Should we have the function in SAC or OAT? Dry Regret 0. 65 0. 7 SAC 0. 3 OAT 0. 7 wet Dry Relieved Perfect 0. 75 0. 9 0. 3 Disaster wet Expected Utility (SAC)= 0. 7 x 0. 65 +0. 3 x. 75= 0. 68 Expected Utility (OAT)= 0. 7 x 0. 9 +0. 3 x 0= 0. 63 0
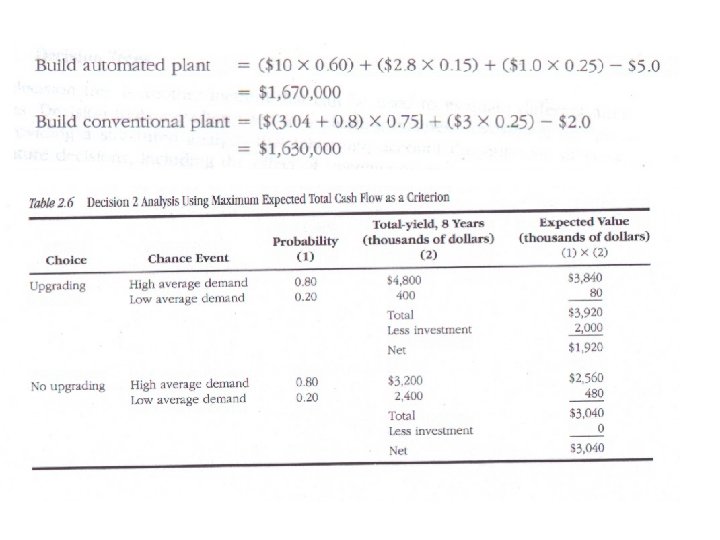
 Example: 2 • A company is trying to decide whether to build a conventional or automated plant to produce a new product with an expected life of 10 yrs. The decision must be based on the size of the market for the product. • Demand is expected to be any of the following 3 cases. – High during the first two years and if found unsatisfactory by the users, low thereafter – High over the next 10 yrs – Low over the 10 years
Example: 2 • A company is trying to decide whether to build a conventional or automated plant to produce a new product with an expected life of 10 yrs. The decision must be based on the size of the market for the product. • Demand is expected to be any of the following 3 cases. – High during the first two years and if found unsatisfactory by the users, low thereafter – High over the next 10 yrs – Low over the 10 years
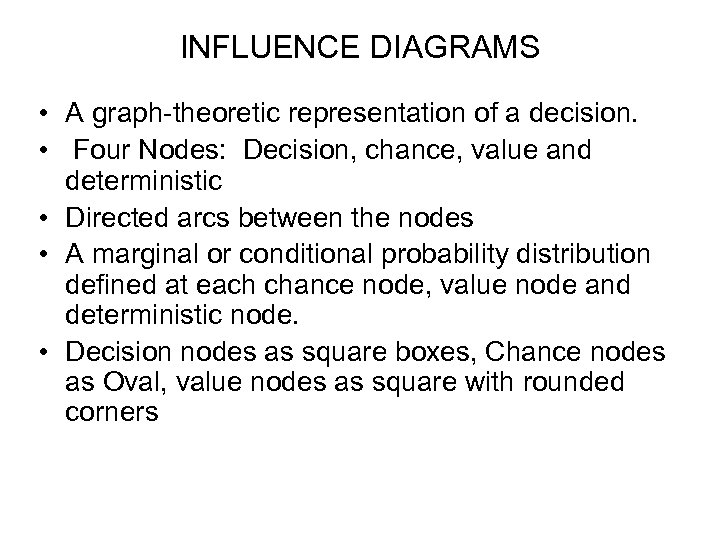 INFLUENCE DIAGRAMS • A graph-theoretic representation of a decision. • Four Nodes: Decision, chance, value and deterministic • Directed arcs between the nodes • A marginal or conditional probability distribution defined at each chance node, value node and deterministic node. • Decision nodes as square boxes, Chance nodes as Oval, value nodes as square with rounded corners
INFLUENCE DIAGRAMS • A graph-theoretic representation of a decision. • Four Nodes: Decision, chance, value and deterministic • Directed arcs between the nodes • A marginal or conditional probability distribution defined at each chance node, value node and deterministic node. • Decision nodes as square boxes, Chance nodes as Oval, value nodes as square with rounded corners
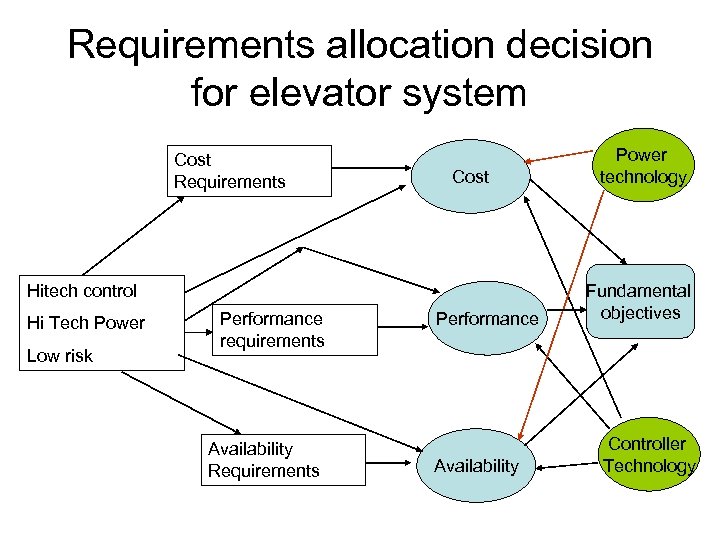 Requirements allocation decision for elevator system Cost Requirements Cost Hitech control Hi Tech Power Low risk Performance requirements Availability Requirements Performance Availability Power technology Fundamental objectives Controller Technology
Requirements allocation decision for elevator system Cost Requirements Cost Hitech control Hi Tech Power Low risk Performance requirements Availability Requirements Performance Availability Power technology Fundamental objectives Controller Technology
 Risk Management Risk= Exposure to the chance of loss Risk: The combination of the probability of an event occurring and the significance of the consequences of the event occurring. Dealing with Risk: Activity of managing the risks through various processes • Strategies – Avoidance, Transference, Management, Analysis Risk Avoidance: Selection of low risk alternative Risk Transference: Options that transfer the risk to others Risk Management: Use of fall back options in case a riskier option fails Risk Analysis: Addresses risk explicitly when decisions are made in uncertain situations.
Risk Management Risk= Exposure to the chance of loss Risk: The combination of the probability of an event occurring and the significance of the consequences of the event occurring. Dealing with Risk: Activity of managing the risks through various processes • Strategies – Avoidance, Transference, Management, Analysis Risk Avoidance: Selection of low risk alternative Risk Transference: Options that transfer the risk to others Risk Management: Use of fall back options in case a riskier option fails Risk Analysis: Addresses risk explicitly when decisions are made in uncertain situations.
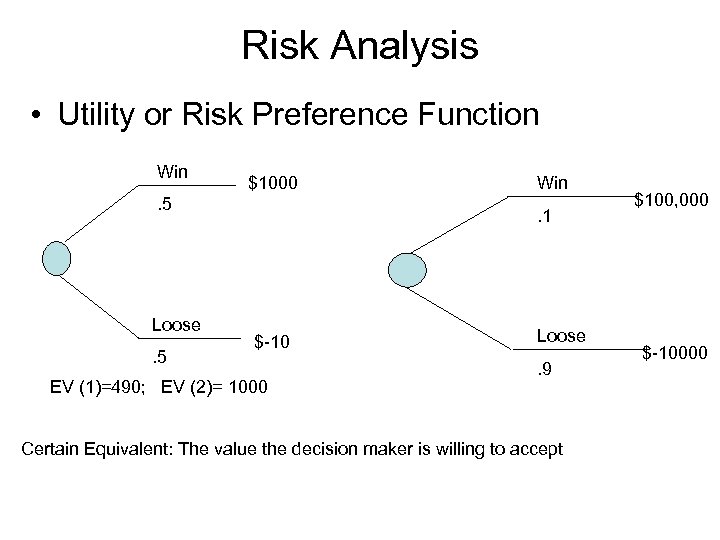 Risk Analysis • Utility or Risk Preference Function Win $1000 . 5 Loose. 5 Win. 1 $-10 EV (1)=490; EV (2)= 1000 Loose. 9 Certain Equivalent: The value the decision maker is willing to accept $100, 000 $-10000
Risk Analysis • Utility or Risk Preference Function Win $1000 . 5 Loose. 5 Win. 1 $-10 EV (1)=490; EV (2)= 1000 Loose. 9 Certain Equivalent: The value the decision maker is willing to accept $100, 000 $-10000
 • Risk Premium xp of an event is the difference between the expected value and the certain equivalent. • Risk-Averse decision: xp > 0
• Risk Premium xp of an event is the difference between the expected value and the certain equivalent. • Risk-Averse decision: xp > 0
 • Decision making under uncertainty is commonly encountered in various stages of system design • Identification and quantification of conflicting criteria is very important. • Various tools are available to help the designer in arriving at a decision THANK YOU
• Decision making under uncertainty is commonly encountered in various stages of system design • Identification and quantification of conflicting criteria is very important. • Various tools are available to help the designer in arriving at a decision THANK YOU


