2d6ffc763bbab6118d3ed89680f4c603.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 21

Principles of Corporate Finance Brealey and Myers u Sixth Edition Real Options Slides by Matthew Will Irwin/Mc. Graw Hill Chapter 21 ©The Mc. Graw-Hill Companies, Inc. , 2000

21 - 2 Topics Covered w Real Options Follow Up Investments è Abandon è Wait è Vary Output or Production è w Binomial Model Irwin/Mc. Graw Hill ©The Mc. Graw-Hill Companies, Inc. , 2000

21 - 3 Corporate Options 4 types of “Real Options” 1 - The opportunity to make follow-up investments. 2 - The opportunity to abandon a project 3 - The opportunity to “wait” and invest later. 4 - The opportunity to vary the firm’s output or production methods. Value “Real Option” = NPV with option - NPV w/o option Irwin/Mc. Graw Hill ©The Mc. Graw-Hill Companies, Inc. , 2000
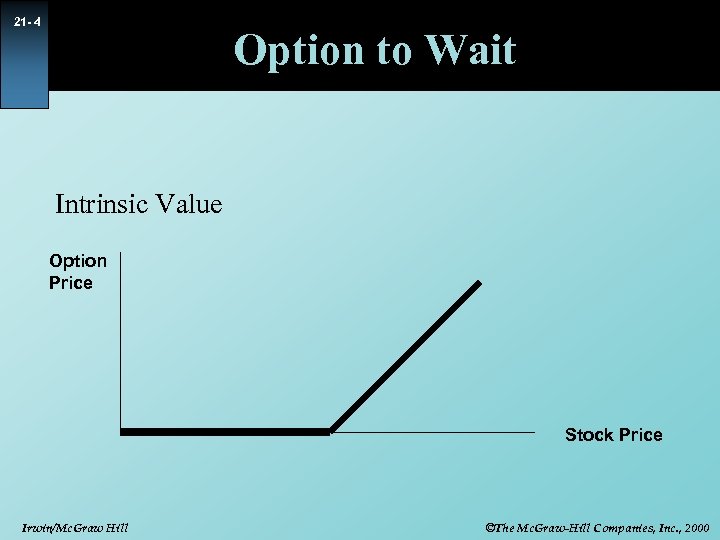
21 - 4 Option to Wait Intrinsic Value Option Price Stock Price Irwin/Mc. Graw Hill ©The Mc. Graw-Hill Companies, Inc. , 2000
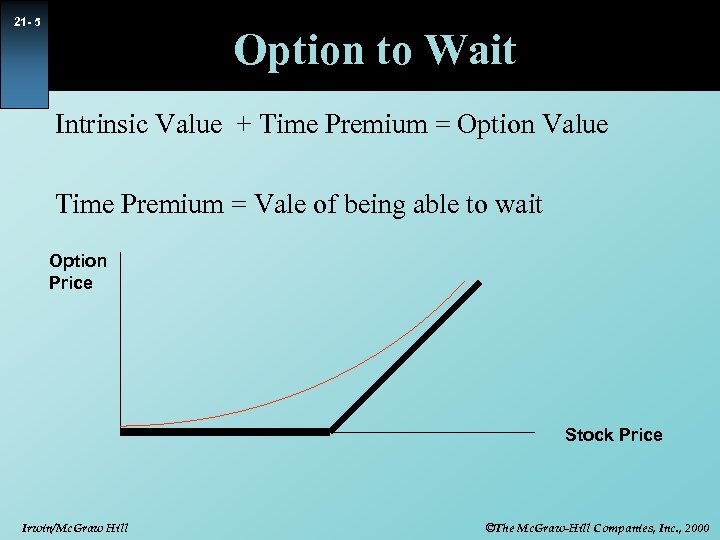
21 - 5 Option to Wait Intrinsic Value + Time Premium = Option Value Time Premium = Vale of being able to wait Option Price Stock Price Irwin/Mc. Graw Hill ©The Mc. Graw-Hill Companies, Inc. , 2000
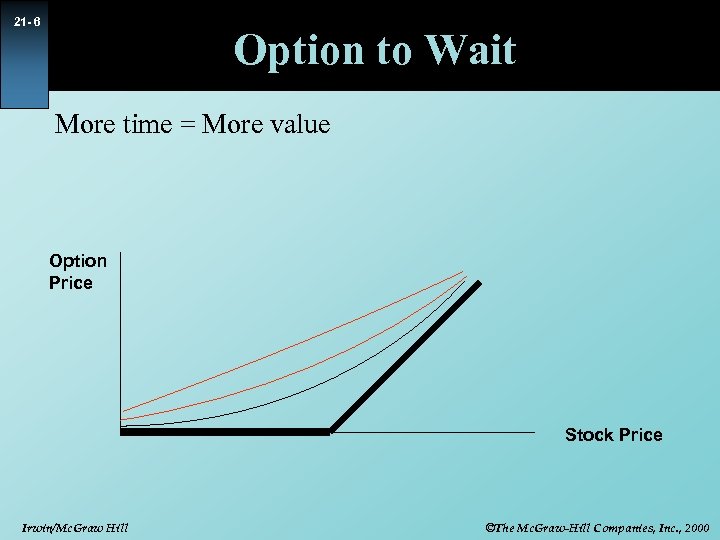
21 - 6 Option to Wait More time = More value Option Price Stock Price Irwin/Mc. Graw Hill ©The Mc. Graw-Hill Companies, Inc. , 2000

21 - 7 Option to Abandon Example - Abandon Mrs. Mulla gives you a non-retractable offer to buy your company for $150 mil at anytime within the next year. Given the following decision tree of possible outcomes, what is the value of the offer (i. e. the put option) and what is the most Mrs. Mulla could charge for the option? Use a discount rate of 10% Irwin/Mc. Graw Hill ©The Mc. Graw-Hill Companies, Inc. , 2000
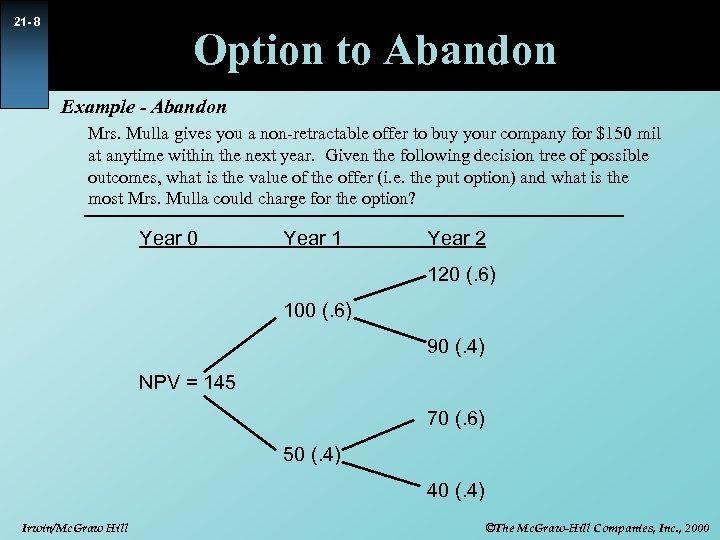
21 - 8 Option to Abandon Example - Abandon Mrs. Mulla gives you a non-retractable offer to buy your company for $150 mil at anytime within the next year. Given the following decision tree of possible outcomes, what is the value of the offer (i. e. the put option) and what is the most Mrs. Mulla could charge for the option? Year 0 Year 1 Year 2 120 (. 6) 100 (. 6) 90 (. 4) NPV = 145 70 (. 6) 50 (. 4) 40 (. 4) Irwin/Mc. Graw Hill ©The Mc. Graw-Hill Companies, Inc. , 2000
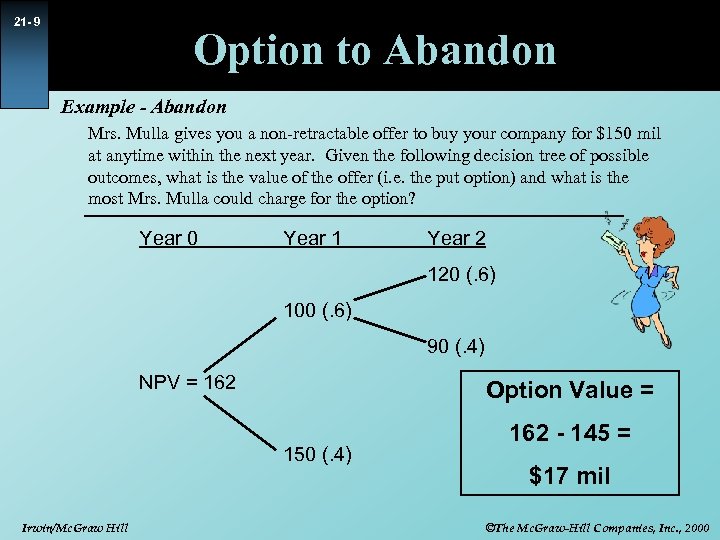
21 - 9 Option to Abandon Example - Abandon Mrs. Mulla gives you a non-retractable offer to buy your company for $150 mil at anytime within the next year. Given the following decision tree of possible outcomes, what is the value of the offer (i. e. the put option) and what is the most Mrs. Mulla could charge for the option? Year 0 Year 1 Year 2 120 (. 6) 100 (. 6) 90 (. 4) NPV = 162 Option Value = 150 (. 4) Irwin/Mc. Graw Hill 162 - 145 = $17 mil ©The Mc. Graw-Hill Companies, Inc. , 2000

21 - 10 Corporate Options Reality w Decision trees for valuing “real options” in a corporate setting can not be practically done by hand. w We must introduce binomial theory & B-S models Irwin/Mc. Graw Hill ©The Mc. Graw-Hill Companies, Inc. , 2000
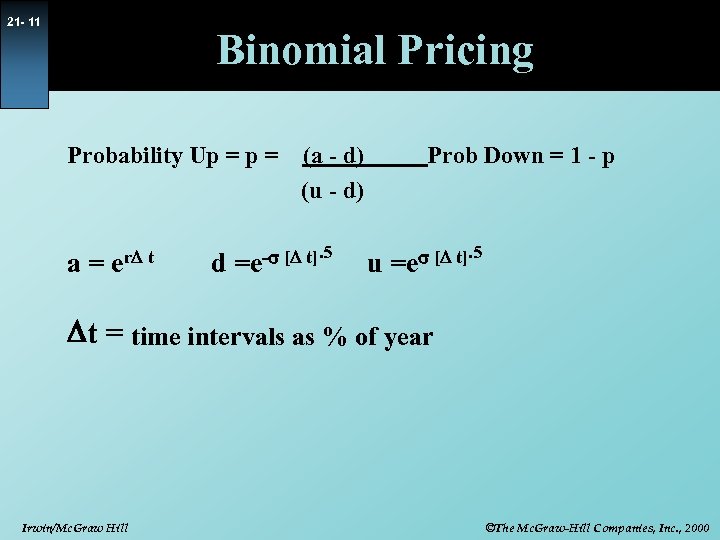
21 - 11 Binomial Pricing Probability Up = a = er. D t (a - d) (u - d) d =e-s [D t]. 5 Prob Down = 1 - p u =es [D t]. 5 Dt = time intervals as % of year Irwin/Mc. Graw Hill ©The Mc. Graw-Hill Companies, Inc. , 2000
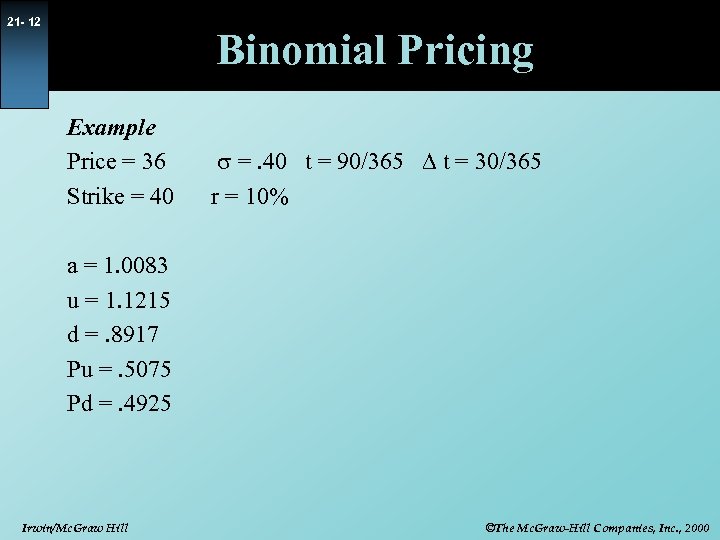
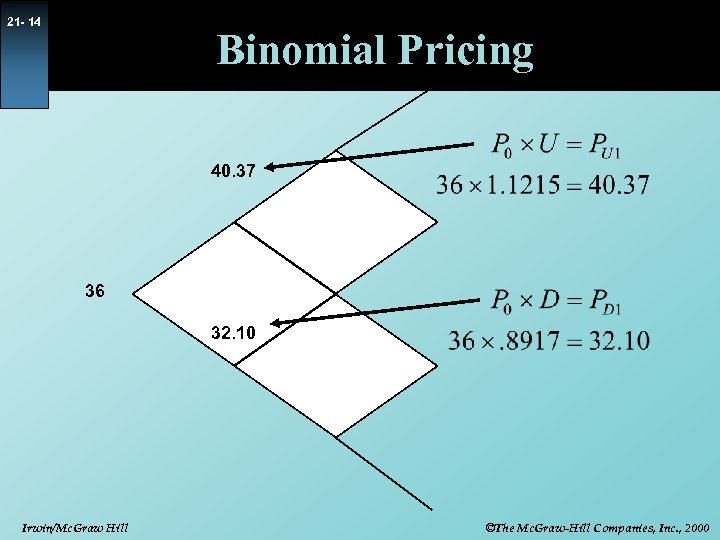
21 - 12 Binomial Pricing Example Price = 36 Strike = 40 s =. 40 t = 90/365 D t = 30/365 r = 10% a = 1. 0083 u = 1. 1215 d =. 8917 Pu =. 5075 Pd =. 4925 Irwin/Mc. Graw Hill ©The Mc. Graw-Hill Companies, Inc. , 2000
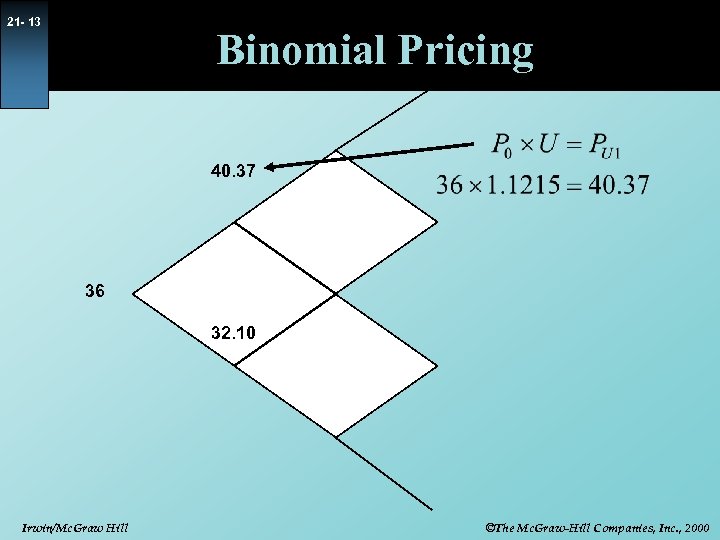
21 - 13 Binomial Pricing 40. 37 36 32. 10 Irwin/Mc. Graw Hill ©The Mc. Graw-Hill Companies, Inc. , 2000
21 - 14 Binomial Pricing 40. 37 36 32. 10 Irwin/Mc. Graw Hill ©The Mc. Graw-Hill Companies, Inc. , 2000
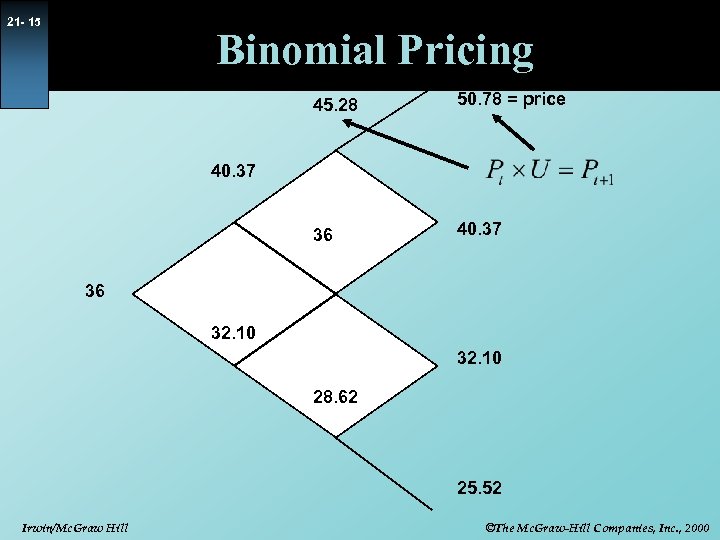
21 - 15 Binomial Pricing 45. 28 50. 78 = price 36 40. 37 36 32. 10 28. 62 25. 52 Irwin/Mc. Graw Hill ©The Mc. Graw-Hill Companies, Inc. , 2000
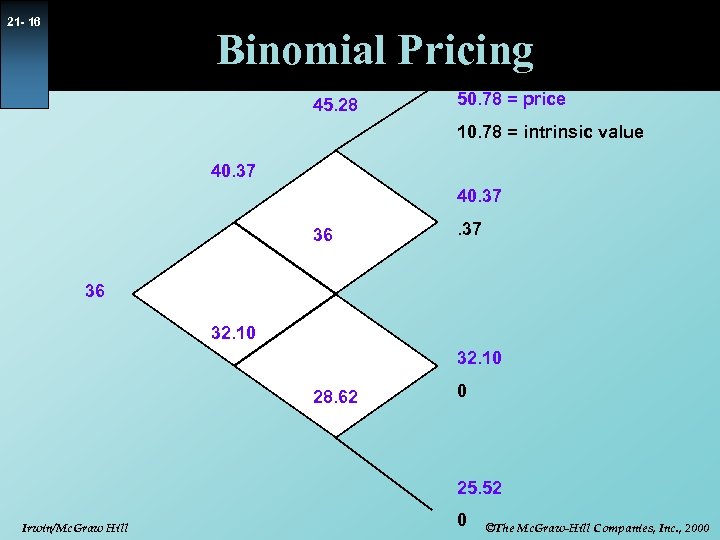
21 - 16 Binomial Pricing 45. 28 50. 78 = price 10. 78 = intrinsic value 40. 37 36 32. 10 28. 62 0 25. 52 Irwin/Mc. Graw Hill 0 ©The Mc. Graw-Hill Companies, Inc. , 2000
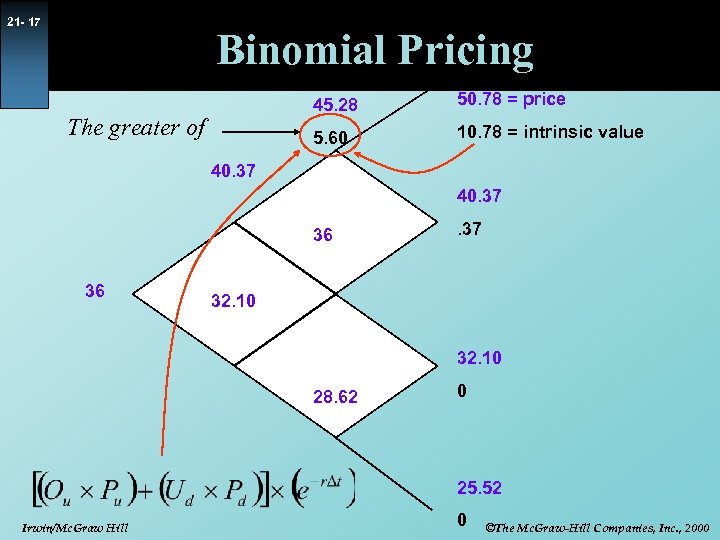
21 - 17 Binomial Pricing 45. 28 5. 60 The greater of 50. 78 = price 10. 78 = intrinsic value 40. 37 36 36 . 37 32. 10 28. 62 0 25. 52 Irwin/Mc. Graw Hill 0 ©The Mc. Graw-Hill Companies, Inc. , 2000
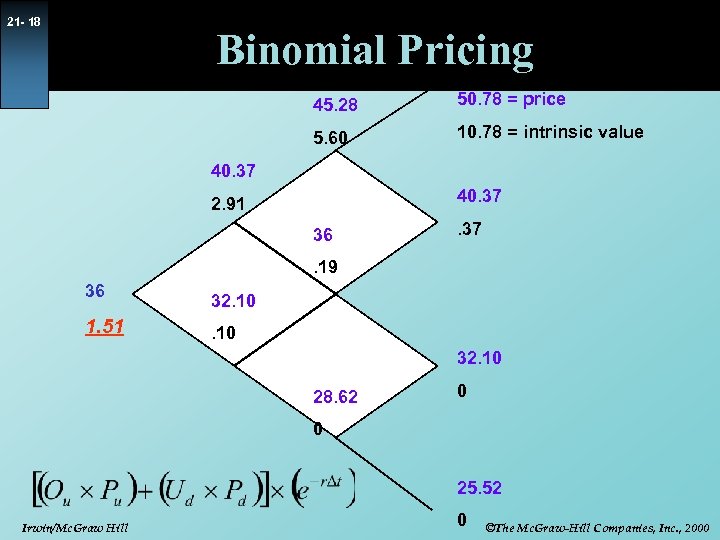
21 - 18 Binomial Pricing 45. 28 50. 78 = price 5. 60 10. 78 = intrinsic value 40. 37 2. 91 36 . 37 . 19 36 1. 51 32. 10 28. 62 0 0 25. 52 Irwin/Mc. Graw Hill 0 ©The Mc. Graw-Hill Companies, Inc. , 2000
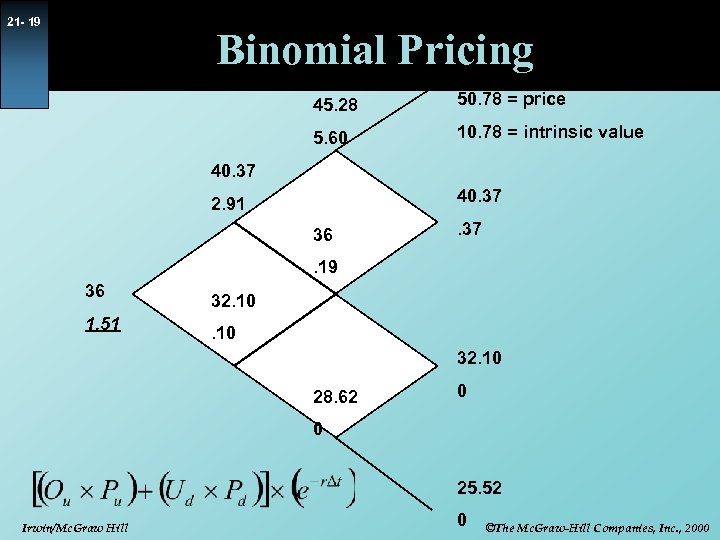
21 - 19 Binomial Pricing 45. 28 50. 78 = price 5. 60 10. 78 = intrinsic value 40. 37 2. 91 36 . 37 . 19 36 1. 51 32. 10 28. 62 0 0 25. 52 Irwin/Mc. Graw Hill 0 ©The Mc. Graw-Hill Companies, Inc. , 2000
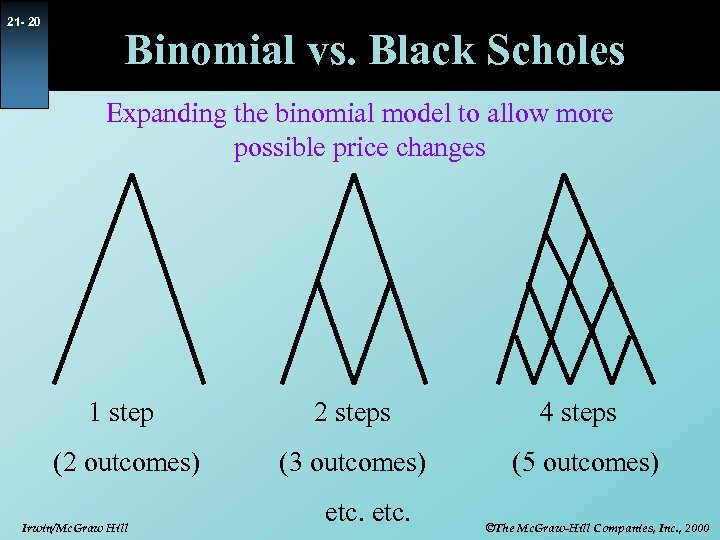
21 - 20 Binomial vs. Black Scholes Expanding the binomial model to allow more possible price changes 1 step 2 steps 4 steps (2 outcomes) (3 outcomes) (5 outcomes) Irwin/Mc. Graw Hill etc. ©The Mc. Graw-Hill Companies, Inc. , 2000

21 - 21 Binomial vs. Black Scholes How estimated call price changes as number of binomial steps increases No. of steps Estimated value 1 48. 1 2 41. 0 3 42. 1 5 41. 8 10 41. 4 50 40. 3 100 40. 6 Black-Scholes 40. 5 Irwin/Mc. Graw Hill ©The Mc. Graw-Hill Companies, Inc. , 2000
2d6ffc763bbab6118d3ed89680f4c603.ppt