b5dd50e612be028b1b1d3ca4701c4895.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 54
Principles of Biomedical Science Day #42 (11/06/17): Journal Question: Answer in PLTW Why would the confidentiality of Anna Garcia’s autopsy information important? journal. Vocabulary Builder — Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act: A comprehensive set of standards and practices designed to give patients specific rights regarding their personal health H. I. P. A. A. 1

Principles of Biomedical Science “Activity 1. 3. 1: The Autopsy”: 1. What are six types of death that require an autopsy? 2. What is the difference between a clinical autopsy and a forensic autopsy? 3. List AND briefly describe the, ‘Tools of the Trade’. Complete on the BACK of your autopsy report vocabulary sheet. 2

Principles of Biomedical Science “Activity 1. 3. 1: The Autopsy”: 1. Most states in the United States have laws that require certain types of deaths be investigated: injury; delayed complications of injuries; poisoning; infectious complications foul play; people who die with no attending physician 1. Forensic autopsies (medical-legal autopsy) try to find answers to the cause of death as part of an overall police investigation. The clinical autopsy is usually performed in hospitals by pathologists or the attending physician to determine a cause of death for research and study purposes. 3

Principles of Biomedical Science “Activity 1. 3. 1: The Autopsy”: Bone saw - used to cut through bone or skull Breadknife - used to shave slices off of organs for examination Enterotome - special scissors used to open the intestines Hagedorn needle - a heavy needle used to sew up the body after examination Hammer with hook - used to pull skull cap off of skull Rib cutter - special shears used to cut through the ribs Scalpel - like a surgeon's scalpel but with largest blade possible for making long deep cuts or scraping away tissue Scissors - used for opening hollow organs and cutting vessels Skull chisel - used for helping to carefully pry the skull cap off Stryker saw - the electric saw used to cut through the skull to remove the brain Toothed forceps - used to pick up heavy organs 4
Principles of Biomedical Science Day #43 (11/07/17): Journal Question: Answer in PLTW What NEW information from the autopsy report may change your, ‘Theory of the Case? journal. Vocabulary Builder — The state of keeping or being kept secret or private, such as medical records. Confidentiality 5

Principles of Biomedical Science “Activity 1. 3. 1: The Autopsy”: 1. Most states in the United States have laws that require certain types of deaths be investigated: injury; delayed complications of injuries; poisoning; infectious complications; foul play; people who die with no attending physician. 1. Forensic autopsies (medical-legal autopsy) try to find answers to the cause of death as part of an overall police investigation. The clinical autopsy is usually performed in hospitals by pathologists or the attending physician to determine a cause of death for research and study purposes. 6

Principles of Biomedical Science “Activity 1. 3. 1: The Autopsy”: Bone saw - used to cut through bone or skull Breadknife - used to shave slices off of organs for examination Enterotome - special scissors used to open the intestines Hagedorn needle - a heavy needle used to sew up the body after examination Hammer with hook - used to pull skull cap off of skull Rib cutter - special shears used to cut through the ribs Scalpel - like a surgeon's scalpel but with largest blade possible for making long deep cuts or scraping away tissue Scissors - used for opening hollow organs and cutting vessels Skull chisel - used for helping to carefully pry the skull cap off Stryker saw - the electric saw used to cut through the skull to remove the brain Toothed forceps - used to pick up heavy organs 7

Principles of Biomedical Science Day #46 (11/09/17): Journal Question: Answer in PLTW journal. Can medical professionals communicate with patients about health care by mail or phone? Vocabulary Builder Health Information — Technology for Economic and HITECH Clinical Health Act. 8

Principles of Biomedical Science Entry Task Follow UP: Yes. They can disclose PHI to a family member or other person involved when the individual is present during the professional’s disclosure. If patient consent is given, voice mail messages with PHI may be left with family members. 9

Principles of Biomedical Science Entry Task Follow UP: HITECH — updated HIPAA rules to include protections against identity theft. Created a nationwide electronic health record. Increased penalties for privacy and security violations. 10
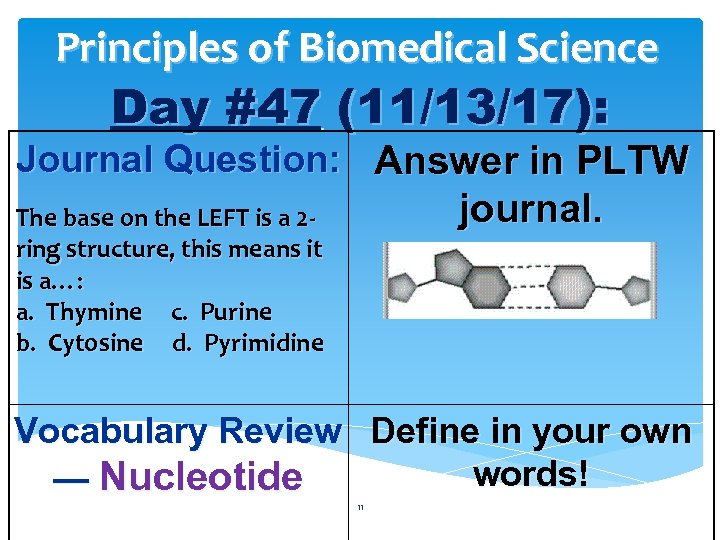
Principles of Biomedical Science Day #47 (11/13/17): Journal Question: Answer in PLTW journal. The base on the LEFT is a 2 ring structure, this means it is a…: a. Thymine c. Purine b. Cytosine d. Pyrimidine Vocabulary Review Define in your own words! — Nucleotide 11

Principles of Biomedical Science Entry Task Follow UP: Purines two rings. A; G Pyrimidines one ring. T; C. Follow UP question? ? ? What do the lines represent between the two bases? ? ? Nucleotide—building block of nucleic acids; composed of a sugar, phosphate, and a nitrogen base (A; T; G; C). 12

Principles of Biomedical Science Day #48 (11/14/17): Journal Question: Answer in PLTW journal. A DNA strand has a base sequence of TTACGGCAA; the complementary base will be: a. TTACGGCAA c. AATGCCGTT b. AATCGGCTT d. CCGATTAGG Vocabulary Review Define in your own words! — Restriction Enzyme 13

Principles of Biomedical Science Entry Task Follow UP: Follow UP question? ? ? What are, ‘Chargaff’s Rules’? ? ? Restriction Enzyme — enzymes used to cut DNA into fragments for gel electrophoresis. 14
Principles of Biomedical Science Day #49 (11/15/17): Journal Question: A DNA sample has 30% Guanine (G); how much of the DNA has the nitrogen base A? Answer in PLTW journal. a. 30% c. 20% b. 40% d. Can not be determined Vocabulary Review — PPE 15 Define in your own words!
Principles of Biomedical Science Day #50 (11/16/17): Journal Question: You want to determine the height at which a victim began to lose blood. You conduct an experiment in which you drop one drop of blood one time from ten different heights. 1. What is the independent variable (manipulated variable) in your experiment? A. Type of blood C. Diameter of blood spatter 16 B. Height of blood drop D. PPE used. Answer in PLTW journal.
Principles of Biomedical Science Entry task follow UP: 2. What is the dependent variable (responding variable) in your experiment? A. Type of blood C. Diameter of blood spatter B. Height of blood drop D. PPE used. 17
Principles of Biomedical Science Entry task follow UP: 3. What can you do to increase the validity of the data from your experiment? A. Wear proper PPE. C. Use the same B. Measure more than pipette and one drop per height. technique D. All of the above. 18
Principles of Biomedical Science Entry task follow UP: 4. What is the reliability in your experiment? A. Wear proper PPE. C. Conduct again. B. Measure more than D. B and C only. one drop per height. 19
Principles of Biomedical Science Day #51 (11/17/17): Journal Question: v. None—Please put away your PLTW journal AND binder. Thank you. v. BUT…please have out your Unit ONE case report. v. You will need a number two pencil to take this exam. 20 Answer in PLTW journal.

Principles of Biomedical Science Day #52 (11/20/17): Journal Question: Answer in PLTW A minute of mental madness: what do you already know about diabetes? ? Vocabulary Review: Homeostasis 21 journal. The maintenance of a stable internal conditions in some organisms even as external conditions fluctuate.
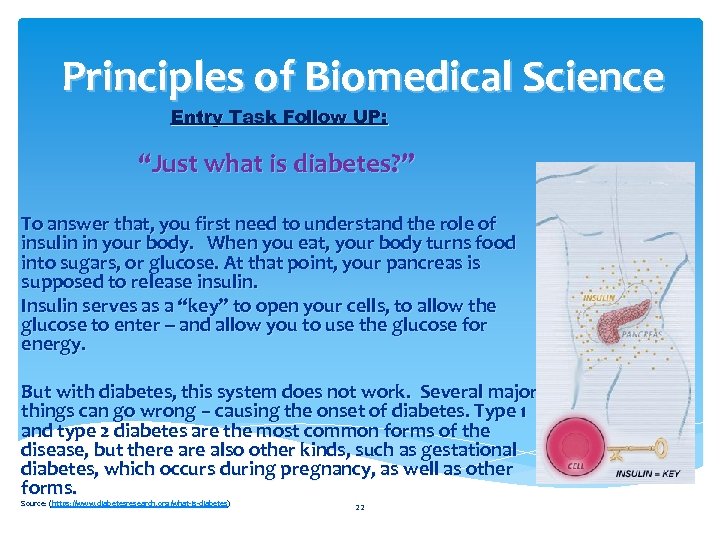
Principles of Biomedical Science Entry Task Follow UP: “Just what is diabetes? ” To answer that, you first need to understand the role of insulin in your body. When you eat, your body turns food into sugars, or glucose. At that point, your pancreas is supposed to release insulin. Insulin serves as a “key” to open your cells, to allow the glucose to enter -- and allow you to use the glucose for energy. But with diabetes, this system does not work. Several major things can go wrong – causing the onset of diabetes. Type 1 and type 2 diabetes are the most common forms of the disease, but there also other kinds, such as gestational diabetes, which occurs during pregnancy, as well as other forms. Source: (https: //www. diabetesresearch. org/what-is-diabetes) 22
Principles of Biomedical Science Day #53 (11/21/17): Journal Question: Answer in PLTW How do you interpret your G. T. T. graph for the three patients? journal. Vocabulary Review: A hormone secreted by the pancreas that is essential for the metabolism of carbohydrates and the regulation of blood glucose. Insulin 23

Principles of Biomedical Science Day #54 (11/22/17): Journal Question: Answer in PLTW How your two graphs compare for the GTT and insulin? Vocabulary Review: Type I Diabetes 24 journal. A form that usually develops in childhood or adolescence; it is characterized by a severe deficiency of insulin and a resulting high level of blood glucose.
Principles of Biomedical Science Day #55 (11/27/17): Journal Question: Answer in PLTW What does it mean if someone is, “prediabetic”? Vocabulary Review: Type II Diabetes 25 journal. A form that develops in adults (many who are obese); is characterized by high blood glucose because of impaired insulin utilization.

Principles of Biomedical Science Entry Task Follow UP: “Pre-diabetes is a ‘pre-diagnosis’ of diabetes: you can think of it as a warning sign. It’s when your blood glucose level (blood sugar level) is higher than normal, but it’s not high enough to be considered diabetes. Pre-diabetes is an indication that you could develop type 2 diabetes if you don’t make some lifestyle changes. ” Is, ‘Patient A’ pre-diabetic? ? https: //www. endocrineweb. com/conditions/pre-diabetes/pre-diabetes 26

Principles of Biomedical Science Entry Task Follow UP: “Oral glucose tolerance test (OGTT): This is another test used to diagnose prediabetes. The doctor will give you instructions on how to prepare for the test, but you won’t be able to eat anything for eight hours before the test; you’ll be fasting. In that way, the oral glucose tolerance test, abbreviated OGTT, is similar to the fasting plasma glucose test. On the day of the test, the doctor will test your blood glucose level at the beginning of the appointment; that’s called your fasting blood glucose level. Then, you’ll drink 75 g of a very sugary mixture. Two hours later, your blood glucose level will be measured. If your blood glucose level is between 140 and 199 mg/d. L two hours after drinking the sugary mixture, you have pre-diabetes. You may hear the doctor use the phrase “impaired glucose tolerance” or IGT, which is another term for pre-diabetes when it’s diagnosed with the OGTT. If your blood glucose level is above 200 mg/DL with the oral glucose tolerance test, you may have diabetes. ” https: //www. endocrineweb. com/conditions/pre-diabetes/pre-diabetes 27
Principles of Biomedical Science Day #56 (11/27/17): Journal Question: Answer in PLTW What are some questions to ask about the author of a website? journal. Vocabulary Review: A change in a physiological variable triggers a response that counteracts the initial fluctuation. Negative Feedback 28

Principles of Biomedical Science Entry Task Follow UP: Ask yourself: v What does the URL tell us about the author? v Who are they? v What are there credentials? v Is contact information provided? 29
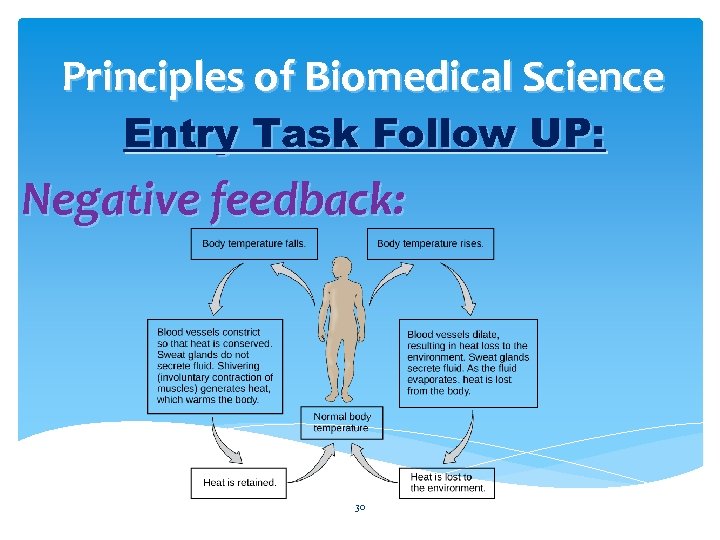
Principles of Biomedical Science Entry Task Follow UP: Negative feedback: 30
Principles of Biomedical Science Day #56 (11/27/17): Journal Question: Answer in PLTW What are some questions to ask about the author of a website? journal. Vocabulary Review: A change in a physiological variable triggers a response that counteracts the initial fluctuation. Negative Feedback 31

Principles of Biomedical Science Entry Task Follow UP: Ask yourself: v What does the URL tell us about the author? v Who are they? v What are there credentials? v Is contact information provided? 32
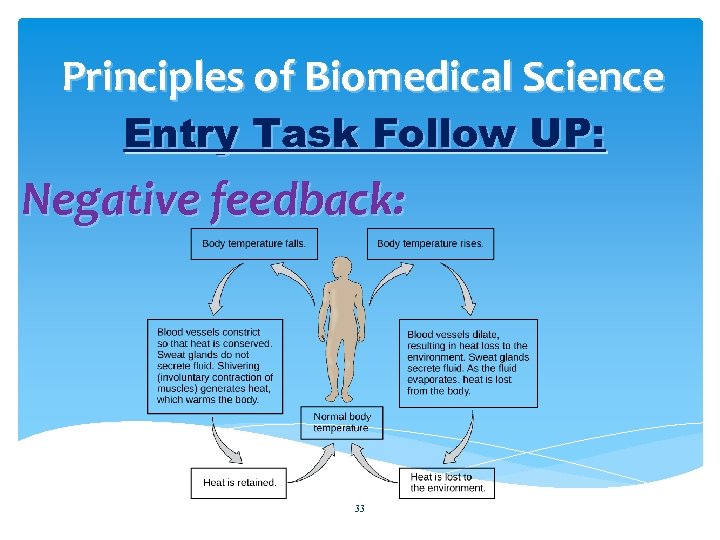
Principles of Biomedical Science Entry Task Follow UP: Negative feedback: 33

Principles of Biomedical Science Objective: You will research the relationship between insulin and glucose in preparation for designing and constructing a 3 -D model of the process. 34

Principles of Biomedical Science ‘This and That’: v Homework STAMP; will become part of 2. 1. 2 packet. v Weekly grades posted in back. v Tutoring support Today and Thursday this week. v Unit ONE exam make ups? ? ? 35

Principles of Biomedical Science ‘ 2. 1. 1. Activity Sheet Review’: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Insulin Table (5 points) 2 A. GTT graph + analysis (10 points) 2 B. Insulin graph + analysis (10 points). 3. Venn Diagram (5 points) 4. Answer to conclusion questions (5 points). 36

Principles of Biomedical Science Project 2. 1. 2 The Insulin-Glucose Connection: v Today: Completion of Part 1: . v Pick up at #5 (Student response sheet). v Complete through #8 by tomorrow. v Engineering team information for me. v Student response sheet STAMP on Wednesday. 37

Principles of Biomedical Science Day #57 (11/29/17): Journal Question: Answer in PLTW What are some questions to ask about the purpose of a website? journal. Vocabulary Review: A change in a physiological variable triggers a magnification of a process or an increase in its output. Positive Feedback 38

Principles of Biomedical Science Entry Task Follow UP: Ask yourself: v Whose site is it? v Are there lots of ads? v What is the, ‘mission’ of the site? v Is the content mostly opinions or facts? 39
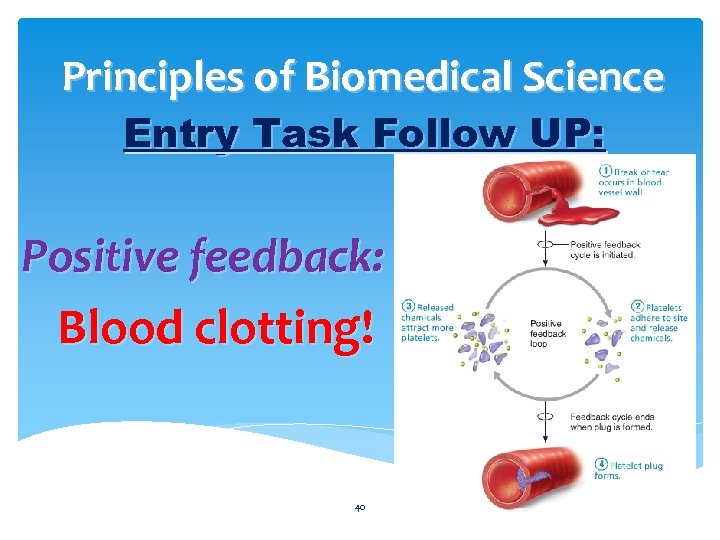
Principles of Biomedical Science Entry Task Follow UP: Positive feedback: Blood clotting! 40
Principles of Biomedical Science Day #58 (11/30/17): Journal Question: Answer in PLTW What are some questions to ask about the CONTENT of a website? journal. Vocabulary Review: Systematic problem-solving strategy, with criteria and constraints, used to develop many possible solutions to solve or satisfy human needs or wants and to narrow down the 41 possible solutions to one final choice. Design process
Principles of Biomedical Science Day #65 (12/11/17): Journal Question: Answer in PLTW Is the blood glucose – insulin system a negative AND positive feedback system? Explain! Vocabulary Review: Glucose, glycogen, and glucagon. 42 journal. Venn Diagram See white board
Principles of Biomedical Science VB Follow UP: v Glucose —simple sugar used as a source of short-term energy by cells. v Glycogen — storage form of glucose (a polysaccharide) in the liver and muscles. v Glucagon — hormone secreted by the alpha cells of the pancreas in response to low blood sugar; stimulated the liver to break down glycogen and release it as glucose in the blood. 43
Principles of Biomedical Science Day #66 (12/12/17): Journal Question: Answer in PLTW How would you modify your concept map to show Type I AND Type II diabetes? Do it!!! journal. Vocabulary Review: Venn Diagram (Hint-use ‘Key Terms’ sheet (Lesson 2. 2) Protein verses Amino Acid 44
Principles of Biomedical Science VB Follow UP: Protein — a type of polymer important for basic life functions, such as for structural components; membrane function; our immune system; chemical reactions. Amino acids — monomers used to make proteins; come in 20 different forms. Same — the monomer and polymer for the SAME macromolecule. 45
Principles of Biomedical Science Day #67 (12/13/17): Journal Question: Answer in PLTW None—please get out your rough draft for a completion STAMP (25 points)!!!! Vocabulary Review: None 46 journal.

Principles of Biomedical Science Day #68 (12/14/17): Journal Question: Answer in PLTW None— please get out your rough draft. Vocabulary Review: None 47 journal.

Principles of Biomedical Science Day #73 (1/05/18): Journal Question: What would be the total fat consumed if you ate an entire package of Oreos!!!? ? ? Answer in PLTW journal. 48
Principles of Biomedical Science Day #59 (12/01/17): Journal Question: Answer in PLTW None—please get out your 2. 1. 2 model resources Vocabulary Review: None — look at ‘model check list sheet’ 49 journal.

Principles of Biomedical Science Day #74 (1/08/18): Journal Question: Answer in PLTW Based on the Cheerios label, is this a good source of dietary fiber? journal. Vocabulary Review: How much of a nutrient is in one serving of the food; as a general rule, 5% DV or less of a nutrient per serving is LOW. 20% DV or more of a nutrient per serving is HIGH. % Daily Value (%DV) 50
Principles of Biomedical Science Day #75 (1/09/18): Journal Question: journal. What elements on the periodic table make up most of the human body? Vocabulary Review: Macromolecule 51 A type of giant molecule formed by joining smaller molecules (called monomers); examples are proteins, polysaccharides, lipids, and
Principles of Biomedical Science Day #76 (1/10/18): Journal Question: journal. What is the difference in how valence electrons are used in ionic and covalent bonding? Vocabulary Review: Monomer verses Polymer 52 Venn Diagram (Hint-use your, ‘Lesson 2. 2: The Science of Food—Key Terms.
Principles of Biomedical Science Day #77 (1/11/18): Journal Question: What do the connection points between puzzle pieces represent? Vocabulary Review: Dehydration synthesis 53 journal. ‘Put together losing water’; The monomers combine with each other via covalent bonds to form polymers and release water molecules as byproducts.
Principles of Biomedical Science Day #78 (1/12/18): Journal Question: How can your body form thousands of types of proteins from just 20 amino acids? Vocabulary Review: Hydrolysis Reaction 54 journal. ‘Water-breaking’; the covalent bonds of a polymer are broken as well as water to form monomers.
b5dd50e612be028b1b1d3ca4701c4895.ppt