4f39fdab0550fb8f3d67dae463e335e3.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 65
 PRINCIPLES OF AQUACULTURE (AKU 3201) POND CULTURE
PRINCIPLES OF AQUACULTURE (AKU 3201) POND CULTURE
 1 Method of culture • POND CULTURE
1 Method of culture • POND CULTURE
 2 Outline • • • Pond culture Types of ponds Pond construction Pond management Types of culture
2 Outline • • • Pond culture Types of ponds Pond construction Pond management Types of culture
 3 • POND
3 • POND
 4 POND • POND = - enclosed space shallow water useful nutrients good physico-chemical parameters
4 POND • POND = - enclosed space shallow water useful nutrients good physico-chemical parameters
 5 POND CULTURE • POND CULTURE = - Cultivation of any aquatic organisms - Natural environment - Provide food in the captivity of pond area
5 POND CULTURE • POND CULTURE = - Cultivation of any aquatic organisms - Natural environment - Provide food in the captivity of pond area
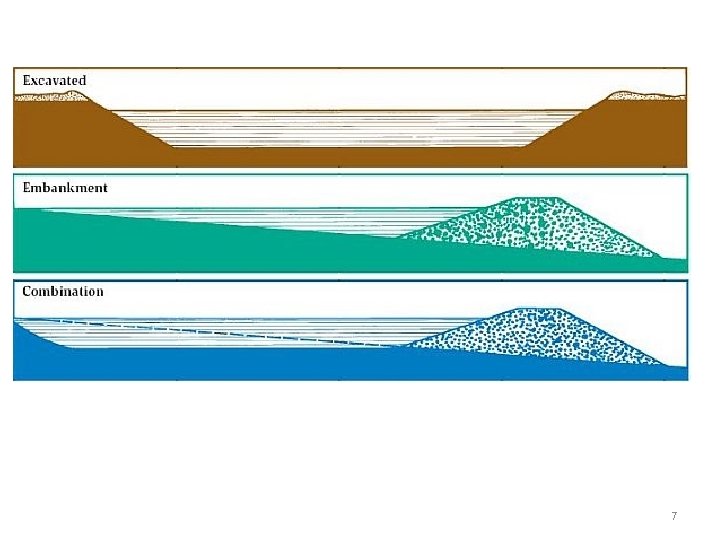
 6 Types pond • 3 types: 1) 2) 3) 4) Dug-out (excavated)pond Embankment pond Concrete pond Combination pond
6 Types pond • 3 types: 1) 2) 3) 4) Dug-out (excavated)pond Embankment pond Concrete pond Combination pond
 7
7
 8 1) Dug-out pond • • • No pond engineering basis Small No commercial purpose One pond/house Excavated
8 1) Dug-out pond • • • No pond engineering basis Small No commercial purpose One pond/house Excavated
 9
9
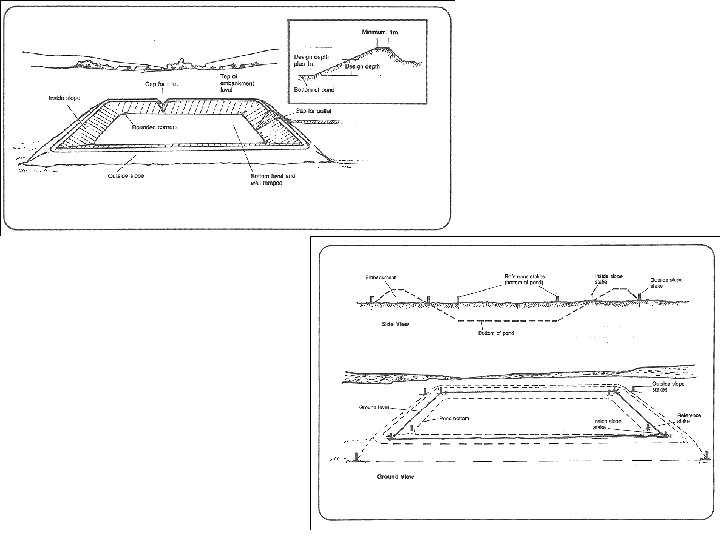
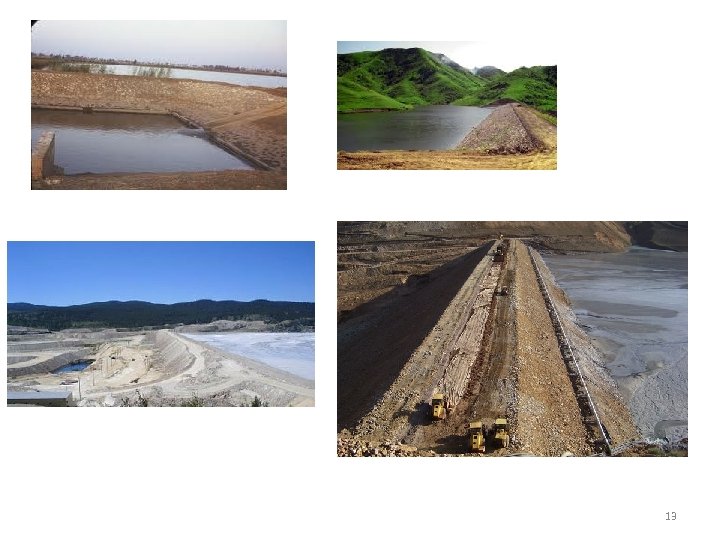
 10 2) Embankment pond • • Fish pond with dikes around Generally earthen ponds Rectangular/square in shape Most common type of aquaculture pond in Malaysia
10 2) Embankment pond • • Fish pond with dikes around Generally earthen ponds Rectangular/square in shape Most common type of aquaculture pond in Malaysia
 11 EARTHEN POND
11 EARTHEN POND
 12
12
 13
13
 14 3) Concrete pond • • Ponds made of concrete or cement Ground level / above ground level Rectangular, square, circular Advantages/ disadvantages
14 3) Concrete pond • • Ponds made of concrete or cement Ground level / above ground level Rectangular, square, circular Advantages/ disadvantages
 15 Concrete pond
15 Concrete pond
 16 4) Combination ponds • Embankment + concrete ponds • Dikes covered by concrete/cement • Bottom is earthen
16 4) Combination ponds • Embankment + concrete ponds • Dikes covered by concrete/cement • Bottom is earthen
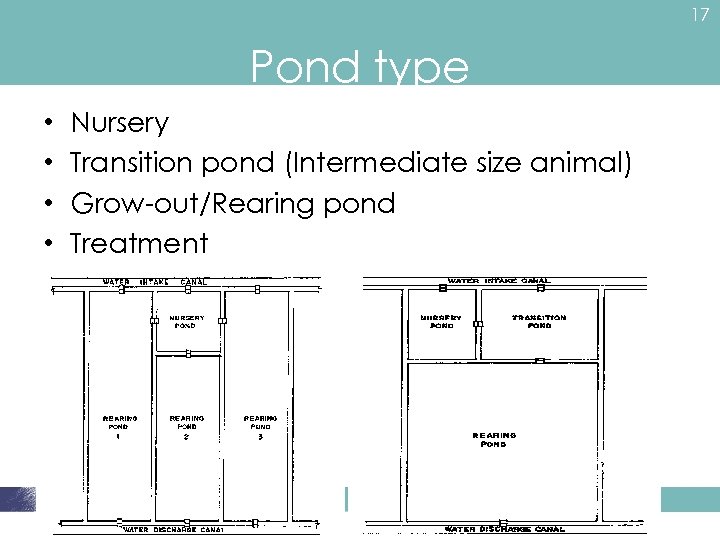 17 Pond type • • Nursery Transition pond (Intermediate size animal) Grow-out/Rearing pond Treatment
17 Pond type • • Nursery Transition pond (Intermediate size animal) Grow-out/Rearing pond Treatment
 18 Typical pond structure
18 Typical pond structure
 19 • POND CONSTRUCTION
19 • POND CONSTRUCTION
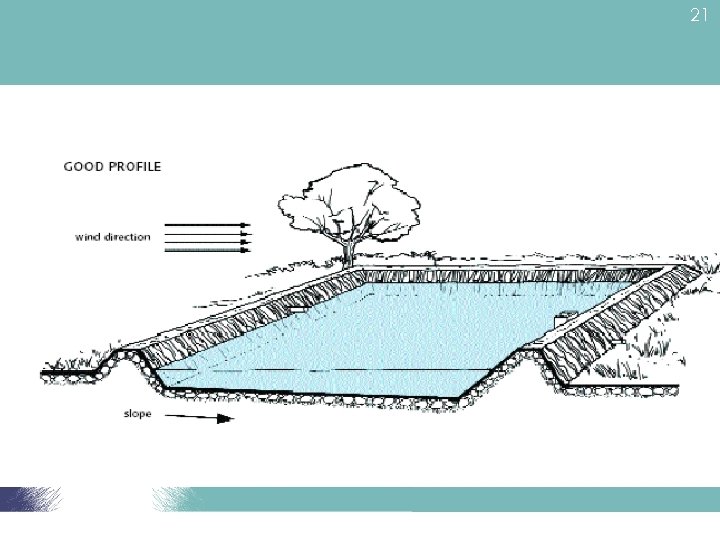
 20 Pond construction • Land • Select the site (soil & water quality) • Prepare the site
20 Pond construction • Land • Select the site (soil & water quality) • Prepare the site
 21
21
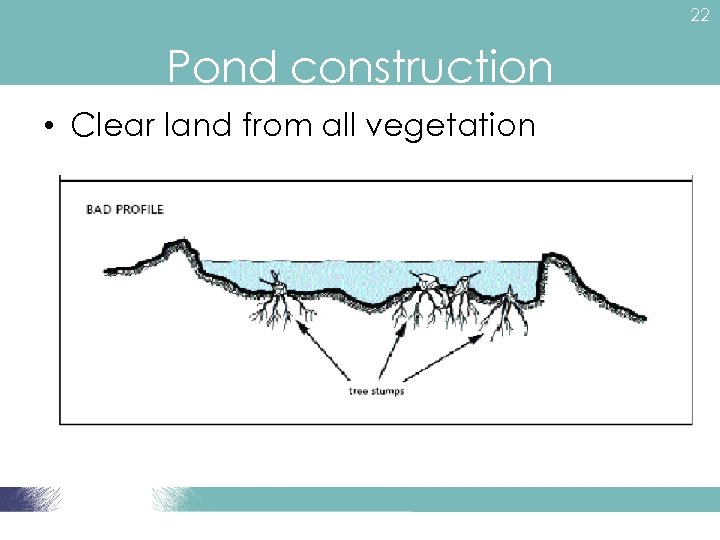 22 Pond construction • Clear land from all vegetation
22 Pond construction • Clear land from all vegetation
 23
23
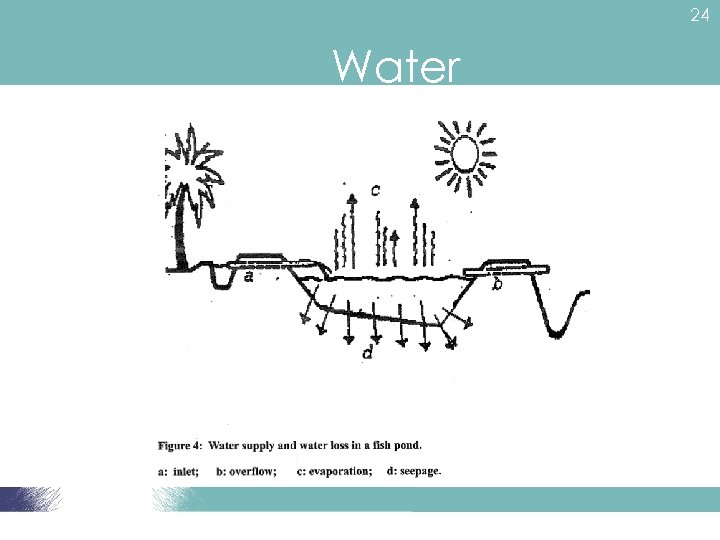 24 Water
24 Water
 25 • Dig pond & compact • Sheep foot roller • The soil can be stockpiled for dike
25 • Dig pond & compact • Sheep foot roller • The soil can be stockpiled for dike
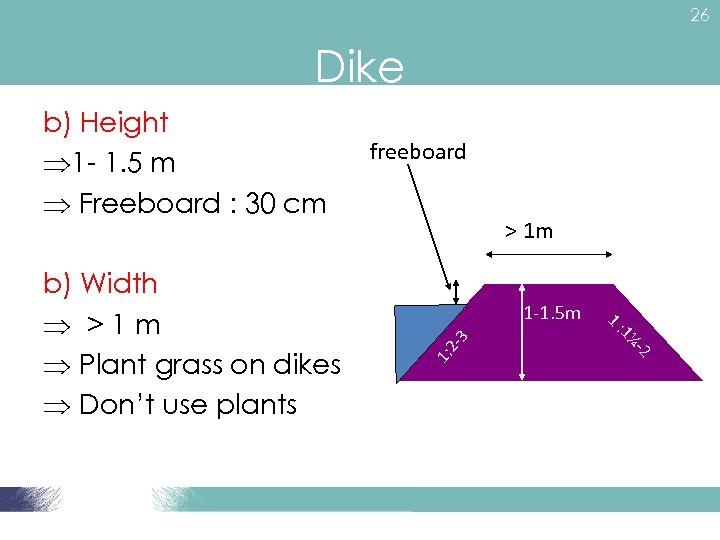 26 Dike > 1 m 3 1 -1. 5 m 2 - b) Width >1 m Plant grass on dikes Don’t use plants freeboard 1: b) Height 1 - 1. 5 m Freeboard : 30 cm 1 : 1 ¼- 2
26 Dike > 1 m 3 1 -1. 5 m 2 - b) Width >1 m Plant grass on dikes Don’t use plants freeboard 1: b) Height 1 - 1. 5 m Freeboard : 30 cm 1 : 1 ¼- 2
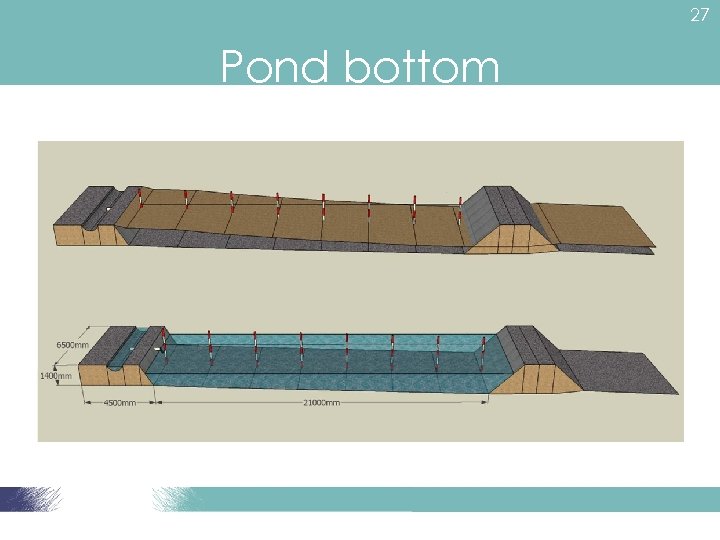 27 Pond bottom
27 Pond bottom
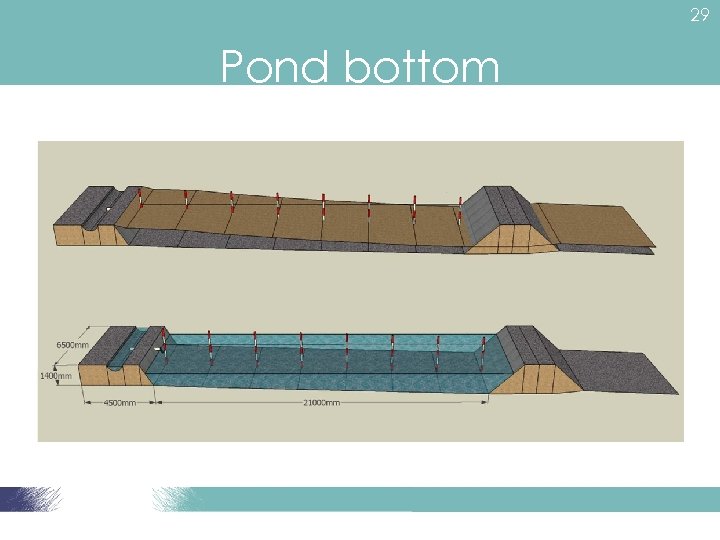
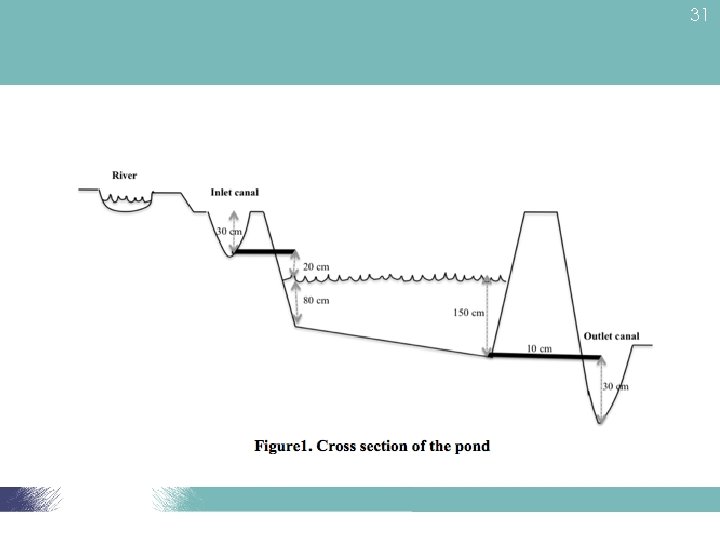
 28 Pond bottom • Pond depth: 1. 0 m – 1. 5 m • Near inlet = 0. 5 -1. 0 m shallow end • Near outlet = Sloping 1. 5 m at the drain end • Drain system – allow water to be removed by gravity
28 Pond bottom • Pond depth: 1. 0 m – 1. 5 m • Near inlet = 0. 5 -1. 0 m shallow end • Near outlet = Sloping 1. 5 m at the drain end • Drain system – allow water to be removed by gravity
 29 Pond bottom
29 Pond bottom
 30 Advantages of sloping bottom • Easy fish harvesting • Easy pond drainage • Easy pond drying
30 Advantages of sloping bottom • Easy fish harvesting • Easy pond drainage • Easy pond drying
 31
31
 32 Inlet & outlet pipe • Inlet & outlet – Polyvinyl chloride (PVC) • Individual inlet & outlet • Filter water entering & leaving ponds
32 Inlet & outlet pipe • Inlet & outlet – Polyvinyl chloride (PVC) • Individual inlet & outlet • Filter water entering & leaving ponds
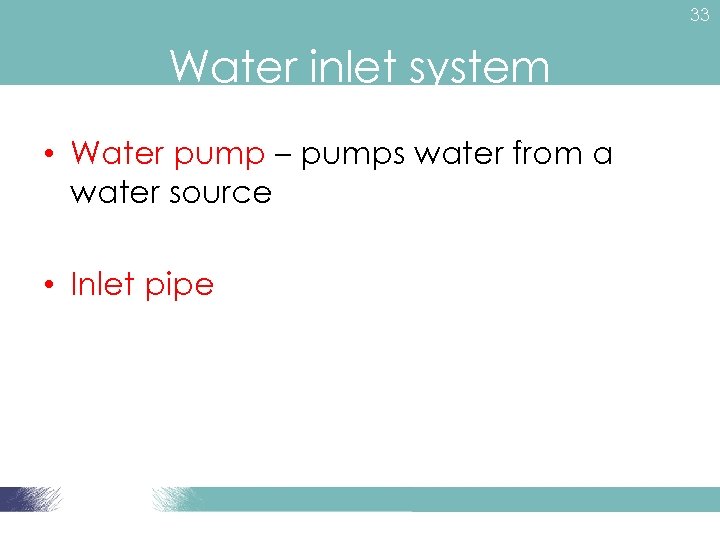 33 Water inlet system • Water pump – pumps water from a water source • Inlet pipe
33 Water inlet system • Water pump – pumps water from a water source • Inlet pipe
 34 Water outlet system • Outlet pipe = removes water from the pond • T-pipe – maintains water level of the pond to avoid flooding
34 Water outlet system • Outlet pipe = removes water from the pond • T-pipe – maintains water level of the pond to avoid flooding
 35
35
 36 Monk
36 Monk
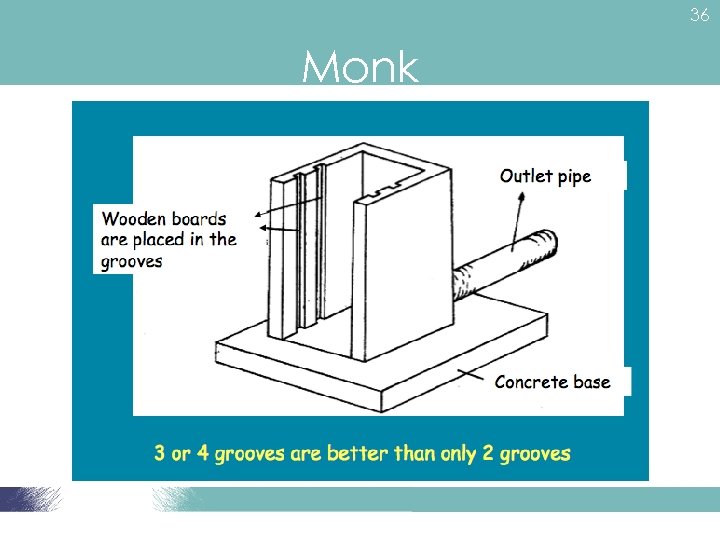
 37 Monk • Control amount of water in & out of pond • Normally concrete
37 Monk • Control amount of water in & out of pond • Normally concrete
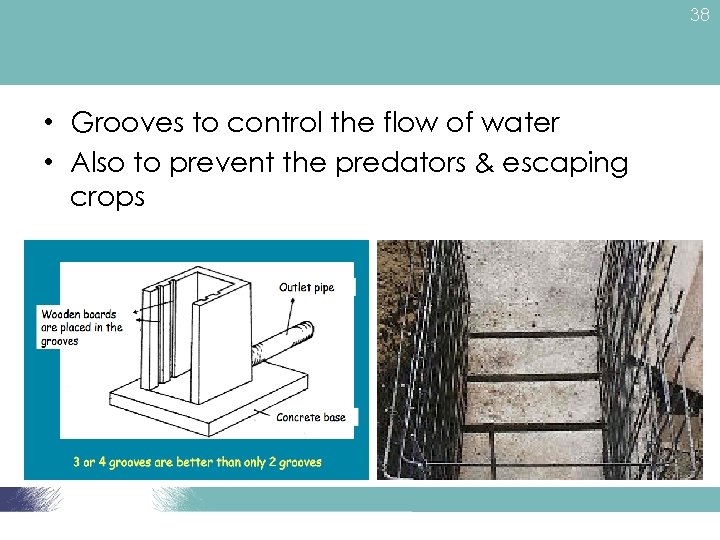 38 • Grooves to control the flow of water • Also to prevent the predators & escaping crops
38 • Grooves to control the flow of water • Also to prevent the predators & escaping crops
 39 Monk • Concrete pipe with appropriate diameter
39 Monk • Concrete pipe with appropriate diameter
 40 Summary
40 Summary
 41
41
 42
42
 43
43
 44
44
 45 Pond management • Cleaning & drying • Liming • Fertilizing
45 Pond management • Cleaning & drying • Liming • Fertilizing
 46 Pond drying • Flush pond with water to remove sediments • Dry the pond until the bottom cracks Advantages - Improve soil texture - Removal of undesirable metabolites e. g H 2 S - Elimination of predators, parasites & their eggs & unwanted macrophytes - Removal of excessive mud from pond bottom
46 Pond drying • Flush pond with water to remove sediments • Dry the pond until the bottom cracks Advantages - Improve soil texture - Removal of undesirable metabolites e. g H 2 S - Elimination of predators, parasites & their eggs & unwanted macrophytes - Removal of excessive mud from pond bottom
 47 • Excessive mud - Increase the height of pond bottom - Decrease depth
47 • Excessive mud - Increase the height of pond bottom - Decrease depth
 48
48
 49 Pond liming • Pond preparation for fertilization Calcium oxide (Ca. O) = Quicklime Calcium carbonate(Ca. CO 3)= Limestone • Neutral-alkaline p. H (7 -8) •
49 Pond liming • Pond preparation for fertilization Calcium oxide (Ca. O) = Quicklime Calcium carbonate(Ca. CO 3)= Limestone • Neutral-alkaline p. H (7 -8) •
 50 Pond liming • Advantages - Favourable environment for microbial growth - Raise p. H to desirable levels - Pond disinfectant – kill parasites - Increase the effectiveness of fertilizer
50 Pond liming • Advantages - Favourable environment for microbial growth - Raise p. H to desirable levels - Pond disinfectant – kill parasites - Increase the effectiveness of fertilizer
 51 Pond fertilization • 2 type of fertilizers A) Organic fertilizers Animal manures, compost, sewage B) Inorganic fertilizers (Synthetic fertilizer) Contain concentrated NPK (Nitrogen, phosphorus, kalium) Superphosphate, triple superphosphate
51 Pond fertilization • 2 type of fertilizers A) Organic fertilizers Animal manures, compost, sewage B) Inorganic fertilizers (Synthetic fertilizer) Contain concentrated NPK (Nitrogen, phosphorus, kalium) Superphosphate, triple superphosphate
 52 Pond fertilization • Increase primary productivity • Stimulate phytoplankton production (autotrophic) • Stimulate bacteria & zooplankton (heterotrophic)
52 Pond fertilization • Increase primary productivity • Stimulate phytoplankton production (autotrophic) • Stimulate bacteria & zooplankton (heterotrophic)
 53 Phytoplankton/ Microalgae
53 Phytoplankton/ Microalgae
 54 Zooplankton
54 Zooplankton
 55 Pond fertilization
55 Pond fertilization
 56 Polyethylene sheet • High-density polyethylene (HDPE) • Pond lining
56 Polyethylene sheet • High-density polyethylene (HDPE) • Pond lining
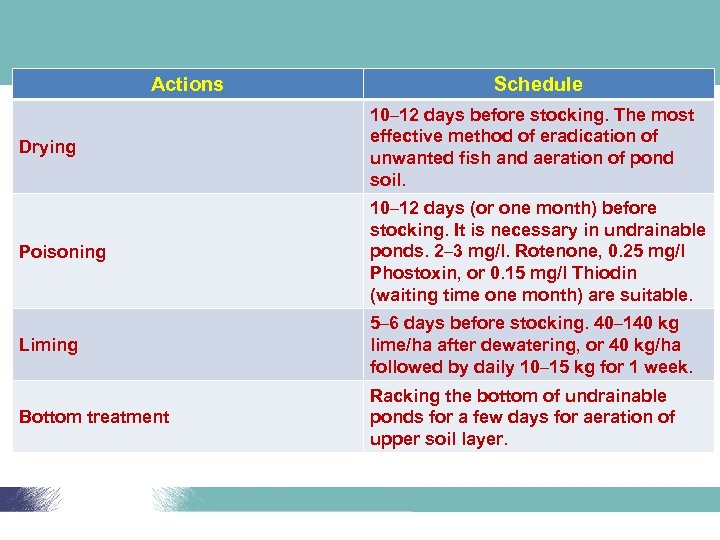 Actions Schedule Drying 10– 12 days before stocking. The most effective method of eradication of unwanted fish and aeration of pond soil. Poisoning 10– 12 days (or one month) before stocking. It is necessary in undrainable ponds. 2– 3 mg/l. Rotenone, 0. 25 mg/l Phostoxin, or 0. 15 mg/l Thiodin (waiting time one month) are suitable. Liming 5– 6 days before stocking. 40– 140 kg lime/ha after dewatering, or 40 kg/ha followed by daily 10– 15 kg for 1 week. Bottom treatment Racking the bottom of undrainable ponds for a few days for aeration of upper soil layer.
Actions Schedule Drying 10– 12 days before stocking. The most effective method of eradication of unwanted fish and aeration of pond soil. Poisoning 10– 12 days (or one month) before stocking. It is necessary in undrainable ponds. 2– 3 mg/l. Rotenone, 0. 25 mg/l Phostoxin, or 0. 15 mg/l Thiodin (waiting time one month) are suitable. Liming 5– 6 days before stocking. 40– 140 kg lime/ha after dewatering, or 40 kg/ha followed by daily 10– 15 kg for 1 week. Bottom treatment Racking the bottom of undrainable ponds for a few days for aeration of upper soil layer.
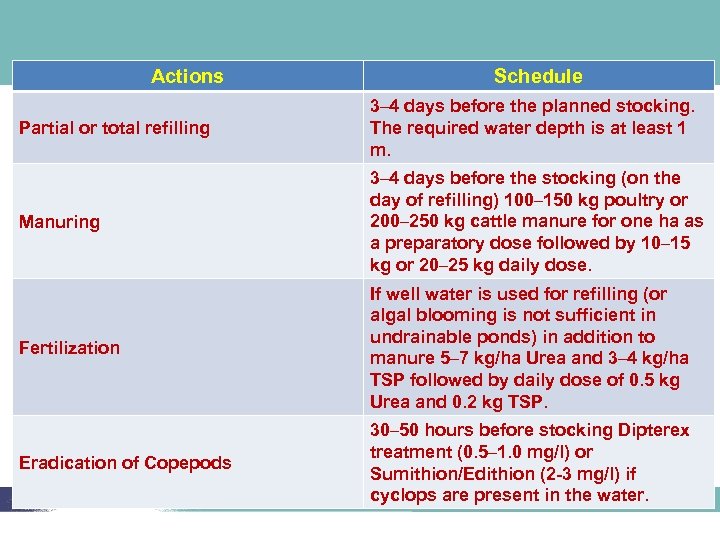 Actions Schedule Partial or total refilling 3– 4 days before the planned stocking. The required water depth is at least 1 m. Manuring 3– 4 days before the stocking (on the day of refilling) 100– 150 kg poultry or 200– 250 kg cattle manure for one ha as a preparatory dose followed by 10– 15 kg or 20– 25 kg daily dose. Fertilization If well water is used for refilling (or algal blooming is not sufficient in undrainable ponds) in addition to manure 5– 7 kg/ha Urea and 3– 4 kg/ha TSP followed by daily dose of 0. 5 kg Urea and 0. 2 kg TSP. Eradication of Copepods 30– 50 hours before stocking Dipterex treatment (0. 5– 1. 0 mg/l) or Sumithion/Edithion (2 -3 mg/l) if cyclops are present in the water.
Actions Schedule Partial or total refilling 3– 4 days before the planned stocking. The required water depth is at least 1 m. Manuring 3– 4 days before the stocking (on the day of refilling) 100– 150 kg poultry or 200– 250 kg cattle manure for one ha as a preparatory dose followed by 10– 15 kg or 20– 25 kg daily dose. Fertilization If well water is used for refilling (or algal blooming is not sufficient in undrainable ponds) in addition to manure 5– 7 kg/ha Urea and 3– 4 kg/ha TSP followed by daily dose of 0. 5 kg Urea and 0. 2 kg TSP. Eradication of Copepods 30– 50 hours before stocking Dipterex treatment (0. 5– 1. 0 mg/l) or Sumithion/Edithion (2 -3 mg/l) if cyclops are present in the water.
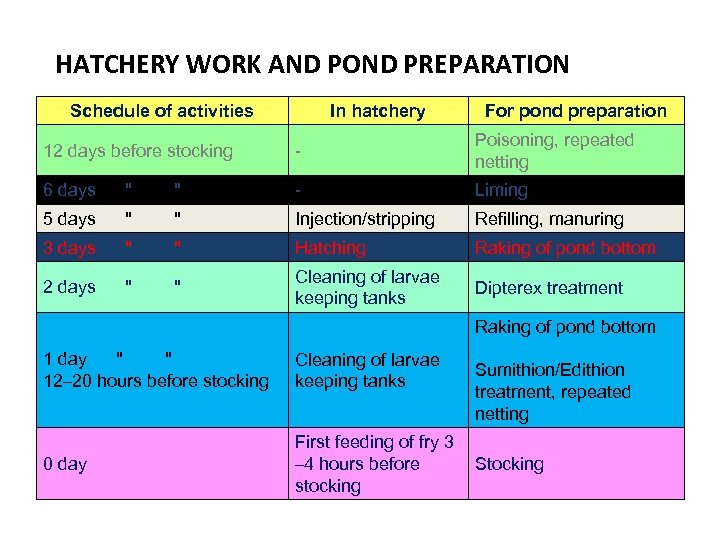 HATCHERY WORK AND POND PREPARATION Schedule of activities In hatchery For pond preparation 12 days before stocking - Poisoning, repeated netting 6 days " " - Liming 5 days " " Injection/stripping Refilling, manuring 3 days " " Hatching Raking of pond bottom 2 days " " Cleaning of larvae keeping tanks Dipterex treatment Raking of pond bottom 1 day " " 12– 20 hours before stocking Cleaning of larvae keeping tanks 0 day First feeding of fry 3 – 4 hours before stocking Sumithion/Edithion treatment, repeated netting Stocking
HATCHERY WORK AND POND PREPARATION Schedule of activities In hatchery For pond preparation 12 days before stocking - Poisoning, repeated netting 6 days " " - Liming 5 days " " Injection/stripping Refilling, manuring 3 days " " Hatching Raking of pond bottom 2 days " " Cleaning of larvae keeping tanks Dipterex treatment Raking of pond bottom 1 day " " 12– 20 hours before stocking Cleaning of larvae keeping tanks 0 day First feeding of fry 3 – 4 hours before stocking Sumithion/Edithion treatment, repeated netting Stocking
 60 Types of culture • Monoculture • Polyculture (Integrated) - Common carp =benthic - Grass carp = herbivor - Silver carp = phytoplankton - Bighead carp = zooplankton
60 Types of culture • Monoculture • Polyculture (Integrated) - Common carp =benthic - Grass carp = herbivor - Silver carp = phytoplankton - Bighead carp = zooplankton
 61 Types of culture • 3 different types a) Extensive b) Semi-intensive c) Intensive - Stocking & fertilization rates Supplementary feed quality Level of technology Level of investment
61 Types of culture • 3 different types a) Extensive b) Semi-intensive c) Intensive - Stocking & fertilization rates Supplementary feed quality Level of technology Level of investment
 62 a) Extensive - Simplest method of culture - Low stocking rate Use fertilizers Low level of technology Investment = low Yield = low Production rate 100 -500 kg/ha/year e. g. , backyard hatchery, wastewater treatment ponds, rice field
62 a) Extensive - Simplest method of culture - Low stocking rate Use fertilizers Low level of technology Investment = low Yield = low Production rate 100 -500 kg/ha/year e. g. , backyard hatchery, wastewater treatment ponds, rice field
 63 b) Semi-intensive - Stocking rate > extensive - Fertilizer + additional feed - Technology > extensive; pond preparation & management - Investment > extensive - Yield > extensive - Production rate 500 -4000 kg/ha/year
63 b) Semi-intensive - Stocking rate > extensive - Fertilizer + additional feed - Technology > extensive; pond preparation & management - Investment > extensive - Yield > extensive - Production rate 500 -4000 kg/ha/year
 64 c) Intensive - High stocking rate - Greater dependence on commercial feeds - High technology = e. g automated feeding, aeration, H 20 purification - High level investment - High yield/ risk - Production rate 5, 00015, 000 kg/ha/year
64 c) Intensive - High stocking rate - Greater dependence on commercial feeds - High technology = e. g automated feeding, aeration, H 20 purification - High level investment - High yield/ risk - Production rate 5, 00015, 000 kg/ha/year


